official documents (opens new window)
自动配置、起步依赖、Actuator、命令行界面(CLI) 是Spring Boot最重要的4大核心特性
Servlet->EJB->Struts->SpringMVC->SpringBoot
New->Factory->容器
# 1.知识点Overview
# 启动加载器 SpringFactoriesLoader
JVM提供了3种类加载器: BootstrapClassLoader、 ExtClassLoader、 AppClassLoader分别加载Java核心类库、扩展类库以及应用的类路径( CLASSPATH)下的类库。JVM通过双亲委派模型进行类的加载,我们也可以通过继承 java.lang.classloader实现自己的类加载器。
何为双亲委派模型?当一个类加载器收到类加载任务时,会先交给自己的父加载器去完成,因此最终加载任务都会传递到最顶层的BootstrapClassLoader,只有当父加载器无法完成加载任务时,才会尝试自己来加载。
采用双亲委派模型的一个好处是保证使用不同类加载器最终得到的都是同一个对象,这样就可以保证Java 核心库的类型安全,比如,加载位于rt.jar包中的 java.lang.Object类,不管是哪个加载器加载这个类,最终都是委托给顶层的BootstrapClassLoader来加载的,这样就可以保证任何的类加载器最终得到的都是同样一个Object对象。
SpringFactoriesLoader,它本质上属于Spring框架私有的一种扩展方案,类似于SPI,Spring Boot在Spring基础上的很多核心功能都是基于此
# Spring IoC容器
# Bean 是什么?(Spring bean)
The objects that form the backbone of your application and that are managed by the Spring IoC container are called beans. A bean is an object that is instantiated, assembled, and otherwise managed by a Spring IoC container. https://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring/spring_bean_definition.htm
Spring Bean VS Java Bean:
Java Beans are simple Java classes that encapsulate objects, while Spring Beans are managed by the Spring Framework and are used for dependency injection and lifecycle management.
IoC容器想要管理各个业务对象以及它们之间的依赖关系,需要通过某种途径来记录和管理这些信息。 BeanDefinition对象就承担了这个责任:容器中的每一个bean都会有一个对应的BeanDefinition实例,该实例负责保存bean对象的所有必要信息,包括bean对象的class类型、是否是抽象类、构造方法和参数、其它属性等等。 当客户端向容器请求相应对象时,容器就会通过这些信息为客户端返回一个完整可用的bean实例; 默认是单例模式;
事先这些bean需要向大管家注册,BeanDefinitionRegistry抽象出bean的注册逻辑,BeanFactory则抽象出了bean的管理逻辑,而各个BeanFactory的实现类就具体承担了bean的注册以及管理工作 然后大管家生成bean也是通过这个工厂模式; DefaultListableBeanFactory作为一个比较通用的BeanFactory实现,它同时也实现了BeanDefinitionRegistry接口,因此它就承担了Bean的注册管理工作, 具体的beanFactory实现类就是实现了DefaultListableBeanFactory这个接口;
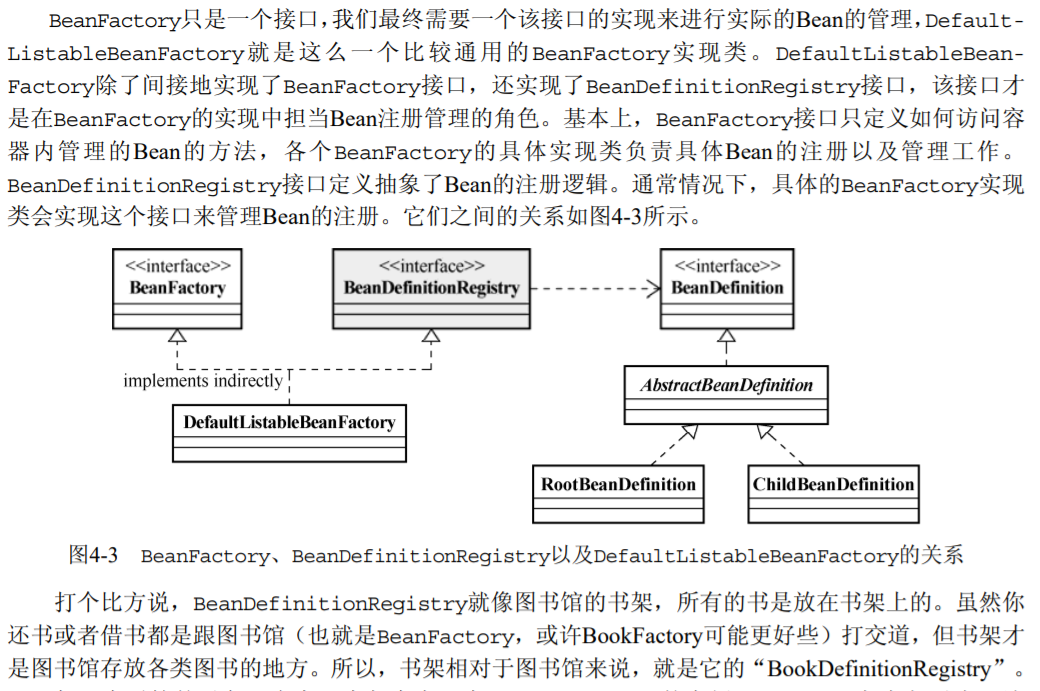
# IoC容器
IoC容器是大管家,你只需要告诉它需要某个bean,它就把对应的实例(instance)扔给你,至于这个bean是否依赖其他组件,怎样完成它的初始化,根本就不需要你关心。
Spring提供了两种容器类型:BeanFactory和ApplicationContext:
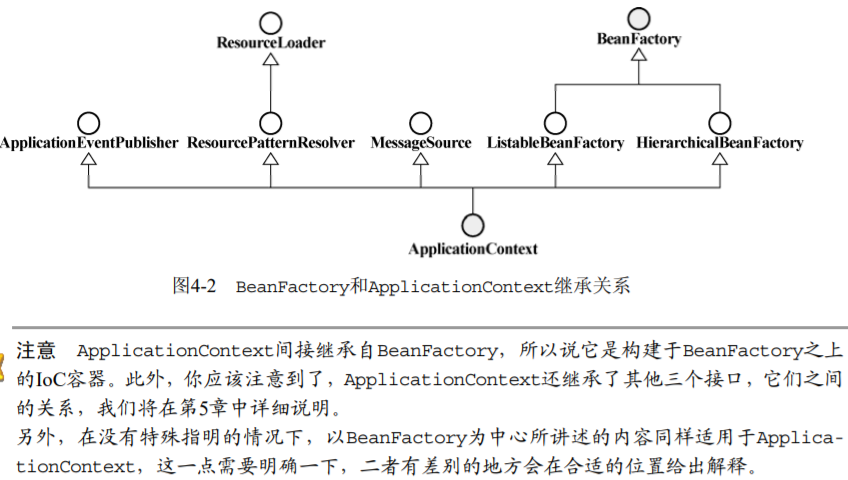
BeanFactory只是Spring IoC容器的一种实现,如果没有特殊指定,它采用采用延迟初始化策略:只有当访问容器中的某个对象时,才对该对象进行初始化和依赖注入操作。 对于资源有限,并且功能要求不是很严格的场景,BeanFactory是比较合适的IoC容器选择。
而在实际场景下,我们更多的使用另外一种类型的容器: ApplicationContext,它构建在BeanFactory之上,属于更高级的容器,除了具有BeanFactory的所有能力之外,还提供对事件监听机制以及国际化的支持等。它管理的bean,在容器启动时全部完成初始化和依赖注入操作。
ApplicationContext所管理的对象,在该类型容器启动之后,默认全部初始化并绑定完成。所以,相对于BeanFactory来说,ApplicationContext要求更多的系统资源,同时,因为在启动时就完成所有初始化,容器启动时间较之BeanFactory也会长一些。
在那些系统资源充足,并且要求更多功能的场景中,ApplicationContext类型的容器是比较合适的选择。
Spring IoC容器的整个工作流程大致可以分为两个阶段:
容器启动阶段
容器启动时,会通过某种途径加载 ConfigurationMetaData, ConfigurationMetaData可能定义在代码中,比如注解方式,也可能在在外部配置文件(XML/Properties)中, ,容器需要依赖某些工具类如BeanDefinitionReader,BeanDefinitionReader会对加载的 ConfigurationMetaData进行解析和分析,并将分析后的信息组装为相应的BeanDefinition, 最后把这些保存了bean定义的BeanDefinition,注册到相应的BeanDefinitionRegistry, 这样容器的启动工作就完成了。
Bean的实例化阶段
这个阶段触发是:当某个请求通过容器的getBean方法请求某个对象,或者因为依赖关系容器需要隐式的调用getBean时(如bean的注解@DependsOn 或者Autowired); 容器会首先检查所请求的对象之前是否已经实例化完成。如果没有,则会根据注册的BeanDefinition所提供的信息实例化被请求对象,并为其注入依赖。当该对象装配完毕后,容器会立即将其返回给请求方法使用。
Notes:Autowire vs getbean:
Injecting a Prototype Bean into a Singleton Bean Problem (opens new window)
# bean生命周期接口
Bean的生命周期:从配置到实例化:
建立Bean定义注册表:Spring容器(如ClassPathXmlApplicationContext)启动时,会读取配置信息(XML、注解等),解析每个
<bean>或@Component注解,在内存中创建一个BeanDefinition对象来存储所有配置信息。这就是配置阶段。实例化Bean:当应用程序向容器请求一个Bean(或容器初始化所有单例Bean)时,容器会根据BeanDefinition的信息,通过Java反射机制调用构造方法来创建对象。这就是new一个对象的过程。
Bean注入(依赖注入):对象被创建后,它里面的属性可能还是null。此时,Spring容器会根据配置(如
<property>标签或@Autowired注解),将这个Bean所依赖的其他Bean注入(设置)到相应的属性中。这就是“注入”发生的关键步骤!
IoC容器负责管理容器中所有bean的生命周期,而在bean生命周期的不同阶段,Spring提供了不同的扩展点来改变bean的命运,例如EnvironmentPostProcessor、BeanFactoryPostProcessor等(具体参照:第2节 SpringApplication启动流程):
单例模式
spring boot默认bean是单例的,spring mvc默认的servlet也是单例的,当然bean @Controller也是单例的,多线程体现在httpservletrequest本身是线程间互相隔离的, 一般都是通过ThreadLocal实现, 之所以默认单例是因为,springboot本身就是ioc容器,启动过程很长,启动时会实例化加载bean(当然也有lazy模式),bean的实例化通常需要读取配置文件或者有很多其他bean的依赖, 所以每次都重建销毁性能很差,而且浪费内存; https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10096483/is-threadlocal-preferable-to-httpservletrequest-setattributekey-value
单例就是为了共享从而减少内存开销,多线程就是为了区别每个线程的上下文或者working thread context,所以线程上下文一定不能被共享, 比如ThreadLocal不能跟ExecutorService共用,就是因为ExecutorService破坏了线程间的隔离 Do Not Use ThreadLocal With ExecutorService https://www.baeldung.com/java-threadlocal https://www.cnblogs.com/MrSaver/p/11191028.html
单例模式 工厂模式 建造者模式
Spring单例Bean与单例模式的区别在于它们关联的环境不一样,单例模式是指在一个JVM进程中仅有一个实例,而Spring单例是指一个Spring Bean容器(ApplicationContext)中仅有一个实例。 首先看单例模式,在一个JVM进程中(理论上,一个运行的JAVA程序就必定有自己一个独立的JVM)仅有一个实例,于是无论在程序中的何处获取实例,始终都返回同一个对象,以Java内置的Runtime为例(现在枚举是单例模式的最佳实践),无论何时何处获取,下面的判断始终为真: Runtime.getRuntime() == Runtime.getRuntime() 与此相比,Spring的单例Bean是与其容器(ApplicationContext)密切相关的,所以在一个JVM进程中,如果有多个Spring容器,即使是单例bean,也一定会创建多个实例,代码示例如下:
// 第一个Spring Bean容器
ApplicationContext context_1 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/ApplicationContext.xml");
Person yiifaa_1 = context_1.getBean("yiifaa", Person.class);
// 第二个Spring Bean容器
ApplicationContext context_2 = new FileSystemXmlApplicationContext("classpath:/ApplicationContext.xml");
Person yiifaa_2 = context_2.getBean("yiifaa", Person.class);
// 这里绝对不会相等,因为创建了多个实例
System.out.println(yiifaa_1 == yiifaa_2);
<!-- 即使声明了为单例,只要有多个容器,也一定会创建多个实例 -->
<bean id="yiifaa" class="com.stixu.anno.Person" scope="singleton">
<constructor-arg name="username">
<value>yiifaa</value>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
# bean定义 - Spring装配bean的三种方法
XML
Java annotations (opens new window): 在业务类上使用注解(如@Component, @Autowired)
Java code / JavaConfig (opens new window): 在专门的配置类中使用Java代码+注解(如@Configuration+@Bean)
混合使用三种装配
- 在类上可以使用 @import(bbsConfig.class)组合其他java注解
- 在类上使用 @importResource("classpath:spring-dao.xml")组合其他xml注解
- 在类上可以使用@ContenxtConfiguration包含class或者xml
- 在xml中可以用引入xml注解,也可以使用引入java注解
# 基于xml配置Bean
Configuration metadata is traditionally supplied in a simple and intuitive XML format
https://docs.spring.io/spring-framework/docs/3.2.x/spring-framework-reference/html/beans.html
//XML装配bean的缺点
//1.当Spring发现这个<bean>元素时,它将会调用SgtPeppers的默认构造器来创建bean.在XML配置中,bean的创建显得更加被动
//2.不如JavaConfig强大,在JavaConfig配置中,可以通过任何想象到的方法来创建bean实例(构造器,set方法等)
//3.在简单的<bean>声明中,将bean的类型以字符串的形式设置在了class属性中,不能保证设置给class属性的值是真正的类
//4.重命名了类,也会引起麻烦
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
---基本
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<beans xmlns="http://........"
xmlns:xsi="http://.....''>
<!-- configuration details go here -->
<bean class="soundsystem.SgtPeppers" />
//这里声明一个很简单的bean,因为没有明确给定ID,所以这个bean将会根据全限定类名来进行命名,
//这里的bean的ID将会是"soundsystem.SgtPeppers#0".其中,"#0"是一个计数的形式,来区分相同类型的bean.
//更好的方法是借助id属性
<bean id="compactDisc" class="soundsystem.SgtPeppers" />
//当Spring遇到<bean>这个元素时,它会创建一个CDPlayer实例.<constructor-arg>元素会告知Spring要将
//一个ID为compactDisc的bean引用传递到CDPlayer的构造器中.
<bean id="cdPlayer" class="soundsystem.CDPlayer">
<constructor-arg ref="compactDisc">
</bean>
</beans>
作为替代方案,也可以使用Spring的c-命名空间(Spring3.0所引入的c-命名空间)
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<beans xmlns="http://........"
xmlns:c="http://www.springframework.org/schema/c"
xmlns:xsi="http://.....''>
<!-- configuration details go here -->
<bean id="cdPlayer" class="soundsystem.CDPlayer"
c:cd-ref="compactDisc">
//"c:" 命名空间的前缀
//"cd" 构造器参数名
//"-ref"注入bean引用
//"compactDisc" 要注入bean 的ID
如果在优化构建的过程,将调试标志移除掉,那么这种方式可能无法正常执行.代替方案:
<bean id="cdPlayer" class="soundsystem.CDPlayer"
c:_0-ref="compactDisc">
//把参数名换成"0",也就是参数的索引,但XML中不允许数字作为属性的第一个字符,因此添加下划线"_"
</beans>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- 字面量string注入
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class BlankDisc implements CompactDisc{
private String title;
private String artist;
public BlandDisc(String title,String artist){
this.title = title;
this.artist = artist;
}
public void paly(){
System.out.println("Playing"+title+"by"+artist);
}
}
<bean id="compactDisc"
class="soundysytem.BlankDisc">
<constructor-arg value="Sgt.Peper's Lonely Hearts" />
<constructor-arg value="The beatles"/>
</bean>
等价
<bean id="compactDisc"
class="soundsystem.BlanDisc"
c:_title="Sgt.Peper's Lonely Hearts"
c:_artist="The beatles"/>
</bean>
或
<bean id="compactDisc"
class="soundsystem.BlanDisc"
c:_0="Sgt.Peper's Lonely Hearts"
c:_1="The beatles"/>
</bean>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- 集合注入
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
public class BlankDisc implements CompactDisc{
private String title;
private String artist;
private List<String> tracks;
public void setTitel(String title){
this.title = title;
}
public void setArtist(String artist){
this.artist= artist;
}
public void setTracks(List<String> tracks){
this.tracks= tracks;
}
public void play(){
....
}
}
<bean id="compactDisc"
class="soundsystem.BlankDisc">
<constructor-arg value="Sgt.Peper's Lonely Hearts" />
<constructor-arg value="The beatles" />
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<value>Sgt. Pepper's Lonely Heats</value>
<value>With a Little Help</value>
<value>Lucy in the Sky</value>
<value>Getting Better</value>
<value>Fixing a Hole</value>
</list>
</constructor-arg>
</bean>
等价于p命名空间
<bean id="compactDisc"
class="soundsystem.BlankDisc"
p:title="Sgt.peper's loney hearts club"
p:artist="The Beatles">
<property name="tracks">
<list>
<value>Sgt.peper's loney hearts club</value>
<value>loney hearts club</value>
<value>hearts club</value>
<value>club hearts</value>
...
</list>
</property>
注意list不能直接使用p空间,可以借用util-命名空间
<util:list id="trackList">
<value>Sgt.peper's loney hearts club</value>
<value>loney hearts club</value>
<value>hearts club</value>
<value>club hearts</value>
</util:lsit>
<bean id="compactDisc"
class = "soundsystem.BlankDisc"
p:title="Sgt.pepers lonely hearts"
p:artist="The Beatles"
p:tracks-ref="trackList">
复杂类型的list:
public Discography(String artist,List<CompactDisc> cds){...}
<bean id="beatlesDiscography" class="soundsystem.Discography">
<constructor-arg value="The Beatles" />
<constructor-arg>
<list>
<ref bean="sgtPeppers" />
<ref bean="whiteAlbum" />
...
</lsit>
</constructor-arg>
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- 属性注入
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
import soundsystem.CompactDisc;
import soundsystem.MediaPlayer;
public class CDPlayer implements MediaPlayer{
private CompactDisc compactDisc;
@Autowired
public void setCompactDisc(CompactDisc compactDisc){
this.compactDisc = compactDisc;
}
public void paly(){
compactDisc.play();
}
}
<bean id="cdPlayer" class="soundsystem.CDPlayer">
<property name="compactDisc" ref="compactDisc" />
</bean>
//通过ref引用了ID为compactDisc的bean,将其注入到compactDisc属性中(通过setCompactDisc()方法)
等价于通过p命名空间
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8">
<beans xmlns="http://........"
xmlns:p="http://www.springframework.org/schema/p"
xmlns:xsi="http://.....''>
<!-- configuration details go here -->
<bean id="cdPlayer" class="soundsystem.CDPlayer"
p:compactDisc-ref="compactDisc" />
</bean>
//"p:" :前缀
//前面的compactDisc: 属性名
//-ref: 注入bean引用
//后面的compactDisc: 所注入bean的ID
</beans>
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8" ?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans
http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd
http://www.springframework.org/schema/context">
<import resource="spring/spring-dao.xml"/>
<bean id="postservice" class="com.bbs.service.impl.PostserviceImpl">
<constructor-arg ref="postdao"/>
<constructor-arg ref="userdao"/>
</bean>
</beans>
配置postservice的bean时需要引入两个bean,postdao和userdao,放到constructor-arg的标签中,ref指的是依赖的bean的ID。如果是在javaConfig中配置的,就写@Bean的内容。如果是@Component就写@Qualifier的内容。这里是引入的是动态实现的dao接口的bean,是在spring-dao.xml中配置的,引入这个配置文件就可以自动获得beanID。
# Annotation-based configuration (opens new window) 使用注解Annotation定义Bean
Spring 2.5 introduced support for annotation-based configuration metadata.
spring从两个角度实现自动化装配:组件扫描和自动装配
- 创建可被发现的bean
@Component
这个简单的注解表明该类会作为组件类,并告知Spring要为这个类创建bean
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- 命名 bean id
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
如果没有个bean设置ID,Spring会根据类名为其指定一个ID,默认名字就是把类名的第一个字母变为小写.
@Component("lonelyHeartsClub") //设置期望的ID
public class SgtPeppers implements CompactDisc{
}
另外还一种为bean命名的方式,使用Java依赖注入规范中所提供的@Named注解来为bean设置ID
@Named("lonelyHeartsClub")
public class SgtPeppers implements CompactDisc{
}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- 设置组件扫描的基础包
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
当对一个类标注@Component注解时,表明该类会作为组件类,spring将为这个类创建bean。当在应用文中引用这个bean,spring会自动扫描事先指定的包查找这个 bean。但spring默认是不启用组件扫描的,可以在XML中配置加上。还有一种方法:在新建一个配置类,类中可以什么不用写,在配置类上加上@ComponentScan注解,spring会自动扫描改配置类所在的包。
//直接在value属性中指明包的名称
@Configuration
@ComponentScan("soundsystem")
public class CDPlayerConfig{}
//通过basePackages属性配置
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages="soundsystem")
public class CDPlayerConfig{}
//设置多个基础包,用数组表示
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackages={"soundsystem","video"})
public class CDPlayerConfig{}
//基础包以String类型表示是不安全的,如果重构代码的话,指定的基础包可能会出现错误,用指定为包中所包含的类或接口的方法
@Configuration
@ComponentScan(basePackageClasses={CDPlayer.class,DVDPlayer.class})
public class CDPlayerConfig{}
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- 添加注解自动装配Autowired
@Autowired可以换成@Inject,@Inject注解来源于Java依赖注入规范,该规范同时还为我们定义了@Named注解.
尽管@Inject和@Autowierd有细微的差别,但大多数场景下,它们都可以互换.
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
@Autowired注解构造器:
@Component
public class CDPlayer implements MediaPlayer{
private CompactDisc cd;
@Autowired//这表明当Spring创建CDPlayer bean的时候,会通过这个构造器来进行实例化并且会传入一个可设置给CompactDisc类型的bean.
public CDPlayer(CompactDisc cd){//构造器
this.cd = cd;
}
public void paly(){
cd.paly();
}
}
@Autowired注解属性的Setter方法:
@Autowired
public void setCompactDisc(CompactDisc cd){
this.cd = cd;
}
如果没有匹配的bean,那么在应用上下文创建的时候,Spring会抛出一个异常,为了避免异常的出现,你可以将@Autowired的requied属性设置为false
@Autowired(required=false)
public void setCompactDisc(CompactDisc cd){
this.cd = cd;
}
如果有多个bean都能满足依赖关系的话,Spring将会抛出一个异常,表明没有明确指定要选择哪个bean进行自动装配, 一般在组件类上添加注解@Qualifier()括号写这个bean的id,在注入时也加上@Qualifier(),写上bean的id
@Component
@Qualifier("postdao")
public interface Postdao{
. . . .
}
@Component
@Qualifier("userdao")
public interface Userdao{
. . . .
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier("usedao")
public void setUserdao(Userdao userdao)
{. . .
}
@Autowired
@Qualifier("postdao")
public void setUserdao(Postdao postdao)
{. . .
}
# Java-based configuration (opens new window) 基于java类提供Bean定义信息
所谓java based 我的理解是这里是说不需要依赖于spring,普通的java项目也可以用
Starting with Spring 3.0, many features provided by the Spring JavaConfig project (opens new window) became part of the core Spring Framework. Thus you can define beans external to your application classes by using Java rather than XML files. To use these new features, see the @Configuration, @Bean, @Import and @DependsOn annotations.
有些情况下,比如说,要将第三方库的组件装配到你的应用中,就不能使用前面的自动化装配方法 到第三方库中去给类加@Component和@Autowired注解, 在这种情况下,就需要采用显示装配的方式.在进行显示配置有Java和XML两种方案显示装配bean.
使用java代码,先新建一个配置类JavaConfig,里面都是配置所需的bean,不应该有业务逻辑代码,所以单独建一个类。
@Configuration
public class AppConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyServiceImpl();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext(AppConfig.class);
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doStuff();
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
AnnotationConfigApplicationContext ctx = new AnnotationConfigApplicationContext();
ctx.register(AppConfig.class, OtherConfig.class);
ctx.register(AdditionalConfig.class);
ctx.refresh();
MyService myService = ctx.getBean(MyService.class);
myService.doStuff();
}
//创建JavaConfig类的关键在于为其添加@Configruation注解,表明这是一个配置类
@Configuration
public class CDPlayerConfig{
@Bean
public CompactDisc sgtPeppers(){
return new SgtPeppers();
}
//@Bean注解会告诉Spring这个方法将会返回一个对象,该对象要注册为Spring应用上下文的bean,默认情况下,
bean的ID于带有@Bean注解的方法名一样,也可以重命名
@Bean(name="lonelyHeartsClubBand")
public CompactDisc sgtPeppers(){
return new SgtPeppers();
}
声明CompactDisc bean是非常简单,它自身没有其他依赖,但现在,我们需要声明CDPlayer bean,它依赖于CompactDisc,在JavaConfig中,如何将他们装配在一起呢?
@Bean
public CDPlayer cdPlayer(){
return new CDPlayer(sgtPeppers()); //因为sgtPeppers()方法上添加了@Bean注解,Spring将会拦截所有对它的调用,
//并确保直接返回该方法创建的bean,而不是每次都对其进行实际的调用.
}
等价于下面这种方式
@Bean
public CDPlayer cdPlayer(CompactDisc compactDisc){//在这里,cdPlayer()方法请求一个CompactDisc作为参数,当Springs调用cdPlayer()创建CDPlayer bean的时候,
//它会自动装配一个CompactDisc到配置方法之中,然后方法体按照合适的方法来使用它.
return new CDPlayer(compactDisc);
}
@Bean(name="lonelyHeartsClubBandPlayer")
public CDPlayer cdPlayer(CompactDisc lonelyHeartsClubBand){
return new CDPlayer(compactDisc);
}
}
More example:
@Configuration
@ContextConfiguration(locations = {"classpath:spring/spring-dao.xml","classpath:scan.xml"})
public class bbsConfig{
private Postdao postdao;
private Userdao userdao;
@Bean(name="postservice")
public PostService getPost()
{
return new PostserviceImpl(postdao,userdao);
}
}
在对PostService的bean注入时,同时又依赖了两个bean,postdao和userdao。直接引用beanID就可以,spring会自动地从容器中获取这些bean,只要他们的配置是正确的就行。这个例子中userdao、postdao是Mybatis配置自动扫描将dao接口生成代理注入到spring的,其实也算是xml装配bean
这里如果再声明一个bean,返回的仍是postserviceImpl对象,和之前的那个bean完全一样,是同一个实例。一般spring @bean如果是同一个beanID,默认返回的是一个单例bean,注入的是同一个实例。如果修改其中一个会都改变的。
不过在这里要注意进行测试时,由于spring的单元测试和springIoc容器是完全独立的,postdao和userdao注入检测时是使用locations加载xml文件,而postservice使用classes加载config类的,但是两个不能同时混用在@ContextConfiguration中。所以非要都测试的话,就分开测试吧。
@SpringBootApplication 等同于 @EnableAutoConfiguration + @ComponentScan + @Configuration, 后面启动原理部分有详解
All of your application components (@Component, @Service, @Repository, @Controller etc.) are automatically registered as Spring Beans.
Components(@Component @Service @Controller @Repository) VS Beans (@Beans): all component types are treated in the same way. The subtypes are mere markers, think code readability rather than features. https://www.tomaszezula.com/2014/02/09/spring-series-part-5-component-vs-bean/
** @ComponentScan**
** @Import**
在4.2之前, @Import注解只支持导入配置类,但是在4.2之后,它支持导入普通类
@Conditional @ConditionalOn*
表示在满足某种条件后才初始化一个bean或者启用某些配置。它一般用在由 @Component、 @Service、 @Configuration等注解标识的类上面,或者由 @Bean标记的方法上。如果一个 @Configuration类标记了 @Conditional,则该类中所有标识了 @Bean的方法和 @Import注解导入的相关类将遵从这些条件。
@ConfigurationProperties与@EnableConfigurationProperties
当某些属性的值需要配置的时候,我们一般会在 application.properties文件中新建配置项,然后在bean中使用 @Value注解来获取配置的值;
@Configuration
public class MyBatisConfiguration {
@Value("${spring.datasource.driverClassName}")
private String jdbcDriverClassName;
@Value("${spring.datasource.url}")
private String jdbcUrl;
@Value("${spring.datasource.username}")
private String jdbcUsername;
@Value("${spring.datasource.password}")
private String jdbcPassword;
@Bean(name = "dataSource",destroyMethod = "close")
public DataSource dataSource() {
DruidDataSource datasource = new DruidDataSource();
datasource.setDriverClassName(jdbcDriverClassName);
datasource.setUrl(jdbcUrl);
datasource.setUsername(jdbcUsername);
datasource.setPassword(jdbcPassword);
return datasource;
}
@Bean(name = {"sqlSessionFactory"})
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(name = {"sqlSessionFactory"})
public SqlSessionFactory sqlSessionFactory(DataSource dataSource) throws Exception {
....
但是如果同一个配置在多个地方使用,也存在不方便维护的问题,对于更为复杂的配置,Spring Boot提供了更优雅的实现方式,那就是 @ConfigurationProperties注解 而@EnableConfigurationProperties的作用是将其注册为bean,否则项目不会将其scan为bean,具体:
In order to use a configuration class in our project, we need to register it as a regular Spring bean.
First of all, we can annotate such a class with @Component. Alternatively, we can use a @Bean factory method.
However, in certain situations, we may prefer to keep a @ConfigurationProperties class as a simple POJO. This is when @EnableConfigurationProperties comes in handy. We can specify all configuration beans directly on this annotation.
This is a convenient way to quickly register @ConfigurationProperties annotated beans.
通过上面等表述,我们大概知道,如果用@component就会将其变成增强类,而不是plain old java object了,而是多了很多冗余的功能;
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "additional")
public class AdditionalProperties {
private String unit;
private int max;
// standard getters and setters
}
@Configuration
@EnableConfigurationProperties(AdditionalProperties.class)
public class AdditionalConfiguration {
@Autowired
private AdditionalProperties additionalProperties;
// make use of the bound properties
}
# bean注入
Spring依赖注入技术演进:
┌────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 配置方式演进 │
├────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 1. XML显式配置 (Spring 1.x) │
│ ├── <property name="..." ref="..."/> │
│ ├── <constructor-arg ref="..."/> │
│ └── 工厂方法注入 │
│ │
│ 2. XML自动装配 (Spring 2.0) │
│ ├── autowire="byName" │
│ ├── autowire="byType" │
│ ├── autowire="constructor" │
│ ├── autowire="default" │
│ └── autowire="no" │
│ │
│ 3. 注解驱动 (Spring 2.5) │
│ ├── @Autowired (字段/构造器/方法注入) │
│ ├── @Resource (JSR-250) │
│ ├── @Inject (JSR-330) │
│ └── @Required │
│ │
│ 4. Java配置 (Spring 3.0) │
│ ├── @Configuration + @Bean │
│ └── 方法参数自动注入 │
└────────────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
# 早期基于XML显式配置三种注入方式
属性注入
package com.java.entity; public class People { private int id; private String name; private int age; public People() { //调用默认的构造方法 } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getAge() { return age; } public void setAge(int age) { this.age = age; } @Override public String toString() { return "People{" + "id=" + id + ", name='" + name + '\'' + ", age=" + age + '}'; } } <?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd"> <bean id="people" class="com.java.entity.People"></bean> //属性注入 <bean id="people2" class="com.java.entity.People"> <property name="id" value="1"></property> <property name="age" value="18"></property> <property name="name" value="张三"></property> </bean> </beans> public class Test2 { public static void main(String[] args) { //加载beans.xml文件,调用Spring接口 ApplicationContext ac=new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("beans.xml"); //通过id获取bean,返回一个对象 People people=(People)ac.getBean("people"); //调用方法 System.out.println(people); //属性注入 People people2=(People)ac.getBean("people2"); System.out.println(people2); } }构造函数注入
public People(int id, String name, int age) { this.id = id; this.name = name; this.age = age; } <!--类型注入--> <bean id="people3" class="com.java.entity.People"> <constructor-arg type="int" value="2"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="String" value="李四"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="int" value="19"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!--索引注入--> <bean id="people4" class="com.java.entity.People"> <constructor-arg index="0" value="3"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="1" value="王五"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg index="2" value="20"></constructor-arg> </bean> <!--联合使用--> <bean id="people5" class="com.java.entity.People"> <constructor-arg type="int" index="0" value="4"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="String" index="1" value="赵六"></constructor-arg> <constructor-arg type="int" index="2" value="21"></constructor-arg> </bean> //类型注入 People people3=(People)ac.getBean("people3"); System.out.println(people3); //类型注入 People people4=(People)ac.getBean("people4"); System.out.println(people4); //联合使用 People people5=(People)ac.getBean("people5"); System.out.println(people5);工厂方法注入,分为静态工厂和非静态工厂; 一般用得多的都是静态工厂;
package com.java.factory; import com.java.entity.People; public class PeopleFactory { //非静态工厂 public People createPeople(){ People p=new People(); p.setId(5); p.setName("阿七"); p.setAge(22); return p; } //静态工厂 public static People createPeople1(){ People p=new People(); p.setId(6); p.setName("阿八"); p.setAge(23); return p; } } <!--工厂模式的非静态方法--> <bean id="peopleFactory" class="com.java.factory.PeopleFactory"></bean> <bean id="people6" factory-bean="peopleFactory" factory-method="createPeople"></bean> <!--工厂模式的静态方法--> <bean id="people7" class="com.java.factory.PeopleFactory" factory-method="createPeople1"></bean> //工厂方式注入,非静态 People people6=(People)ac.getBean("people6"); System.out.println(people6); //工厂方式注入,静态 People people7=(People)ac.getBean("people7"); System.out.println(people7);
# 中期基于XML autowire="no|byName|byType|constructor|default"
# 现代基于Autowired 的三种注入方式
如果你使用的是构造器注入 恭喜你,当你有十几个甚至更多对象需要注入时,你的构造函数的参数个数可能会长到无法想像。
如果你使用的是field反射注入 如果不使用Spring框架,这个属性只能通过反射注入,太麻烦了!这根本不符合JavaBean规范。 还有,当你不是用过Spring创建的对象时,还可能引起NullPointerException。 并且,你不能用final修饰这个属性。
如果你使用的是setter方法注入 那么你将不能将属性设置为final。 两者取其轻
Spring3.0官方文档建议使用setter注入覆盖构造器注入。 Spring4.0官方文档建议使用构造器注入。 结论
如果注入的属性是必选的属性,则通过构造器注入。 如果注入的属性是可选的属性,则通过setter方法注入。 至于field注入,不建议使用。
通过field反射注入, field injection (不推荐)
@Component public class Dependency(){ } @Component public class DI(){ @Autowired private Dependency dependency; }通过构造器注入
public class DI(){ //通过构造器注入 private DependencyA a; @Autowired public DI(DependencyA a){ this.a = a; } }通过setter方法注入
public class DI(){ //通过setter方法注入 private DependencyB b; @Autowired public void setDependencyB(DependencyB b){ this.b = b; } }
# 配置属性加载顺序
1、开发者工具 `Devtools` 全局配置参数;
2、单元测试上的 `@TestPropertySource` 注解指定的参数;
3、单元测试上的 `@SpringBootTest` 注解指定的参数;
4、命令行指定的参数,如 `java -jar springboot.jar --name="Java技术栈"`;
5、命令行中的 `SPRING_APPLICATION_JSONJSON` 指定参数, 如 `java -Dspring.application.json='{"name":"Java技术栈"}' -jar springboot.jar`
6、`ServletConfig` 初始化参数;
7、`ServletContext` 初始化参数;
8、JNDI参数(如 `java:comp/env/spring.application.json`);
9、Java系统参数(来源:`System.getProperties()`);
10、操作系统环境变量参数;
11、`RandomValuePropertySource` 随机数,仅匹配:`ramdom.*`;
12、JAR包外面的配置文件参数(`application-{profile}.properties(YAML)`)
13、JAR包里面的配置文件参数(`application-{profile}.properties(YAML)`)
14、JAR包外面的配置文件参数(`application.properties(YAML)`)
15、JAR包里面的配置文件参数(`application.properties(YAML)`)
16、`@Configuration`配置文件上 `@PropertySource` 注解加载的参数;
17、默认参数(通过 `SpringApplication.setDefaultProperties` 指定);
# Spring容器的事件监听机制
Java提供了实现事件监听机制的两个基础类:自定义事件类型扩展自 java.util.EventObject、事件的监听器扩展自 java.util.EventListener
Spring的ApplicationContext容器内部中的所有事件类型均继承自 org.springframework.context.AppliationEvent,容器中的所有监听器都实现 org.springframework.context.ApplicationListener接口,并且以bean的形式注册在容器中。一旦在容器内发布ApplicationEvent及其子类型的事件,注册到容器的ApplicationListener就会对这些事件进行处理。
ApplicationEvent继承自EventObject,Spring提供了一些默认的实现,比如: ContextClosedEvent表示容器在即将关闭时发布的事件类型, ContextRefreshedEvent表示容器在初始化或者刷新的时候发布的事件类型......
容器内部使用ApplicationListener作为事件监听器接口定义,它继承自EventListener。ApplicationContext容器在启动时,会自动识别并加载EventListener类型的bean,一旦容器内有事件发布,将通知这些注册到容器的EventListener。
ApplicationContext接口继承了ApplicationEventPublisher接口,该接口提供了 voidpublishEvent(ApplicationEventevent)方法定义,不难看出,ApplicationContext容器担当的就是事件发布者的角色。如果有兴趣可以查看 AbstractApplicationContext.publishEvent(ApplicationEventevent)方法的源码:ApplicationContext将事件的发布以及监听器的管理工作委托给 ApplicationEventMulticaster接口的实现类。在容器启动时,会检查容器内是否存在名为applicationEventMulticaster的ApplicationEventMulticaster对象实例。如果有就使用其提供的实现,没有就默认初始化一个SimpleApplicationEventMulticaster作为实现。
最后,如果我们业务需要在容器内部发布事件,只需要为其注入ApplicationEventPublisher依赖即可:实现ApplicationEventPublisherAware接口或者ApplicationContextAware接口
# 自动配置原理
@SpringBootApplication开启组件扫描和自动配置, 而 SpringApplication.run则负责启动引导应用程序。 @SpringBootApplication是一个复合 Annotation,它将三个注解组合在一起:
@SpringBootConfiguration就是 @Configuration,它是Spring框架的注解,标明该类是一个 JavaConfig配置类; allow to register extra beans in the context or import additional configuration classes;
@ComponentScan启用组件扫描;enable @Component scan on the package where the application is located;
@EnableAutoConfiguration注解: 表示开启Spring Boot自动配置功能,Spring Boot会根据应用的依赖、自定义的bean、classpath下有没有某个类 等等因素来猜测你需要的bean,然后注册到IOC容器中; enable Spring Boot’s auto-configuration mechanism (opens new window)
Notes:
You should only ever add one @SpringBootApplication or @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation. We generally recommend that you add one or the other to your primary @Configuration class only. https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-auto-configuration
开始讲解原理,先看EnableAutoConfiguration:
@Target(value=TYPE)
@Retention(value=RUNTIME)
@Documented
@Inherited
@AutoConfigurationPackage
@Import(value=AutoConfigurationImportSelector.class)
public @interface EnableAutoConfiguration
重点是@Import(EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.class),这里它将把 EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector作为bean注入到容器中,
@Override
public String[] selectImports(AnnotationMetadata metadata) {
try {
AnnotationAttributes attributes = getAttributes(metadata);
List<String> configurations = getCandidateConfigurations(metadata,
attributes);
configurations = removeDuplicates(configurations);
Set<String> exclusions = getExclusions(metadata, attributes);
configurations.removeAll(exclusions);
configurations = sort(configurations);
recordWithConditionEvaluationReport(configurations, exclusions);
return configurations.toArray(new String[configurations.size()]);
}
catch (IOException ex) {
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
}
EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector.selectImports()是何时执行的?其实这个方法会在容器启动过程中执行: AbstractApplicationContext.refresh(), 这个EnableAutoConfigurationImportSelector类会扫描所有的jar包,将所有符合条件的@Configuration配置类注入的容器中,何为符合条件,看看 META-INF/spring.factories的文件内容:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/master/spring-boot-project/spring-boot-autoconfigure/src/main/resources/META-INF/spring.factories
.....
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.jdbc.DataSourceAutoConfiguration,\
.....
然后举例看 DataSourceAutoConfiguration:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/master/spring-boot-project/spring-boot-autoconfigure/src/main/java/org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/jdbc/DataSourceAutoConfiguration.java
@Configuration(proxyBeanMethods = false)
@ConditionalOnClass({ DataSource.class, EmbeddedDatabaseType.class })
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(type = "io.r2dbc.spi.ConnectionFactory")
@EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class)
@Import({ DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class, DataSourceInitializationConfiguration.class })
public class DataSourceAutoConfiguration {
@ConditionalOnClass({DataSource.class,EmbeddedDatabaseType.class}):当Classpath中存在DataSource或者EmbeddedDatabaseType类时才启用这个配置,否则这个配置将被忽略。 注意上面的DataSourceProperties, @EnableConfigurationProperties(DataSourceProperties.class):将DataSource的默认配置类注入到IOC容器中,DataSourceproperties定义为:
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.datasource")
public class DataSourceProperties implements BeanClassLoaderAware, InitializingBean {
private ClassLoader classLoader;
/**
* Name of the datasource. Default to "testdb" when using an embedded database.
*/
private String name;
/**
* Whether to generate a random datasource name.
*/
private boolean generateUniqueName = true;
/**
* Fully qualified name of the connection pool implementation to use. By default, it
* is auto-detected from the classpath.
*/
private Class<? extends DataSource> type;
/**
* Fully qualified name of the JDBC driver. Auto-detected based on the URL by default.
*/
private String driverClassName;
/**
* JDBC URL of the database.
*/
private String url;
/**
* Login username of the database.
*/
private String username;
/**
* Login password of the database.
*/
private String password;
很清晰对应配置spring.datasource,然后是连接池配置:
@Import({ Registrar.class, DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration.class }):导入其他额外的配置,就以DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration为例吧, DataSourcePoolMetadataProvidersConfiguration是数据库连接池提供者的一个配置类,即Classpath中存在 org.apache.tomcat.jdbc.pool.DataSource.class,则使用tomcat-jdbc连接池,如果Classpath中存在 HikariDataSource.class则使用Hikari连接池。
# Environment vs ApplicationContext
Environment是ApplicationContext的一部分
Environment(环境):
- 配置数据管理
- 属性、Profile、配置源
- 房子的水电配置系统
- 配置信息存取
ApplicationContext(应用上下文):
- 完整的容器生态系统
- Bean工厂、事件发布、资源加载等
- 整个房子+家具+设施
- 完整的应用生命周期管理
ApplicationContext(应用上下文) ├── Environment(环境配置) │ ├── PropertySources(属性源) │ ├── Profiles(环境配置) │ └── 配置数据存取API │ ├── BeanFactory(Bean管理) ├── MessageSource(国际化) ├── ApplicationEventPublisher(事件发布) ├── ResourceLoader(资源加载) └── 其他容器服务
# 2. SpringApplication启动流程
Spring Boot应用启动流程:
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 1. JVM启动阶段 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 加载JVM → 类加载器初始化 → 字节码验证 │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 2. SpringApplication.run() │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 设置无头模式 → 启动监听器 → 发布启动事件 │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 3. 环境准备阶段 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 创建应用参数 → 准备环境 → 加载配置 → 打印Banner │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 4. 应用上下文创建 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 创建空容器实例 → 初始化异常报告器 │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 5. 上下文预处理 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 设置环境 → 执行ApplicationContextInitializer │
│ → 加载Bean定义源 │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 6. ApplicationContext.refresh() │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 这是Spring容器的核心启动方法,包含所有子阶段 │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 7. 嵌套子阶段(按顺序执行) │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 7.1 prepareRefresh() │
│ 7.2 obtainFreshBeanFactory() │
│ 7.3 prepareBeanFactory() │
│ 7.4 postProcessBeanFactory() │
│ 7.5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() ← 重要! │
│ ├── 扫描@Component注解类 │
│ ├── 创建BeanDefinition │
│ ├── 注册到BeanFactory │
│ └── 处理@AutoConfiguration │
│ 7.6 registerBeanPostProcessors() │
│ 7.7 initMessageSource() │
│ 7.8 initApplicationEventMulticaster() │
│ 7.9 onRefresh() ← 启动内嵌服务器! │
│ 7.10 registerListeners() │
│ 7.11 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() ← 重要! │
│ ├── 实例化所有非懒加载单例Bean │
│ ├── 注入依赖 │
│ └── 调用生命周期回调 │
│ 7.12 finishRefresh() │
└───────────────────────┬─────────────────────────┘
↓
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ 8. 启动收尾阶段 │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 后处理 → 发布启动事件 → 执行Runner → 发布就绪事件│
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
# JVM启动和类加载
// 阶段1:JVM层面的准备工作
public class JVMStartupPhase {
public void execute() {
// 1. 加载JVM核心库
loadJVMCoreLibraries(); // rt.jar, charsets.jar等
// 2. 初始化类加载器层次结构
initializeClassLoaders(); // Bootstrap → Extension → Application
// 3. 加载SpringApplication主类
Class<?> mainClass = Class.forName("com.example.MyApplication");
// 4. 验证字节码安全性
verifyBytecode(mainClass); // 检查魔数、版本、指令合法性
// 5. 准备静态变量和常量池
prepareStaticFields(); // 初始化静态常量
// 6. 调用main方法入口
Method mainMethod = mainClass.getMethod("main", String[].class);
mainMethod.invoke(null, (Object) args);
}
}
// SpringBootApplication.java
@SpringBootApplication
public class MyApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 阶段1: JVM启动
SpringApplication.run(MyApplication.class, args);
}
}
1. 加载SpringApplication类到方法区
2. 加载@SpringBootApplication注解元数据
3. 验证字节码,准备静态变量
4. 初始化Spring核心类(BeanFactory、ApplicationContext等)
# 初始化SpringApplication对象
SpringBoot整个启动流程分为两个步骤:初始化一个SpringApplication对象、执行该对象的run方法。看下SpringApplication的初始化流程,SpringApplication的构造方法:
public SpringApplication(ResourceLoader resourceLoader, Class<?>... primarySources) {
this.resourceLoader = resourceLoader;
Assert.notNull(primarySources, "PrimarySources must not be null");
this.primarySources = new LinkedHashSet<>(Arrays.asList(primarySources));
this.webApplicationType = WebApplicationType.deduceFromClasspath();
setInitializers((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationContextInitializer.class));
setListeners((Collection) getSpringFactoriesInstances(ApplicationListener.class));
this.mainApplicationClass = deduceMainApplicationClass();
}
初始化流程中最重要的就是通过 SpringFactoriesLoader 找到 spring.factories 文件中配置的 ApplicationContextInitializer 和 ApplicationListener 两个接口的实现类名称,以便后期构造相应的实例。 ApplicationContextInitializer 的主要目的是在 ConfigurableApplicationContext 做 refresh之前,对ConfigurableApplicationContext实例做进一步的设置或处理。ConfigurableApplicationContext继承自 ApplicationContext ,其主要提供了对 ApplicationContext 进行设置的能力。
Spring Boot提供两种方式来添加自定义监听器:
通过 SpringApplication.addListeners()或者 SpringApplication.setListeners()两个方法来添加一个或者多个自定义监听器
既然SpringApplication的初始化流程中已经从 spring.factories中获取到 ApplicationListener的实现类,那么我们直接在自己的jar包的 META-INF/spring.factories文件中新增配置即可:
# 执行该对象的run方法
Spring Boot应用的整个启动流程都封装在 SpringApplication.run 方法中,其整个流程真的是太长太长了,但本质上就是在Spring容器启动的基础上做了大量的扩展,按照这个思路来看看源码
Spring Boot启动调用栈(层次化视图):
┌─────────────────────────────────────────────────┐
│ SpringApplication.run() │
├─────────────────────────────────────────────────┤
│ 1. 启动准备 │
│ ├── configureHeadlessProperty() │
│ ├── getRunListeners() │
│ └── listeners.starting() ← 发布启动事件 │
│ │
│ 2. 环境准备 │
│ ├── new DefaultApplicationArguments(args) │
│ ├── prepareEnvironment() ← 核心! │
│ │ └── 加载所有配置源 │
│ │ ├── application.properties │
│ │ ├── application.yml │
│ │ ├── 环境变量 │
│ │ └── 命令行参数 │
│ ├── configureIgnoreBeanInfo() │
│ └── printBanner() │
│ │
│ 3. 应用上下文创建 │
│ └── createApplicationContext() │
│ ├── Web应用: AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext│
│ └── 普通应用: AnnotationConfigApplicationContext│
│ │
│ 4. 异常报告器初始化 │
│ └── getSpringFactoriesInstances() │
│ │
│ 5. 上下文预处理 │
│ └── prepareContext() │
│ ├── 设置环境environment │
│ ├── 执行ApplicationContextInitializer │
│ ├── 发布ApplicationPreparedEvent │
│ └── 加载Bean定义源 │
│ │
│ 6. 容器刷新 ← 真正核心! │
│ └── refreshContext() → context.refresh() │
│ ├── 6.1 prepareRefresh() │
│ ├── 6.2 obtainFreshBeanFactory() │
│ ├── 6.3 prepareBeanFactory() │
│ ├── 6.4 postProcessBeanFactory() │
│ ├── 6.5 invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() ← 重要!│
│ │ ├── 处理@Configuration类 │
│ │ ├── 扫描@Component注解类 │
│ │ ├── 解析@PropertySource │
│ │ └── 加载@AutoConfiguration │
│ ├── 6.6 registerBeanPostProcessors() │
│ ├── 6.7 initMessageSource() │
│ ├── 6.8 initApplicationEventMulticaster()│
│ ├── 6.9 onRefresh() ← 重要! │
│ │ └── 创建并启动内嵌服务器 │
│ ├── 6.10 registerListeners() │
│ ├── 6.11 finishBeanFactoryInitialization() ← 重要!│
│ │ └── 实例化所有非懒加载单例Bean │
│ │ ├── 创建Bean实例 │
│ │ ├── 依赖注入 │
│ │ └── 初始化回调 │
│ └── 6.12 finishRefresh() │
│ │
│ 7. 启动收尾 │
│ ├── afterRefresh() │
│ ├── listeners.started() ← 发布启动完成事件 │
│ ├── callRunners() ← 执行ApplicationRunner │
│ └── listeners.running() ← 发布应用就绪事件 │
└─────────────────────────────────────────────────┘
核心代码
/**
* Run the Spring application, creating and refreshing a new
* {@link ApplicationContext}.
* @param args the application arguments (usually passed from a Java main method)
* @return a running {@link ApplicationContext}
*/
public ConfigurableApplicationContext run(String... args) {
// ============ 阶段0: 启动准备 ============
StopWatch stopWatch = new StopWatch();
stopWatch.start();
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = null;
Collection<SpringBootExceptionReporter> exceptionReporters = new ArrayList<>();
// 1. 设置无头模式(确保在服务器环境运行)
configureHeadlessProperty();
// 2. 获取并启动所有SpringApplicationRunListener
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(); // 发布ApplicationStartingEvent
try {
// ============ 阶段1: 环境准备 ============
// 3. 创建应用参数封装
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 4. 准备环境(⚠️ 这是真正的第一步核心操作!)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, applicationArguments);
// ✅ 这里加载所有配置:application.properties → application.yml → 环境变量 → 命令行参数
// 5. 配置忽略的Bean信息(AOP相关)
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 6. 打印Banner(应用启动logo)
Banner printedBanner = printBanner(environment);
// ============ 阶段2: 上下文创建 ============
// 7. 创建应用上下文(根据应用类型)
context = createApplicationContext();
// Web应用: AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext
// 普通应用: AnnotationConfigApplicationContext
// 8. 初始化异常报告器
exceptionReporters = getSpringFactoriesInstances(SpringBootExceptionReporter.class,
new Class[] { ConfigurableApplicationContext.class }, context);
// ============ 阶段3: 上下文预处理 ============
// 9. 准备上下文(⚠️ 关键预处理)
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, applicationArguments, printedBanner);
// ✅ 这里包含:设置环境、执行ApplicationContextInitializer、加载Bean定义等
// ============ 阶段4: 容器刷新 ============
// 10. 刷新上下文(⚠️ 最核心的阶段!)
refreshContext(context);
// ✅ 这里执行完整的ApplicationContext.refresh(),包含:
// - BeanFactory准备
// - 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor(包括组件扫描)
// - 注册BeanPostProcessor
// - 初始化MessageSource
// - 初始化事件广播器
// - onRefresh() → 创建内嵌Web服务器
// - 注册监听器
// - 实例化所有非懒加载单例Bean
// - 完成刷新
// 11. 后刷新处理(空方法,可扩展)
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// ============ 阶段5: 启动完成 ============
stopWatch.stop();
if (this.logStartupInfo) {
new StartupInfoLogger(this.mainApplicationClass).logStarted(getApplicationLog(), stopWatch);
}
// 12. 发布应用启动完成事件
listeners.started(context); // 发布ApplicationStartedEvent
// 13. 执行所有Runner(ApplicationRunner/CommandLineRunner)
callRunners(context, applicationArguments);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, listeners);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
try {
// 14. 发布应用就绪事件
listeners.running(context);
}
catch (Throwable ex) {
handleRunFailure(context, ex, exceptionReporters, null);
throw new IllegalStateException(ex);
}
return context;
}
# 获取并启动所有SpringApplicationRunListener
通过 SpringFactoriesLoader 查找并加载所有的 SpringApplicationRunListeners,通过调用starting()方法通知所有的SpringApplicationRunListener:应用开始启动了。SpringApplicationRunListener 其本质上就是一个事件发布者,它在SpringBoot应用启动的不同时间点发布不同应用事件类型(ApplicationEvent),如果有哪些事件监听者(ApplicationListener)对这些事件感兴趣,则可以接收并且处理。前面的初始化流程中,SpringApplication 加载了一系列 ApplicationListener。发布事件的代码已经在SpringApplicationRunListeners中实现了。 SpringApplicationRunListener只有一个实现类: EventPublishingRunListener。此处的代码只会返回一个 SpringApplicationRunListeners ,注意后面多了一个s字母,看下源码就会发现该类就是包含了一个SpringApplicationRunListener的List。操作SpringApplicationRunListeners ,在内部会遍历每一个SpringApplicationRunListener,调用每一个SpringApplicationRunListener的实现类的starting方法
# 准备环境
创建并配置当前应用将要使用的 Environment,Environment用于描述应用程序当前的运行环境,其抽象了两个方面的内容:配置文件(profile)和属性(properties),开发经验丰富的同学对这两个东西一定不会陌生:不同的环境(eg:生产环境、预发布环境)可以使用不同的配置文件,而属性则可以从配置文件、环境变量、命令行参数等来源获取。因此,当Environment准备好后,在整个应用的任何时候,都可以从Environment中获取资源。
总结起来,主要完成以下几件事:
- 判断Environment是否存在,不存在就创建(如果是web项目就创建 StandardServletEnvironment,否则创建 StandardEnvironment)
- 配置Environment:配置profile以及properties
- 调用SpringApplicationRunListener的 environmentPrepared()方法,通知事件监听者:应用的Environment已经准备好
# 打印Banner图案
# 创建应用上下文
根据不同的ApplicationType创建不同的Context,具体的类型回顾初始化中App类型的介绍
# 准备上下文
初始化ApplicationContext,主要完成以下工作:
- 将准备好的Environment设置给ApplicationContext
- 遍历调用所有的ApplicationContextInitializer的 initialize()方法来对已经创建好的ApplicationContext进行进一步的处理
- 调用SpringApplicationRunListener的 contextPrepared()方法,通知所有的监听者:ApplicationContext已经准备完毕
- 将所有的bean加载到容器中
- 调用SpringApplicationRunListener的 contextLoaded()方法,通知所有的监听者:ApplicationContext已经装载完毕
# 容器刷新
refresh完成配置类的解析、各种BeanFactoryPostProcessor和BeanPostProcessor的注册、国际化配置的初始化、web内置容器的构造等等。
以上就是Spring Boot的整个启动流程,其核心就是在Spring容器初始化并启动的基础上加入各种扩展点,这些扩展点包括:
- ApplicationContextInitializer
- ApplicationListener
- 自动配置自定义 org.springframework.boot.env.EnvironmentPostProcessor: Allows for customization of the application's {@link Environment} prior to the application context being refreshed.
- 各种BeanFactoryPostProcessor等等 org.springframework.beans.factory.config.BeanFactoryPostProcessor: 允许我们在容器实例化相应对象之前,对注册到容器的BeanDefinition所保存的信息做一些额外的操作,比如修改bean定义的某些属性或者增加其他信息等。
# 实例分析启动流程
// 1. 主启动类
@SpringBootApplication
public class SimpleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SimpleApplication.class, args);
}
}
// 2. 一个简单的RestController
@RestController
public class HelloController {
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return "Hello World!";
}
}
// 3. 配置文件application.properties
server.port=8080
spring.application.name=simple-demo
# 阶段1: JVM启动(底层准备)
java -jar simple-app.jar
加载JVM核心库
初始化类加载器层次结构
加载SimpleApplication.class到内存
验证字节码安全性
调用main方法入口
# 阶段2: SpringApplication.run() 初始化
SpringApplication.run(SimpleApplication.class, args);
// 内部创建SpringApplication实例
SpringApplication app = new SpringApplication(SimpleApplication.class);
app.run(args);
// 2.1 配置无头模式(确保在服务器环境运行)
configureHeadlessProperty(); // java.awt.headless=true
// 2.2 获取并启动监听器
SpringApplicationRunListeners listeners = getRunListeners(args);
listeners.starting(); // 发布ApplicationStartingEvent
// 2.3 创建应用参数封装
ApplicationArguments appArgs = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
// 解析命令行参数:--server.port=9090 等
# 发布启动事件 ⭐扩展点1: 启动事件监听
listeners.starting(); // 发布ApplicationStartingEvent
开发者扩展方式:
// 方式1: 实现ApplicationListener
@Component
public class MyStartingListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationStartingEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
System.out.println("应用开始启动...");
// 场景:记录启动日志、初始化监控指标
}
}
// 方式2: 使用@EventListener注解
@Component
public class EventListenerService {
@EventListener
public void handleStartingEvent(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
// 场景:验证环境配置、检查依赖服务
checkRequiredProperties();
}
private void checkRequiredProperties() {
// 检查必需配置是否存在
if (System.getProperty("required.config") == null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("缺少必需配置");
}
}
}
常见场景:
启动日志记录:记录应用启动时间和参数
环境验证:检查必需的环境变量和配置
资源预加载:提前加载常用资源
监控指标初始化:设置应用监控
完整事件顺序:
ApplicationStartingEvent- 最早,环境还未准备
ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent- 环境已准备,上下文未创建
ApplicationContextInitializedEvent- 上下文已创建,Initializer已执行
ApplicationPreparedEvent- 上下文已准备,refresh()未调用
ApplicationStartedEvent- refresh()已完成,Runner未执行
ApplicationReadyEvent- 完全就绪,Runner已执行
# 阶段3: 环境准备(加载配置)
// 3.1 加载所有配置源(按优先级)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = prepareEnvironment(listeners, appArgs);
// 1. application.properties → server.port=8080
// 2. application.yml (不存在)
// 3. 环境变量 (SPRING_APPLICATION_JSON等)
// 4. 命令行参数 (--server.port=9090)
// 5. 默认属性
=>
// SpringApplication.java
private ConfigurableEnvironment prepareEnvironment(...) {
// 1. 创建环境对象(根据应用类型)
ConfigurableEnvironment environment = createEnvironment();
// Web应用: StandardServletEnvironment
// 普通应用: StandardEnvironment
// 2. 配置PropertySource(配置源加载在这里发生!)
configurePropertySources(environment, args);
// 3. 配置Profile
configureProfiles(environment, args);
return environment;
}
// configurePropertySources内部的加载顺序:
public void configurePropertySources(ConfigurableEnvironment environment, String[] args) {
// 配置源优先级(从高到低):
// 1. 命令行参数 (--server.port=8080)
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(new SimpleCommandLinePropertySource(args));
// 2. ServletConfig参数 (Web应用)
// 3. ServletContext参数 (Web应用)
// 4. JNDI属性
// 5. 系统环境变量
// 6. 系统属性
// 7. 随机值属性
// 8. 应用配置文件 ← 主要配置来源!
// - application.properties
// - application.yml
// - application-{profile}.properties
// 9. 默认属性
}
# 加载配置源 ⭐扩展点2: 自定义PropertySource
开发者扩展方式:
@Component
public class CustomPropertySourceConfig {
@PostConstruct
public void addCustomPropertySource() {
// 添加自定义配置源
MapPropertySource customSource = new MapPropertySource("custom",
Collections.singletonMap("custom.property", "value"));
environment.getPropertySources().addFirst(customSource);
}
}
// 或者实现EnvironmentPostProcessor
public class CustomEnvironmentPostProcessor implements EnvironmentPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessEnvironment(ConfigurableEnvironment env,
SpringApplication application) {
// 修改或添加配置源
env.getPropertySources().addFirst(...);
// 开发者在这里操作PropertySources
MutablePropertySources propertySources = environment.getPropertySources();
// 添加自定义配置源或修改现有配置
Map<String, Object> customProperties = new HashMap<>();
customProperties.put("custom.property", "value");
propertySources.addFirst(new MapPropertySource("custom", customProperties));
}
}
常见场景:
数据库配置加密:解密加密的数据库密码
外部配置集成:从外部配置中心加载配置
环境特定配置:根据运行环境动态调整配置
# printBanner
// 3.2 配置忽略的Bean信息(AOP相关)
configureIgnoreBeanInfo(environment);
// 3.3 打印Banner
// 控制台输出Spring logo和版本信息
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
=>
// configureIgnoreBeanInfo的实际作用:
protected void configureIgnoreBeanInfo(ConfigurableEnvironment environment) {
// 设置系统属性,告诉Spring跳过某些Bean的元数据解析
// 这可以显著提高启动性能,特别是当有大量Bean时
String ignore = environment.getProperty("spring.aop.ignore", "true");
if ("true".equals(ignore)) {
// 设置系统属性,优化AOP处理
System.setProperty("spring.aop.auto", "false");
// 对于某些已知的基础设施Bean,跳过AOP代理创建
// 比如:BeanFactoryPostProcessor, BeanPostProcessor等
// 这些Bean不需要AOP代理,跳过检查可以提高性能
}
}
开发者扩展方式:
// 自定义Banner
public class CustomBanner implements Banner {
@Override
public void printBanner(Environment environment,
Class<?> sourceClass, PrintStream out) {
out.println("=== 我的应用 ===");
out.println("版本: " + environment.getProperty("app.version"));
}
}
// 在application.properties中指定
spring.banner.location=classpath:my-banner.txt
# 阶段4: 应用上下文创建
context = createApplicationContext();
// 对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext:
// 在构造器中就创建了DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 但此时是空的,只有基础设施
=>
// 检测到有spring-web依赖,创建Web容器
return new AnnotationConfigServletWebServerApplicationContext();
// 此时还是空容器,没有任何Bean
# 阶段5: 上下文预处理
prepareContext(context, environment, listeners, appArgs, printedBanner);
=>
// 5.1 设置环境到上下文
context.setEnvironment(environment);
// 5.2 执行ApplicationContextInitializer(如果有)
applyInitializers(context);
// 发布ApplicationContextInitializedEvent
listeners.contextInitialized(context);
// 注册特定的单例Bean
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 这里注册的是已经实例化的对象,不是BeanDefinition
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
if (printedBanner != null) {
beanFactory.registerSingleton("springBootBanner", printedBanner);
}
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
}
// 设置懒初始化(Spring Boot 2.2+)
if (this.lazyInitialization) {
context.addBeanFactoryPostProcessor(new LazyInitializationBeanFactoryPostProcessor());
}
// 加载源(不是register(SimpleApplication.class))
// 将SimpleApplication.class转换为BeanDefinition存入BeanFactory
// 但此时只是蓝图,还没有实例化
Set<Object> sources = getAllSources(); // 获取所有配置源,包括主类SimpleApplication
// load方法会处理配置类
load(context, sources.toArray(new Object[0]));
// BeanDefinitionLoader.load() 方法会:
// 1. 如果source是Class且有@Configuration注解,注册为配置类
// 2. 处理@ComponentScan,扫描指定包下的@Component类
// 3. 处理@Import、@ImportResource等注解
// 4. 为SimpleApplication创建BeanDefinition并注册到BeanFactory
// 简单说:load()将SimpleApplication.class转换为BeanDefinition并注册
// SimpleApplication.class → 作为配置类注册 → 解析注解 → 扫描包 → 注册其他Bean
// 所以不是注册SimpleApplication本身,而是:
// 注册SimpleApplication为配置类(BeanDefinition)
// 解析其上的注解(@ComponentScan, @EnableAutoConfiguration)
// 执行组件扫描找到其他Bean
// 处理自动配置加载spring.factories中的配置
// 5.4 发布ApplicationPreparedEvent
listeners.contextPrepared(context);
# 执行ApplicationContextInitializer ⭐扩展点3: 上下文初始化器
applyInitializers(context);
=>
// 执行所有ApplicationContextInitializer
for (ApplicationContextInitializer initializer : initializers) {
initializer.initialize(context);
}
开发者扩展方式:
// 方式1: 实现ApplicationContextInitializer
public class MyContextInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer<ConfigurableApplicationContext> {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 场景1: 早期Bean注册,实际用例:需要在其他组件的配置阶段就提供服务的基础设施Bean。
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("earlyService", new EarlyService());
// 这个Bean现在可以在任何BeanFactoryPostProcessor中使用
// 比如在自定义的BeanFactoryPostProcessor中:
// ConfigService config = beanFactory.getBean("configService");
// 场景2: 环境验证
Environment env = context.getEnvironment();
if (!env.containsProperty("db.url")) {
throw new IllegalStateException("数据库配置缺失");
}
// 场景3: 动态配置
if (env.acceptsProfiles("cloud")) {
System.setProperty("server.port", "8081");
}
}
}
// 注册方式1: spring.factories
// META-INF/spring.factories:
org.springframework.context.ApplicationContextInitializer=com.example.MyContextInitializer
// 注册方式2: 启动类设置
new SpringApplicationBuilder(MyApp.class)
.initializers(new MyContextInitializer())
.run(args);
常见场景:
早期Bean注册:在容器刷新前注册单例Bean
环境验证:检查必需配置是否就绪
动态配置:根据环境动态修改配置
自定义BeanFactory设置:修改BeanFactory配置
# beanFactory.registerSingleton
注意: beanFactory.registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments", applicationArguments);
# 启动Spring Boot应用时传入命令行参数
java -jar myapp.jar --debug --server.port=9090 --spring.profiles.active=dev inputfile.txt
在Spring Boot中,这些参数被封装为:
ApplicationArguments applicationArguments = new DefaultApplicationArguments(args);
选项参数(Option Arguments):以--开头
--debug→ 选项名:"debug",值:空列表
--server.port=9090→ 选项名:"server.port",值:["9090"]
--spring.profiles.active=dev→ 选项名:"spring.profiles.active",值:["dev"]
非选项参数(Non-option Arguments):不以--开头
inputfile.txt→ 非选项参数
// 方式1:注入使用
@Component
public class MyComponent {
@Autowired
private ApplicationArguments args;
public void checkArgs() {
// 检查是否有debug选项
if (args.containsOption("debug")) {
System.out.println("Debug模式已启用");
}
// 获取server.port的值
List<String> portValues = args.getOptionValues("server.port");
if (!portValues.isEmpty()) {
String port = portValues.get(0);
System.out.println("端口号: " + port);
}
// 获取非选项参数
List<String> nonOptionArgs = args.getNonOptionArgs();
System.out.println("非选项参数: " + nonOptionArgs);
}
}
// 方式2:在BeanFactoryPostProcessor中使用
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
ApplicationArguments args = beanFactory.getBean("springApplicationArguments", ApplicationArguments.class);
if (args.containsOption("dev")) {
// 开发环境特殊配置
enableDevelopmentFeatures();
}
}
}
# 为什么需要类型判断 beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 在prepareContext方法中:
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
// 只有DefaultListableBeanFactory才有这个方法
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.setAllowBeanDefinitionOverriding(this.allowBeanDefinitionOverriding);
// true:允许同名Bean定义覆盖(后注册的覆盖先注册的)
// false:不允许覆盖,遇到同名Bean定义时抛出异常
}
核心原因:Spring的设计支持多种BeanFactory实现, 虽然Spring Boot默认使用DefaultListableBeanFactory,但框架设计上支持多种实现:
// Spring支持的不同BeanFactory实现:
public interface ConfigurableListableBeanFactory
extends ListableBeanFactory, ConfigurableBeanFactory, AutowireCapableBeanFactory {
// 基础接口
}
// 主要实现类:
public class DefaultListableBeanFactory extends AbstractAutowireCapableBeanFactory
implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory, BeanDefinitionRegistry, Serializable {
// Spring默认使用的实现
}
// 其他可能的实现(理论上):
public class CustomBeanFactory implements ConfigurableListableBeanFactory {
// 用户自定义的BeanFactory实现
}
实际应用场景:
// 场景1:Spring Boot测试中可能使用不同的BeanFactory
@SpringBootTest
@TestPropertySource(properties = "spring.main.allow-bean-definition-overriding=true")
public class MyTest {
// 测试环境可能使用特殊的BeanFactory配置
}
// 场景2:自定义BeanFactory(虽然少见,但框架设计上支持)
@Configuration
public class CustomBeanFactoryConfig {
@Bean
public ConfigurableListableBeanFactory customBeanFactory() {
return new CustomBeanFactoryImplementation(); // 用户自定义实现
}
}
# 发布准备事件 ⭐扩展点4: 准备事件监听
listeners.contextPrepared(context); // ApplicationPreparedEvent
开发者扩展方式:
@Component
public class PreparedEventListener implements ApplicationListener<ApplicationPreparedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ApplicationPreparedEvent event) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = context.getBeanFactory();
// 场景1: Bean定义分析(在实例化前)
String[] beanNames = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionNames();
log.info("已注册Bean定义数量: {}", beanNames.length);
// 场景2: 条件配置验证
if (!beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition("requiredBean")) {
throw new IllegalStateException("必需Bean未配置");
}
// 场景3: 动态注册配置(基于现有Bean定义)
if (beanFactory.containsBeanDefinition("dataSource")) {
// 根据现有配置决定是否注册额外组件
registerAdditionalComponents(beanFactory);
}
// 场景4: 性能监控设置
setupPerformanceMonitoring(beanFactory);
// 预加载缓存
preloadCacheData();
}
}
# 阶段6: 容器刷新(核心!)
refreshContext(context); // → 调用context.refresh()
=>
AbstractApplicationContext:
public void refresh() {
// 7.1 prepareRefresh() - 设置上下文激活状态、初始化属性源等
prepareRefresh();
// 7.2 obtainFreshBeanFactory() - 获取或刷新BeanFactory
// 对于AnnotationConfigApplicationContext,这里会创建DefaultListableBeanFactory
// 但此时是空的,还没有Bean定义
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = obtainFreshBeanFactory();
// 7.3 prepareBeanFactory() - 配置BeanFactory的基础设施
// 设置类加载器、表达式解析器、属性编辑器
// 注册环境Bean等基础配置:environment、systemProperties、systemEnvironment
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// 此时BeanFactory中已有:
// - 几个registerSingleton的单例Bean
// - 一些BeanDefinition(来自load())
// 但基础设施(如环境Bean、解析器等)还需要配置
// 7.4 postProcessBeanFactory() - 空方法,子类可重写
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
// Web应用在这里注册Servlet相关的Scope
}
# 6.1-6.4: 准备阶段
prepareRefresh();
obtainFreshBeanFactory();
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory);
postProcessBeanFactory(beanFactory);
=>
// BeanFactory基础设施设置过程:
prepareBeanFactory(beanFactory)
│
├── 设置类加载器
│ └── beanFactory.setBeanClassLoader()
│
├── 设置表达式解析器
│ └── beanFactory.setBeanExpressionResolver()
│ └── StandardBeanExpressionResolver ← 支持SPEL表达式
│
├── 添加属性编辑器注册器
│ └── beanFactory.addPropertyEditorRegistrar()
│ └── ResourceEditorRegistrar ← 注册资源编辑器
│
├── 添加ApplicationContextAware处理器
│ └── beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor()
│ └── ApplicationContextAwareProcessor ← 处理Aware接口
│
├── 设置忽略的依赖接口
│ └── beanFactory.ignoreDependencyInterface()
│ └── 避免某些接口的自动注入
│
├── 注册可解析的依赖
│ └── beanFactory.registerResolvableDependency()
│ └── 注册BeanFactory、ResourceLoader等
│
└── 添加其他后处理器
└── beanFactory.addBeanPostProcessor()
└── ApplicationListenerDetector ← 检测应用监听器
Spring基础设施组件对比总结表
| 组件 | 在BeanFactory中的角色 | 主要功能 | 典型使用场景 | 关联注解/表达式 | 配置时机 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| EmbeddedValueResolver(嵌入式值解析器) | 解析字符串中的占位符和SpEL表达式 | 将包含${...}和#{...}的字符串解析为实际值 | @Value注解处理配置文件占位符解析SpEL表达式求值 | @Value("${server.port}")@Value("#{T(java.lang.Math).random() * 100.0}")@Value("#{systemProperties['user.home']}") | prepareBeanFactory()阶段 |
| PropertyEditor(属性编辑器) | 传统类型转换机制 | 将字符串转换为目标类型(如String→Date) | XML配置中的类型转换@Value注解的简单类型转换表单数据绑定 | @Value("2023-01-01") → Date对象XML配置中的属性转换 | prepareBeanFactory()阶段注册 |
| ExpressionParser(表达式解析器) | SpEL表达式求值引擎 | 解析和执行Spring表达式语言 | @Value中的复杂表达式安全导航操作符条件表达式 | @Value("#{user?.address?.city}")@Value("#{environment.acceptsProfiles('dev') ? 'dev' : 'prod'}")@Value("#{users.}") | prepareBeanFactory()阶段配置 |
| ScopeManager(作用域管理器) | 管理Bean的生命周期范围 | 控制Bean的创建、缓存和销毁策略 | 单例vs原型作用域Request/Session作用域自定义作用域 | @Scope("prototype")@Scope("request")@Scope("session") | BeanFactory初始化阶段 |
| ConversionService(类型转换服务) | 现代统一类型转换API | 提供类型安全的转换机制,支持泛型和集合 | 配置属性转换表单数据绑定自定义类型转换 | @Value("${some.list}") List@Value("${some.map}") Map自定义类型转换 | BeanFactory后处理阶段 |
| Conditional系统(条件化配置) | 基于条件的Bean创建 | 根据条件决定是否创建Bean | 环境特定配置特性开关控制类路径检测 | @Profile("cloud")@ConditionalOnProperty("feature.enabled")@ConditionalOnClass("com.example.Service") | Bean定义加载阶段 |
# 6.5: 执行BeanFactoryPostProcessor ⭐扩展点5: Bean工厂后处理
invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors();
=>
// 6.5.1 处理@SpringBootApplication
// → 包含@ComponentScan,扫描com.example包
// 6.5.2 找到HelloController(有@RestController注解)
// @RestController包含@Component,所以被扫描到
// 6.5.3 创建BeanDefinition(Bean蓝图)
BeanDefinition controllerDef = new RootBeanDefinition(HelloController.class);
controllerDef.setScope(SCOPE_SINGLETON);
// 6.5.4 注册到BeanFactory
beanFactory.registerBeanDefinition("helloController", controllerDef);
// 6.5.5 处理自动配置(@EnableAutoConfiguration)
// 自动配置内嵌服务器、JSON转换器等
为什么需要 BeanFactoryPostProcessor(后处理)
核心答案:动态性和条件化。有些配置无法在编写代码时确定,需要在运行时根据环境决定.
处理对象:BeanDefinition(Bean蓝图)
开发者扩展方式:
// 方式1: 实现BeanFactoryPostProcessor
@Component
public class MyBeanFactoryPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
Environment env = beanFactory.getBean(Environment.class);
// 场景1: 根据环境动态修改配置
if (env.acceptsProfiles("cloud")) {
BeanDefinition dbDef = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("dataSource");
// 云环境使用连接池配置
dbDef.getPropertyValues().add("url", env.getProperty("CLOUD_DB_URL"));
}
// 场景2: 条件注册Bean
if (isFeatureEnabled(env)) {
GenericBeanDefinition featureBean = new GenericBeanDefinition();
featureBean.setBeanClass(FeatureService.class);
((DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory)
.registerBeanDefinition("featureService", featureBean);
}
// 场景3: 属性解密
BeanDefinition[] beanDefs = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitions();
for (BeanDefinition beanDef : beanDefs) {
decryptPropertyValues(beanDef); // 解密加密的属性值
}
}
}
常见场景:
Bean定义修改:改变作用域、懒加载设置等
条件注册:根据条件动态注册Bean
AOP代理设置:为特定Bean设置代理
属性加密解密:处理加密的配置属性
# 6.6: 注册BeanPostProcessor ⭐扩展点6: Bean后处理
// 注册AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor
// 用于后续处理@Autowired注入
registerBeanPostProcessors(beanFactory);
处理对象:Bean实例(实际对象)
开发者扩展方式:
@Component
public class MyBeanPostProcessor implements BeanPostProcessor {
// Bean初始化前调用
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
// 场景1: 监控统计
if (bean instanceof RestController) {
monitorBeanCreation(beanName, bean.getClass());
}
// 场景2: 自定义注解处理
if (bean.getClass().isAnnotationPresent(MyAnnotation.class)) {
processCustomAnnotation(bean);
}
return bean;
}
// Bean初始化后调用
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
// 场景1: AOP代理创建 这个不是正常的场景而是springboot源码spring-boot-starter-aop的实现,纯粹是举例
if (bean instanceof MyService) {
return createProxy(bean); // 返回代理对象
}
// 场景2: 缓存包装
if (bean instanceof Repository) {
return new CachingRepositoryWrapper((Repository) bean);
}
return bean;
}
}
常见场景:
AOP代理:为Bean创建动态代理
监控统计:记录Bean创建和调用统计
缓存包装:为数据访问层添加缓存
自定义注解处理:处理业务自定义注解
# 6.7-6.8: 消息源和事件广播器
initMessageSource();
initApplicationEventMulticaster();
# 6.9: 子类特定刷新 ⭐扩展点7: 内嵌服务器自定义
onRefresh(); // ServletWebServerApplicationContext.onRefresh()
=>
// 6.9.1 创建内嵌Tomcat服务器
Tomcat tomcat = new Tomcat();
tomcat.setPort(8080); // 从配置读取
// 6.9.2 创建DispatcherServlet(Spring MVC核心)
DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet = new DispatcherServlet(context);
// 6.9.3 注册Servlet映射
context.addServlet("dispatcher", dispatcherServlet).addMapping("/");
// 6.9.4 启动Tomcat(但还没开始监听端口)
tomcat.start();
开发者扩展方式:
// 自定义内嵌服务器配置
@Configuration
public class ServerConfig {
@Bean
public ServletWebServerFactory servletContainer() {
TomcatServletWebServerFactory tomcat = new TomcatServletWebServerFactory();
tomcat.setPort(8080);
tomcat.addConnectorCustomizers(connector -> {
// 自定义连接器配置
connector.setProperty("maxThreads", "200");
});
return tomcat;
}
@Bean
public DispatcherServlet dispatcherServlet() {
return new DispatcherServlet();
}
}
# 6.10: 注册监听器
registerListeners();
# 6.11: 完成BeanFactory初始化 ⭐扩展点8: Bean生命周期回调
finishBeanFactoryInitialization();
=>
// 6.11.1 实例化HelloController
HelloController controller = new HelloController(); // 调用构造方法
// 6.11.2 依赖注入(本例没有依赖,跳过)
// 6.11.3 初始化回调
// 调用@PostConstruct方法(本例没有)
// 6.11.4 注册到单例池
singletonObjects.put("helloController", controller);
开发者扩展方式:
@Component
public class MyService implements InitializingBean, DisposableBean {
// InitializingBean - 初始化回调
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
// 场景:资源初始化
initializeResources();
loadReferenceData();
}
// DisposableBean - 销毁回调
@Override
public void destroy() throws Exception {
// 场景:资源清理
cleanupResources();
closeConnections();
}
// 或使用注解方式
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
// 初始化逻辑
}
@PreDestroy
public void cleanup() {
// 清理逻辑
}
}
# 6.12: 完成刷新 ⭐扩展点9: 上下文刷新事件
// 发布ContextRefreshedEvent事件
// 完成容器初始化
finishRefresh();
开发者扩展方式:
@Component
public class ContextRefreshedListener implements ApplicationListener<ContextRefreshedEvent> {
@Override
public void onApplicationEvent(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
// 场景:容器刷新完成后执行初始化
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
// 验证所有必需Bean是否就绪
validateRequiredBeans(context);
// 启动后台任务
startBackgroundJobs();
}
}
# 阶段7: 启动收尾
// 7.1 后处理(空方法,可扩展)
afterRefresh(context, applicationArguments);
// 7.2 发布启动完成事件 ⭐扩展点10: 启动完成事件
listeners.started(context); // ApplicationStartedEvent
// 7.3 执行Runner(如果有ApplicationRunner/CommandLineRunner)⭐扩展点11: 启动Runner
callRunners(context, appArgs);
// 7.4 发布应用就绪事件 ⭐扩展点12: 应用就绪事件
listeners.running(context); // ApplicationReadyEvent
// 7.5 Tomcat开始监听端口(真正接受请求)
// 控制台输出: Tomcat started on port(s): 8080 (http)
Runner扩展方式:
@Component
public class MyApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
// 场景1: 数据初始化
if (args.containsOption("init-data")) {
initializeSampleData();
}
// 场景2: 连接检查
checkExternalServices();
// 场景3: 缓存预热
warmUpCaches();
}
}
@Component
public class MyCommandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
// 处理命令行参数
for (String arg : args) {
if (arg.equals("--debug")) {
enableDebugMode();
}
}
}
}
# 时序状态和最终状态
时间点 T0: 创建BeanFactory(空)
// 刚创建时的BeanFactory内容:
BeanFactory状态:
├── singletonObjects: {} // 空单例池
├── beanDefinitionMap: {} // 空Bean定义映射
├── embeddedValueResolvers: [] // 空值解析器
└── 基本基础设施:
├── 类加载器
├── 类型转换服务
└── 基本属性编辑器
时间点 T1: registerSingleton("springApplicationArguments") → 添加具体对象
// 添加具体对象后的状态:
BeanFactory状态:
├── singletonObjects:
│ └── "springApplicationArguments" → ApplicationArguments实例
├── beanDefinitionMap: {} // 仍然无Bean定义
├── embeddedValueResolvers: []
└── 基本基础设施
时间点 T2: load() → 注册BeanDefinition(蓝图)
// load()处理SimpleApplication.class后的状态:
BeanFactory状态:
├── singletonObjects:
│ └── "springApplicationArguments" → ApplicationArguments实例
├── beanDefinitionMap:
│ ├── "simpleApplication" → BeanDefinition(SimpleApplication.class)
│ ├── "helloController" → BeanDefinition(HelloController.class) // 扫描到的
│ ├── "userService" → BeanDefinition(UserService.class) // 扫描到的
│ └── 其他自动配置的BeanDefinition...
├── embeddedValueResolvers: []
└── 基本基础设施
时间点 T3: prepareBeanFactory() → 配置BeanFactory基础设施
// 配置基础设施后的状态:
BeanFactory状态:
├── singletonObjects:
│ ├── "springApplicationArguments" → ApplicationArguments实例
│ └── "environment" → Environment实例 // 新添加的环境Bean
├── beanDefinitionMap:
│ ├── "simpleApplication" → BeanDefinition
│ ├── "helloController" → BeanDefinition
│ └── ...
├── embeddedValueResolvers: [默认值解析器] // 新增
└── 增强的基础设施:
├── 完整的属性编辑器
├── 表达式解析器
├── 作用域管理器
└── 类型转换服务
时间点 T4: invokeBeanFactoryPostProcessors() → 处理所有BeanDefinition
// 处理后处理器后的状态(可能的变化):
BeanFactory状态:
├── singletonObjects:
│ ├── "springApplicationArguments" → ApplicationArguments实例
│ └── "environment" → Environment实例
├── beanDefinitionMap:
│ ├── "simpleApplication" → BeanDefinition(可能被修改)
│ ├── "helloController" → BeanDefinition(可能被修改)
│ ├── "userService" → BeanDefinition(可能被修改)
│ ├── "newDynamicBean" → BeanDefinition(可能新增) // 动态注册的
│ └── ...
├── embeddedValueResolvers: [默认值解析器]
└── 基础设施
时间点 T5: finishBeanFactoryInitialization() → 实例化所有单例Bean
// 实例化所有单例Bean后的状态:
BeanFactory状态:
├── singletonObjects:
│ ├── "springApplicationArguments" → ApplicationArguments实例
│ ├── "environment" → Environment实例
│ ├── "simpleApplication" → SimpleApplication实例(已实例化)
│ ├── "helloController" → HelloController实例(已实例化+依赖注入)
│ ├── "userService" → UserService实例(已实例化+依赖注入)
│ └── 所有其他单例Bean...
├── beanDefinitionMap:
│ ├── "simpleApplication" → BeanDefinition
│ ├── "helloController" → BeanDefinition
│ └── ...(定义仍然保留)
├── embeddedValueResolvers: [默认值解析器]
└── 基础设施
应用启动完成后的状态:
├── BeanFactory中有:
│ └── helloController : HelloController实例
├── Web服务器:
│ └── Tomcat运行在8080端口
├── URL映射:
│ └── /hello → HelloController.hello()方法
└── 可以处理请求:
GET http://localhost:8080/hello → "Hello World!"
# Bean的时序状态细节
# 创建-注入-回调
更深一步观察bean的整个生命周期:
// Spring容器启动入口
SpringApplication.run()
└── AbstractApplicationContext.refresh()
└── finishBeanFactoryInitialization(beanFactory)
└── DefaultListableBeanFactory.preInstantiateSingletons()
└── 遍历所有Bean定义,对每个Bean执行:
getBean(beanName) → doGetBean() → createBean() → doCreateBean()
├── createBeanInstance() // 阶段1: 实例化(构造器注入)
├── populateBean() // 阶段2: 依赖注入 (字段/setter注入)
└── initializeBean() // 阶段3: 初始化生命周期回调)
// 单个Bean的详细创建过程:
doCreateBean(beanName, mbd, args)
│
├── 1. createBeanInstance() ← 实例化阶段(构造器注入在这里完成)
│ │
│ ├── 1.1 确定实例化策略
│ │ ├── determineConstructorsFromBeanPostProcessors() // 通过后处理器选择构造器
│ │ └── 根据配置选择三种路径之一:
│ │
│ ├── 1.2 构造器注入路径 (autowireConstructor) ← 主要注入方式
│ │ ├── determineConstructor() // 确定使用哪个构造器
│ │ ├── resolveConstructorArguments() // 解析构造器参数(核心依赖解析!)
│ │ │ └── resolveDependency() // 解析单个依赖
│ │ │ └── getBean() // 可能递归获取依赖Bean
│ │ └── constructor.newInstance(args) // 使用参数创建实例
│ │
│ ├── 1.3 默认构造器路径 (instantiateBean)
│ │ ├── getInstantiationStrategy() // 获取实例化策略
│ │ └── instantiate() // 反射创建空实例
│ │
│ └── 1.4 工厂方法路径 (instantiateUsingFactoryMethod)
│ ├── determineFactoryMethod() // 确定工厂方法
│ ├── resolveArguments() // 解析方法参数
│ └── method.invoke() // 调用工厂方法
│
├── 2. populateBean() ← 依赖注入阶段(字段/setter注入在这里完成)
│ │
│ ├── 2.1 自动注入基础支持
│ │ ├── autowireByName() // 按名称自动注入
│ │ └── autowireByType() // 按类型自动注入
│ │
│ ├── 2.2 注解驱动注入(核心!)
│ │ └── postProcessProperties() // 调用InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor
│ │ └── AutowiredAnnotationBeanPostProcessor工作流程:
│ │ ├── findAutowiringMetadata() // 查找@Autowired、@Value、@Inject注解
│ │ ├── resolveDependency() // 解析依赖
│ │ ├── Field.set(bean, value) // 字段反射注入
│ │ └── Method.invoke(bean, args) // setter方法调用注入
│ │
│ └── 2.3 应用属性值
│ └── applyPropertyValues() // 最终设置属性值
│
└── 3. initializeBean() ← 初始化阶段(方法注入在这里完成 这里说的"方法注入"不是依赖注入,而是指初始化方法的调用)
│
├── 3.1 Aware接口回调
│ └── invokeAwareMethods()
│ ├── setBeanName() // BeanNameAware
│ ├── setBeanFactory() // BeanFactoryAware
│ └── setApplicationContext() // ApplicationContextAware
│
├── 3.2 前置初始化处理
│ └── applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
│ └── CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理:
│ └── postProcessBeforeInitialization() // 调用@PostConstruct方法
│
├── 3.3 初始化方法调用
│ └── invokeInitMethods()
│ ├── afterPropertiesSet() // InitializingBean接口
│ └── initMethod.invoke() // 自定义init方法
│
└── 3.4 后置初始化处理
└── applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
└── AbstractAutoProxyCreator处理:
└── postProcessAfterInitialization() // AOP代理在这里创建
# 增强实例
// 1. 主启动类(不变)
@SpringBootApplication
public class SimpleApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SimpleApplication.class, args);
}
}
// 2. 增强的RestController,添加各种初始化方法
@RestController
public class HelloController implements InitializingBean, ApplicationContextAware {
private ApplicationContext applicationContext;
private String startupTime;
// 构造器注入(阶段1)
public HelloController() {
System.out.println("1. 构造器调用 - HelloController实例创建");
// environment.getProperty("spring.application.name"); // ❌ 这里不能调用 environment,可以用下面方法:
/**
public HelloController(Environment environment) {
this.environment = environment;
this.appName = environment.getProperty("spring.application.name");
System.out.println("构造器中使用配置: " + appName); // ✅ 安全
}**/
// ❌ 输出: applicationContext = null
// ❌ 不能在这里使用applicationContext!
// 跟environment不同,不建议构造器注入ApplicationContext public HelloController(ApplicationContext applicationContext) ⚠️ 技术上可用,但有风险! 有循环依赖风险,比如:
//❌ 危险操作1: 获取其他Bean可能触发循环依赖 SomeService service = context.getBean(SomeService.class);
// ❌ 危险操作2: 如果SomeService也依赖HelloController,会导致栈溢出 service.initialize();
// ❌ 危险操作3: Bean可能还未完全初始化 SomeBean bean = context.getBean(SomeBean.class);
}
// 字段注入(阶段2)
@Autowired
private Environment environment;
// Setter注入(阶段2)
private MessageService messageService;
@Autowired
public void setMessageService(MessageService messageService) {
System.out.println("2. Setter注入 - MessageService注入");
this.messageService = messageService;
// ❌ 不安全操作:
// - 调用messageService的方法(可能其他依赖还未注入)
// - 访问其他@Autowired字段(可能还未注入)
}
// ApplicationContextAware接口(阶段3-1)
@Override
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext applicationContext) throws BeansException {
System.out.println("3. Aware接口 - ApplicationContext设置");
this.applicationContext = applicationContext;
}
// @PostConstruct方法(阶段3-2)
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("4. @PostConstruct - 自定义初始化");
this.startupTime = LocalDateTime.now().format(DateTimeFormatter.ISO_LOCAL_DATE_TIME);
// 此时所有依赖都已注入完成
String appName = environment.getProperty("spring.application.name"); // 可以安全调用 environment
System.out.println("应用名称: " + appName);
// ✅ 这里可以安全使用 context
// 1. 获取Bean
MyService service = context.getBean(MessageService.class);
// 2. 发布应用事件
context.publishEvent(new CustomEvent(this, "事件数据"));
// 3. 获取环境信息(Environment是ApplicationContext的一部分)
Environment env = context.getEnvironment();
String configValue = env.getProperty("some.config");
// 4. 国际化消息
String message = context.getMessage("hello.message", null, Locale.CHINA);
// 5. 资源访问
Resource resource = context.getResource("classpath:config/file.txt");
}
// InitializingBean接口(阶段3-3)
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
System.out.println("5. InitializingBean - 属性设置后初始化");
// 可以执行额外的初始化逻辑
}
// 业务方法
@GetMapping("/hello")
public String hello() {
return messageService.getMessage() + " at " + startupTime;
}
}
// 3. 简单的Service类,用于演示依赖
@Service
public class MessageService {
public MessageService() {
System.out.println("1. MessageService构造器调用");
}
@PostConstruct
public void init() {
System.out.println("4. MessageService @PostConstruct");
}
public String getMessage() {
return "Hello World from Spring Boot!";
}
}
// 4. 配置文件application.properties
server.port=8080
spring.application.name=simple-demo
# Bean时序状态
// HelloController的完整创建过程:
doCreateBean("helloController")
│
├── 阶段1: createBeanInstance() ← 实例化
│ └── 调用HelloController构造器
│ ✅ 状态: Bean实例已创建,但所有字段为null
│ 📝 控制台输出: "1. 构造器调用 - HelloController实例创建"
│
├── 阶段2: populateBean() ← 依赖注入
│ ├── 注入@Autowired字段: Environment environment
│ ├── 调用setter方法: setMessageService(messageService实例)
│ ✅ 状态: 依赖已注入,但未初始化
│ 📝 控制台输出: "2. Setter注入 - MessageService注入"
│ └── MessageService的创建过程(递归):
│ doCreateBean("messageService")
│ ├── createBeanInstance() → "1. MessageService构造器调用"
│ ├── populateBean() // 无依赖需要注入
│ └── initializeBean() → "4. MessageService @PostConstruct"
│
└── 阶段3: initializeBean() ← 初始化
├── 3.1 invokeAwareMethods()
│ └── 调用setApplicationContext()
│ ✅ 状态: ApplicationContext已设置
│ 📝 控制台输出: "3. Aware接口 - ApplicationContext设置"
│
├── 3.2 applyBeanPostProcessorsBeforeInitialization()
│ └── CommonAnnotationBeanPostProcessor处理@PostConstruct
│ └── 调用init()方法
│ ✅ 状态: 自定义初始化完成,Bean已就绪
│ 📝 控制台输出: "4. @PostConstruct - 自定义初始化"
│
├── 3.3 invokeInitMethods()
│ ├── 调用afterPropertiesSet() (InitializingBean接口)
│ 📝 控制台输出: "5. InitializingBean - 属性设置后初始化"
│ └── 如果有自定义init-method,也会在这里调用
│
└── 3.4 applyBeanPostProcessorsAfterInitialization()
└── 可能创建AOP代理(本例不需要)
✅ 最终状态: Bean完全初始化完成,可正常使用
# 扩展点场景
# 具体业务场景1:加密配置解密服务
// 在ApplicationContextInitializer中早期注册解密服务
public class DecryptionInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
// 早期注册解密服务
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("configDecryptor", new ConfigDecryptor());
// 现在其他BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以使用这个解密服务
// 例如:解密数据库密码、API密钥等敏感配置
}
}
// 在BeanFactoryPostProcessor中使用早期注册的Bean
@Component
public class DecryptionPostProcessor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) {
// 获取早期注册的解密服务
ConfigDecryptor decryptor = beanFactory.getBean("configDecryptor", ConfigDecryptor.class);
// 解密所有加密属性
BeanDefinition definition = beanFactory.getBeanDefinition("dataSource");
String encryptedPassword = (String) definition.getPropertyValues().get("password");
String decryptedPassword = decryptor.decrypt(encryptedPassword);
definition.getPropertyValues().add("password", decryptedPassword);
}
}
# 具体业务场景2:环境检测服务
// 早期注册环境检测服务
public class EnvironmentDetectorInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
EnvironmentDetector detector = new EnvironmentDetector();
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("envDetector", detector);
// 根据环境动态设置配置
if (detector.isCloudEnvironment()) {
System.setProperty("server.port", "8081");
System.setProperty("spring.profiles.active", "cloud");
}
}
}
# 具体业务场景3:功能开关服务
// 早期注册功能开关服务,用于控制后续Bean的注册
public class FeatureToggleInitializer implements ApplicationContextInitializer {
@Override
public void initialize(ConfigurableApplicationContext context) {
FeatureToggle toggle = new FeatureToggle();
context.getBeanFactory().registerSingleton("featureToggle", toggle);
// 其他BeanFactoryPostProcessor可以查询功能开关状态
// 决定是否注册某些Bean
}
}
# 3. Spring Boot应用监控与调优方案
生产环境监控:使用APM工具(如SkyWalking、Pinpoint)
开发阶段:集成Spring Boot DevTools进行热加载监控
整体监控架构
┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐ ┌─────────────────┐
│ 应用层监控 │ │ JVM层监控 │ │ 系统层监控 │
│ │ │ │ │ │
│ • 启动时间监控 │ │ • 内存使用 │ │ • CPU使用率 │
│ • Bean加载监控 │ │ • GC统计 │ │ • 磁盘IO │
│ • 请求响应监控 │ │ • 线程状态 │ │ • 网络流量 │
└─────────┬───────┘ └─────────┬───────┘ └─────────┬───────┘
│ │ │
└──────────────────────┼──────────────────────┘
│
┌─────────────▼─────────────┐
│ 监控数据收集层 │
│ │
│ • Micrometer │
│ • Spring Boot Actuator │
│ • 自定义监控组件 │
└─────────────┬─────────────┘
│
┌─────────────▼─────────────┐
│ 数据存储与可视化 │
│ │
│ • Prometheus + Grafana │
│ • ELK Stack │
│ • 时序数据库 │
└───────────────────────────┘
# 依赖配置
<!-- Spring Boot Actuator -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-actuator</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- Micrometer Prometheus -->
<dependency>
<groupId>io.micrometer</groupId>
<artifactId>micrometer-registry-prometheus</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 性能监控 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 日志监控 -->
<dependency>
<groupId>net.logstash.logback</groupId>
<artifactId>logstash-logback-encoder</artifactId>
<version>7.2</version>
</dependency>
# 启动过程专项监控
@Component
public class StartupMonitor {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(StartupMonitor.class);
private long appStartTime;
private Map<String, Long> phaseTimestamps = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@EventListener
public void handleApplicationStarting(ApplicationStartingEvent event) {
appStartTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
phaseTimestamps.put("starting", appStartTime);
logger.info("应用开始启动: {}", appStartTime);
}
@EventListener
public void handleEnvironmentPrepared(ApplicationEnvironmentPreparedEvent event) {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
phaseTimestamps.put("environmentPrepared", time);
logger.info("环境准备完成, 耗时: {}ms", time - appStartTime);
// 记录环境配置信息
Environment env = event.getEnvironment();
logger.info("Active Profiles: {}", Arrays.toString(env.getActiveProfiles()));
logger.info("Config Locations: {}", env.getProperty("spring.config.location", "default"));
}
@EventListener
public void handleContextPrepared(ApplicationPreparedEvent event) {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
phaseTimestamps.put("contextPrepared", time);
logger.info("上下文准备完成, 总耗时: {}ms", time - appStartTime);
// 记录Bean定义数量
ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory = event.getApplicationContext().getBeanFactory();
int beanDefinitionCount = beanFactory.getBeanDefinitionCount();
logger.info("Bean定义数量: {}", beanDefinitionCount);
}
@EventListener
public void handleContextRefreshed(ContextRefreshedEvent event) {
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
phaseTimestamps.put("contextRefreshed", time);
ApplicationContext context = event.getApplicationContext();
String[] beanNames = context.getBeanDefinitionNames();
logger.info("容器刷新完成, Bean实例化数量: {}, 总耗时: {}ms",
beanNames.length, time - appStartTime);
// 分析Bean依赖关系
analyzeBeanDependencies(context, beanNames);
// 识别慢加载Bean
identifySlowLoadingBeans();
// 记录启动性能指标
recordStartupMetrics();
}
@EventListener
public void handleApplicationReady(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
long totalTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - appStartTime;
logger.info("应用启动完成, 总耗时: {}ms", totalTime);
// 发布启动性能报告
publishStartupReport(totalTime);
}
private void analyzeBeanDependencies(ApplicationContext context, String[] beanNames) {
logger.info("=== Bean依赖分析 ===");
for (String beanName : beanNames) {
if (beanName.contains("Service") || beanName.contains("Controller")) {
BeanDefinition bd = ((DefaultListableBeanFactory)
context.getAutowireCapableBeanFactory()).getBeanDefinition(beanName);
if (bd.hasAttribute("dependsOn")) {
String[] dependsOn = (String[]) bd.getAttribute("dependsOn");
logger.info("Bean {} 依赖: {}", beanName, Arrays.toString(dependsOn));
}
}
}
}
private void identifySlowLoadingBeans() {
logger.info("=== 慢加载Bean识别 ===");
phaseTimestamps.entrySet().stream()
.filter(entry -> entry.getValue().getMaxTime() > 500) // 超过500ms
.sorted((e1, e2) -> Long.compare(e2.getValue().getMaxTime(),
e1.getValue().getMaxTime()))
.forEach(entry -> {
logger.warn("慢加载Bean: {}, 最大耗时: {}ms",
entry.getKey(), entry.getValue().getMaxTime());
});
}
private void recordStartupMetrics() {
// 记录到Micrometer指标
Metrics.gauge("application.startup.duration",
System.currentTimeMillis() - appStartTime);
Metrics.gauge("application.beans.count",
phaseTimestamps.size());
}
private void publishStartupReport(long totalTime) {
logger.info("=== Spring Boot启动性能报告 ===");
logger.info("总启动时间: {}ms", totalTime);
phaseTimestamps.entrySet().stream()
.sorted(Map.Entry.comparingByValue())
.forEach(entry -> {
logger.info("阶段 {}: {}ms", entry.getKey(), entry.getValue() - appStartTime);
});
}
}
# Bean加载性能监控
@Component
public class BeanLoadingMonitor implements BeanPostProcessor {
private final Map<String, Long> beanCreationStartTimes = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
private final Map<String, BeanMetrics> beanMetrics = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
beanCreationStartTimes.put(beanName, System.currentTimeMillis());
return bean;
}
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
Long startTime = beanCreationStartTimes.remove(beanName);
if (startTime != null) {
long duration = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
BeanMetrics metrics = beanMetrics.computeIfAbsent(beanName,
k -> new BeanMetrics(bean.getClass().getSimpleName()));
metrics.recordCreation(duration);
if (duration > 100) { // 超过100ms记录警告
logger.warn("Bean [{}] 初始化耗时较长: {}ms", beanName, duration);
}
}
return bean;
}
@EventListener
public void handleApplicationReady(ApplicationReadyEvent event) {
// 启动完成后输出Bean加载性能报告
logger.info("=== Bean加载性能报告 ===");
beanMetrics.entrySet().stream()
.sorted((e1, e2) -> Long.compare(e2.getValue().getMaxTime(), e1.getValue().getMaxTime()))
.limit(10) // 只显示最慢的10个Bean
.forEach(entry -> {
BeanMetrics metrics = entry.getValue();
logger.info("Bean [{}]: 最大耗时={}ms, 平均耗时={}ms",
entry.getKey(), metrics.getMaxTime(), metrics.getAverageTime());
});
}
static class BeanMetrics {
private final String className;
private long totalTime;
private long maxTime;
private int count;
BeanMetrics(String className) {
this.className = className;
}
void recordCreation(long duration) {
totalTime += duration;
maxTime = Math.max(maxTime, duration);
count++;
}
long getAverageTime() {
return count > 0 ? totalTime / count : 0;
}
long getMaxTime() {
return maxTime;
}
}
}
# 配置类加载监控
@Component
public class ConfigurationLoadMonitor implements BeanFactoryPostProcessor {
@Override
public void postProcessBeanFactory(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory) throws BeansException {
if (beanFactory instanceof DefaultListableBeanFactory) {
DefaultListableBeanFactory dlbf = (DefaultListableBeanFactory) beanFactory;
// 监控配置类解析
dlbf.addBeanPostProcessor(new BeanPostProcessor() {
@Override
public Object postProcessBeforeInitialization(Object bean, String beanName) {
if (beanName != null && beanName.endsWith("Configuration")) {
logger.debug("配置类加载: {}", beanName);
}
return bean;
}
});
}
}
}
# JVM级别监控配置
# application-monitor.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: health,info,metrics,prometheus,startup
endpoint:
metrics:
enabled: true
prometheus:
enabled: true
metrics:
export:
prometheus:
enabled: true
enable:
jvm: true
system: true
logback: true
tracing:
sampling:
probability: 1.0
# JVM监控配置
server:
port: 8080
spring:
application:
name: my-monitored-app
# 自定义健康检查与指标
@Component
public class ApplicationHealthIndicator implements HealthIndicator {
@Override
public Health health() {
// 检查应用健康状态
boolean isHealthy = checkApplicationHealth();
if (isHealthy) {
return Health.up()
.withDetail("启动时间", ManagementFactory.getRuntimeMXBean().getUptime() + "ms")
.withDetail("内存使用", getMemoryUsage())
.build();
} else {
return Health.down()
.withDetail("错误原因", "应用运行异常")
.build();
}
}
private String getMemoryUsage() {
Runtime runtime = Runtime.getRuntime();
long usedMemory = runtime.totalMemory() - runtime.freeMemory();
long maxMemory = runtime.maxMemory();
return String.format("%.2fMB/%.2fMB",
usedMemory / 1024.0 / 1024.0, maxMemory / 1024.0 / 1024.0);
}
}
@Component
public class CustomMetrics {
private final MeterRegistry meterRegistry;
private final Counter beanCreationCounter;
private final Timer startupTimer;
public CustomMetrics(MeterRegistry meterRegistry) {
this.meterRegistry = meterRegistry;
this.beanCreationCounter = Counter.builder("application.beans.created")
.description("应用创建的Bean数量")
.register(meterRegistry);
this.startupTimer = Timer.builder("application.startup.time")
.description("应用启动时间")
.register(meterRegistry);
}
public void recordBeanCreation() {
beanCreationCounter.increment();
}
public void recordStartupTime(long duration) {
startupTimer.record(duration, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
}
# 日志监控配置
<!-- logback-spring.xml -->
<configuration>
<appender name="JSON" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<encoder class="net.logstash.logback.encoder.LogstashEncoder">
<customFields>{"application":"${spring.application.name}"}</customFields>
</encoder>
</appender>
<appender name="METRICS" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<file>logs/metrics.log</file>
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss} - %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
<rollingPolicy class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.TimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<fileNamePattern>logs/metrics.%d{yyyy-MM-dd}.log</fileNamePattern>
</rollingPolicy>
</appender>
<logger name="com.example.monitor" level="DEBUG" additivity="false">
<appender-ref ref="METRICS" />
<appender-ref ref="JSON" />
</logger>
<root level="INFO">
<appender-ref ref="JSON" />
</root>
</configuration>
# Grafana监控面板配置
{
"title": "Spring Boot应用监控",
"panels": [
{
"title": "启动时间监控",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "application_startup_time_seconds",
"legendFormat": "启动耗时"
}
],
"type": "stat"
},
{
"title": "Bean加载性能",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "rate(application_beans_created_total[5m])",
"legendFormat": "Bean创建速率"
}
],
"type": "graph"
},
{
"title": "JVM内存使用",
"targets": [
{
"expr": "jvm_memory_used_bytes{area=\"heap\"}",
"legendFormat": "堆内存"
}
],
"type": "graph"
}
]
}
# 4. 使用springboot开发应用
# 4.0 项目技巧
# include
application.yml
application-datasource.yml
spring:
profiles:
#split into multiple profile files
include: datasource
# multiple env: dev prod
application.properties
spring.profiles.active:@spring.profiles.active@
application-dev.yml
application-prod.yml
mvn spring-boot:run -Dspring.profiles.active=dev
mvn clean install -Dspring.profiles.active=dev
~pom.xml(不需要)~
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>dev</id>
<properties>
<myActiveProfile>dev</myActiveProfile>
</properties>
</profile>
<profile>
<id>prod</id>
<properties>
<myActiveProfile>prod</myActiveProfile>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
# 4.1 业务开发
# 4.1.1 使用starter
# POM depenedency
spring boot官方提供了很多现成的starter,可以直接引用其depdendency使用比如 starters (opens new window)
spring-boot-starter | Core starter, including auto-configuration support, logging and YAML |
|---|---|
| spring-boot-starter-web | Starter for building web, including RESTful, applications using Spring MVC. Uses Tomcat as the default embedded container |
| spring-boot-starter-jdbc | Starter for using JDBC with the HikariCP connection pool |
但是问题是引用时需要加版本号,很多starter之间以及跟其他的dependency之间可能有版本依赖冲突, 所以官方推荐使用parent方式或者import方式引入某个版本的spring-boot-starter-parent,因为这个parent里面已经定义好了各个版本号, 所以在引用比如spring-boot-starter-web的时候就不需要添加版本号了
<!-- Inherit defaults from Spring Boot -->
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.2.6.RELEASE</version>
</parent>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<!--The spring-boot-starter-parent POM includes <executions> configuration to bind the repackage goal.-->
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
<!-- Dependence Override
full list: https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/v2.2.6.RELEASE/spring-boot-project/spring-boot-dependencies/pom.xml
-->
<properties>
<spring-data-releasetrain.version>Fowler-SR2</spring-data-releasetrain.version>
</properties>
# Configuration
默认是 application.properties,也可以使用yaml
都在这里:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/appendix-application-properties.html
另外一种稍微硬核的通过查阅代码获取的方式:
所有的配置都可以在 spring-boot-autoconfigure里面找到,比如
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.data.redis/RedisProperties
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "spring.redis")
public class RedisProperties {
/**
* Database index used by the connection factory.
*/
private int database = 0;
/**
* Connection URL. Overrides host, port, and password. User is ignored. Example:
* redis://user:[email protected]:6379
*/
private String url;
/**
* Redis server host.
*/
private String host = "localhost";
/**
* Login password of the redis server.
*/
private String password;
/**
* Redis server port.
*/
private int port = 6379;
/**
* Whether to enable SSL support.
*/
private boolean ssl;
/**
* Connection timeout.
*/
private Duration timeout;
private Sentinel sentinel;
private Cluster cluster;
private final Jedis jedis = new Jedis();
private final Lettuce lettuce = new Lettuce();
public int getDatabase() {
return this.database;
}
public void setDatabase(int database) {
this.database = database;
}
public String getUrl() {
return this.url;
}
public void setUrl(String url) {
this.url = url;
}
public String getHost() {
return this.host;
}
public void setHost(String host) {
this.host = host;
}
public String getPassword() {
return this.password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public int getPort() {
return this.port;
}
public void setPort(int port) {
this.port = port;
}
public boolean isSsl() {
return this.ssl;
}
public void setSsl(boolean ssl) {
this.ssl = ssl;
}
public void setTimeout(Duration timeout) {
this.timeout = timeout;
}
public Duration getTimeout() {
return this.timeout;
}
public Sentinel getSentinel() {
return this.sentinel;
}
public void setSentinel(Sentinel sentinel) {
this.sentinel = sentinel;
}
public Cluster getCluster() {
return this.cluster;
}
public void setCluster(Cluster cluster) {
this.cluster = cluster;
}
public Jedis getJedis() {
return this.jedis;
}
public Lettuce getLettuce() {
return this.lettuce;
}
/**
* Pool properties.
*/
public static class Pool {
/**
* Maximum number of "idle" connections in the pool. Use a negative value to
* indicate an unlimited number of idle connections.
*/
private int maxIdle = 8;
/**
* Target for the minimum number of idle connections to maintain in the pool. This
* setting only has an effect if it is positive.
*/
private int minIdle = 0;
/**
* Maximum number of connections that can be allocated by the pool at a given
* time. Use a negative value for no limit.
*/
private int maxActive = 8;
/**
* Maximum amount of time a connection allocation should block before throwing an
* exception when the pool is exhausted. Use a negative value to block
* indefinitely.
*/
private Duration maxWait = Duration.ofMillis(-1);
public int getMaxIdle() {
return this.maxIdle;
}
public void setMaxIdle(int maxIdle) {
this.maxIdle = maxIdle;
}
public int getMinIdle() {
return this.minIdle;
}
public void setMinIdle(int minIdle) {
this.minIdle = minIdle;
}
public int getMaxActive() {
return this.maxActive;
}
public void setMaxActive(int maxActive) {
this.maxActive = maxActive;
}
public Duration getMaxWait() {
return this.maxWait;
}
public void setMaxWait(Duration maxWait) {
this.maxWait = maxWait;
}
}
/**
* Cluster properties.
*/
public static class Cluster {
/**
* Comma-separated list of "host:port" pairs to bootstrap from. This represents an
* "initial" list of cluster nodes and is required to have at least one entry.
*/
private List<String> nodes;
/**
* Maximum number of redirects to follow when executing commands across the
* cluster.
*/
private Integer maxRedirects;
public List<String> getNodes() {
return this.nodes;
}
public void setNodes(List<String> nodes) {
this.nodes = nodes;
}
public Integer getMaxRedirects() {
return this.maxRedirects;
}
public void setMaxRedirects(Integer maxRedirects) {
this.maxRedirects = maxRedirects;
}
}
..........
/**
* Lettuce client properties.
*/
public static class Lettuce {
/**
* Shutdown timeout.
*/
private Duration shutdownTimeout = Duration.ofMillis(100);
/**
* Lettuce pool configuration.
*/
private Pool pool;
public Duration getShutdownTimeout() {
return this.shutdownTimeout;
}
public void setShutdownTimeout(Duration shutdownTimeout) {
this.shutdownTimeout = shutdownTimeout;
}
public Pool getPool() {
return this.pool;
}
public void setPool(Pool pool) {
this.pool = pool;
}
}
}
可以看到前缀是 spring.redis ,具体配置举例:
其中最简单的string类型
spring.redis.host=x.x.x.48 spring.redis.port=6379复杂类型如private Cluster cluster,很简单,进去看Cluster的成员即可,只是注意maxRedirects在application.properties写作:
spring.redis.cluster.nodes=x.x.x.48:6379,x.x.x.48:6380,x.x.x.48:6381,x.x.x.49:6379,x.x.x.49:6380,x.x.x.49:6381,x.x.x.50:6379,x.x.x.50:6380,x.x.x.50:6381 spring.redis.cluster.max-redirects=3使用yaml
spring: #Redis缓存配置(RedisProperties) redis: # database: 0 # host: localhost # port: 6380 # password: #timeout: 6000 #redis cluster cluster: nodes: 1.1.1.1:6379,1.1.1.1:6380,1.1.1.1:6381 maxRedirects: 3 lettuce: pool: max-active: 200 max-wait: 3000 max-idle: -1 min-idle: 10
# 案例分析:
某次项目使用 spring-boot-starter版本为2.0.5
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.0.5.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath />
</parent>
使用其 spring-boot-starter-data-redis 遇到RedisExcpetion 后来没能重现,不过也能重现出类似的WARN级别信息:
l.c.c.t.ClusterTopologyRefresh^[[m : Unable to connect to xxxx:6379
java.util.concurrent.CompletionException: io.netty.channel.ConnectTimeoutException: connection timed out: /xxxx:6379
经过查阅,client端的RedisConnectionFactory需要增加 ClusterTopologyRefreshOptions 这个option,
@Autowired
private RedisProperties redisProperties;
@Value("${redis.maxRedirects:3}")
private int maxRedirects;
@Value("${redis.refreshTime:5}")
private int refreshTime;
@Bean
public LettuceConnectionFactory redisConnectionFactory() {
RedisClusterConfiguration redisClusterConfiguration = new RedisClusterConfiguration(redisProperties.getCluster().getNodes());
redisClusterConfiguration.setMaxRedirects(maxRedirects);
/ / Support adaptive cluster topology refresh and static refresh source
ClusterTopologyRefreshOptions clusterTopologyRefreshOptions = ClusterTopologyRefreshOptions.builder()
.enablePeriodicRefresh()
.enableAllAdaptiveRefreshTriggers()
.refreshPeriod(Duration.ofSeconds(refreshTime))
.build();
ClusterClientOptions clusterClientOptions = ClusterClientOptions.builder()
.topologyRefreshOptions(clusterTopologyRefreshOptions).build();
/ / From the priority, read and write separation, read from the possible inconsistency, the final consistency CP
LettuceClientConfiguration lettuceClientConfiguration = LettuceClientConfiguration.builder()
.readFrom(ReadFrom.SLAVE_PREFERRED)
.clientOptions(clusterClientOptions).build();
return new LettuceConnectionFactory(redisClusterConfiguration, lettuceClientConfiguration);
}
而实际上为什么这个不提供配置呢,查阅了前面说的官方配置:
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/appendix-application-properties.html
发现实际有这个选项
spring.redis.lettuce.cluster.refresh.dynamic-refresh-sources
spring.redis.lettuce.cluster.refresh.period
而进一步看到第一个config是在spring boot 2.4.0引入的
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.4.0-Configuration-Changelog
而第二个period是2.3.0
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/wiki/Spring-Boot-2.3.0-Configuration-Changelog
直接搜源码 ClusterTopologyRefreshOptions 确认下:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/blob/47516b50c39bd6ea924a1f6720ce6d4a71088651/spring-boot-project/spring-boot-autoconfigure/src/main/java/org/springframework/boot/autoconfigure/data/redis/LettuceConnectionConfiguration.java
点击blame,找到这行
if (refreshProperties.getPeriod() != null) {
refreshBuilder.enablePeriodicRefresh(refreshProperties.getPeriod());
}
点击左侧对应的提交:
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/commit/dfac3a282b98bd480c5acf778dbfbce994051dad
可以看到这次提交的comment:Add configuration to enable Redis Cluster topology refresh
然后从左上角可以看到是从 v2.3.0.M4 (opens new window) 最开始引入的,之后是 v2.3.0.RC1,v2.3.0.RELEASE,直到最新的v2.5.0-RC1
REFERENCE:
https://github.com/javastacks/spring-boot-best-practice https://github.com/YunaiV/SpringBoot-Labs
给你一份超详细 Spring Boot 知识清单 (opens new window)
About AutoConfig (opens new window) Gradually Replacing Auto-configuration Disabling Specific Auto-configuration Classes (exclude={DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class})
spring boot 中的 Parent POM 和 Starter 的作用什么 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1362790
EnvironmentPostProcessor BeanPostProcessor
# 4.1.2 springboot mvc
so by default, tomcat will create some temp folder under /tmp and use it later on
spring.servlet.multipart.location (opens new window)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50523407/the-temporary-upload-location-tmp-tomcat-4296537502689403143-5000-work-tomcat/50523578
# 4.2 框架开发(starter)
ConfigurationProperties和EnableConfigurationProperties是一对, 前者定义对应配置文件的属性,后者是激活读取; 同样, Configuration或AutoConfiguration跟EnableAutoConfiguration是一对, 前者相当于component就是定义为bean,而后者是激活这个自动配置/装配(具体参考springboot源码分析一文),
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/1.3.8.RELEASE/reference/html/using-boot-auto-configuration.html
Create a Custom Auto-Configuration with Spring Boot
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-custom-auto-configuration
创建一个starter hello-spring-boot-starter
写一个服务类
public class HelloService {
private String msg;
public String sayHello() {
return "hello " + msg;
}
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
@ConfigurationProperties(prefix = "hello") //获取属性值
public class HelloProperties {
private static final String MSG = "world";
private String msg = MSG ;
public String getMsg() {
return msg;
}
public void setMsg(String msg) {
this.msg = msg;
}
}
@Configuration
//为带有@ConfigurationProperties注解的Bean提供有效的支持。
// 这个注解可以提供一种方便的方式来将带有@ConfigurationProperties注解的类注入为Spring容器的Bean。
@EnableConfigurationProperties(HelloProperties.class)//开启属性注入,通过@autowired注入
@ConditionalOnClass(Hello.class)//判断这个类是否在classpath中存在,如果存在,才会实例化一个Bean
// The Hello bean will be created if the hello.enable property exists and has a value other than false
// or the property doesn't exist at all.
@ConditionalOnProperty(prefix="hello", value="enabled", matchIfMissing = true)
public class HelloAutoConfiguration {
@Autowired
private HelloProperties helloProperties;
@Bean
@ConditionalOnMissingBean(Hello.class)//容器中如果没有Hello这个类,那么自动配置这个Hello
public HelloService hello() {
HelloService hello = new HelloService();
hello.setMsg(helloProperties.getMsg());
return hello;
}
}
application.properties
\#可以不配置
hello.enabled=true
hello.msg=charmingfst
\#以debug模式运行
debug=true
\src\main\resources\META-INF\spring.factories
org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.EnableAutoConfiguration=\
com.chm.test.HelloAutoConfiguration
https://blog.csdn.net/zxc123e/article/details/80222967
# 4.3 AOP切面编程
Aspect(切面)横切关注点的模块化 @Aspect注解的类
Join Point(连接点)程序执行过程中的点 方法调用、异常抛出
Pointcut(切点)匹配连接点的表达式 execution(* UserService.*(..))
Advice(通知)在连接点执行的动作 @Before, @After, @Around
Target(目标)被代理的对象 UserService实例
Proxy(代理)AOP创建的包装对象 CGLIB或JDK动态代理
Weaving(织入)将切面应用到目标对象的过程 编译期、类加载期、运行期
# 什么是AOP
传统OOP的问题:
// 业务类中混杂着横切关注点
public class UserService {
public void createUser(User user) {
// 事务开始
Transaction tx = beginTransaction();
try {
// 权限检查
checkPermission();
// 日志记录
log.info("创建用户: {}", user.getName());
// 业务逻辑
userDao.save(user);
// 事务提交
tx.commit();
} catch (Exception e) {
// 事务回滚
tx.rollback();
// 错误日志
log.error("创建用户失败", e);
throw e;
}
}
}
AOP解决方案:
// 纯净的业务逻辑
public class UserService {
public void createUser(User user) {
userDao.save(user); // 只关注业务逻辑
}
}
// 横切关注点通过AOP处理
@Aspect
@Component
public class TransactionAspect {
@Around("execution(* UserService.*(..))")
public Object manageTransaction(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) {
// 事务管理逻辑在这里统一处理
}
}
# Spring AOP实现机制-spring-boot-starter-aop
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-aop</artifactId>
</dependency>
// 对于每个Bean:
1. Bean正常实例化、依赖注入、初始化
2. AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator.postProcessAfterInitialization()被调用
3. 检查Bean是否需要AOP代理
4. 如果需要,创建JDK动态代理或CGLIB代理
5. 返回代理对象(替代原始Bean)
// Spring框架真实的AOP代理创建类结构:
Object
└── BeanPostProcessor (接口)
└── InstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor (接口)
└── SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor (接口)
└── AbstractAutoProxyCreator (抽象类) ← 核心实现
└── AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator (抽象类)
└── AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator (具体类) ← 实际工作的类!
这是Spring AOP的核心引擎
// 真实的Spring源码(简化版)
public abstract class AbstractAutoProxyCreator extends ProxyProcessorSupport
implements SmartInstantiationAwareBeanPostProcessor {
// 核心方法:在Bean初始化后创建代理
@Override
public Object postProcessAfterInitialization(@Nullable Object bean, String beanName) {
if (bean != null) {
Object cacheKey = getCacheKey(bean.getClass(), beanName);
// 检查是否已经处理过(避免循环)
if (!this.earlyProxyReferences.contains(cacheKey)) {
// 包装Bean(如果需要代理)
return wrapIfNecessary(bean, beanName, cacheKey);
}
}
return bean;
}
// 核心方法:决定是否创建代理
protected Object wrapIfNecessary(Object bean, String beanName, Object cacheKey) {
// 1. 检查是否应该跳过代理
if (isInfrastructureClass(bean.getClass()) || shouldSkip(bean, beanName)) {
return bean;
}
// 2. 获取适用的Advisors(切面逻辑)
Object[] specificInterceptors = getAdvicesAndAdvisorsForBean(bean.getClass(), beanName, null);
// 3. 如果需要代理,创建代理对象
if (specificInterceptors != DO_NOT_PROXY) {
this.advisedBeans.put(cacheKey, Boolean.TRUE);
return createProxy(bean.getClass(), beanName, specificInterceptors, new SingletonTargetSource(bean));
}
return bean;
}
}
这是Spring Boot默认使用的具体实现
// 真实的Spring Boot AOP处理器
public class AnnotationAwareAspectJAutoProxyCreator extends AspectJAwareAdvisorAutoProxyCreator {
// 重写方法:支持@AspectJ注解风格的切面
@Override
protected List<Advisor> findCandidateAdvisors() {
// 调用父类方法查找基于配置的Advisor
List<Advisor> advisors = super.findCandidateAdvisors();
// 添加基于@Aspect注解的Advisor
if (this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder != null) {
advisors.addAll(this.aspectJAdvisorsBuilder.buildAspectJAdvisors());
}
return advisors;
}
// 重写方法:支持JDK动态代理和CGLIB代理
@Override
protected boolean shouldProxyTargetClass(ConfigurableListableBeanFactory beanFactory, String beanName) {
// 检查@EnableAspectJAutoProxy配置
return (this.beanFactory != null &&
this.beanFactory.getBeanDefinition(beanName).isProxyTargetClass());
}
}
# 示例1:性能监控AOP
@Aspect
@Component
public class PerformanceMonitoringAspect {
private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(PerformanceMonitoringAspect.class);
// 监控Service层方法性能
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*.*(..))")
public Object monitorPerformance(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) throws Throwable {
String methodName = joinPoint.getSignature().getName();
String className = joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName();
long startTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
try {
// 执行原始方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
// 记录性能指标
if (executionTime > 100) { // 超过100ms记录警告
logger.warn("方法执行缓慢: {}.{}, 耗时: {}ms",
className, methodName, executionTime);
}
// 记录到监控系统
Metrics.timer("service.method.duration")
.tag("class", className)
.tag("method", methodName)
.record(executionTime, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
long executionTime = System.currentTimeMillis() - startTime;
logger.error("方法执行异常: {}.{}, 耗时: {}ms",
className, methodName, executionTime, e);
throw e;
}
}
}
# 示例2:事务管理AOP
@Aspect
@Component
public class TransactionAspect {
@Autowired
private PlatformTransactionManager transactionManager;
// 为所有@Transactional方法添加事务管理
@Around("@annotation(transactional)")
public Object manageTransaction(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,
Transactional transactional) throws Throwable {
TransactionDefinition definition = new DefaultTransactionDefinition();
TransactionStatus status = transactionManager.getTransaction(definition);
try {
logger.debug("开始事务: {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
// 执行业务方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 提交事务
transactionManager.commit(status);
logger.debug("提交事务: {}", joinPoint.getSignature());
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
// 回滚事务
transactionManager.rollback(status);
logger.debug("回滚事务: {}, 原因: {}", joinPoint.getSignature(), e.getMessage());
throw e;
}
}
// 使用示例
@Service
public class UserService {
@Transactional
public void createUser(User user) {
// 业务逻辑,自动享有事务管理
userRepository.save(user);
userAuditRepository.logCreation(user);
}
}
}
# 示例3:缓存AOP
@Aspect
@Component
public class CacheAspect {
@Autowired
private CacheManager cacheManager;
// 方法缓存
@Around("@annotation(cacheable)")
public Object handleCacheable(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,
Cacheable cacheable) throws Throwable {
String cacheName = cacheable.value();
String key = generateCacheKey(joinPoint);
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
ValueWrapper cachedValue = cache.get(key);
if (cachedValue != null) {
logger.debug("缓存命中: {}.{}",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
return cachedValue.get();
}
// 缓存未命中,执行方法
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
// 缓存结果
cache.put(key, result);
logger.debug("缓存设置: {}.{}",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
return result;
}
// 缓存失效
@After("@annotation(cacheEvict)")
public void handleCacheEvict(JoinPoint joinPoint, CacheEvict cacheEvict) {
String cacheName = cacheEvict.value();
Cache cache = cacheManager.getCache(cacheName);
if (cacheEvict.allEntries()) {
cache.clear(); // 清空整个缓存
} else {
String key = generateCacheKey(joinPoint);
cache.evict(key); // 清除特定key
}
}
private String generateCacheKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint) {
// 基于方法签名和参数生成缓存key
return joinPoint.getSignature().toShortString() +
Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs());
}
}
# 示例4:安全权限AOP
@Aspect
@Component
public class SecurityAspect {
@Autowired
private AuthenticationService authService;
// 方法级权限控制
@Around("@annotation(requiresPermission)")
public Object checkPermission(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint,
RequiresPermission requiresPermission) throws Throwable {
String permission = requiresPermission.value();
User currentUser = authService.getCurrentUser();
if (!authService.hasPermission(currentUser, permission)) {
throw new AccessDeniedException(
"用户 " + currentUser.getUsername() + " 没有权限: " + permission);
}
logger.info("权限检查通过: {} 执行 {}.{}",
currentUser.getUsername(),
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
return joinPoint.proceed();
}
// 参数级权限控制
@Before("execution(* delete*(..)) && args(id,..)")
public void checkDeletePermission(JoinPoint joinPoint, Long id) {
User currentUser = authService.getCurrentUser();
if (!authService.canDelete(currentUser, id)) {
throw new AccessDeniedException("无权删除资源: " + id);
}
}
}
# 示例5:日志记录AOP
@Aspect
@Component
public class LoggingAspect {
// 方法调用日志
@Before("execution(* com.example.controller.*.*(..))")
public void logMethodEntry(JoinPoint joinPoint) {
logger.info("→ 进入方法: {}.{}",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("方法参数: {}", Arrays.toString(joinPoint.getArgs()));
}
}
// 方法退出日志
@AfterReturning(pointcut = "execution(* com.example.controller.*.*(..))",
returning = "result")
public void logMethodExit(JoinPoint joinPoint, Object result) {
logger.info("← 退出方法: {}.{}",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName());
if (logger.isDebugEnabled() && result != null) {
logger.debug("方法返回值: {}", result.toString());
}
}
// 异常日志
@AfterThrowing(pointcut = "execution(* com.example..*.*(..))",
throwing = "ex")
public void logException(JoinPoint joinPoint, Exception ex) {
logger.error("✗ 方法执行异常: {}.{}",
joinPoint.getTarget().getClass().getSimpleName(),
joinPoint.getSignature().getName(), ex);
}
}
# AOP最佳实践
- 切点表达式优化
@Aspect
@Component
public class OptimizedPointcutAspect {
// 不好的写法:过于宽泛
// @Around("execution(* com.example..*(..))")
// 好的写法:精确匹配
@Around("execution(* com.example.service.*Service.*(..))")
public Object serviceLayerMonitoring(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// 只监控Service层
return pjp.proceed();
}
// 使用注解驱动更精确
@Around("@annotation(com.example.annotation.Monitored)")
public Object monitoredMethods(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// 只监控有@Monitored注解的方法
return pjp.proceed();
}
}
- 性能考虑
@Aspect
@Component
public class PerformanceOptimizedAspect {
// 避免在切面中执行耗时操作
@Around("execution(* com.example..*(..))")
public Object optimizedAdvice(ProceedingJoinPoint pjp) throws Throwable {
// 不好的做法:每次都生成复杂日志
// String detailedLog = createDetailedLog(pjp); // 耗时操作
// 好的做法:延迟计算
if (logger.isDebugEnabled()) {
logger.debug("执行方法: {}", pjp.getSignature());
}
return pjp.proceed();
}
}
# 5. Spring Boot启动优化
启动性能监控和分析
使用Spring Boot Actuator监控启动时间
# application.yml
management:
endpoints:
web:
exposure:
include: startup
endpoint:
startup:
enabled: true
spring:
application:
name: myapp
// 启动时间监控端点
@RestController
public class StartupMetricsController {
@Autowired
private ApplicationStartup startup;
@GetMapping("/startup-metrics")
public StartupMetrics getStartupMetrics() {
return startup.getMetrics();
}
}
// 启动时间分析结果示例
public class StartupAnalysis {
public void analyzeStartupTime() {
System.out.println("启动阶段耗时分析:");
System.out.println("JVM启动: 0.8秒");
System.out.println("组件扫描: 4.2秒 (51%) ← 优化重点!");
System.out.println("Bean实例化: 2.1秒 (26%)");
System.out.println("自动配置: 1.1秒 (13%)");
System.out.println("服务器启动: 0.3秒 (4%)");
System.out.println("总启动时间: 8.5秒");
}
}
使用JVM参数优化启动性能
# 优化启动速度的JVM参数
java -jar myapp.jar \
-Xms512m -Xmx512m \ # 固定堆大小,避免动态调整
-XX:+UseG1GC \ # 使用G1垃圾回收器
-XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=200 \ # 控制GC停顿时间
-noverify \ # 关闭字节码验证(开发环境)
-Dspring.jmx.enabled=false \ # 关闭JMX监控
-Dspring.main.lazy-initialization=true \ # 启用懒加载
-Dspring.context.index.enabled=true # 启用类路径索引
案例1:减少组件扫描范围
优化前(扫描整个包路径):
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan("com.example") // 扫描整个项目包
public class MyApplication {
// 启动时间: 8.2秒(扫描2000个类)
}
优化后(精确扫描必要包):
@SpringBootApplication
@ComponentScan({
"com.example.controller",
"com.example.service",
"com.example.config"
// 不扫描: com.example.entity, com.example.dto等
})
public class MyApplication {
// 启动时间: 3.1秒(只扫描500个类)
}
案例2:使用懒加载优化
优化前(所有Bean立即加载):
@Service
public class HeavyService {
// 启动时立即初始化,耗时2秒
public HeavyService() {
loadLargeDataSet(); // 耗时的初始化操作
}
}
优化后(按需懒加载):
@Service
@Lazy // 添加懒加载注解
public class HeavyService {
// 第一次使用时才初始化
public HeavyService() {
loadLargeDataSet();
}
}
@RestController
public class MyController {
@Autowired
private HeavyService heavyService; // 启动时不初始化
@GetMapping("/data")
public Data getData() {
// 第一次调用时才初始化HeavyService
return heavyService.processData();
}
}
案例3:排除不必要的自动配置
优化前(加载所有自动配置):
@SpringBootApplication // 默认加载100+个自动配置
public class MyApplication {
// 启动时间: 6.5秒
}
优化后(排除不需要的配置):
@SpringBootApplication(exclude = {
DataSourceAutoConfiguration.class, // 不使用数据库
SecurityAutoConfiguration.class, // 不需要安全配置
MailSenderAutoConfiguration.class, // 不需要邮件发送
CacheAutoConfiguration.class // 不使用缓存
})
public class MyApplication {
// 启动时间: 3.8秒
}
案例4:类路径索引优化
优化前(类路径扫描):
// Maven依赖包含大量不需要的jar
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-jpa</artifactId> <!-- 不用数据库 -->
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-security</artifactId> <!-- 不用安全 -->
</dependency>
</dependencies>
优化后(精简依赖):
// 只引入必要的starter
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<!-- 移除不必要的starter -->
</dependencies>
// 添加类路径索引(Spring 5.2+)
spring:
context:
index:
enabled: true # 启用编译时类路径索引
案例5:使用Spring Fu进行函数式配置
传统配置方式:
@Configuration
public class TraditionalConfig {
@Bean
public MyService myService() {
return new MyService(); // 反射创建,性能一般
}
}
函数式配置(Spring Fu):
public class FunctionalConfig {
public static void main(String[] args) {
var app = new SpringApplication(Application.class)
.run(args);
// 函数式注册Bean,避免反射开销
app.addInitializer((context) -> {
context.registerBean(MyService.class,
() -> new MyService()); // 直接lambda创建
});
}
}
案例6:编译时处理优化
使用Micronaut或Quarkus的编译时处理:
// Quarkus示例:编译时处理依赖注入
@ApplicationScoped
public class MyService {
@Inject
MyRepository repository; // 编译时生成注入代码,避免运行时反射
}
# 6. Troubleshooting
# BeanDefinitionOverrideException
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-bean-definition-override-exception
# BeanCurrentlyInCreationException/circular reference
Caused by: org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanCurrentlyInCreationException: Error creating bean with name 'AAAA': Bean with name 'AAAA' has been injected into other beans [BBBB] in its raw version as part of a circular reference, but has eventually been wrapped. This means that said other beans do not use the final version of the bean. This is often the result of over-eager type matching - consider using 'getBeanNamesForType' with the 'allowEagerInit' flag turned off, for example.
解决:加@Lazy
# nohup: ignoring input no main manifest attribute
执行
nohup java -server -jar test.jar > `date +\%F`_funding-rate-datasource_`date +\%H.%M.%S`.log 2>&1
log中内容为:
nohup: ignoring input no main manifest attribute
解决方法,pom增加:
<build>
<finalName>funding-rate-datasource</finalName>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-source-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<attach>true</attach>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<phase>compile</phase>
<goals>
<goal>jar</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
<!-- package -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<fork>true</fork>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<!-- deploy -->
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-deploy-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<skip>true</skip>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
ref:
@bean方法调用的特殊性:
https://www.racecoder.com/archives/787/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27990060/calling-a-bean-annotated-method-in-spring-java-configuration
Spring Boot 2.0 :深入分析Spring Boot原理 (opens new window)
spring boot之自动装配(spring-boot-autoconfigure) https://blog.csdn.net/wangjie5540/article/details/99542777
原创 | 我被面试官给虐懵了,竟然是因为我不懂Spring中的@Configuration https://juejin.im/post/5d005860f265da1b7f297630
https://blog.csdn.net/yiifaa/java/article/details/74852425 https://www.huaweicloud.com/articles/b59be8ffdcfbd1f8a1fe28bffe848d20.html https://www.cnblogs.com/wuchanming/p/5426746.html https://stackoverflow.com/questions/39890849/what-exactly-is-field-injection-and-how-to-avoid-it
https://medium.com/@ilyailin7777/all-dependency-injection-types-spring-336da7baf51b
SpringBoot常见异步编程 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Z-GE_qBtnSgLQTVr9bQYcQ