https://flink.apache.org/
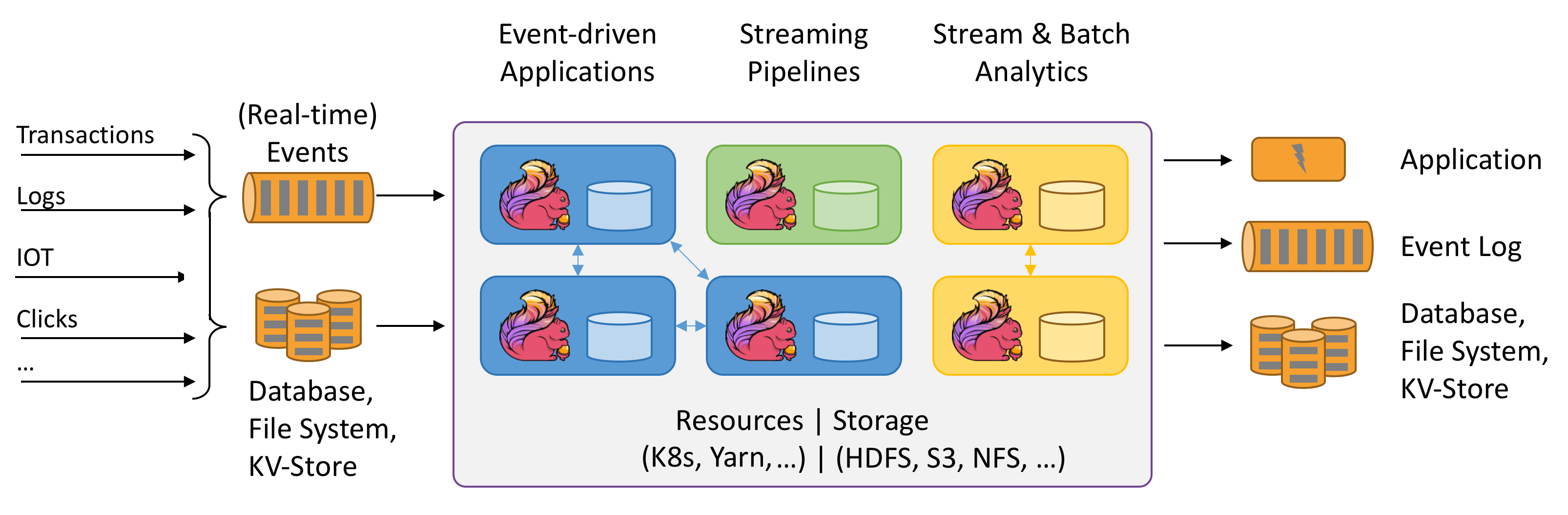
Is Flink a Hadoop Project? Flink is a data processing system and an alternative to Hadoop’s MapReduce component. It comes with its own runtime rather than building on top of MapReduce. As such, it can work completely independently of the Hadoop ecosystem. However, Flink can also access Hadoop’s distributed file system (HDFS) to read and write data, and Hadoop’s next-generation resource manager (YARN) to provision cluster resources. Since most Flink users are using Hadoop HDFS to store their data, Flink already ships the required libraries to access HDFS.
Do I have to install Apache Hadoop to use Flink? No. Flink can run without a Hadoop installation. However, a very common setup is to use Flink to analyze data stored in the Hadoop Distributed File System (HDFS). To make these setups work out of the box, Flink bundles the Hadoop client libraries by default.
Additionally, we provide a special YARN Enabled download of Flink for users with an existing Hadoop YARN cluster. Apache Hadoop YARN is Hadoop’s cluster resource manager that allows use of different execution engines next to each other on a cluster.
An Alternative to Hadoop MapReduce? Apache Flink is considered an alternative to Hadoop MapReduce. Flink offers cyclic data, a flow which is missing in MapReduce. Flink offers APIs, which are easier to implement compared to MapReduce APIs. It supports in-memory processing, which is much faster. Flink is also capable of working with other file systems along with HDFS. Flink can analyze real-time stream data along with graph processing and using machine learning algorithms. It also extends the MapReduce model with new operators like join, cross and union. Flink offers lower latency, exactly one processing guarantee, and higher throughput. Flink is also considered as an alternative to Spark and Storm. (To learn more about Spark, see How Apache Spark Helps Rapid Application Development.)
Flink可以完全独立于Hadoop,在不依赖Hadoop组件下运行。但是做为大数据的基础设施,Hadoop体系是任何大数据框架都绕不过去的。Flink可以集成众多Hadooop 组件,例如Yarn、Hbase、HDFS等等。例如,Flink可以和Yarn集成做资源调度,也可以读写HDFS,或者利用HDFS做检查点
# 1. Intro
# 1.1 Architecture
Flink is a distributed system and requires effective allocation and management of compute resources in order to execute streaming applications. It integrates with all common cluster resource managers such as Hadoop YARN and Kubernetes, but can also be set up to run as a standalone cluster or even as a library.
The Client is not part of the runtime and program execution, but is used to prepare and send a dataflow to the JobManager. After that, the client can disconnect (detached mode), or stay connected to receive progress reports (attached mode). The client runs either as part of the Java/Scala program that triggers the execution, or in the command line process ./bin/flink run ....
Flink 集群是由 JobManager(JM)、TaskManager(TM)两大组件组成的,每个 JM/TM 都是运行在一个独立的 JVM 进程中。JM 相当于 Master,是集群的管理节点,TM 相当于 Worker,是集群的工作节点,每个 TM 最少持有 1 个 Slot,Slot 是 Flink 执行 Job 时的最小资源分配单位,在 Slot 中运行着具体的 Task 任务。
- Flink Memory Model
Set up Flink’s Process Memory (opens new window) Total Process Memory(The total process memory of Flink JVM processes) = JVM Off heap Memory to run the flink application(means the job manager)[=JVM Metaspace+JVM Overhead] + Total Flink Memory(consumed by the flink application)[=JVM heap + Off heap Memory(direct/native memory)]
Set up TaskManager Memory (opens new window) the TaskManager memory components have a similar but more sophisticated structure compared to the memory model of the JobManager process.
Total Process Memory(configed e.g taskmanager.memory.process.size:16G) = JVM Specific Memory to run the flink application(means the taskmanager) + Total Flink Memory(consumed by the flink application) JVM Specific Memory= JVM Metaspace(taskmanager.memory.jvm-metaspace.size:256M) + JVM Overhead(taskmanager.memory.jvm-overhead.fraction,taskmanager.memory.jvm-overhead.max) JVM Overhead= 0.1*totalProcessMemory=1.6G>1G=1G Total Flink Memory= JVM Heap{=Framework Heap(taskmanager.memory.framework.heap.size)+Task Heap} + Off-Heap Memory Total Flink Memory=Total Process Memory-JVM Metaspace - JVM Overhead=16G-256M-1G=14.75G Off-Heap Memory= Managed Memory(taskmanager.memory.managed.fraction,taskmanager.memory.managed.size) + Direct Memory The following workloads use managed memory: a) Streaming jobs can use it for RocksDB state backend. b) Both streaming and batch jobs can use it for sorting, hash tables, caching of intermediate results. c) Both streaming and batch jobs can use it for executing User Defined Functions in Python processes Direct Memory= Framework Off-heap(taskmanager.memory.framework.off-heap.size) + Task Off-heap(taskmanager.memory.task.off-heap.size) + Network(taskmanager.memory.network.fraction,taskmanager.memory.network.max) Managed Memory=0.4*totalFlinkMemory=0.4*14.75=5.9G Network Memory=0.1*totalFlinkMemory=0.1*14.75=1.475G>1G=1G Direct Memory=128M+0bytes+1G=1.125G Off-Heap Memory=5.9G+1.125G=7.025G JVM Heap(Framework Heap+Task Heap)=Total Flink Memory-Off-Heap Memory=14.75G-7.025G=7.725G=7.73G Task Heap=JVM Heap-Framework Heap=7.725G-128M=7.6G
Note: If you want to guarantee that a certain amount of JVM Heap is available for your user code, you can set the task heap memory explicitly (taskmanager.memory.task.heap.size). It will be added to the JVM Heap size and will be dedicated to Flink’s operators running the user code. specify explicitly both task heap and managed memory. It gives more control over the available JVM Heap to Flink’s tasks and its managed memory.
# 1.1.1 JobManager
The JobManager has a number of responsibilities related to coordinating the distributed execution of Flink Applications: it decides when to schedule the next task (or set of tasks), reacts to finished tasks or execution failures, coordinates checkpoints, and coordinates recovery on failures, among others. This process consists of three different components:
# ResourceManager
is responsible for resource de-/allocation and provisioning in a Flink cluster — it manages task slots, which are the unit of resource scheduling in a Flink cluster (see TaskManagers). Flink implements multiple ResourceManagers for different environments and resource providers such as YARN, Kubernetes and standalone deployments. In a standalone setup, the ResourceManager can only distribute the slots of available TaskManagers and cannot start new TaskManagers on its own.
# Dispatcher
provides a REST interface to submit Flink applications for execution and starts a new JobMaster for each submitted job. It also runs the Flink WebUI to provide information about job executions.
# JobMaster
is responsible for managing the execution of a single JobGraph. Multiple jobs can run simultaneously in a Flink cluster, each having its own JobMaster.
# 1.1.2 TaskManagers
# Flink Job
A Flink Job is the runtime representation of a logical graph (also often called dataflow graph) that is created and submitted by calling execute() in a Flink Application.
一个Job代表一个可以独立提交给Flink执行的作业,我们向JobManager提交任务的时候就是以Job为单位的,只不过一份代码里可以包含多个Job(每个Job对应一个类的main函数)
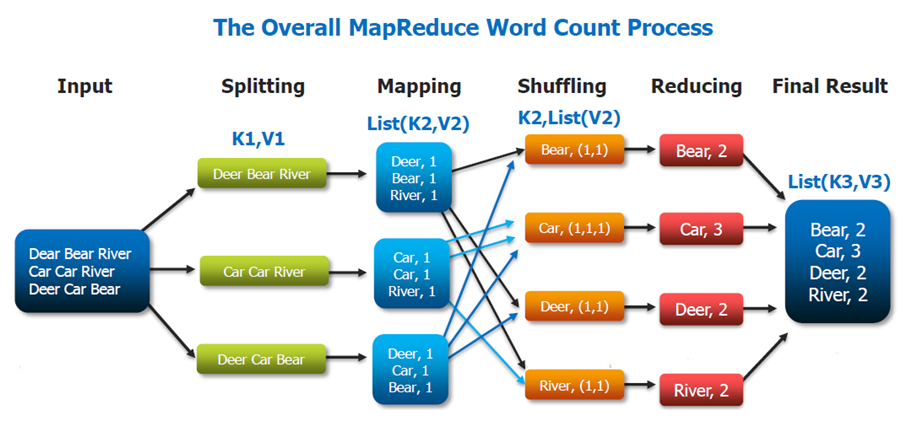
Example:
# JobGraph / Logical Graph
A logical graph is a directed graph where the nodes are Operators and the edges define input/output-relationships of the operators and correspond to data streams or data sets. A logical graph is created by submitting jobs from a Flink Application. Logical graphs are also often referred to as dataflow graphs.
# ExecutionGraph/Physical Graph
A physical graph is the result of translating a Logical Graph for execution in a distributed runtime. The nodes are Tasks and the edges indicate input/output-relationships or partitions of data streams or data sets.
# TM: Task Manager
- is a JVM process, (also called workers) execute the tasks of a dataflow, and buffer and exchange the data streams. There must always be at least one TaskManager. Each worker (TaskManager) is a JVM process, and may execute one or more subtasks in separate threads. To control how many tasks a TaskManager accepts, it has so called task slots (at least one).
# TS: Task Slot
- each TS represents a fixed subset of resources of the TaskManager (No CPU isolation happens between the slots, just the managed memory is divided.) The smallest unit of resource scheduling in a TaskManager is a task slot. The number of task slots in a TaskManager indicates the number of concurrent processing tasks. Note that multiple operators may execute in a task slot
One Slot is not one thread. One slot can have multiple threads. A Task can have multiple parallel instances which are called Sub-tasks. Each sub-task is ran in a separate thread. Multiple sub-tasks from different tasks can come together and share a slot. This group of sub-tasks is called a slot-sharing group. Please note that two sub-tasks of the same task (parallel instances of the same task) can not share a slot together. https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61791811/how-to-understand-slot-and-task-in-apache-flink
Each task slot represents a fixed subset of resources of the TaskManager. A TaskManager with three slots, for example, will dedicate 1/3 of its managed memory to each slot. Slotting the resources means that a subtask will not compete with subtasks from other jobs for managed memory, but instead has a certain amount of reserved managed memory. Note that no CPU isolation happens here; currently slots only separate the managed memory of tasks.
By adjusting the number of task slots, users can define how subtasks are isolated from each other. Having one slot per TaskManager means that each task group runs in a separate JVM (which can be started in a separate container, for example). Having multiple slots means more subtasks share the same JVM. Tasks in the same JVM share TCP connections (via multiplexing) and heartbeat messages. They may also share data sets and data structures, thus reducing the per-task overhead.
# Task
- Node of a Physical Graph.
A task is the basic unit of work, which is executed by Flink’s runtime. Tasks encapsulate exactly one parallel instance of an Operator or Operator Chain. For distributed execution, Flink chains operator subtasks together into tasks.
Task是逻辑概念,一个Operator就代表一个Task(多个Operator被chain之后产生的新Operator算一个Operator), 真正运行的时候,Task会按照并行度分成多个Subtask,Subtask是执行/调度的基本单元,每个Subtask需要一个线程(Thread)来执行。
A Sub-Task is a Task responsible for processing a partition of the data stream. The term “Sub-Task” emphasizes that there are multiple parallel Tasks for the same Operator or Operator Chain. Each subtask is executed by one thread.
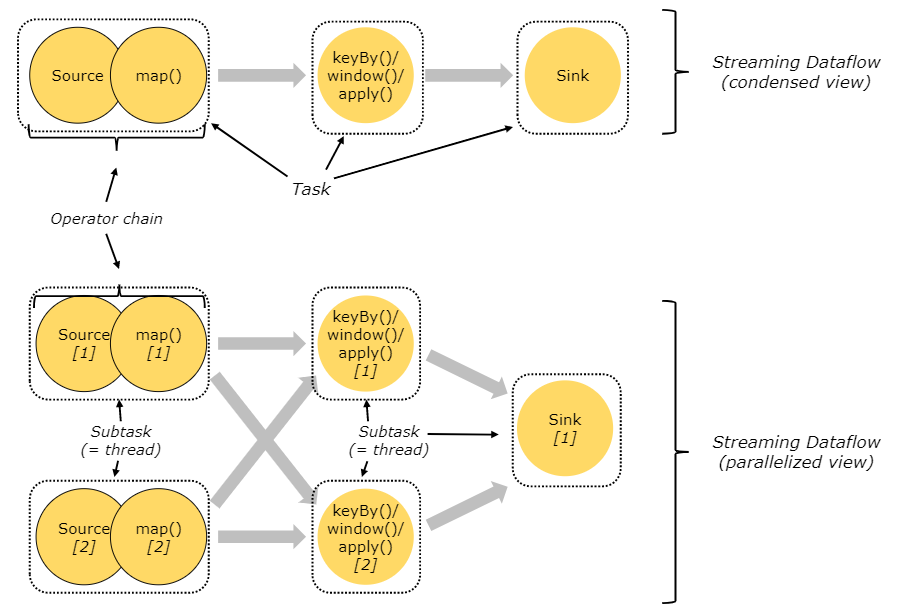
A task is an abstraction representing a chain of operators that could be executed in a single thread. Something like a keyBy (which causes a network shuffle to partition the stream by some key) or a change in the parallelism of the pipeline will break the chaining and force operators into separate tasks. In the diagram above, the application has three tasks.
举例:source.map().filter().sink() 如果parallel=1,会看到只有一个subtask 跑在一个slot里面,所有操作都是链接在里面,如果想打破chain,可以使用startNewChain,disableChaining 或者采用分区策略,让上下游的并行度不同
A subtask is one parallel slice of a task. This is the schedulable, runable unit of execution. In the diagram above, the application is to be run with a parallelism of two for the source/map and keyBy/Window/apply tasks, and a parallelism of one for the sink -- resulting in a total of 5 subtasks.
A job is a running instance of an application. Clients submit jobs to the jobmanager, which slices them into subtasks and schedules those subtasks for execution by the taskmanagers.
Update:
The community decided to re-align the definitions of task and sub-task to match how these terms are used in the code -- which means that task and sub-task now mean the same thing: exactly one parallel instance of an operator or operator chain. -- https://stackoverflow.com/questions/53610342/difference-between-job-task-and-subtask-in-flink
Note: TaskSlot = Thread only (!) if slot sharing is disabled. It is an optimization that is on by default and in most cases, you would want to keep it that way. It is more precise to say that an Operator Chain = a Thread. Chaining operators together into tasks is a useful optimization: it reduces the overhead of thread-to-thread handover and buffering, and increases overall throughput while decreasing latency.
By default, Flink allows subtasks to share slots even if they are subtasks of different tasks, so long as they are from the same job. The result is that one slot may hold an entire pipeline of the job. Allowing this slot sharing has two main benefits:
# parallelism
A Flink cluster needs exactly as many task slots as the highest parallelism used in the job. No need to calculate how many tasks (with varying parallelism) a program contains in total. slot的个数不能多于cpu-cores
It is easier to get better resource utilization. Without slot sharing, the non-intensive source/map() subtasks would block as many resources as the resource intensive window subtasks. With slot sharing, increasing the base parallelism in our example from two to six yields full utilization of the slotted resources, while making sure that the heavy subtasks are fairly distributed among the TaskManagers.
Operator Level / Execution Environment Level / Client Level / System Level (opens new window)
- Operator Level
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); DataStream<String> text = [...] DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordCounts = text .flatMap(new LineSplitter()) .keyBy(0) .timeWindow(Time.seconds(5)) .sum(1).setParallelism(5); wordCounts.print(); env.execute("Word Count Example"); operators、data sources、data sinks都可以调用setParallelism()方法来设置parallelism - Execution Environment Level
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment(); env.setParallelism(3); DataStream<String> text = [...] DataStream<Tuple2<String, Integer>> wordCounts = [...] wordCounts.print(); env.execute("Word Count Example"); 在ExecutionEnvironment里头可以通过setParallelism来给operators、data sources、data sinks设置默认的parallelism;如果operators、data sources、data sinks自己有设置parallelism则会覆盖ExecutionEnvironment设置的parallelism - Client Level
./bin/flink run -p 10 ../examples/*WordCount-java*.jar 或者 try { PackagedProgram program = new PackagedProgram(file, args); InetSocketAddress jobManagerAddress = RemoteExecutor.getInetFromHostport("localhost:6123"); Configuration config = new Configuration(); Client client = new Client(jobManagerAddress, config, program.getUserCodeClassLoader()); // set the parallelism to 10 here client.run(program, 10, true); } catch (ProgramInvocationException e) { e.printStackTrace(); } 使用CLI client,可以在命令行调用是用-p来指定,或者Java/Scala调用时在Client.run的参数中指定parallelism - System Level
# The parallelism used for programs that did not specify and other parallelism. parallelism.default: 1 可以在flink-conf.yaml中通过parallelism.default配置项给所有execution environments指定系统级的默认parallelism
example:
If run with parallelism of two in a cluster with 2 task managers, each offering 3 slots, the scheduler will use 5 task slots, like this:
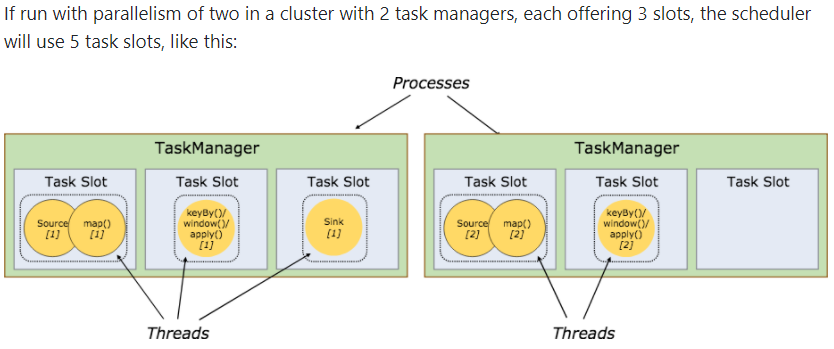
However, if the base parallelism is increased to six, then the scheduler will do this (note that the sink remains at a parallelism of one in this example):

实测 1 task manager with 4 slots, run wordcount with p=2/3/4/5:
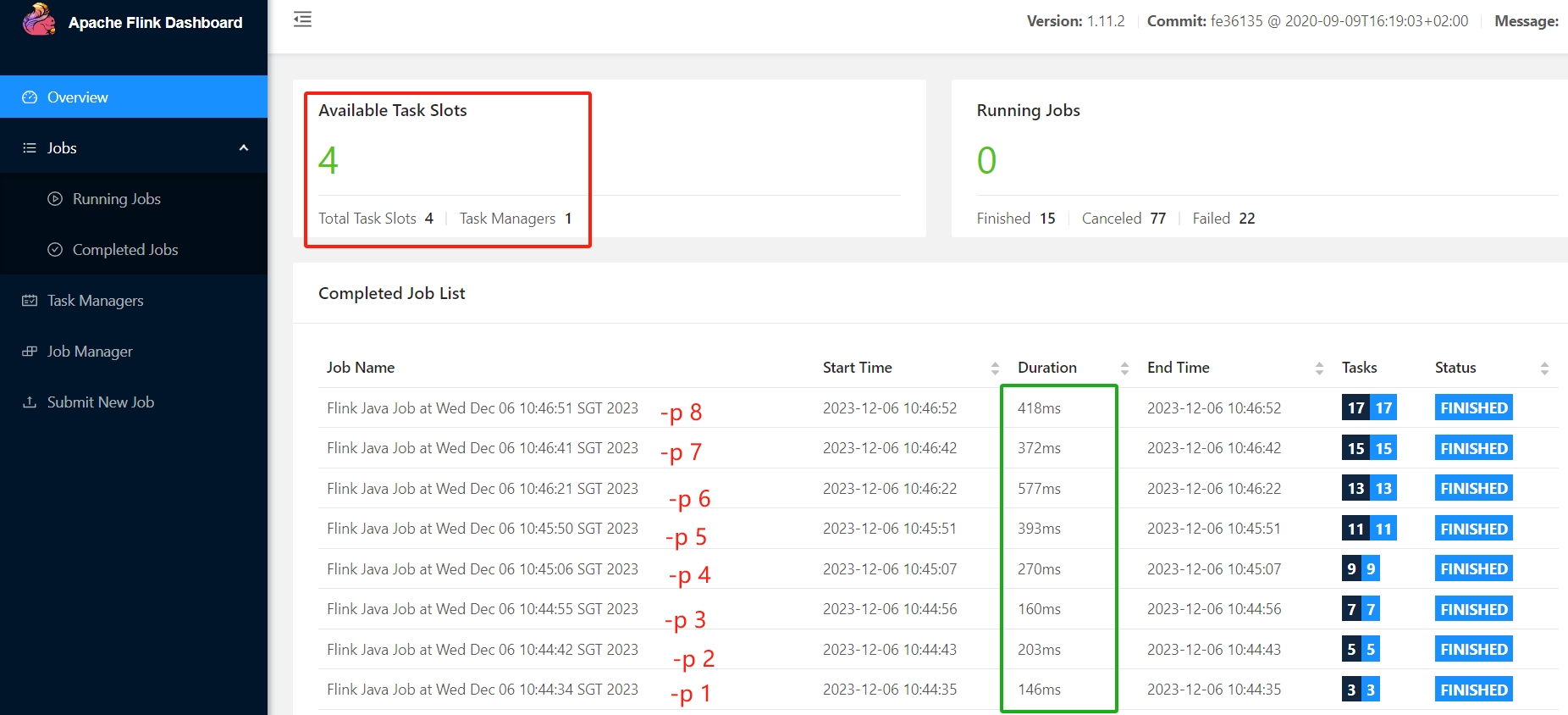 这个测试很有意思,p=1的时候最快,p=2反而慢了(因为增加了任务分割和聚合的过程吧),p从2到3,用时降低在预期之内,但是p=4反而更久(后来又测了几次,这个耗时不稳定),另外p>4居然也能成功,不过耗时变长,找到解释:
这个测试很有意思,p=1的时候最快,p=2反而慢了(因为增加了任务分割和聚合的过程吧),p从2到3,用时降低在预期之内,但是p=4反而更久(后来又测了几次,这个耗时不稳定),另外p>4居然也能成功,不过耗时变长,找到解释:
在Flink中,Slot和并行度是相互影响的。如果一个任务的并行度大于Slot的数量,那么这个任务就无法完全并行执行。在这种情况下,Flink会根据一定的算法将任务的子任务分配到不同的Slot中执行,从而实现部分并行执行。另外,如果一个任务的并行度小于Slot的数量,那么有些Slot可能会闲置,从而浪费资源。
就是说实际上p=5是把并行度是5的子任务中只有4个是真正并行的,另外一个是放在等某个slots空闲的时候再跑
日志: p=1
2023-12-06 10:44:35,152 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Receive slot request 1040904f312d051825b9205caf4c87de for job cab7d3dd7306786f754237f2771c0a62 from resource manager with leader id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2023-12-06 10:44:35,152 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Allocated slot for 1040904f312d051825b9205caf4c87de.
..............................
2023-12-06 10:44:35,206 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 1040904f312d051825b9205caf4c87de.
2023-12-06 10:44:35,207 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/1).
2023-12-06 10:44:35,211 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/1) (4e89f2aef62b7d61bbafc9fff95cd9aa) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
p=2
2023-12-06 10:44:43,328 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Receive slot request 5bd806ad550923769e95d4d86a4744e5 for job fd43c3b3c49c0afe0be4c6706b904cc3 from resource manager with leader id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2023-12-06 10:44:43,328 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Allocated slot for 5bd806ad550923769e95d4d86a4744e5.
...................................
2023-12-06 10:44:43,365 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 5bd806ad550923769e95d4d86a4744e5.
2023-12-06 10:44:43,366 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/2).
2023-12-06 10:44:43,370 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot bae54b7f4b9437bf81acafd292978241.
2023-12-06 10:44:43,370 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot bae54b7f4b9437bf81acafd292978241.
2023-12-06 10:44:43,371 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/2).
2023-12-06 10:44:43,371 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/2) (1acde70402c0fe9c43e309b6f2f4b4cd) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:44:43,373 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/2) (c347c9c47c4b81fb954311a874b7d79d) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
p=3
2023-12-06 10:44:56,191 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Receive slot request 413728b6858e88e8be8ddeb986d865c1 for job 1851bfb11c5dc283209bbda14a5b7a91 from resource manager with leader id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,191 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Allocated slot for 413728b6858e88e8be8ddeb986d865c1.
.......................................
2023-12-06 10:44:56,252 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 413728b6858e88e8be8ddeb986d865c1.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,252 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3).
2023-12-06 10:44:56,253 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 46bc54661e712a95825369cac5cc6af6.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,253 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 46bc54661e712a95825369cac5cc6af6.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot c7a90293611545315fb34eefd29ce7d3.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) (ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) (ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 46bc54661e712a95825369cac5cc6af6.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) (ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3).
2023-12-06 10:44:56,254 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) (ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,255 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot c7a90293611545315fb34eefd29ce7d3.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,255 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/3).
2023-12-06 10:44:56,256 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) (ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,256 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) (ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:44:56,256 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) (ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:44:56,256 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) (ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,256 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/3) (a25fcb1abd5fa545eb5f055335661f2a) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,256 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/3) (a25fcb1abd5fa545eb5f055335661f2a) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:44:56,257 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/3) (a25fcb1abd5fa545eb5f055335661f2a) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:44:56,257 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/3) (a25fcb1abd5fa545eb5f055335661f2a) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,297 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) (ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,297 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) (ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097).
2023-12-06 10:44:56,298 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/3) ae17aca0dbc22c6cc0b3ef75ec03e097.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,299 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) (ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2023-12-06 10:44:56,299 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) (ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae).
2023-12-06 10:44:56,299 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/3) ced34a25137bf391bafb0044262f04ae.
p=4
2023-12-06 10:45:07,403 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Receive slot request 02585101726cd4ee416a88da77fc4618 for job bc618f19d10f2973cbdb4e74b1def0f0 from resource manager with leader id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,404 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Allocated slot for 02585101726cd4ee416a88da77fc4618.
................................
10:45:07,449 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 02585101726cd4ee416a88da77fc4618.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,449 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/4).
2023-12-06 10:45:07,452 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot eb4fbc442d7c400158fe9a9ebfa2691c.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,452 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot eb4fbc442d7c400158fe9a9ebfa2691c.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,452 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot fa67f55e86b4b171eb32e58df1ab73ac.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,452 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot eb4fbc442d7c400158fe9a9ebfa2691c.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,452 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot fa67f55e86b4b171eb32e58df1ab73ac.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,452 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 4fb95f5d1a690c5954e6a0f4d4e96828.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,453 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot eb4fbc442d7c400158fe9a9ebfa2691c.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,453 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/4).
2023-12-06 10:45:07,453 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/4) (a36fef48a5c8328355d9630b67947b14) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,465 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot fa67f55e86b4b171eb32e58df1ab73ac.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,466 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/4).
2023-12-06 10:45:07,466 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/4) (3d4d2bfeada831e87d50771c71809e63) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,468 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 4fb95f5d1a690c5954e6a0f4d4e96828.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,468 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/4).
2023-12-06 10:45:07,468 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/4) (8c8d42092ff829ac4aef87f9371116c4) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/4) (a36fef48a5c8328355d9630b67947b14) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/4) (a36fef48a5c8328355d9630b67947b14) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/4) (a36fef48a5c8328355d9630b67947b14) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/4) (8c8d42092ff829ac4aef87f9371116c4) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/4) (8c8d42092ff829ac4aef87f9371116c4) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/4) (8c8d42092ff829ac4aef87f9371116c4) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,470 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/4) (def950d6feb829be9cd06a581c6f3089) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,522 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/4) (3d4d2bfeada831e87d50771c71809e63) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,522 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/4) (3d4d2bfeada831e87d50771c71809e63) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,522 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/4) (3d4d2bfeada831e87d50771c71809e63) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:07,534 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/4) (def950d6feb829be9cd06a581c6f3089) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,535 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/4) (def950d6feb829be9cd06a581c6f3089) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:07,535 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/4) (def950d6feb829be9cd06a581c6f3089) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
p=5
2023-12-06 10:45:51,425 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Receive slot request 36baecc30276e70935cea5246ce9738d for job 1fd73f83a716da9f0b3aa769687287e2 from resource manager with leader id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,425 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Allocated slot for 36baecc30276e70935cea5246ce9738d.
..............................................
2023-12-06 10:45:51,463 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Offer reserved slots to the leader of job 1fd73f83a716da9f0b3aa769687287e2.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,463 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 36baecc30276e70935cea5246ce9738d.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,464 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot f2b43e2529e1649dbdd931214c9f94ea.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot f2b43e2529e1649dbdd931214c9f94ea.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 8158510413de83b2cf98f1b610fbc85d.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot f2b43e2529e1649dbdd931214c9f94ea.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 8158510413de83b2cf98f1b610fbc85d.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot a305dcf6190e4f1ce377a8dd4bff7461.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot f2b43e2529e1649dbdd931214c9f94ea.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,475 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/5).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,489 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) (b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,490 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 8158510413de83b2cf98f1b610fbc85d.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,491 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,491 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/5) (d8864a3c570049ce4eca5a353564e6df) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,492 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot a305dcf6190e4f1ce377a8dd4bff7461.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,492 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,492 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) (c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,494 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) (130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,494 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) (b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,494 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) (b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,494 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) (b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,495 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) (130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,495 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) (130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,495 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) (130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,508 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) (c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,509 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) (c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,509 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) (c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,522 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/5) (d8864a3c570049ce4eca5a353564e6df) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,522 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/5) (d8864a3c570049ce4eca5a353564e6df) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,522 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (2/5) (d8864a3c570049ce4eca5a353564e6df) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,524 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) (b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,524 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) (b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,524 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (1/5) b42996ba5c2dd049f48bdf145a958284.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,549 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) (130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,549 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) (130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,549 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (4/5) 130f7afca9aef9f118f3a8bf2ef0faf0.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,550 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) (c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,550 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) (c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,550 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (3/5) c5916f065223d42e912caaedfacf84c8.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,551 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot f2b43e2529e1649dbdd931214c9f94ea.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,551 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task DataSink (collect()) (1/5).
2023-12-06 10:45:51,557 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 36baecc30276e70935cea5246ce9738d.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,557 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (5/5).
.....
2023-12-06 10:45:51,562 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (5/5) (98314de2f88839e8129230fdec72e1c0) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2023-12-06 10:45:51,562 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (5/5) (98314de2f88839e8129230fdec72e1c0) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,563 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Registering task at network: Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (5/5) (98314de2f88839e8129230fdec72e1c0) [DEPLOYING].
2023-12-06 10:45:51,563 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Reduce (SUM(1), at main(WordCount.java:87) (5/5) (98314de2f88839e8129230fdec72e1c0) switched from DEPLOYING to RUNNING.
.....................
不过需要注意,再高就会出问题 Flink: fail fast if job parallelism is larger than the total number of slots (opens new window)
中文解读:Apache Flink——任务(Tasks)和任务槽(Task Slots) (opens new window) Flink: fail fast if job parallelism is larger than the total number of slots (opens new window) Re: Is there any way to set the parallelism of operators like group by, join? (opens new window)
# operator chaining
An Operator Chain consists of two or more consecutive Operators without any repartitioning in between. Operators within the same Operator Chain forward records to each other directly without going through serialization or Flink’s network stack.
The sample dataflow in the figure below is executed with five subtasks, and hence with five parallel threads:

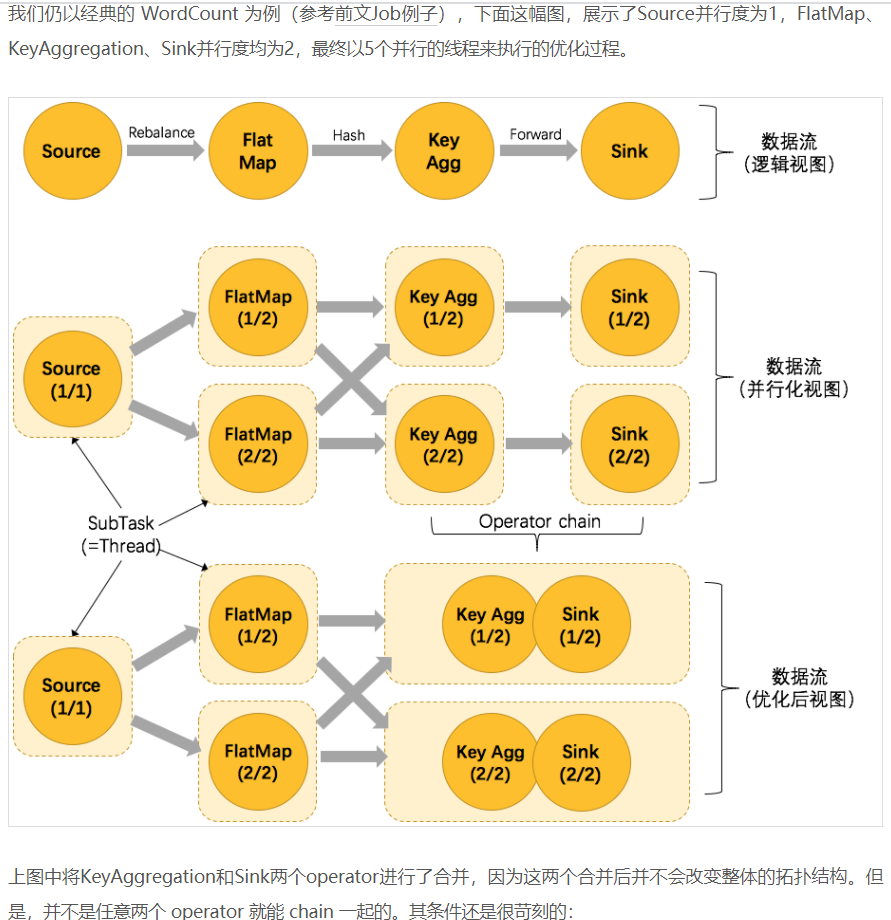
http://wuchong.me/blog/2016/05/09/flink-internals-understanding-execution-resources/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62664972/what-happens-if-total-parallel-instances-of-operators-are-higher-than-the-parall
# 总结:
一个程序Process可以运行在多个TM上,一个TM有多个TS(TS的总和代表支持的最高并行度),一个TS中可以运行多个sub task(task实例),每个subtask都对应一个Thread
对 TM 而言:它占用着一定数量的 CPU 和 Memory 资源,具体可通过 taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots, taskmanager.heap.size 来配置,实际上 taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots 只是指定 TM 的 Slot 数量,并不能隔离指定数量的 CPU 给 TM 使用。在不考虑 Slot Sharing的情况下,一个 Slot 内运行着一个 SubTask(Task 实现 Runable,SubTask 是一个执行 Task 的具体实例),所以官方建议 taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots 配置的 Slot 数量和 CPU 相等或成比例。
当然,我们可以借助 Yarn 等调度系统,用 Flink On Yarn 的模式来为 Yarn Container 分配指定数量的 CPU 资源,以达到较严格的 CPU 隔离(Yarn 采用 Cgroup 做基于时间片的资源调度,每个 Container 内运行着一个 JM/TM 实例)。而 taskmanager.heap.size 用来配置 TM 的 Memory,如果一个 TM 有 N 个 Slot,则每个 Slot 分配到的 Memory 大小为整个 TM Memory 的 1/N,同一个 TM 内的 Slots 只有 Memory 隔离,CPU 是共享的。
对 Job 而言:一个 Job 所需的 Slot 数量大于等于 Operator 配置的最大 Parallelism 数,在保持所有 Operator 的 slotSharingGroup 一致的前提下 Job 所需的 Slot 数量与 Job 中 Operator 配置的最大 Parallelism 相等。
# 1.1.3 StreamGraph/JobGraph/ExecutionGraph

StreamGraph:根据用户通过 Stream API 编写的代码生成的最初的图。
- StreamNode:用来代表 operator 的类,并具有所有相关的属性,如并发度、入边和出边等。
- StreamEdge:表示连接两个StreamNode的边。
JobGraph:StreamGraph经过优化后生成了 JobGraph,提交给JobManager 的数据结构。
- JobVertex:经过优化后符合条件的多个StreamNode可能会chain在一起生成一个JobVertex,即一个JobVertex包含一个或多个operator,JobVertex的输入是JobEdge,输出是IntermediateDataSet。
- IntermediateDataSet:表示JobVertex的输出,即经过operator处理产生的数据集。producer是JobVertex,consumer是JobEdge。
- JobEdge:代表了job graph中的一条数据传输通道。source 是 IntermediateDataSet,target 是 JobVertex。即数据通过JobEdge由IntermediateDataSet传递给目标JobVertex。
ExecutionGraph:JobManager 根据 JobGraph 生成ExecutionGraph。ExecutionGraph是JobGraph的并行化版本,是调度层最核心的数据结构。
- ExecutionJobVertex:和JobGraph中的JobVertex一一对应。每一个ExecutionJobVertex都有和并发度一样多的 ExecutionVertex。
- ExecutionVertex:表示ExecutionJobVertex的其中一个并发子任务,输入是ExecutionEdge,输出是IntermediateResultPartition。
- IntermediateResult:和JobGraph中的IntermediateDataSet一一对应。一个IntermediateResult包含多个IntermediateResultPartition,其个数等于该operator的并发度
- IntermediateResultPartition:表示ExecutionVertex的一个输出分区,producer是ExecutionVertex,consumer是若干个ExecutionEdge。
- ExecutionEdge:表示ExecutionVertex的输入,source是IntermediateResultPartition,target是ExecutionVertex。source和target都只能是一个。
- Execution:是执行一个 ExecutionVertex 的一次尝试。当发生故障或者数据需要重算的情况下 ExecutionVertex 可能会有多个 ExecutionAttemptID。一个 Execution 通过 ExecutionAttemptID 来唯一标识。JM和TM之间关于 task 的部署和 task status 的更新都是通过 ExecutionAttemptID 来确定消息接受者。
物理执行图:JobManager 根据 ExecutionGraph 对 Job 进行调度后,在各个TaskManager 上部署 Task 后形成的“图”,并不是一个具体的数据结构。
- Task:Execution被调度后在分配的 TaskManager 中启动对应的 Task。Task 包裹了具有用户执行逻辑的 operator。
- ResultPartition:代表由一个Task的生成的数据,和ExecutionGraph中的IntermediateResultPartition一一对应。
- ResultSubpartition:是ResultPartition的一个子分区。每个ResultPartition包含多个ResultSubpartition,其数目要由下游消费 Task 数和 DistributionPattern 来决定。
- InputGate:代表Task的输入封装,和JobGraph中JobEdge一一对应。每个InputGate消费了一个或多个的ResultPartition。
- InputChannel:每个InputGate会包含一个以上的InputChannel,和ExecutionGraph中的ExecutionEdge一一对应,也和ResultSubpartition一对一地相连,即一个InputChannel接收一个ResultSubpartition的输出。
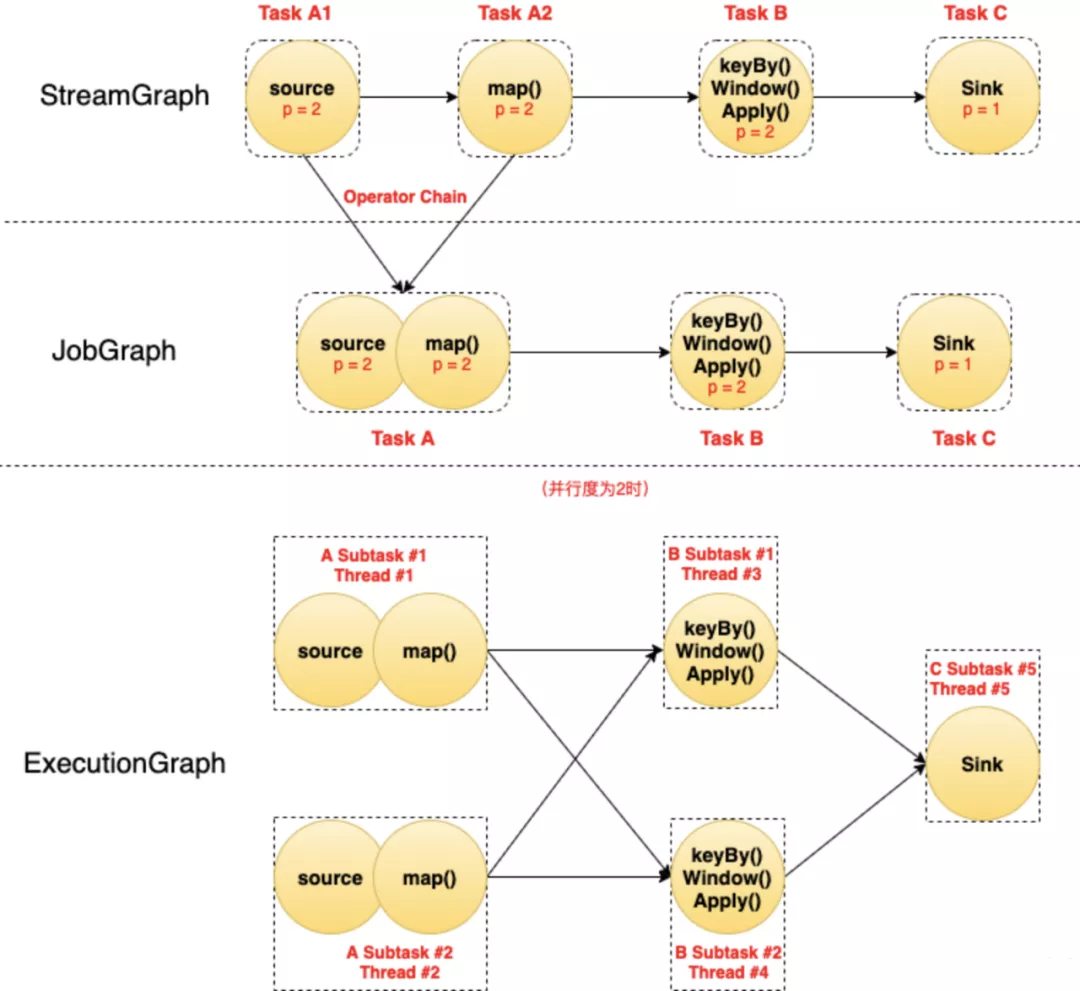
图中每个圆代表一个Operator(算子),每个虚线圆角框代表一个Task,每个虚线直角框代表一个Subtask,其中的p表示算子的并行度。 最上面是StreamGraph,在没有经过任何优化时,可以看到包含4个Operator/Task:Task A1、Task A2、Task B、Task C。
StreamGraph经过Chain优化(后面讲)之后,Task A1和Task A2两个Task合并成了一个新的Task A(可以认为合并产生了一个新的Operator),得到了中间的JobGraph。
然后以并行度为2(需要2个Slot)执行的时候,Task A产生了2个Subtask,分别占用了Thread #1和Thread #2两个线程;Task B产生了2个Subtask,分别占用了Thread #3和Thread #4两个线程;Task C产生了1个Subtask,占用了Thread #5。
# 1.2 Key Concepts
# Streams
Obviously, streams are a fundamental aspect of stream processing. However, streams can have different characteristics that affect how a stream can and should be processed. Flink is a versatile processing framework that can handle any kind of stream.
Bounded and unbounded streams: Streams can be unbounded or bounded, i.e., fixed-sized data sets. Flink has sophisticated features to process unbounded streams, but also dedicated operators to efficiently process bounded streams.
Unbounded streams have a start but no defined end. They do not terminate and provide data as it is generated. Unbounded streams must be continuously processed, i.e., events must be promptly handled after they have been ingested. It is not possible to wait for all input data to arrive because the input is unbounded and will not be complete at any point in time. Processing unbounded data often requires that events are ingested in a specific order, such as the order in which events occurred, to be able to reason about result completeness.
Bounded streams have a defined start and end. Bounded streams can be processed by ingesting all data before performing any computations. Ordered ingestion is not required to process bounded streams because a bounded data set can always be sorted. Processing of bounded streams is also known as batch processing.
Real-time and recorded streams: All data are generated as streams. There are two ways to process the data. Processing it in real-time as it is generated or persisting the stream to a storage system, e.g., a file system or object store, and processed it later. Flink applications can process recorded or real-time streams.
# State
Every non-trivial streaming application is stateful, i.e., only applications that apply transformations on individual events do not require state. Any application that runs basic business logic needs to remember events or intermediate results to access them at a later point in time, for example when the next event is received or after a specific time duration. Application state is a first-class citizen in Flink. You can see that by looking at all the features that Flink provides in the context of state handling.
- Multiple State Primitives: Flink provides state primitives for different data structures, such as atomic values, lists, or maps. Developers can choose the state primitive that is most efficient based on the access pattern of the function.
- Pluggable State Backends: Application state is managed in and checkpointed by a pluggable state backend. Flink features different state backends that store state in memory or in RocksDB, an efficient embedded on-disk data store. Custom state backends can be plugged in as well.
- Exactly-once state consistency: Flink’s checkpointing and recovery algorithms guarantee the consistency of application state in case of a failure. Hence, failures are transparently handled and do not affect the correctness of an application.
- Very Large State: Flink is able to maintain application state of several terabytes in size due to its asynchronous and incremental checkpoint algorithm.
- Scalable Applications: Flink supports scaling of stateful applications by redistributing the state to more or fewer workers.
# Time
- Event-time Mode: Applications that process streams with event-time semantics compute results based on timestamps of the events. Thereby, event-time processing allows for accurate and consistent results regardless whether recorded or real-time events are processed.
- Watermark Support: Flink employs watermarks to reason about time in event-time applications. Watermarks are also a flexible mechanism to trade-off the latency and completeness of results.
- Late Data Handling: When processing streams in event-time mode with watermarks, it can happen that a computation has been completed before all associated events have arrived. Such events are called late events. Flink features multiple options to handle late events, such as rerouting them via side outputs and updating previously completed results.
- Processing-time Mode: In addition to its event-time mode, Flink also supports processing-time semantics which performs computations as triggered by the wall-clock time of the processing machine. The processing-time mode can be suitable for certain applications with strict low-latency requirements that can tolerate approximate results.
# Other Terms
Cluster
- Flink Cluster A distributed system consisting of (typically) one JobManager and one or more Flink TaskManager processes.
- Flink Application Cluster A Flink Application Cluster is a dedicated Flink Cluster that only executes Flink Jobs from one Flink Application. The lifetime of the Flink Cluster is bound to the lifetime of the Flink Application.
- Flink Job Cluster A Flink Job Cluster is a dedicated Flink Cluster that only executes a single Flink Job. The lifetime of the Flink Cluster is bound to the lifetime of the Flink Job. This deployment mode has been deprecated since Flink 1.15.
- Flink Session Cluster A long-running Flink Cluster which accepts multiple Flink Jobs for execution. The lifetime of this Flink Cluster is not bound to the lifetime of any Flink Job. Formerly, a Flink Session Cluster was also known as a Flink Cluster in session mode. Compare to Flink Application Cluster.
Manager
- Flink TaskManager TaskManagers are the worker processes of a Flink Cluster. Tasks are scheduled to TaskManagers for execution. They communicate with each other to exchange data between subsequent Tasks.
- Flink JobManager
The JobManager is the orchestrator of a Flink Cluster. It contains three distinct components:
- Flink Resource Manager,
- Flink Dispatcher
- and one Flink JobMaster per running Flink Job. JobMasters are one of the components running in the JobManager. A JobMaster is responsible for supervising the execution of the Tasks of a single job.
Flink Application A Flink application is a Java Application that submits one or multiple Flink Jobs from the main() method (or by some other means). Submitting jobs is usually done by calling execute() on an execution environment. The jobs of an application can either be submitted to a long running Flink Session Cluster, to a dedicated Flink Application Cluster, or to a Flink Job Cluster.
Record Records are the constituent elements of a data set or data stream. Operators and Functions receive records as input and emit records as output.
Event An event is a statement about a change of the state of the domain modelled by the application. Events can be input and/or output of a stream or batch processing application. Events are special types of records.
Instance The term instance is used to describe a specific instance of a specific type (usually Operator or Function) during runtime. As Apache Flink is mostly written in Java, this corresponds to the definition of Instance or Object in Java. In the context of Apache Flink, the term parallel instance is also frequently used to emphasize that multiple instances of the same Operator or Function type are running in parallel.
- Operator Node of a Logical Graph. An Operator performs a certain operation, which is usually executed by a Function. Sources and Sinks are special Operators for data ingestion and data egress. https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.15/docs/dev/datastream/operators/overview/
- Function Functions are implemented by the user and encapsulate the application logic of a Flink program. Most Functions are wrapped by a corresponding Operator. https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.15/docs/dev/datastream/user_defined_functions/
JobResultStore The JobResultStore is a Flink component that persists the results of globally terminated (i.e. finished, cancelled or failed) jobs to a filesystem, allowing the results to outlive a finished job. These results are then used by Flink to determine whether jobs should be subject to recovery in highly-available clusters.
Managed State Managed State describes application state which has been registered with the framework. For Managed State, Apache Flink will take care about persistence and rescaling among other things.
Checkpoint Storage The location where the State Backend will store its snapshot during a checkpoint (Java Heap of JobManager or Filesystem).
Partition A partition is an independent subset of the overall data stream or data set. A data stream or data set is divided into partitions by assigning each record to one or more partitions. Partitions of data streams or data sets are consumed by Tasks during runtime. A transformation which changes the way a data stream or data set is partitioned is often called repartitioning.
(Runtime) Execution Mode DataStream API programs can be executed in one of two execution modes: BATCH or STREAMING. See Execution Mode for more details.
State Backend For stream processing programs, the State Backend of a Flink Job determines how its state is stored on each TaskManager (Java Heap of TaskManager or (embedded) RocksDB).
Table Program A generic term for pipelines declared with Flink’s relational APIs (Table API or SQL).
Transformation A Transformation is applied on one or more data streams or data sets and results in one or more output data streams or data sets. A transformation might change a data stream or data set on a per-record basis, but might also only change its partitioning or perform an aggregation. While Operators and Functions are the “physical” parts of Flink’s API, Transformations are only an API concept. Specifically, most transformations are implemented by certain Operators.
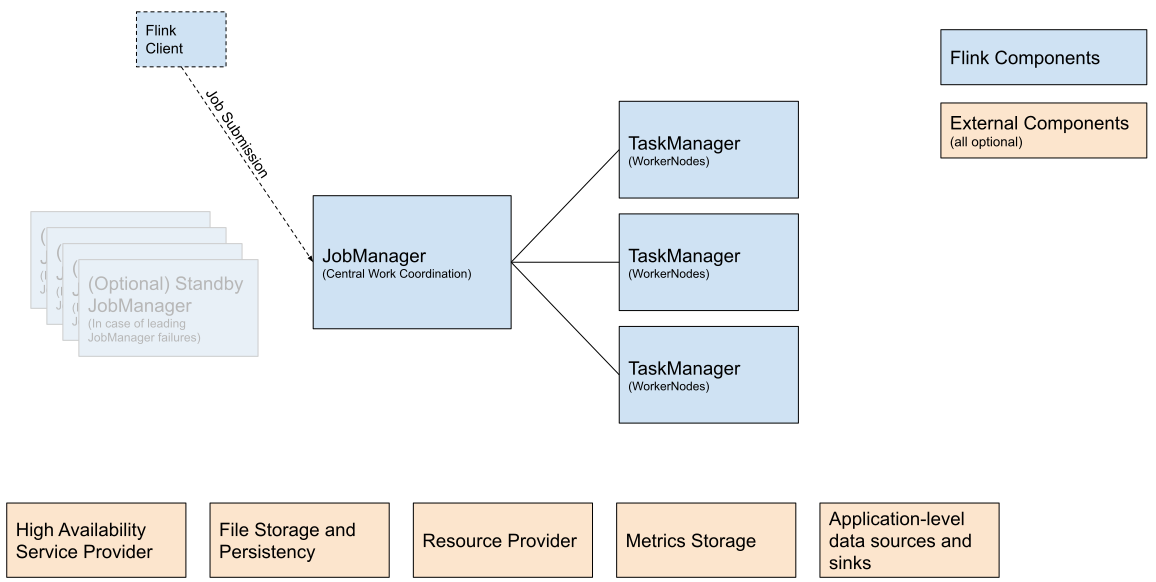
# 2. Deployment
# 2.0 Deployment Mode
Deployment Modes (opens new window)
# Flink Client
Compiles batch or streaming applications into a dataflow graph, which it then submits to the JobManager.
Implementation:
$ ./bin/flink list
./bin/flink run -p 2 ./examples/*WordCount-java*.jar
post http://localhost:8081/jars/${jarId}/run
# JobManager
JobManager is the name of the central work coordination component of Flink. It has implementations for different resource providers, which differ on high-availability, resource allocation behavior and supported job submission modes.
JobManager modes for job submissions:
- Application Mode:
runs the cluster exclusively for one application. The job's main method (or client) gets executed on the JobManager. Calling
execute/executeAsyncmultiple times in an application is supported. -Per-Job Mode: runs the cluster exclusively for one job. The job's main method (or client) runs only prior to the cluster creation. - Session Mode: one JobManager instance manages multiple jobs sharing the same cluster of TaskManagers
Implementation:
- Standalone (this is the barebone mode that requires just JVMs to be launched. Deployment with Docker, Docker Swarm / Compose, non-native Kubernetes and other models is possible through manual setup in this mode)
- Kubernetes
- YARN
# TaskManager
TaskManagers are the services actually performing the work of a Flink job.
# Optional External Components - High Availability Service Provider
Flink's JobManager can be run in high availability mode which allows Flink to recover from JobManager faults. In order to failover faster, multiple standby JobManagers can be started to act as backups.
- Zookeeper
- Kubernetes HA
# Optional External Components - File Storage and Persistency
For checkpointing (recovery mechanism for streaming jobs) Flink relies on external [file storage systems](https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/filesystems/overview/)
- Local File System Flink has built-in support for the file system of the local machine, including any NFS or SAN drives mounted into that local file system. It can be used by default without additional configuration. Local files are referenced with the file:// URI scheme.
- hadoop-compatible
- Pluggable File Systems (Amazon S3, Aliyun OSS and Azure Blob Storage.)
# Optional External Components - Resource Provider
Flink can be deployed through different Resource Provider Frameworks, such as Kubernetes or YARN. See JobManager implementations above.
# Optional External Components - Metrics Storage
# Optional External Components - Application-level data sources and sinks
While application-level data sources and sinks are not technically part of the deployment of Flink cluster components, they should be considered when planning a new Flink production deployment. Colocating frequently used data with Flink can have significant performance benefits
Predefined Sources (opens new window) and Sinks (opens new window) A few basic data sources and sinks are built into Flink and are always available. The predefined data sources include reading from files, directories, and sockets, and ingesting data from collections and iterators. The predefined data sinks support writing to files, to stdout and stderr, and to sockets.
Bundled Connectors Connectors provide code for interfacing with various third-party systems. Currently these systems are supported:
- Apache Kafka (source/sink) (opens new window)
- Apache Cassandra (source/sink) (opens new window)
- Amazon DynamoDB (sink) (opens new window)
- Amazon Kinesis Data Streams (source/sink) (opens new window)
- Amazon Kinesis Data Firehose (sink) (opens new window)
- DataGen (source) (opens new window)
- Elasticsearch (sink) (opens new window)
- Opensearch (sink) (opens new window)
- FileSystem (source/sink) (opens new window)
- RabbitMQ (source/sink) (opens new window)
- Google PubSub (source/sink) (opens new window)
- Hybrid Source (source) (opens new window)
- Apache Pulsar (source) (opens new window)
- JDBC (sink) (opens new window)
- MongoDB (source/sink) (opens new window)
Connectors in Apache Bahir Additional streaming connectors for Flink are being released through Apache Bahir, including:
- Apache ActiveMQ (source/sink) (opens new window)
- Apache Flume (sink) (opens new window)
- Redis (sink) (opens new window)
- Akka (sink) (opens new window)
- Netty (source) (opens new window)
- Data Enrichment via Async I/O (opens new window) Using a connector isn’t the only way to get data in and out of Flink. One common pattern is to query an external database or web service in a Map or FlatMap in order to enrich the primary datastream. Flink offers an API for Asynchronous I/O to make it easier to do this kind of enrichment efficiently and robustly.
# 2.1 Resource Provider Standalone Mode: Local Standalone
The standalone mode is the most barebone way of deploying Flink: The Flink services described in the deployment overview are just launched as processes on the operating system. Unlike deploying Flink with a resource provider such as Kubernetes or YARN, you have to take care of restarting failed processes, or allocation and de-allocation of resources during operation.
Deployment/Standalone (opens new window)
# Insall
# Session Mode
$ java -version
$ tar -xzf flink-*.tgz
$ cd flink-* && ls -l
$ ./bin/start-cluster.sh //started 2 processes: A JVM for the JobManager, and a JVM for the TaskManager.
localhost:8081 to view the Flink dashboard
$ ./bin/stop-cluster.sh
$ ./bin/flink run examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
$ tail log/flink-*-taskexecutor-*.out
WordCount: https://github.com/apache/flink/blob/master/flink-examples/flink-examples-streaming/src/main/java/org/apache/flink/streaming/examples/wordcount/WordCount.java
public class WordCount
{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
MultipleParameterTool params = MultipleParameterTool.fromArgs(args);
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.getConfig().setGlobalJobParameters(params);
DataStreamSource dataStreamSource = null;
if (params.has("input")) {
DataStream dataStream;
for (String input : params.getMultiParameterRequired("input")) {
if (dataStreamSource == null) {
DataStreamSource dataStreamSource1; dataStreamSource1 = env.readTextFile(input); continue;
}
dataStream = dataStreamSource1.union(new DataStream[] { env.readTextFile(input) });
}
Preconditions.checkNotNull(dataStream, "Input DataStream should not be null.");
} else {
System.out.println("Executing WordCount example with default input data set.");
System.out.println("Use --input to specify file input.");
dataStreamSource = env.fromElements(WordCountData.WORDS);
}
SingleOutputStreamOperator singleOutputStreamOperator = dataStreamSource.flatMap(new Tokenizer()).keyBy(value -> (String)value.f0).sum(1);
if (params.has("output")) {
singleOutputStreamOperator.writeAsText(params.get("output"));
} else {
System.out.println("Printing result to stdout. Use --output to specify output path.");
singleOutputStreamOperator.print();
}
env.execute("Streaming WordCount");
}
public static final class Tokenizer extends Object implements FlatMapFunction<String, Tuple2<String, Integer>> {
public void flatMap(String value, Collector<Tuple2<String, Integer>> out) { // Byte code:
// 0: aload_1
// 1: invokevirtual toLowerCase : ()Ljava/lang/String;
// 4: ldc '\W+'
// 6: invokevirtual split : (Ljava/lang/String;)[Ljava/lang/String;
// 9: astore_3
// 10: aload_3
// 11: astore #4
// 13: aload #4
// 15: arraylength
// 16: istore #5
// 18: iconst_0
// 19: istore #6
// 21: iload #6
// 23: iload #5
// 25: if_icmpge -> 68
// 28: aload #4
// 30: iload #6
// 32: aaload
// 33: astore #7
// 35: aload #7
// 37: invokevirtual length : ()I
// 40: ifle -> 62
// 43: aload_2
// 44: new org/apache/flink/api/java/tuple/Tuple2
// 47: dup
// 48: aload #7
// 50: iconst_1
// 51: invokestatic valueOf : (I)Ljava/lang/Integer;
// 54: invokespecial <init> : (Ljava/lang/Object;Ljava/lang/Object;)V
// 57: invokeinterface collect : (Ljava/lang/Object;)V
// 62: iinc #6, 1
// 65: goto -> 21
// 68: return
// Line number table:
// Java source line number -> byte code offset
// #115 -> 0
// #118 -> 10
// #119 -> 35
// #120 -> 43
// #118 -> 62
// #123 -> 68
// Local variable table:
// start length slot name descriptor
// 35 27 7 token Ljava/lang/String;
// 0 69 0 this Lorg/apache/flink/streaming/examples/wordcount/WordCount$Tokenizer;
// 0 69 1 value Ljava/lang/String;
// 0 69 2 out Lorg/apache/flink/util/Collector;
// 10 59 3 tokens [Ljava/lang/String;
// Local variable type table:
// start length slot name signature
// 0 69 2 out Lorg/apache/flink/util/Collector<Lorg/apache/flink/api/java/tuple/Tuple2<Ljava/lang/String;Ljava/lang/Integer;>;>; }
}
}
# Application Mode
The application jar file needs to be available in the classpath. The easiest approach to achieve that is putting the jar into the lib/ folder:
$ cp ./examples/streaming/TopSpeedWindowing.jar lib/
To start a Flink JobManager with an embedded application, we use the bin/standalone-job.sh script. We demonstrate this mode by locally starting the TopSpeedWindowing.jar example, running on a single TaskManager.
$ ./bin/standalone-job.sh start --job-classname org.apache.flink.streaming.examples.windowing.TopSpeedWindowing
The web interface is now available at localhost:8081. However, the application won’t be able to start, because there are no TaskManagers running yet:
$ ./bin/taskmanager.sh start //Note: You can start multiple TaskManagers, if your application needs more resources.
Stopping the services is also supported via the scripts. Call them multiple times if you want to stop multiple instances, or use stop-all:
$ ./bin/taskmanager.sh stop
$ ./bin/standalone-job.sh stop
# Multiple Instances
bin/start-cluster.sh and bin/stop-cluster.sh rely on conf/masters and conf/workers to determine the number of cluster component instances.
Example 1: Start a cluster with 2 TaskManagers locally
conf/masters contents:
localhost
conf/workers contents:
localhost
localhost
If password-less SSH access to the listed machines is configured, and they share the same directory structure, the scripts also support starting and stopping instances remotely.
Example 2: Start a distributed cluster JobManagers
This assumes a cluster with 4 machines (master1, worker1, worker2, worker3), which all can reach each other over the network.
conf/masters contents:
master1
conf/workers contents:
worker1
worker2
worker3
Note that the configuration key jobmanager.rpc.address needs to be set to master1 for this to work.
High-Availability Example 3: Standalone HA Cluster with 2 JobManagers
1. In order to enable HA for a standalone cluster, you have to use the ZooKeeper HA services.
Configure high availability mode and ZooKeeper quorum in conf/flink-conf.yaml:
high-availability.type: zookeeper
high-availability.zookeeper.quorum: localhost:2181
high-availability.zookeeper.path.root: /flink
high-availability.cluster-id: /cluster_one # important: customize per cluster
high-availability.storageDir: hdfs:///flink/recovery
2. In order to start an HA-cluster configure the masters file in conf/masters, the masters file contains all hosts, on which JobManagers are started, and the ports to which the web user interface binds.
Configure masters in conf/masters:
localhost:8081
localhost:8082
3. Configure ZooKeeper server in conf/zoo.cfg (currently it’s only possible to run a single ZooKeeper server per machine):
server.0=localhost:2888:3888
4. Start ZooKeeper quorum:
$ ./bin/start-zookeeper-quorum.sh
Starting zookeeper daemon on host localhost.
5. Start an HA-cluster:
$ ./bin/start-cluster.sh
Starting HA cluster with 2 masters and 1 peers in ZooKeeper quorum.
Starting standalonesession daemon on host localhost.
Starting standalonesession daemon on host localhost.
Starting taskexecutor daemon on host localhost.
6. Stop ZooKeeper quorum and cluster:
$ ./bin/stop-cluster.sh
Stopping taskexecutor daemon (pid: 7647) on localhost.
Stopping standalonesession daemon (pid: 7495) on host localhost.
Stopping standalonesession daemon (pid: 7349) on host localhost.
$ ./bin/stop-zookeeper-quorum.sh
Stopping zookeeper daemon (pid: 7101) on host localhost.
By default, the JobManager will pick a random port for inter process communication. You can change this via the high-availability.jobmanager.port key. This key accepts single ports (e.g. 50010), ranges (50000-50025), or a combination of both (50010,50011,50020-50025,50050-50075).
# Log Analysis
# Job Manager Log
vim log/flink-root-standalonesession-0-vm01.log
# 启动
2022-05-26 14:14:26,762 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.DispatcherRestEndpoint [] - Rest endpoint listening at localhost:8081
2022-05-26 14:14:26,763 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.DispatcherRestEndpoint [] - http://localhost:8081 was granted leadership with leaderSessionID=00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000
2022-05-26 14:14:26,765 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.DispatcherRestEndpoint [] - Web frontend listening at http://localhost:8081.
2022-05-26 14:14:26,816 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.runner.DefaultDispatcherRunner [] - DefaultDispatcherRunner was granted leadership with leader id 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000. Creating new DispatcherLeaderProcess.
2022-05-26 14:14:26,823 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.runner.SessionDispatcherLeaderProcess [] - Start SessionDispatcherLeaderProcess.
2022-05-26 14:14:26,825 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.ResourceManagerServiceImpl [] - Starting resource manager service.
2022-05-26 14:14:26,827 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.runner.SessionDispatcherLeaderProcess [] - Recover all persisted job graphs.
2022-05-26 14:14:26,827 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.ResourceManagerServiceImpl [] - Resource manager service is granted leadership with session id 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000.
2022-05-26 14:14:26,827 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.runner.SessionDispatcherLeaderProcess [] - Successfully recovered 0 persisted job graphs.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,481 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcService [] - Starting RPC endpoint for org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.StandaloneDispatcher at akka://flink/user/rpc/dispatcher_0 .
2022-05-26 14:14:27,516 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcService [] - Starting RPC endpoint for org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.StandaloneResourceManager at akka://flink/user/rpc/resourcemanager_1 .
2022-05-26 14:14:27,543 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.StandaloneResourceManager [] - Starting the resource manager.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,927 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.StandaloneResourceManager [] - Registering TaskManager with ResourceID 10.136.100.48:35016-a4d337 (akka.tcp://[email protected]:35016/user/rpc/taskmanager_0) at ResourceManager
# 接收job,create->running/schedule->deploy
2022-05-27 16:13:00,098 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.StandaloneDispatcher [] - Received JobGraph submission 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,100 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.StandaloneDispatcher [] - Submitting job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,151 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcService [] - Starting RPC endpoint for org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster at akka://flink/user/rpc/jobmanager_2 .
2022-05-27 16:13:00,165 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Initializing job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,211 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Using restart back off time strategy NoRestartBackoffTimeStrategy for Streaming WordCount (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,279 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Running initialization on master for job Streaming WordCount (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,279 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Successfully ran initialization on master in 0 ms.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,321 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.scheduler.adapter.DefaultExecutionTopology [] - Built 1 pipelined regions in 0 ms
2022-05-27 16:13:00,393 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - No state backend has been configured, using default (HashMap) org.apache.flink.runtime.state.hashmap.HashMapStateBackend@3a91353f
2022-05-27 16:13:00,394 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.state.StateBackendLoader [] - State backend loader loads the state backend as HashMapStateBackend
2022-05-27 16:13:00,396 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Checkpoint storage is set to 'jobmanager'
2022-05-27 16:13:00,417 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.checkpoint.CheckpointCoordinator [] - No checkpoint found during restore.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,444 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Using failover strategy org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.failover.flip1.RestartPipelinedRegionFailoverStrategy@6e20b54e for Streaming WordCount (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,460 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Starting execution of job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467) under job master id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,463 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Starting scheduling with scheduling strategy [org.apache.flink.runtime.scheduler.strategy.PipelinedRegionSchedulingStrategy]
2022-05-27 16:13:00,463 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Job Streaming WordCount (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467) switched from state CREATED to RUNNING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,468 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1) (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from CREATED to SCHEDULED.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,468 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1) (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from CREATED to SCHEDULED.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,492 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Connecting to ResourceManager akka.tcp://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/resourcemanager_*(00000000000000000000000000000000)
2022-05-27 16:13:00,499 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Resolved ResourceManager address, beginning registration
2022-05-27 16:13:00,502 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.StandaloneResourceManager [] - Registering job manager [email protected]://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/jobmanager_2 for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,509 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.StandaloneResourceManager [] - Registered job manager [email protected]://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/jobmanager_2 for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,512 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - JobManager successfully registered at ResourceManager, leader id: 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,514 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.slotmanager.DeclarativeSlotManager [] - Received resource requirements from job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467: [ResourceRequirement{resourceProfile=ResourceProfile{UNKNOWN}, numberOfRequiredSlots=1}]
2022-05-27 16:13:00,636 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1) (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from SCHEDULED to DEPLOYING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,637 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Deploying Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1) (attempt #0) with attempt id c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1 to 10.136.100.48:35016-a4d337 @ vm-v08 (dataPort=59281) with allocation id 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb
2022-05-27 16:13:00,646 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1) (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from SCHEDULED to DEPLOYING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,646 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Deploying Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1) (attempt #0) with attempt id a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083 to 10.136.100.48:35016-a4d337 @ vm-v08 (dataPort=59281) with allocation id 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb
2022-05-27 16:13:00,905 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1) (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from DEPLOYING to INITIALIZING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,908 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1) (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from DEPLOYING to INITIALIZING.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,166 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1) (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from INITIALIZING to RUNNING.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,196 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1) (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from INITIALIZING to RUNNING.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,223 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1) (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,246 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1) (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,249 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.executiongraph.ExecutionGraph [] - Job Streaming WordCount (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467) switched from state RUNNING to FINISHED.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,249 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.checkpoint.CheckpointCoordinator [] - Stopping checkpoint coordinator for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,250 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.slotmanager.DeclarativeSlotManager [] - Clearing resource requirements of job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467
2022-05-27 16:13:01,279 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.dispatcher.StandaloneDispatcher [] - Job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467 reached terminal state FINISHED.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,314 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Stopping the JobMaster for job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:01,320 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.checkpoint.StandaloneCompletedCheckpointStore [] - Shutting down
2022-05-27 16:13:01,322 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.slotpool.DefaultDeclarativeSlotPool [] - Releasing slot [3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb].
2022-05-27 16:13:01,328 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.JobMaster [] - Close ResourceManager connection 4a2508526d0621625a55daa90f37e499: Stopping JobMaster for job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:01,330 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.resourcemanager.StandaloneResourceManager [] - Disconnect job manager [email protected]://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/jobmanager_2 for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467 from the resource manager.
# Task Manager Log
vim flink-root-taskexecutor-0-vm01.log
# 启动
INFO [] - Final TaskExecutor Memory configuration:
INFO [] - Total Process Memory: 1.688gb (1811939328 bytes)
INFO [] - Total Flink Memory: 1.250gb (1342177280 bytes)
INFO [] - Total JVM Heap Memory: 512.000mb (536870902 bytes)
INFO [] - Framework: 128.000mb (134217728 bytes)
INFO [] - Task: 384.000mb (402653174 bytes)
INFO [] - Total Off-heap Memory: 768.000mb (805306378 bytes)
INFO [] - Managed: 512.000mb (536870920 bytes)
INFO [] - Total JVM Direct Memory: 256.000mb (268435458 bytes)
INFO [] - Framework: 128.000mb (134217728 bytes)
INFO [] - Task: 0 bytes
INFO [] - Network: 128.000mb (134217730 bytes)
INFO [] - JVM Metaspace: 256.000mb (268435456 bytes)
INFO [] - JVM Overhead: 192.000mb (201326592 bytes)
2022-05-26 14:14:23,738 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskManagerRunner [] - --------------------------------------------------------------------------------
2022-05-26 14:14:23,739 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskManagerRunner [] - Starting TaskManager (Version: 1.14.4, Scala: 2.11, Rev:895c609, Date:2022-02-25T11:57:14+01:00)
................
2022-05-26 14:14:27,050 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.NettyShuffleEnvironment [] - Starting the network environment and its components.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,134 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.netty.NettyClient [] - Transport type 'auto': using EPOLL.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,137 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.netty.NettyClient [] - Successful initialization (took 86 ms).
2022-05-26 14:14:27,143 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.netty.NettyServer [] - Transport type 'auto': using EPOLL.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,186 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.io.network.netty.NettyServer [] - Successful initialization (took 47 ms). Listening on SocketAddress /0.0.0.0:59281.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,187 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.KvStateService [] - Starting the kvState service and its components.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,519 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcService [] - Starting RPC endpoint for org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor at akka://flink/user/rpc/taskmanager_0 .
2022-05-26 14:14:27,541 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.DefaultJobLeaderService [] - Start job leader service.
2022-05-26 14:14:27,543 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.filecache.FileCache [] - User file cache uses directory /tmp/flink-dist-cache-b87b98d1-b215-449a-b134-71cb2efd67e5
2022-05-26 14:14:27,546 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Connecting to ResourceManager akka.tcp://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/resourcemanager_*(00000000000000000000000000000000).
....
2022-05-26 14:14:24,566 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.util.LeaderRetrievalUtils [] - Trying to select the network interface and address to use by connecting to the leading JobManager.
....
2022-05-26 14:14:27,812 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Resolved ResourceManager address, beginning registration
2022-05-26 14:14:27,950 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Successful registration at resource manager akka.tcp://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/resourcemanager_* under registration id 82d6263f9d0c12c01c047caa988f2d1a.
# 接收task,具体执行
2022-05-27 16:13:00,529 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Receive slot request 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467 from resource manager with leader id 00000000000000000000000000000000.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,548 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Allocated slot for 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,551 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.DefaultJobLeaderService [] - Add job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467 for job leader monitoring.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,554 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.DefaultJobLeaderService [] - Try to register at job manager akka.tcp://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/jobmanager_2 with leader id 00000000-0000-0000-0000-000000000000.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,589 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.DefaultJobLeaderService [] - Resolved JobManager address, beginning registration
2022-05-27 16:13:00,613 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.DefaultJobLeaderService [] - Successful registration at job manager akka.tcp://flink@localhost:6123/user/rpc/jobmanager_2 for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,614 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Establish JobManager connection for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,618 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Offer reserved slots to the leader of job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,682 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,706 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.state.changelog.StateChangelogStorageLoader [] - Creating a changelog storage with name 'memory'.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,737 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1), deploy into slot with allocation id 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,739 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,746 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,748 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) [DEPLOYING].
2022-05-27 16:13:00,754 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Activate slot 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,754 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.blob.BlobClient [] - Downloading f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467/p-1e9bc735196982c3db4e502b3af82b3579da2836-dbdb712e9143718fee67e7aab9708f9a from localhost/127.0.0.1:34934
2022-05-27 16:13:00,782 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Received task Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083), deploy into slot with allocation id 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,784 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from CREATED to DEPLOYING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,786 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Loading JAR files for task Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) [DEPLOYING].
2022-05-27 16:13:00,867 INFO org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.StreamTask [] - No state backend has been configured, using default (HashMap) org.apache.flink.runtime.state.hashmap.HashMapStateBackend@47ff2446
2022-05-27 16:13:00,867 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.state.StateBackendLoader [] - State backend loader loads the state backend as HashMapStateBackend
2022-05-27 16:13:00,870 INFO org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.StreamTask [] - Checkpoint storage is set to 'jobmanager'
2022-05-27 16:13:00,874 INFO org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.StreamTask [] - No state backend has been configured, using default (HashMap) org.apache.flink.runtime.state.hashmap.HashMapStateBackend@4f8c0490
2022-05-27 16:13:00,874 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.state.StateBackendLoader [] - State backend loader loads the state backend as HashMapStateBackend
2022-05-27 16:13:00,874 INFO org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.StreamTask [] - Checkpoint storage is set to 'jobmanager'
2022-05-27 16:13:00,894 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from DEPLOYING to INITIALIZING.
2022-05-27 16:13:00,895 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from DEPLOYING to INITIALIZING.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,162 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from INITIALIZING to RUNNING.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,165 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.state.heap.HeapKeyedStateBackendBuilder [] - Finished to build heap keyed state-backend.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,178 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.state.heap.HeapKeyedStateBackend [] - Initializing heap keyed state backend with stream factory.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,194 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from INITIALIZING to RUNNING.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,197 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,197 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 (c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1).
2022-05-27 16:13:01,199 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Source: Collection Source -> Flat Map (1/1)#0 c83c41ff9f43c36e7a6aea483e073ec1.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,240 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083) switched from RUNNING to FINISHED.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,240 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task [] - Freeing task resources for Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 (a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083).
2022-05-27 16:13:01,242 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Un-registering task and sending final execution state FINISHED to JobManager for task Keyed Aggregation -> Sink: Print to Std. Out (1/1)#0 a602bd7b23ece40a69422f7b36701083.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,338 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.slot.TaskSlotTableImpl [] - Free slot TaskSlot(index:0, state:ACTIVE, resource profile: ResourceProfile{cpuCores=1, taskHeapMemory=384.000mb (402653174 bytes), taskOffHeapMemory=0 bytes, managedMemory=512.000mb (536870920 bytes), networkMemory=128.000mb (134217730 bytes)}, allocationId: 3b41f2b6c9f47bf531ac47e91afde9fb, jobId: f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:01,342 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.DefaultJobLeaderService [] - Remove job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467 from job leader monitoring.
2022-05-27 16:13:01,343 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.taskexecutor.TaskExecutor [] - Close JobManager connection for job f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467.
# 具体执行输出
vim log/flink-root-taskexecutor-0-vm01.out
(to,1)
(be,1)
(or,1)
(not,1)
(to,2)
(be,2)
(that,1)
(is,1)
(the,1)
# Client Log
vim log/flink-root-client-vm01.log
2022-05-27 16:12:57,601 INFO org.apache.flink.client.cli.CliFrontend [] - Program Arguments:
2022-05-27 16:12:57,603 INFO org.apache.flink.client.cli.CliFrontend [] - run
2022-05-27 16:12:57,603 INFO org.apache.flink.client.cli.CliFrontend [] - examples/streaming/WordCount.jar
2022-05-27 16:12:58,065 INFO org.apache.flink.client.cli.CliFrontend [] - Running 'run' command.
2022-05-27 16:12:58,098 INFO org.apache.flink.client.cli.CliFrontend [] - Building program from JAR file
2022-05-27 16:12:58,118 INFO org.apache.flink.client.ClientUtils [] - Starting program (detached: false)
2022-05-27 16:12:59,179 INFO org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration [] - Config uses fallback configuration key 'jobmanager.rpc.address' instead of key 'rest.address'
2022-05-27 16:12:59,310 INFO org.apache.flink.client.program.rest.RestClusterClient [] - Submitting job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467).
2022-05-27 16:13:00,207 INFO org.apache.flink.client.program.rest.RestClusterClient [] - Successfully submitted job 'Streaming WordCount' (f69c1ca4892ecbc08d4247ded254f467) to 'http://localhost:8081'.
2022-05-27 16:13:03,555 INFO org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration [] - Config uses fallback configuration key 'jobmanager.rpc.address' instead of key 'rest.address'
# 2.2 Resource Provider Stanalone Mode: Hadoop file system
在文件存储 HDFS 版上使用Apache Flink (opens new window) 阿里巴巴 Flink 踩坑经验:如何大幅降低 HDFS 压力? (opens new window)
# Install with Hadoop
# Hadoop
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/stable/hadoop-project-dist/hadoop-common/ClusterSetup.html#Slaves_File
Typically one machine in the cluster is designated as the NameNode and another machine as the ResourceManager, exclusively. These are the masters. Other services (such as Web App Proxy Server and MapReduce Job History server) are usually run either on dedicated hardware or on shared infrastructure, depending upon the load.
The rest of the machines in the cluster act as both DataNode and NodeManager. These are the workers.
准备:
download hadoop (opens new window)
target:
10.1.1.1: JournalNode, NameNode (active), DataNode, ZKFailoverController
10.1.1.2: JournalNode, NameNode (standby), DataNode, ZKFailoverController
10.1.1.3: JournalNode, NameNode (standby), DataNode, ZKFailoverController
ON MAIN VM:
useradd -m -d /home/hadoop hadoop
passwd hadoop
chmod 755 /home/hadoop
tar -zxvf /tmp/hadoop-3.3.0.tar.gz -C /home/hadoop
ln -s hadoop-3.3.0 hadoop-current
ssh-keygen
ssh-copy-id hadoop@vm-v01
ssh-copy-id hadoop@vm-v02
ssh-copy-id hadoop@vm-v03
yum install -y psmisc
配置Hadoop
cd hadoop-current/etc/hadoop/
cp -p hadoop-env.sh hadoop-env.sh_factory
vi hadoop-env.sh
export JAVA_HOME=/usr/lib/jvm/java-1.8.0-openjdk-1.8.0.332.b09-1.el7_9.x86_64/jre
chmod u+x hadoop-env.sh
cp core-site.xml core-site.xml_factory
vim core-site.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<!--
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License. See accompanying LICENSE file.
-->
<!-- Put site-specific property overrides in this file. -->
<configuration>
<property>
<name>fs.defaultFS</name>
<value>hdfs://test</value>
</property>
</configuration>
cp hdfs-site.xml hdfs-site.xml_factory
HA集群需要使用命名空间区分一个HDFS集群。同一个集群中的不同NameNode,使用不同的NameNode ID区分。为了支持所有NameNode使用相同的配置文件,因此在配置参数中,需要把“nameservice ID”作为NameNode ID的前缀。
dfs.nameservices 命名空间的逻辑名称。提供服务的NS(nameservices)逻辑名称,与core-site.xml里的对应。如果有多个HDFS集群,可以配置多个命名空间的名称,使用逗号分开即可。
dfs.ha.namenodes.[nameservice ID] 命名空间中所有NameNode的唯一标示名称。可以配置多个,使用逗号分隔。该名称是可以让DataNode知道每个集群的所有NameNode。
dfs.namenode.rpc-address.[nameservice ID].[name node ID] 每个namenode监听的RPC地址。
dfs.namenode.http-address.[nameservice ID].[name node ID] 每个namenode监听的http地址。
vim hdfs-site.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<?xml-stylesheet type="text/xsl" href="configuration.xsl"?>
<!--
Licensed under the Apache License, Version 2.0 (the "License");
you may not use this file except in compliance with the License.
You may obtain a copy of the License at
http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0
Unless required by applicable law or agreed to in writing, software
distributed under the License is distributed on an "AS IS" BASIS,
WITHOUT WARRANTIES OR CONDITIONS OF ANY KIND, either express or implied.
See the License for the specific language governing permissions and
limitations under the License. See accompanying LICENSE file.
-->
<!-- Put site-specific property overrides in this file. -->
<configuration>
<property>
<name>dfs.permissions.enabled</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.datanode.registration.ip-hostname-check</name>
<value>false</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.nameservices</name>
<value>test</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.ha.namenodes.test</name>
<value>nn1,nn2,nn3</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.rpc-address.test.nn1</name>
<value>10.1.1.1:13101</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.rpc-address.test.nn2</name>
<value>10.1.1.2:13101</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.rpc-address.test.nn3</name>
<value>10.1.1.3:13101</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.http-address.test.nn1</name>
<value>10.1.1.1:13102</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.http-address.test.nn2</name>
<value>10.1.1.2:13102</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.http-address.test.nn3</name>
<value>10.1.1.3:13102</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.shared.edits.dir</name>
<value>qjournal://10.1.1.1:13106;10.1.1.2:13106;10.1.1.3:13106/test</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.namenode.name.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoop-current/data/dfs/name</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.data.dir</name>
<value>file:///home/hadoop/hadoop-current/data/dfs/data</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.address</name>
<value>0.0.0.0:13103</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.http.address</name>
<value>0.0.0.0:13104</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.datanode.ipc.address</name>
<value>0.0.0.0:13105</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.journalnode.edits.dir</name>
<value>/home/hadoop/hadoop-current/data/dfs/journal</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.journalnode.rpc-address</name>
<value>0.0.0.0:13106</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.journalnode.http-address</name>
<value>0.0.0.0:13107</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.ha.automatic-failover.enabled</name>
<value>true</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.client.failover.proxy.provider.test</name>
<value>org.apache.hadoop.hdfs.server.namenode.ha.ConfiguredFailoverProxyProvider</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.ha.fencing.methods</name>
<value>sshfence</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>dfs.ha.fencing.ssh.private-key-files</name>
<value>/home/hadoop/.ssh/id_rsa</value>
</property>
<property>
<name>ha.zookeeper.quorum</name>
<value>10.1.1.1:12006,10.1.1.2:12006,10.1.1.3:12006</value>
</property>
</configuration>
cp workers workers_factory
vim workers
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.2
10.1.1.3
启动
cd ~/hadoop-current
#In all hosts, start the JournalNode.
./bin/hdfs --daemon start journalnode / sbin/hadoop-daemon.sh start journalnode
tail -f logs/hadoop-hadoop-journalnode-vm-v01.log
# If this is the host for active NameNode (only execute in one host)
# Format (initialize metadata) the NameNode.
# Caution: pls wait for all journalnode fully started first otherwise will get connection refused error
./bin/hdfs namenode -format
# If above commend executed successfully, it will gracefully quit.
# Start the NameNode (the first NameNode started will be the active NameNode).
./bin/hdfs --daemon start namenode / sbin/hadoop-daemon.sh start namenode
# If this is the host for standby NameNode (only execute in hosts other than active namenode)
# Copy metadata from formatted NameNode to this NameNode.
./bin/hdfs namenode -bootstrapStandby
# Start the NameNode (the NameNodes started later will be standby NameNodes).
./bin/hdfs --daemon start namenode / sbin/hadoop-daemon.sh start namenode
此时两个NameNode都是standby模式,需要强制转换一个
bin/hdfs haadmin -transitionToActive --forcemanual nn1
##查看一下状态
bin/hdfs haadmin -getServiceState nn1
bin/hdfs haadmin -getServiceState nn2
#In all hosts, start the DataNode.
./bin/hdfs --daemon start datanode
#Initialize Zookeeper state (execute the following command in only one of the hosts).
./bin/hdfs zkfc -formatZK
#In all hosts, start the ZKFailoverController.
./bin/hdfs --daemon start zkfc
tail -f logs/hadoop-hadoop-journalnode-vm-v01.log
// check
./bin/hdfs getconf -namenodes
./bin/hdfs getconf -secondaryNameNodes
//clearn up and Restart
ps -lef|grep "hadoop"
kill -9 31156
cd hadoop-current/
./sbin/stop-dfs.sh
ps -lef|grep "hadoop"
rm -r ~/hadoop-current/data/ ~/hadoop-current/logs/
#In Zookeeper, delete the directory storing HDFS HA information.
./bin/zkCli.sh -server localhost:12006
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 0] rmr /hadoop-ha
then repeat previous boot up process
# Flink
HOME: /home/flink
download: https://downloads.apache.org/flink/flink-1.11.2/flink-1.11.2-bin-scala_2.11.tgz
Target Setup
10.1.1.1: active JobManager, TaskManager
10.1.1.2: standby JobManager, TaskManager
10.1.1.3: standby JobManager, TaskManager
useradd -m -d /home/flink flink
passwd flink
su - flink
tar zxvf /tmp/flink-1.11.2-bin-scala_2.11.tgz
ln -s flink-1.11.2 flink-current
chmod -R 755 /home/hadoop
ssh-keygen
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
ssh-copy-id [email protected]
vi .bash_profile
PATH=$PATH:$HOME/.local/bin:$HOME/bin
export PATH
export HADOOP_HOME=/home/hadoop/hadoop-current
export HADOOP_CLASSPATH=$(/home/hadoop/hadoop-current/bin/hadoop classpath)
cd ~/flink-current/conf/
cp flink-conf.yaml flink-conf.yaml.bak
vi flink-conf.yaml
env.hadoop.conf.dir: /home/hadoop/hadoop-current/etc/hadoop
env.log.dir: /home/flink/flink-current/log
io.tmp.dirs: /home/flink/flink-current/iotmp
parallelism.default: 1
rest.port: 13001
# Enable uploading JAR files via web UI.
web.submit.enable: true
web.upload.dir: /home/flink/flink-current/upload
high-availability: zookeeper
high-availability.zookeeper.quorum: 10.1.1.1:12006,10.1.1.2:12006,10.1.1.3:12006
high-availability.zookeeper.path.root: /flink
#keeps the hostname without underscore
high-availability.storageDir: hdfs://vm-v01:13101/flink/ha/
high-availability.cluster-id: /default_ns
high-availability.jobmanager.port: 13002
jobmanager.memory.process.size: 16384m
#jobmanager.heap.size: 4096m
jobmanager.execution.failover-strategy: region
# JobManager blob server port used for data transfer.
blob.server.port: 13003
taskmanager.memory.process.size: 16384m
#taskmanager.memory.flink.size: 8192m
taskmanager.memory.jvm-metaspace.size: 4096m
taskmanager.numberOfTaskSlots: 8
taskmanager.data.port: 13004
taskmanager.rpc.port: 13005
restart-strategy: failure-rate
restart-strategy.failure-rate.max-failures-per-interval: 10
restart-strategy.failure-rate.failure-rate-interval: 300s
restart-strategy.failure-rate.delay: 15s
# JobManager and TaskManager expose /metrics REST API for Prometheus to scrape.
metrics.reporters: prom
metrics.reporter.prom.class: org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter
metrics.reporter.prom.port: 13006-13007
vim masters
10.1.1.1:50001
10.1.1.2:50001
10.1.1.3:50001
vim slaves
10.1.1.1
10.1.1.2
10.1.1.3
cd ~/flink-current
mkdir upload
mkdir iotmp
./bin/start-cluster.sh (start only one host)
./bin/stop-cluster.sh
./flink-current/bin/flink -v
#clean up & restart
./bin/stop-cluster.sh
rm -r ~/flink-current/log/* ~/flink-current/iotmp/* ~/flink-current/upload/*
#In HDFS, delete the directory storing Flink HA information (according to flink-conf.yaml high-availability.storageDir).
./bin/hdfs dfs -rm -r /flink/ha
#In Zookeeper, delete the znode storing Flink HA information (according to flink-conf.yaml high-availability.zookeeper.path.root and high-availability.cluster-id).
./bin/zkCli.sh -server localhost:12006
[zk: localhost:2181(CONNECTED) 0] rmr /flink/default_ns
# Log Analysis
# Job Manager Log
vim log/flink-root-standalonesession-0-vm01.log
# Task Manager Log
vim flink-root-taskexecutor-0-vm01.log
2022-05-26 19:05:08,330 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.util.LeaderRetrievalUtils - Trying to select the network interface and address to use by connecting to the leading JobManager.
2022-05-26 19:05:08,330 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.util.LeaderRetrievalUtils - TaskManager will try to connect for PT10S before falling back to heuristics
2022-05-26 19:05:08,474 INFO org.apache.flink.runtime.net.ConnectionUtils - Retrieved new target address /X.X.X.3:13002.
# Failover&Recoery
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.15/docs/try-flink/flink-operations-playground/
# 2.3 Resource Provider Cluster Mode: Hadoop YARN cluster
Apache Hadoop YARN is a resource provider popular with many data processing frameworks. Flink services are submitted to YARN’s ResourceManager, which spawns containers on machines managed by YARN NodeManagers. Flink deploys its JobManager and TaskManager instances into such containers.
Flink can dynamically allocate and de-allocate TaskManager resources depending on the number of processing slots required by the job(s) running on the JobManager.
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/resource-providers/yarn/
# 2.4 Configuration
# Working Directory
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/resource-providers/standalone/working_directory/
Flink supports to configure a working directory (FLIP-198) for Flink processes (JobManager and TaskManager). The working directory is used by the processes to store information that can be recovered upon a process restart. The requirement for this to work is that the process is started with the same identity and has access to the volume on which the working directory is stored.
# dynamic properties
The following scripts also allow configuration parameters to be set via dynamic properties:
jobmanager.sh standalone-job.sh taskmanager.sh historyserver.sh
# log debug:
conf/log4.properties rootLogger.level = DEBUG
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/advanced/logging/
# basics
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/config/
- web.upload.dir
JAR files are renamed when they are uploaded and stored in a directory that can be configured with the web.upload.dir configuration key.
If the web.upload.dir parameter is not set, the JAR files are stored in a dynamically generated directory under the jobmanager.web.tmpdir (default is System.getProperty("java.io.tmpdir")).
# 2.4 Advanced
# History Server
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/advanced/historyserver/
Flink has a history server that can be used to query the statistics of completed jobs after the corresponding Flink cluster has been shut down.
Furthermore, it exposes a REST API that accepts HTTP requests and responds with JSON data.
# External Resource Framework
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/advanced/external_resources/
In addition to CPU and memory, many workloads also need some other resources, e.g. GPUs for deep learning. To support external resources, Flink provides an external resource framework. The framework supports requesting various types of resources from the underlying resource management systems (e.g., Kubernetes), and supplies information needed for using these resources to the operators. Different resource types can be supported. You can either leverage built-in plugins provided by Flink (currently only for GPU support), or implement your own plugins for custom resource types.
# Custom failure enrichers
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.18/docs/deployment/advanced/failure_enrichers/
Flink provides a pluggable interface for users to register their custom logic and enrich failures with extra metadata labels (string key-value pairs). This enables users to implement their own failure enrichment plugins to categorize job failures, expose custom metrics, or make calls to external notification systems.
FailureEnrichers are triggered every time an exception is reported at runtime by the JobManager. Every FailureEnricher may asynchronously return labels associated with the failure that are then exposed via the JobManager’s REST API (e.g., a ’type:System’ label implying the failure is categorized as a system error).
# 3. API&Libs
# Layered APIs
# Stateful Event-Driven Applications - ProcessFunctions(events,state,time)
ProcessFunctions are the most expressive function interfaces that Flink offers. Flink provides ProcessFunctions to process individual events from one or two input streams or events that were grouped in a window. ProcessFunctions provide fine-grained control over time and state. A ProcessFunction can arbitrarily modify its state and register timers that will trigger a callback function in the future. Hence, ProcessFunctions can implement complex per-event business logic as required for many stateful event-driven applications.
/**
* Matches keyed START and END events and computes the difference between
* both elements' timestamps. The first String field is the key attribute,
* the second String attribute marks START and END events.
*/
public static class StartEndDuration
extends KeyedProcessFunction<String, Tuple2<String, String>, Tuple2<String, Long>> {
private ValueState<Long> startTime;
@Override
public void open(Configuration conf) {
// obtain state handle
startTime = getRuntimeContext()
.getState(new ValueStateDescriptor<Long>("startTime", Long.class));
}
/** Called for each processed event. */
@Override
public void processElement(
Tuple2<String, String> in,
Context ctx,
Collector<Tuple2<String, Long>> out) throws Exception {
switch (in.f1) {
case "START":
// set the start time if we receive a start event.
startTime.update(ctx.timestamp());
// register a timer in four hours from the start event.
ctx.timerService()
.registerEventTimeTimer(ctx.timestamp() + 4 * 60 * 60 * 1000);
break;
case "END":
// emit the duration between start and end event
Long sTime = startTime.value();
if (sTime != null) {
out.collect(Tuple2.of(in.f0, ctx.timestamp() - sTime));
// clear the state
startTime.clear();
}
default:
// do nothing
}
}
/** Called when a timer fires. */
@Override
public void onTimer(
long timestamp,
OnTimerContext ctx,
Collector<Tuple2<String, Long>> out) {
// Timeout interval exceeded. Cleaning up the state.
startTime.clear();
}
}
# Stream-&Batch Data Processing - DataStream API(streams,windows)
The DataStream API provides primitives for many common stream processing operations, such as windowing, record-at-a-time transformations, and enriching events by querying an external data store. The DataStream API is available for Java and Scala and is based on functions, such as map(), reduce(), and aggregate(). Functions can be defined by extending interfaces or as Java or Scala lambda functions.
// a stream of website clicks
DataStream<Click> clicks = ...
DataStream<Tuple2<String, Long>> result = clicks
// project clicks to userId and add a 1 for counting
.map(
// define function by implementing the MapFunction interface.
new MapFunction<Click, Tuple2<String, Long>>() {
@Override
public Tuple2<String, Long> map(Click click) {
return Tuple2.of(click.userId, 1L);
}
})
// key by userId (field 0)
.keyBy(0)
// define session window with 30 minute gap
.window(EventTimeSessionWindows.withGap(Time.minutes(30L)))
// count clicks per session. Define function as lambda function.
.reduce((a, b) -> Tuple2.of(a.f0, a.f1 + b.f1));
try out: https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.15/docs/try-flink/datastream/
# High-level Analytics API - SQL/TableAPI(dynamic tables)
Flink features two relational APIs, the Table API and SQL. Both APIs are unified APIs for batch and stream processing, i.e., queries are executed with the same semantics on unbounded, real-time streams or bounded, recorded streams and produce the same results. The Table API and SQL leverage Apache Calcite for parsing, validation, and query optimization. They can be seamlessly integrated with the DataStream and DataSet APIs and support user-defined scalar, aggregate, and table-valued functions.
SELECT userId, COUNT(*)
FROM clicks
GROUP BY SESSION(clicktime, INTERVAL '30' MINUTE), userId
try out: https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.15/docs/try-flink/table_api/
SQL GATEWAY https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.19/docs/dev/table/sql-gateway/overview/#/starting-the-sql-gateway
# Advanced APIs
# Stateful Functions: A Platform-Independent Stateful Serverless Stack
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-statefun-docs-stable/
# Flink ML: Apache Flink Machine Learning Library
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-ml-docs-stable/ https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-ml-docs-release-2.0/docs/try-flink-ml/quick-start/
# Libraries
# Complex Event Processing (CEP):
Pattern detection is a very common use case for event stream processing. Flink’s CEP library provides an API to specify patterns of events (think of regular expressions or state machines). The CEP library is integrated with Flink’s DataStream API, such that patterns are evaluated on DataStreams. Applications for the CEP library include network intrusion detection, business process monitoring, and fraud detection.
# DataSet API:
The DataSet API is Flink’s core API for batch processing applications. The primitives of the DataSet API include map, reduce, (outer) join, co-group, and iterate. All operations are backed by algorithms and data structures that operate on serialized data in memory and spill to disk if the data size exceed the memory budget. The data processing algorithms of Flink’s DataSet API are inspired by traditional database operators, such as hybrid hash-join or external merge-sort.
# Gelly:
Gelly is a library for scalable graph processing and analysis. Gelly is implemented on top of and integrated with the DataSet API. Hence, it benefits from its scalable and robust operators. Gelly features built-in algorithms, such as label propagation, triangle enumeration, and page rank, but provides also a Graph API that eases the implementation of custom graph algorithms.
# Exmaples:
Flink State管理和使用 https://juejin.cn/post/7194847015677722681#heading-2
# 4. Operations
# Run Your Applications Non-Stop 24/7
Machine and process failures are ubiquitous in distributed systems. A distributed stream processors like Flink must recover from failures in order to be able to run streaming applications 24/7. Obviously, this does not only mean to restart an application after a failure but also to ensure that its internal state remains consistent, such that the application can continue processing as if the failure had never happened.
- Consistent Checkpoints: Flink’s recovery mechanism is based on consistent checkpoints of an application’s state. In case of a failure, the application is restarted and its state is loaded from the latest checkpoint. In combination with resettable stream sources, this feature can guarantee exactly-once state consistency.
- Efficient Checkpoints: Checkpointing the state of an application can be quite expensive if the application maintains terabytes of state. Flink’s can perform asynchronous and incremental checkpoints, in order to keep the impact of checkpoints on the application’s latency SLAs very small.
- End-to-End Exactly-Once: Flink features transactional sinks for specific storage systems that guarantee that data is only written out exactly once, even in case of failures.
- Integration with Cluster Managers: Flink is tightly integrated with cluster managers, such as Hadoop YARN, Mesos, or Kubernetes. When a process fails, a new process is automatically started to take over its work.
- High-Availability Setup: Flink feature a high-availability mode that eliminates all single-points-of-failure. The HA-mode is based on Apache ZooKeeper, a battle-proven service for reliable distributed coordination.
# Update, Migrate, Suspend, and Resume Your Applications
Streaming applications that power business-critical services need to be maintained. Bugs need to be fixed and improvements or new features need to be implemented. However, updating a stateful streaming application is not trivial. Often one cannot simply stop the applications and restart a fixed or improved version because one cannot afford to lose the state of the application.
Flink’s Savepoints are a unique and powerful feature that solves the issue of updating stateful applications and many other related challenges. A savepoint is a consistent snapshot of an application’s state and therefore very similar to a checkpoint. However in contrast to checkpoints, savepoints need to be manually triggered and are not automatically removed when an application is stopped. A savepoint can be used to start a state-compatible application and initialize its state. Savepoints enable the following features:
- Application Evolution: Savepoints can be used to evolve applications. A fixed or improved version of an application can be restarted from a savepoint that was taken from a previous version of the application. It is also possible to start the application from an earlier point in time (given such a savepoint exists) to repair incorrect results produced by the flawed version.
- Cluster Migration: Using savepoints, applications can be migrated (or cloned) to different clusters.
- Flink Version Updates: An application can be migrated to run on a new Flink version using a savepoint.
- Application Scaling: Savepoints can be used to increase or decrease the parallelism of an application.
- A/B Tests and What-If Scenarios: The performance or quality of two (or more) different versions of an application can be compared by starting all versions from the same savepoint.
- Pause and Resume: An application can be paused by taking a savepoint and stopping it. At any later point in time, the application can be resumed from the savepoint.
- Archiving: Savepoints can be archived to be able to reset the state of an application to an earlier point in time.
# Monitor and Control Your Applications
Just like any other service, continuously running streaming applications need to be supervised and integrated into the operations infrastructure, i.e., monitoring and logging services, of an organization. Monitoring helps to anticipate problems and react ahead of time. Logging enables root-cause analysis to investigate failures. Finally, easily accessible interfaces to control running applications are an important feature.
Flink integrates nicely with many common logging and monitoring services and provides a REST API to control applications and query information.
- Web UI: Flink features a web UI to inspect, monitor, and debug running applications. It can also be used to submit executions for execution or cancel them.
- Logging: Flink implements the popular slf4j logging interface and integrates with the logging frameworks log4j or logback.
- Metrics: Flink features a sophisticated metrics system to collect and report system and user-defined metrics. Metrics can be exported to several reporters, including JMX, Ganglia, Graphite, Prometheus, StatsD, Datadog, and Slf4j.
- REST API: Flink exposes a REST API to submit a new application, take a savepoint of a running application, or cancel an application. The REST API also exposes meta data and collected metrics of running or completed applications.
# Debug
User jars & Classpath (opens new window)
In Standalone mode, the following jars will be recognized as user-jars and included into user classpath:
Session Mode: The JAR file specified in startup command. Application Mode: The JAR file specified in startup command and all JAR files in Flink’s usrlib folder.
# 5. Integration
dashboard: localhost:8081
jars:
http://localhost:8081/jars http://localhost:8081/jars/${jarId}/run http://localhost:8081/v1/config http://localhost:8081/v1/jobmanager/config http://localhost:8081/v1/jobmanager/logs
# 6. Monitoring
Monitoring Apache Flink Applications 101 (opens new window)
# Customized
package common;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.metrics.Counter;
import org.apache.flink.metrics.Gauge;
import org.apache.flink.metrics.MetricGroup;
import org.apache.flink.shaded.jackson2.com.fasterxml.jackson.databind.node.ObjectNode;
public class MetricMapper extends RichMapFunction<ObjectNode, ObjectNode> {
private transient Counter totalcounter;
private transient Counter mycounter;
private transient long currenttimestamp;
private SimpleDateFormat dateFormatter = new SimpleDateFormat ("yyyyMMdd HH:mm:ss.S");
@Override
public void open(Configuration config) {
MetricGroup metricGroup=getRuntimeContext().getMetricGroup();
this.totalcounter = metricGroup.addGroup("nss").counter("totalcount");
this.mycounter = metricGroup.addGroup("nss").counter("mycounter");
metricGroup.addGroup("nss").gauge("currenttime", new Gauge<Long>() {
@Override
public Long getValue() {
return currenttimestamp;
}
});
}
@Override
public ObjectNode map(ObjectNode value) throws Exception {
if(value.has("MsgType")){
switch(value.get("MsgType").asText()){
case Constant.TYPE1:
this.ordercounter.inc();
this.totalcounter.inc();
if(value.has("time")){
this.currenttimestamp=dateFormatter.parse(value.get("time").asText()).getTime();
}
break;
}
}
return value;
}
}
# View Metric
# flink webui
job => overview => click on the job=> scroll to the end => metric
# Rest Monitoring API
In order to query the metric via Flink's REST interface you need to first figure some ids out:
flink_cluster: Address of your flink cluster port: Port of REST endpoint jobId: Id of your job which can be figured out via http://flink_cluster:port/jobs vertexId: Id of the vertex to query. This can be figured out via http://flink_cluster:port/jobs/:jobId which gives you the job information with all vertexIds subtaskindex: Index of the parallel subtask to query http://flink_cluster:port/jobs/:jobId/vertices/:vertexId/subtasks/:subtaskindex/metrics?get=MyCustomMetric
http://X.X.X.X:8081//jobs/44dd9736f9f84bd6a545f7fea059245e/#/
{"jid":"44dd9736f9f84bd6a545f7fea059245e","name":"TEST Postgres (TEST20240607) > Flink > Redis","isStoppable":false,"state":"FINISHED","start-time":1717989261618,"end-time":1717989299500,"duration":37882,"now":1717990389537,"timestamps":{"INITIALIZING":1717989261618,"CANCELLING":0,"CANCELED":0,"FAILING":0,"FAILED":0,"RESTARTING":0,"SUSPENDED":0,"FINISHED":1717989299500,"RUNNING":1717989261639,"RECONCILING":0,"CREATED":1717989261630},
"vertices":[{"id":"cbc357ccb763df2852fee8c4fc7d55f2","name":"Source: Custom Source -> Map -> Map -> Map -> Sink: Unnamed","parallelism":1,"status":"FINISHED","start-time":1717989261685,"end-time":1717989299499,"duration":37814,"tasks":{"DEPLOYING":0,"CANCELED":0,"RECONCILING":0,"FINISHED":1,"SCHEDULED":0,"RUNNING":0,"FAILED":0,"CREATED":0,"CANCELING":0},"metrics":{"read-bytes":0,"read-bytes-complete":true,"write-bytes":0,"write-bytes-complete":true,"read-records":0,"read-records-complete":true,"write-records":0,"write-records-complete":true}}],"status-counts":{"DEPLOYING":0,"CANCELED":0,"RECONCILING":0,"FINISHED":1,"SCHEDULED":0,"RUNNING":0,"FAILED":0,"CREATED":0,"CANCELING":0},"plan":{"jid":"44dd9736f9f84bd6a545f7fea059245e","name":"TEST Postgres (TEST20240607) > Flink > Redis","nodes":[{"id":"cbc357ccb763df2852fee8c4fc7d55f2","parallelism":1,"operator":"","operator_strategy":"","description":"Source: Custom Source -> Map -> Map -> Map -> Sink: Unnamed","optimizer_properties":{}}]}}
http://X.X.X.X:8081//jobs/44dd9736f9f84bd6a545f7fea059245e/vertices/cbc357ccb763df2852fee8c4fc7d55f2/#/
{"id":"cbc357ccb763df2852fee8c4fc7d55f2","name":"Source: Custom Source -> Map -> Map -> Map -> Sink: Unnamed","parallelism":1,"now":1717990526875,
"subtasks":[{"subtask":0,"status":"FINISHED","attempt":0,"host":"sghc5-stag-nss-beta-v01","start-time":1717989261685,"end-time":1717989299499,"duration":37814,"metrics":{"read-bytes":0,"read-bytes-complete":true,"write-bytes":0,"write-bytes-complete":true,"read-records":0,"read-records-complete":true,"write-records":0,"write-records-complete":true},"taskmanager-id":"X.X.X.X:43268-200172","start_time":1717989261685}]}
http://X.X.X.X:8081//jobs/44dd9736f9f84bd6a545f7fea059245e/vertices/cbc357ccb763df2852fee8c4fc7d55f2/subtasks/0/metrics#/
[{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Output.Buffers.outPoolUsage"},{"id":"checkpointStartDelayNanos"},{"id":"numBytesInLocal"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBytesInRemotePerSecond"},{"id":"numBytesInRemotePerSecond"},{"id":"Source__Custom_Source.numRecordsInPerSecond"},{"id":"numBytesOut"},{"id":"Map.MyGauge"},{"id":"numBytesIn"},{"id":"Map.numRecordsInPerSecond"},{"id":"numBuffersOut"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBuffersInLocal"},{"id":"numBuffersInRemotePerSecond"},{"id":"numBytesOutPerSecond"},{"id":"Map.myCounter"},{"id":"buffers.outputQueueLength"},{"id":"numBuffersOutPerSecond"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.Buffers.inputExclusiveBuffersUsage"},{"id":"isBackPressured"},{"id":"Sink__Unnamed.numRecordsIn"},{"id":"numBytesInLocalPerSecond"},{"id":"Map.currentOutputWatermark"},{"id":"Source__Custom_Source.numSplitsProcessed"},{"id":"Sink__Unnamed.numRecordsOut"},{"id":"buffers.inPoolUsage"},{"id":"idleTimeMsPerSecond"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBytesInLocalPerSecond"},{"id":"numBytesInRemote"},{"id":"Source__Custom_Source.numRecordsOut"},{"id":"Map.numRecordsOutPerSecond"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBytesInLocal"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBytesInRemote"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Output.Buffers.outputQueueLength"},{"id":"Sink__Unnamed.currentInputWatermark"},{"id":"buffers.inputFloatingBuffersUsage"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.Buffers.inPoolUsage"},{"id":"Map.currentInputWatermark"},{"id":"numBuffersInLocalPerSecond"},{"id":"numRecordsOut"},{"id":"numBuffersInLocal"},{"id":"Source__Custom_Source.currentOutputWatermark"},{"id":"numBuffersInRemote"},{"id":"Map.numRecordsOut"},{"id":"buffers.inputQueueLength"},{"id":"Source__Custom_Source.numRecordsOutPerSecond"},{"id":"Sink__Unnamed.numRecordsInPerSecond"},{"id":"numRecordsIn"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBuffersInRemote"},{"id":"numBytesInPerSecond"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.Buffers.inputQueueLength"},{"id":"Source__Custom_Source.numRecordsIn"},{"id":"buffers.inputExclusiveBuffersUsage"},{"id":"Map.numRecordsIn"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBuffersInRemotePerSecond"},{"id":"numRecordsOutPerSecond"},{"id":"buffers.outPoolUsage"},{"id":"Sink__Unnamed.numRecordsOutPerSecond"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.numBuffersInLocalPerSecond"},{"id":"numRecordsInPerSecond"},{"id":"Shuffle.Netty.Input.Buffers.inputFloatingBuffersUsage"},{"id":"Sink__Unnamed.currentOutputWatermark"}]
http://X.X.X.X:8081//jobs/44dd9736f9f84bd6a545f7fea059245e/vertices/cbc357ccb763df2852fee8c4fc7d55f2/subtasks/0/metrics?get=Map.myCounter#/
[{"id":"Map.myCounter","value":"63509"}]
# Metric Reporters
https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-release-1.13/docs/deployment/metric_reporters/#/
# Prometheus
前面都很顺利,到这里就有问题了! https://github.com/mbode/flink-prometheus-example#/ https://juejin.cn/post/7037379343248523295#/
首先是要配置flink的plugin metric-Prometheus reporter
有人说还需要把flink-metrics-prometheus-1.12.0.jar放到 flink/lib下面,貌似不必要 $ find / -name "flink-metrics-prometheus*" /apex/ngs/svl/flink/flink-1.12.0/plugins/metrics-prometheus/flink-metrics-prometheus-1.12.0.jar
刚开始根据文档这么配置
metrics.reporter.prom.class: org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter
$ grep -r "prometheus" ../log/*
../log/flink-flink-standalonesession-0-sghc5-stag-nss-beta-v01.apex.com.log:INFO [] - Loading configuration property: metrics.reporter.prom.class, org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter
../log/flink-flink-standalonesession-0-sghc5-stag-nss-beta-v01.apex.com.log:2024-06-11 17:08:31,267 INFO org.apache.flink.configuration.GlobalConfiguration [] - Loading configuration property: metrics.reporter.prom.class, org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter
../log/flink-flink-standalonesession-0-sghc5-stag-nss-beta-v01.apex.com.log:2024-06-11 17:08:32,620 INFO org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter [] - Started PrometheusReporter HTTP server on port 9249.
打开localhost:9249就会发现只有flink_jobmanager的信息,没有flink_taskmanager, 应该改成如下配置,port给个区间,至少大于1
# JobManager and TaskManager expose /metrics REST API for Prometheus to scrape.
metrics.reporters: prom
metrics.reporter.prom.class: org.apache.flink.metrics.prometheus.PrometheusReporter
metrics.reporter.prom.port: 9250-9260
查看监听端口就会发现至少有两个 9250 9251, 一般 localhost:9250里面就是flink_jobmanager,localhost:9251就是flink_taskmanager和自定义的metric
接着配置Prometheus,就可以接入grafana了(注意一旦接入Prometheus,自定义的Metric在上面的localhost:9251中可能就消失了,至少低版本比如flink1.12是这样)
scrape_configs:
- job_name: 'flink'
static_configs:
- targets: ['flink-host:9249]
乐于助人贴:https://stackoverflow.com/questions/74386011/not-able-to-see-flink-custom-metrics-to-prometheus/78622484#/78622484
# backpressure 背压
A Deep-Dive into Flink's Network Stack (opens new window) How to identify the source of backpressure? (opens new window)
# 7. 深度解析
# Version 版本
Flink 1.12 release notes (opens new window)
# 运行模式和机制
Execution Behavior (opens new window)
# 数据重分布分区和并发 maintain partition
算子数据传递的两种方式:
- One-to-one:数据不需要重新分布,上游SubTask生产的数据与下游SubTask受到的数据完全一致,数据不需要重分区,也就是数据不需要经过IO,比如下图中source->map的数据传递形式就是One-to-One方式。常见的map、fliter、flatMap等算子的SubTask的数据传递都是one-to-one的对应关系。类似于spark中的窄依赖。
- Redistributing:数据需要通过shuffle过程重新分区,需要经过IO,比如上图中的map->keyBy。创建的keyBy、broadcast、rebalance、shuffle等算子的SubTask的数据传递都是Redistributing方式,但它们具体数据传递方式是不同的。类似于spark中的宽依赖。
根据partitioner的分类来进行分析,主要分为四种大类型,即RoundRobinChannelSelector、StreamPartitioner、DataSkewChannelSelector、OutputEmitter四种 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1863680#/
Flink 9种分区策略:
- GlobalPartitioner 数据发到下游算子的第一个实例
dataStream.global() - ShufflePartitioner 数据随机分发到下游算子
dataStream.shuffle() - RebalancePartitioner 数据循环发送到下游的实例
dataStream.setParallelism(2); dataStreamAfter.setParallelism(3); dataStream.rebalance() - BroadcastPartitioner 输出到下游算子的每个实例中
dataStream.broadcast() - ForwardPartitioner 上下游算子并行度一致
dataStream.forward()对于ForwardPartitioner,必须保证上下游算子并行度一致,否则会抛出异常。 既然如此有什么用?- Minimizing Shuffling Overhead When you have multiple operators in a Flink job connected by data streams, each operator may have a different degree of parallelism. Flink distributes data between operators based on keys or partitioning strategies. However, when you know that the downstream operator logically follows the upstream operator without any need for key-based shuffling or redistribution, you can use forward().
- Efficiency in Data Movement By using forward(), Flink avoids unnecessary data serialization, deserialization, and network overhead associated with key-based shuffling. This can lead to improved performance, especially in scenarios where data doesn't need to be redistributed across operators based on keys or partitions.
- KeyGroupStreamPartitioner 按Key的Hash值输出到下游算子 Key分区策略根据元素Key的Hash值输出到下游算子指定的实例。keyBy()算子底层正是使用的该分区策略,底层最终会调用KeyGroupStreamPartitioner的selectChannel()方法,计算每个Key对应的通道索引(通道编号,可理解为分区编号),根据通道索引将Key发送到下游相应的分区中。 总的来说,Flink底层计算通道索引(分区编号)的流程如下: 计算Key的HashCode值。 将Key的HashCode值进行特殊的Hash处理,即MathUtils.murmurHash(keyHash),返回一个非负哈希码。 将非负哈希码除以最大并行度取余数,得到keyGroupId,即Key组索引。 使用公式keyGroupId×parallelism/maxParallelism得到分区编号。parallelism为当前算子的并行度,即通道数量;maxParallelism为系统默认支持的最大并行度,即128。
- RescalePartitioner 根据上下游算子的并行度,循环输出到下游算子
dataStream.rescale() - BinaryHashPartitioner 对 BinaryRowData 这种数据进行hash分区 该分区策略位于 Flink的Table API的org.apache.flink.table.runtime.partitioner包中,是一种针对BinaryRowData的哈希分区器。BinaryRowData是RowData的实现,可以显著减少Java对象的序列化/反序列化。RowData用于表示结构化数据类型,运行时通过Table API或SQL管道传递的所有顶级记录都是RowData的实例
- CustomPartitionerWrapper 用户自定义分区器
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_42596142/article/details/103727918 https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37555071/article/details/122415430 https://www.51cto.com/article/782165.html
测试代码
public class PartitionerTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
env.setParallelism(3);
DataStream<Integer> dataStream = env.fromElements(1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6);
//1.分区策略前的操作
//输出dataStream每个元素及所属的子任务编号
dataStream.map(new RichMapFunction<Integer, Object>() {
@Override
public Object map(Integer value) throws Exception {
System.out.println(String.format("元素值: %s, 分区策略前,子任务编号: %s", value,
getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask()));
return value;
}
});
//2.设置分区策略
//设置DataStream向下游发送数据时使用的策略
DataStream<Integer> dataStreamAfter = dataStream.broadcast();
//3.分区策略后的操作
dataStreamAfter.map(new RichMapFunction<Integer, Object>() {
@Override
public Object map(Integer value) throws Exception {
System.out.println(String.format("元素值: %s, 分区策略后,子任务编号: %s", value,
getRuntimeContext().getIndexOfThisSubtask()));
return value;
}
}).print();
env.execute("PartitionerTest Job");
}
}
# others
深入了解 Apache Flink 的网络协议栈 https://tianchi.aliyun.com/forum/post/61976#/
Flink 已经拥有了强大的 DataStream/DataSet API,可以基本满足流计算和批计算中的所有需求。为什么还需要 Table & SQL API 呢? https://flink-learning.org.cn/article/detail/5133eced98854eff56cc2eaa2150b1e4#/
Continuous Queries on Dynamic Tables https://flink.apache.org/2017/03/30/continuous-queries-on-dynamic-tables/#/
# Troubleshooting
# flink启动后无法正常关闭
$ ./stop-cluster.sh
No taskexecutor daemon to stop on host xxx.
No standalonesession daemon to stop on host xxx.
flink的进程默认存储在/tmp目录下,该目录为临时目录,会被系统清理,当存储在/tmp下的进程被清理后,执行stop-cluster.sh就无法找到对应的进程并进行停止了。
修改flink bin目录下的config.sh文件。 DEFAULT_ENV_PID_DIR="/tmp",将tmp修改为指定的不会被清理的目录即可。 jps 查询进程 kill xxxx
# flink task manager not starting
1.检查每个节点的日志,看是否是因为host或端口连不上,然后检查相应端口是否正常监听以及防火墙配置 2.flink已经rename slave=》workers,注意文件改动
# Could not start actor system on any port in port range 6123
现象:使用普通用户停止flink,但是web ui仍然可以访问
原因:root用户启动了flink
# NoResourceAvailableException
org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmanager.scheduler.NoResourceAvailableException: Could not allocate the required slot within slot request timeout. Please make sure that the cluster has enough resources.
at org.apache.flink.runtime.scheduler.DefaultScheduler.maybeWrapWithNoResourceAvailableException(DefaultScheduler.java:441) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.scheduler.DefaultScheduler.lambda$assignResourceOrHandleError$6(DefaultScheduler.java:422) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniHandle(CompletableFuture.java:836) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$UniHandle.tryFire(CompletableFuture.java:811) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.postComplete(CompletableFuture.java:488) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeExceptionally(CompletableFuture.java:1990) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.slotpool.SchedulerImpl.lambda$internalAllocateSlot$0(SchedulerImpl.java:168) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniWhenComplete(CompletableFuture.java:774) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$UniWhenComplete.tryFire(CompletableFuture.java:750) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.postComplete(CompletableFuture.java:488) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeExceptionally(CompletableFuture.java:1990) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.slotpool.SlotSharingManager$SingleTaskSlot.release(SlotSharingManager.java:726) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.slotpool.SlotSharingManager$MultiTaskSlot.release(SlotSharingManager.java:537) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.jobmaster.slotpool.SlotSharingManager$MultiTaskSlot.lambda$new$0(SlotSharingManager.java:432) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniHandle(CompletableFuture.java:836) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$UniHandle.tryFire(CompletableFuture.java:811) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.postComplete(CompletableFuture.java:488) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeExceptionally(CompletableFuture.java:1990) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.concurrent.FutureUtils.lambda$forwardTo$21(FutureUtils.java:1132) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniWhenComplete(CompletableFuture.java:774) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$UniWhenComplete.tryFire(CompletableFuture.java:750) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.postComplete(CompletableFuture.java:488) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeExceptionally(CompletableFuture.java:1990) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.concurrent.FutureUtils$Timeout.run(FutureUtils.java:1036) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcActor.handleRunAsync(AkkaRpcActor.java:402) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcActor.handleRpcMessage(AkkaRpcActor.java:195) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.FencedAkkaRpcActor.handleRpcMessage(FencedAkkaRpcActor.java:74) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at org.apache.flink.runtime.rpc.akka.AkkaRpcActor.handleMessage(AkkaRpcActor.java:152) ~[flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.japi.pf.UnitCaseStatement.apply(CaseStatements.scala:26) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.japi.pf.UnitCaseStatement.apply(CaseStatements.scala:21) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at scala.PartialFunction$class.applyOrElse(PartialFunction.scala:123) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.japi.pf.UnitCaseStatement.applyOrElse(CaseStatements.scala:21) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at scala.PartialFunction$OrElse.applyOrElse(PartialFunction.scala:170) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at scala.PartialFunction$OrElse.applyOrElse(PartialFunction.scala:171) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at scala.PartialFunction$OrElse.applyOrElse(PartialFunction.scala:171) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.actor.Actor$class.aroundReceive(Actor.scala:517) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.actor.AbstractActor.aroundReceive(AbstractActor.scala:225) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.actor.ActorCell.receiveMessage(ActorCell.scala:592) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.actor.ActorCell.invoke(ActorCell.scala:561) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.Mailbox.processMailbox(Mailbox.scala:258) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.Mailbox.run(Mailbox.scala:225) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.Mailbox.exec(Mailbox.scala:235) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.forkjoin.ForkJoinTask.doExec(ForkJoinTask.java:260) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.forkjoin.ForkJoinPool$WorkQueue.runTask(ForkJoinPool.java:1339) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.forkjoin.ForkJoinPool.runWorker(ForkJoinPool.java:1979) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
at akka.dispatch.forkjoin.ForkJoinWorkerThread.run(ForkJoinWorkerThread.java:107) [flink-dist_2.11-1.11.2.jar:1.11.2]
Caused by: java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.encodeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:292) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.completeThrowable(CompletableFuture.java:308) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture.uniApply(CompletableFuture.java:607) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
at java.util.concurrent.CompletableFuture$UniApply.tryFire(CompletableFuture.java:591) ~[?:1.8.0_372]
... 25 more
Caused by: java.util.concurrent.TimeoutException
... 23 more
# verify using official example
/bin/flink run -p 5 ./examples/batch/WordCount.jar
# Task distribution in Apache Flink
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/34773379/task-distribution-in-apache-flink
cluster.evenly-spread-out-slots: true
# 分区问题
# rescale 有无状态
https://flink.apache.org/2017/07/04/a-deep-dive-into-rescalable-state-in-apache-flink/#/
# kafka source issue
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/70096166/parallelism-in-flink-kafka-source-causes-nothing-to-execute#/
# sink Can Apache Flink write to files that are named based on a key?
That is not possible ouf-of-the-box. However, you can implement an own output format
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39276290/can-apache-flink-write-to-files-that-are-named-based-on-a-key#/
Apache Flink can write to files with names based on a key. This functionality is typically achieved using Flink's KeyedProcessFunction or KeyedCoProcessFunction in conjunction with the ProcessFunction API.
Here's a general approach you can take:
KeyedStream: Start with a KeyedStream using the keyBy() method to partition your stream by a specific key. ProcessFunction: Use a ProcessFunction or KeyedProcessFunction to process each element in the stream. Within this function, you can implement the logic to write to files based on the key. File Output: Utilize Flink's OutputFileConfig or custom file sink implementations to control the file writing process. You can specify the file name based on the key within the ProcessFunction.
DataStream<MyEvent> stream = ... // your event stream
DataStream<MyEvent> keyedStream = stream.keyBy(event -> event.getKey());
keyedStream.process(new KeyedProcessFunction<KeyType, MyEvent, Void>() {
@Override
public void processElement(MyEvent event, Context ctx, Collector<Void> out) throws Exception {
// Write event to file named based on event.getKey()
String fileName = "file_" + event.getKey() + ".txt";
String content = event.toString(); // Convert event to string or desired format
// Write content to file with fileName
// Example: Files.write(Paths.get(fileName), content.getBytes(), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
}
});
OR
import org.apache.flink.api.common.serialization.SimpleStringEncoder;
import org.apache.flink.core.fs.FileSystem;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.filesystem.StreamingFileSink;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.filesystem.bucketassigners.SimpleVersionedStringSerializer;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.filesystem.bucketassigners.StringElementBucketAssigner;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.filesystem.rollingpolicies.DefaultRollingPolicy;
import org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.sink.filesystem.rollingpolicies.RollingPolicy;
public class KeyedFileSink extends RichSinkFunction<MyEvent> {
private String basePath;
public KeyedFileSink(String basePath) {
this.basePath = basePath;
}
@Override
public void invoke(MyEvent event, Context context) throws Exception {
String key = event.getKey();
String fileName = basePath + "/file_" + key + ".txt";
String content = event.toString(); // Convert event to string or desired format
// Write content to file with fileName
// Example: Files.write(Paths.get(fileName), content.getBytes(), StandardOpenOption.CREATE, StandardOpenOption.APPEND);
}
}
.....
DataStream<MyEvent> stream = ... // your event stream
stream.addSink(new KeyedFileSink("/path/to/output"));
# Partition the whole dataStream in flink at the start of source and maintain the partition till sink
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62303722/partition-the-whole-datastream-in-flink-at-the-start-of-source-and-maintain-the#/
# 数据库并行读取 only one slot is actively processing data and the others quickly finish with 0 bytes
代码片段
DataStream<Row> streamSource = env.createInput(createInputFormat(url,username,password,tablename));
DataStream<String> streamJsonString = streamSource.map(row -> (String) row.getField(0));
DataStream<ObjectNode> streamJson = streamJsonString.map(string -> (ObjectNode) JsonUtil.fromJson(string));
streamJson.addSink(new RedisAutoKeyExpirationSink<>(new SampleExtractor(), config));
env.setParallelism(3);
public static JDBCInputFormat createInputFormat(String url, String username, String password, String tablename) {
return JDBCInputFormat.buildJDBCInputFormat()
.setDrivername("org.postgresql.Driver")
.setDBUrl(url)
.setUsername(username)
.setPassword(password)
.setQuery(String.format("SELECT CAST(info AS TEXT) FROM %s ORDER BY id;", tablename))
.setRowTypeInfo(new RowTypeInfo(BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO))
.setFetchSize(100)
.finish();
}
在flink dashboard发现运行时图像显示并行度虽然是3,但是2个快速结束(0 bytes)实际只有一个在跑
If you set the parallelism of your Flink job to 5 and notice that only one slot is actively processing data while the other four slots quickly finish with 0 bytes, there could be a few reasons for this behavior:
- Data Distribution: The data fetched from the database may not be evenly distributed among the parallel instances of the JDBC source. If the data distribution is skewed, one instance may fetch significantly more data than the others, leading to uneven processing.
- Parallelism Mismatch: The parallelism of the JDBC source may not match the parallelism of downstream operators. Even if you set the parallelism of your Flink job to 5, if the JDBC source has a lower parallelism or if it fetches data serially, only one instance of the source will be actively fetching data while the others remain idle.
- Resource Constraints: If the actively processing slot is starved of resources (CPU, memory, etc.), it may not be able to process data as efficiently as expected, causing other slots to finish quickly with 0 bytes.
显然是第一种情况,仔细琢磨了下,上面代码实际上用的是datastream,jdbc读取出的数据转成JDBCInputFormat作为输入,
有意思的是查看datastream api文档 (opens new window),JDBC是作为sink,MongoDB才有原生的source支持(在官方例子中可以看到可以直接设置partition分区类型)
JDBC (sink) (opens new window) MongoDB (source/sink) (opens new window)
所以大概是datastream对jdbc支持的一般,所以虽然设置并行度为3,只有一个线程连接数据库读取数据,其他两个线程空转,
可能的解决办法: 对接数据库采用flink tableAPI的默认BinaryHashPartitioner分区策略 https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-master/docs/dev/table/tableapi/#/ ,然后下游转成datastream重分区 Converting between DataStream and Table https://nightlies.apache.org/flink/flink-docs-master/docs/dev/table/data_stream_api/#/
partitionby() https://blog.csdn.net/dinghua_xuexi/article/details/107759503#/ https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/139101137#/ https://www.cnblogs.com/Springmoon-venn/p/16540664.html#/
解决方法二: 使用DataStream也行,不过出了设置并行度还需要设置NumericBetweenParametersProvider https://blog.csdn.net/SVDJASFHIAU/article/details/119416169#/
解决方法三: 又发现了 cdc connector (opens new window) 里面明确标明了哪些支持 Parallel Read (opens new window),所以cdc是flink官方提供的一种更强大的连接方式
# 千万级数据断崖式变慢
现象描述:
仍然是前面提到的代码片段,taskmanger jvm memory 5G,taskmanager内存,只不过:
- 为了监控增加了自定义的 MetricMapper 统计数据量和处理进度
- 并行度设置为1
DataStream<Row> streamSource = env.createInput(createInputFormat(url,username,password,tablename));
DataStream<String> streamJsonString = streamSource.map(row -> (String) row.getField(0));
DataStream<ObjectNode> streamJson = streamJsonString.map(new MetricMapper()).map(string -> (ObjectNode) JsonUtil.fromJson(string));
.....
肉眼观察: 300万数据量以下很快跑完,500万跑到快结束的时候迅速变慢,更多的数据跑到后面会挂掉,注意不是一下挂掉,而是跑着跑着挂掉
metric指标:
flink_taskmanager_job_task_operator_numRecordsOutPerSecond迅速变小; flink_taskmanager_Status_JVM_Memory_Heap_Max-flink_taskmanager_Status_JVM_Memory_Heap_Used 负责跑job的taskmanager只剩下几十M的容量,然后开始疯狂的gc,而且是从年轻代的minor gc升级为老年代的full gc
delta(flink_taskmanager_Status_JVM_GarbageCollector_G1_Young_Generation_Time[30s]) delta(flink_taskmanager_Status_JVM_GarbageCollector_G1_Old_Generation_Count[30s])
接着尝试监控flink jvm 发生full gc前 生成内存快照文件: 修改flink.conf (opens new window):
#(Java options to start the JVM of the TaskManager with.)
env.java.opts.taskmanager: -XX:+HeapDumpBeforeFullGC -XX:HeapDumpPath=保存dump文件的文件绝对路径
visualvm分析 发现 Dominators by Retained Size(The retained size for an object is the quantity of memory this objects preserves from garbage collection): 下面这个对象实例占用了95%的内存,并且可以清晰的可以看到其中 resultset 从数据库拉回的所有数据的大小和size org.apache.flink.streaming.api.functions.source.InputFormatSourceFunction#1 [GC root - Java frame]
flink分析 既然已经定位到了问题所在
DataStream<Row> streamSource = env.createInput(createInputFormat(url,username,password,tablename));
=>
public static JDBCInputFormat createInputFormat(String url, String username, String password, String tablename) {
return JDBCInputFormat.buildJDBCInputFormat()
.setDrivername("org.postgresql.Driver")
.setDBUrl(url)
.setUsername(username)
.setPassword(password)
.setQuery(String.format("SELECT CAST(info AS TEXT) FROM %s ORDER BY id;", tablename))
.setRowTypeInfo(new RowTypeInfo(BasicTypeInfo.STRING_TYPE_INFO))
.setFetchSize(100)
.finish();
}
private <OUT> DataStreamSource<OUT> createInput(InputFormat<OUT, ?> inputFormat,
TypeInformation<OUT> typeInfo,
String sourceName) {
InputFormatSourceFunction<OUT> function = new InputFormatSourceFunction<>(inputFormat, typeInfo);
return addSource(function, sourceName, typeInfo);
}
所以flink的这个sourcejdbc不断的从db捞数据,一次100条,但是永不释放,全存在了resultset里面,这样早晚也得爆啊,为什么flink这么设计?肯定是我们用错了,仔细的对应查找了flink的data stream api,结果就是没找到这个InputFormatSourceFunction,版本flink1.12,终于在dataset api下面才找到,并且看到warning:
Starting with Flink 1.12 the DataSet API has been soft deprecated.
We recommend that you use the Table API and SQL to run efficient batch pipelines in a fully unified API. Table API is well integrated with common batch connectors and catalogs.
Alternatively, you can also use the DataStream API with BATCH execution mode. The linked section also outlines cases where it makes sense to use the DataSet API but those cases will become rarer as development progresses and the DataSet API will eventually be removed. Please also see FLIP-131 for background information on this decision.
原因是 too many api? (opens new window),不过感觉这里跟我们的问题相关:
- DataSet API: All-or-nothing output: a job either produces data or it doesn't
- DataStream API: "Incremental" output, based on watermarks or checkpoints
# 解决方案
总之现在的问题变成:
# 1.为什么 dataset api读取数据库的数据一直会在resultset里面hold住所有的数据,不管下游是否处理了都一点不释放?
经过测试发现个有意思的现象,如果把setQuery的where条件每次改变,比如自己维护一个id的offset(startid,endid),这样反而能够正常跑完数据,猜测jdbc每次执行的query不同,所以会垃圾回收前一个query对应的resultset
import org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichMapFunction;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.ExecutionEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.io.jdbc.JDBCInputFormat;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.tuple.Tuple2;
import org.apache.flink.api.java.typeutils.RowTypeInfo;
import org.apache.flink.configuration.Configuration;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;
public class FlinkJDBCExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final ExecutionEnvironment env = ExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
// Configure JDBCInputFormat
String driverName = "org.postgresql.Driver";
String dbUrl = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/mydatabase";
String queryTemplate = "SELECT id, name FROM my_table WHERE id >= ? AND id < ?";
String username = "username";
String password = "password";
int fetchSize = 100; // Set fetch size
int batchSize = 100; // Number of records per batch
int startId = 0; // Initial start id
JDBCInputFormat jdbcInputFormat = JDBCInputFormat.buildJDBCInputFormat()
.setDrivername(driverName)
.setDBUrl(dbUrl)
.setQuery(queryTemplate)
.setUsername(username)
.setPassword(password)
.setRowTypeInfo(new RowTypeInfo(org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.Types.INT, org.apache.flink.api.common.typeinfo.Types.STRING))
.setFetchSize(fetchSize)
.setParametersProvider(new DynamicParameterProvider(batchSize, startId))
.finish();
// Create input DataSet using JDBCInputFormat
env.createInput(jdbcInputFormat)
.map(new RichMapFunction<Row, Tuple2<Integer, String>>() {
private int batchSize;
private int startId;
@Override
public void open(Configuration parameters) throws Exception {
super.open(parameters);
this.batchSize = getRuntimeContext().getExecutionConfig().getGlobalJobParameters().getInt("batchSize", 100);
this.startId = getRuntimeContext().getExecutionConfig().getGlobalJobParameters().getInt("startId", 0);
}
@Override
public Tuple2<Integer, String> map(Row row) throws Exception {
// Map Row to Tuple2
return Tuple2.of((Integer) row.getField(0), (String) row.getField(1));
}
})
.print(); // Example: Print the result
// Execute the Flink job
env.execute("Flink JDBC Example");
}
public static class DynamicParameterProvider implements JDBCInputFormat.ParameterProvider {
private final int batchSize;
private int startId;
public DynamicParameterProvider(int batchSize, int startId) {
this.batchSize = batchSize;
this.startId = startId;
}
@Override
public Object[][] getParameters() {
int endId = startId + batchSize;
Object[][] params = new Object[][] { { startId }, { endId } };
startId = endId; // Update startId for the next batch
return params;
}
}
}
但是注意,这么写会引入另一个潜在问题:当我们提供了ParameterValuesProvider,会触发jdbc的并行模式,导致从数据库分批次拿的数据不是顺序执行!如果数据前后有依赖会造成问题
/**
* Connects to the source database and executes the query in a <b>parallel
* fashion</b> if
* this {@link InputFormat} is built using a parameterized query (i.e. using
* a {@link PreparedStatement})
* and a proper {@link ParameterValuesProvider}, in a <b>non-parallel
* fashion</b> otherwise.
*
* @param inputSplit which is ignored if this InputFormat is executed as a
* non-parallel source,
* a "hook" to the query parameters otherwise (using its
* <i>splitNumber</i>)
* @throws IOException if there's an error during the execution of the query
*/
@Override
public void open(InputSplit inputSplit) throws IOException {
调用栈:
at org.apache.flink.api.java.ExecutionEnvironment.execute(ExecutionEnvironment.java:123)
at org.apache.flink.api.java.DataSet.collect(DataSet.java:456)
at org.apache.flink.api.java.DataSet.output(DataSet.java:789)
at org.apache.flink.connector.jdbc.JdbcInputFormat.open(JdbcInputFormat.java:101)
at org.apache.flink.api.common.functions.RichFunction.open(RichFunction.java:95)
at org.apache.flink.streaming.runtime.tasks.SourceStreamTask.run(SourceStreamTask.java:117)
at org.apache.flink.runtime.taskmanager.Task.run(Task.java:705)
# 2.那么datastream api和table api 呢
When executing a SQL query, conventional database systems and query engines read and process a data set, which is completely available, and produce a fixed sized result. In contrast, data streams continuously provide new records such that data arrives over time. Hence, streaming queries have to continuously process the arriving data and never “complete”.
API演进: The JdbcRowInputFormat in Apache Flink was introduced in version 1.11.0: the JdbcRowInputFormat to read data from PostgreSQL in a streaming fashion, which avoids loading the entire dataset into memory at once.
However, JdbcRowInputFormat was removed in subsequent versions like Apache Flink 1.12.0: Simplification and Consolidation: Flink's ecosystem and API have undergone continuous improvements to streamline and simplify usage patterns. In many cases, having multiple ways to achieve similar functionality can lead to confusion and maintenance overhead. Thus, the decision might have been made to consolidate and standardize the approach to reading from JDBC sources.
API Evolution: As Flink evolves, APIs and functionalities sometimes undergo changes to better align with the overall architecture and user needs. The removal of JdbcRowInputFormat could be part of such an evolution, where newer or more integrated solutions (like the JDBC connector via Table API or SQL) are preferred.
Community and Usage Patterns: Feedback from the Flink community and users often plays a crucial role in shaping the direction of the framework. If a feature is found to be underutilized or if better alternatives are available, it may be deprecated or removed to focus development efforts on more impactful features.
Extension and Compatibility: In later versions of Flink (post 1.11.0), JDBC connectivity is still supported but through separate extensions or connectors (like flink-jdbc-connector). This modular approach allows users to include only the dependencies they need, reducing the overall footprint and complexity.
# 2.1. flink server version 1.11.* 可以使用 JdbcRowInputFormat,但是1.12后被废弃
# 2.2. flink server version 1.12.* 可以使用 SourceFunction
public class FlinkJdbcExample {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
final StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
//env.setRuntimeMode(RuntimeMode.BATCH);
// Add JDBC source function
env.addSource(new JdbcSourceFunction())
.print();
// Execute the program
env.execute("Flink JDBC Example");
}
public static class JdbcSourceFunction implements SourceFunction<Row> {
private volatile boolean isRunning = true;
private transient Connection connection;
private transient PreparedStatement preparedStatement;
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<Row> ctx) throws Exception {
connection = DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/your_database", "your_username", "your_password");
preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement("SELECT * FROM your_table");
preparedStatement.setFetchSize(fetchSize); // Set fetchSize
while (isRunning) {
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
while (resultSet.next()) {
// Convert ResultSet row to Flink Row object
Row row = Row.of(resultSet.getInt("id"), resultSet.getString("name"));
ctx.collect(row);
}
Thread.sleep(1000); // Example: Sleep for 1 second before querying again
}
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
isRunning = false;
try {
if (preparedStatement != null) {
preparedStatement.close();
}
if (connection != null) {
connection.close();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// Log or handle the exception
}
}
}
how it work:
In Apache Flink, when using the JdbcSourceFunction or similar custom implementations to read from JDBC sources, the number of records fetched in one batch and the timing of querying the next batch are influenced by several factors and settings:
1. Batch Size
The batch size, or the number of records fetched in one JDBC query execution, is typically determined by the database driver and configuration settings. This is not explicitly controlled by Flink's JdbcSourceFunction, but rather by how the JDBC driver interacts with the database.
Default Settings: The default batch size is controlled by the JDBC driver's implementation and can vary. Some drivers may fetch all results at once (especially for smaller result sets), while others may use a cursor to fetch a certain number of rows at a time.
Database Configuration: You can configure the batch fetching behavior in some JDBC drivers using properties like fetchSize or through specific driver configurations. This can influence how many rows are fetched per round trip to the database.
2. Timing of Querying Next Batch
The timing of when the JdbcSourceFunction queries the database for the next batch of data depends on your implementation:
Thread Sleep: In the example provided (Thread.sleep(1000);), after fetching a batch of records and emitting them into the Flink stream, the function sleeps for 1 second before executing the query again. This introduces a delay between successive queries to the database.
Backpressure and Internal Strategy: Flink's runtime manages backpressure internally. When downstream operators (like transformations or sinks) cannot keep up with the rate of incoming data, Flink's streaming runtime applies backpressure. This means it slows down or pauses upstream sources (such as JdbcSourceFunction) to balance the flow of data through the pipeline.
Effect on Querying Next Batch: When backpressure is applied, Flink's runtime will pause the execution of the JdbcSourceFunction (specifically, it won't call run() again) until downstream operators indicate readiness to process more data. This helps prevent overwhelming downstream operators and ensures efficient resource usage.
注意: 1.流处理该程序会一直执行不会终止,如果需要处理完数据就终止则必须设置条件主动终止
while (running) {
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery(query);
boolean hasRecords = false;
while (resultSet.next()) {
hasRecords = true;
MyDataType record = new MyDataType(
resultSet.getString("column1"),
resultSet.getInt("column2")
);
ctx.collect(record);
}
// If no records were found, exit the loop
if (!hasRecords) {
break; // Exit after processing all records
}
注意 虽然可以使用 env.setRuntimeMode(RuntimeMode.BATCH); 切换到batch模式,Flink will eventually terminate the job if no records are emitted and if there are no further tasks to process, but this behavior is not guaranteed. It may lead to an indefinite execution state if the loop doesn't exit correctly.
笔者还犯了个错误,由于flink server版本是1.11,而client端这边误用了1.12,虽然setFetchSize可以编译通过,但是1.11并不支持,所以提交任务之后,因为fetchsize失效,jdbc直接一次性将所有数据都load进来,导致oom
当然也可以喂给 table api
tableEnv.registerFunction("myFunction", new MyCustomTableFunction());
Table resultTable = tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT * FROM MyTable, LATERAL TABLE(myFunction(...)) AS T(...) WHERE ...");
或者干脆直接使用 table api
tableEnv.executeSql("CREATE TEMPORARY TABLE jdbc_table (\n" +
" id INT,\n" +
" name STRING\n" +
") WITH (\n" +
" 'connector' = 'jdbc',\n" +
" 'url' = 'jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/database',\n" +
" 'table-name' = 'your_table',\n" +
" 'username' = 'user',\n" +
" 'password' = 'password'\n" +
")");
tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT * FROM jdbc_table").toAppendStream(Row.class).print();
然后再转成 datastream
# 2.3. flink server version 1.12.* 可以使用flink-jdbc-connector
import org.apache.flink.table.api.TableSchema;
import org.apache.flink.table.api.bridge.java.StreamTableEnvironment;
import org.apache.flink.table.sources.DefinedRowtimeAttributes;
import org.apache.flink.table.sources.RowtimeAttributeDescriptor;
import org.apache.flink.table.sources.TableSource;
import org.apache.flink.types.Row;
import java.util.Collections;
import java.util.List;
public class PostgreSQLTableSource implements TableSource<Row>, DefinedRowtimeAttributes {
private final String url = "jdbc:postgresql://localhost:5432/your_database";
private final String username = "your_username";
private final String password = "your_password";
private final String tableName = "your_table";
@Override
public DataStream<Row> getDataStream(StreamExecutionEnvironment execEnv) {
JDBCOptions jdbcOptions = JDBCOptions.builder()
.setDBUrl(url)
.setTableName(tableName)
.setDriverName("org.postgresql.Driver")
.setUsername(username)
.setPassword(password)
.build();
return JDBCInputFormat.buildJDBCInputFormat()
.setOptions(jdbcOptions)
.setRowTypeInfo(...) // Set your RowTypeInfo according to table schema
.finish()
.createInput(execEnv);
}
@Override
public TableSchema getTableSchema() {
// Define your table schema based on the PostgreSQL table structure
return TableSchema.builder()
.field("field1", DataTypes.STRING())
.field("field2", DataTypes.INT())
.build();
}
@Override
public String explainSource() {
return "PostgreSQL Table Source";
}
@Override
public List<RowtimeAttributeDescriptor> getRowtimeAttributeDescriptors() {
// Return descriptors if your table has rowtime attributes
return Collections.emptyList();
}
}
tableEnv.registerTableSource("source_table", new PostgreSQLTableSource());
tableEnv.sqlQuery("SELECT * FROM source_table").toAppendStream(Row.class).print();
# 2.4 flink server version 1.11.* 强行使用sourcefunction
因为setFetchSize是1.12引入的,所以1.11需要自己控制每个批次要拿的size
StreamExecutionEnvironment env = StreamExecutionEnvironment.getExecutionEnvironment();
DataStream<String> streamJsonString = env.addSource(new SourceFunction<String>(){
private volatile boolean running = true;
private PGPoolConnection pgPoolConnection = new PGPoolConnection(config);
private Connection conn;
private PreparedStatement stmt;
private ResultSet rs;
private int windowSize = 1000000;
private int total = 0;
private int processedCount = 0;
private String tablename = config.getPostgresTable();
@Override
public void run(SourceContext<String> ctx) throws Exception {
pgPoolConnection.open();
conn = pgPoolConnection.getDataSource().getConnection();
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(String.format("SELECT count(*) AS total FROM %s", tablename));
stmt.setFetchSize(1);
rs = stmt.executeQuery();
if (rs.next()) {
total = rs.getInt("total");
System.out.println("Total:: " + total);
}
this.close();
while (running) {
pgPoolConnection.open();
conn = pgPoolConnection.getDataSource().getConnection();
stmt = conn.prepareStatement(String.format("SELECT CAST(info AS TEXT) AS info FROM %s ORDER BY id ASC LIMIT ? OFFSET ?", tablename));
stmt.setInt(1, windowSize);
stmt.setInt(2, processedCount);
rs = stmt.executeQuery();
while (running && rs.next()) {
ctx.collect(rs.getString("info"));
processedCount++;
}
System.out.println("PCount:: " + processedCount + (processedCount >= total));
if (processedCount >= total) {
running = false;
}
this.close();
}
//FOR STREAMING MODE, CODE NEVER COME HERE UNTIL PROGRAM TERMINATED
this.terminated();
}
@Override
public void cancel() {
isRunning = false;
this.finish();
}
private void close() {
try {
if (rs != null) {
rs.close();
}
if (stmt != null) {
stmt.close();
}
if (conn != null) {
conn.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
rs = null;
stmt = null;
conn = null;
}
}
private void terminated() {
this.close();
try {
pgPoolConnection.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
pgPoolConnection = null;
}
}
});
flink自定义函数加线程锁 https://juejin.cn/s/flink%E8%87%AA%E5%AE%9A%E4%B9%89%E5%87%BD%E6%95%B0%E5%8A%A0%E7%BA%BF%E7%A8%8B%E9%94%81
使用Flink前必知的10个『陷阱』 https://dbaplus.cn/news-73-3769-1.html
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/63668191/flink-workflow-parallelism-with-custom-source#/
Refer:
Flink Slot 详解与 Job Execution Graph 优化 (opens new window)
Flink中: 你的Function是如何被执行的 (opens new window) 如何实现 Flink 读写数据到 Redis ? (opens new window)