回目录 《Servlet到底是什么?》
# What is?
servlet and servlet container The servlet container provides the runtime environment for the servlet. The Agent handles the details of network programming, receives and parses requests, transmits responses, and manages connections. The servlet container instantiates the servlets and maintains state. The servlet itself focuses on application logic.
Web/HTTP Server,Application Server, Web/Servlet Container(Servlet Engines)关系和区别?
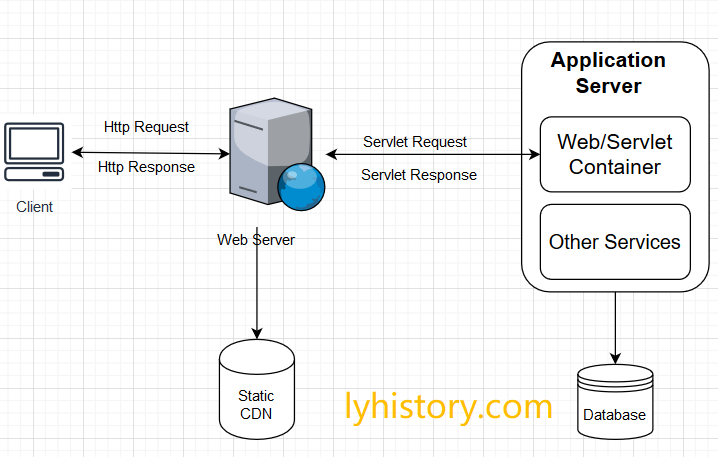
The servlet container is attached to a webserver which listens on HTTP requests on a certain port number, which is usually 80. When a client (user with a web-browser) sends a HTTP request, the servlet container will create new HttpServletRequest and HttpServletResponse objects and pass it through the methods of the already-created Filter and Servlet instances whose URL-pattern matches the request URL, all in the same thread. When the HTTP response is committed and finished, then both the request and response objects will be trashed. https://medium.com/@viveklata/how-web-servers-work-d880cc99b676
Web/HTTP Servers:
- 接收客户端http request,返回http response;
- meant for receiving the user request and identifying the resource to be processed and sending the response to the client; Web servers are responsible for serving static content and interat with servlet for dynamic content;
- Apache and IIS are two popular web servers, Apache is used everywhere including Java world but IIS is more popular in Microsoft ASP .NET world.
Web/Servlet container:
- 接收web server的http servlet request,返回http servlet response;
- only responsible for generating HTML by executing JSP and Servlet on Server side, compiling the servlet using the javac and then executing the class file, The output of the servlet excution would be routed to the Web/HTTP Servers which would send it as a response to the client.
- Apache Tomcat and Jetty are two of the most popular Servlet engine in Java web world.
Application Server:
- 一般就是将Web/Servlet container wrap up作为一个应用程序服务;
- is responsible for serving dynamic content, managing EJB pool, facilitating distributed transaction, facilitating application lookup over JNDI, application security and others;
- From Java EE perspective couple of popular application servers are IBM WebSphere, Oracle WebLogic, Glassfish and Redhat's JBoss.
spring mvc, tomcat, servlet?
Tomcat:The Apache Tomcat software is an open source implementation of the Java Servlet, JavaServer Pages, Java Expression Language and Java WebSocket technologies. SpringMVC:Spring推出的基于Servlet标准的MVC框架实现。 可以看出SpringMVC和Tomcat的结合点是Servlet。其实SpringMVC的DispatchServlet实现了HttpServlet,那么SpringMVC在Tomcat看来,其实就是一个Servlet
Tomcat下Servlet的配置文件:web.xml: web.xml的作用是配置Http和Servlet之间的映射关系、filter、context参数等。这样通过这份约定的配置文件,Tomcat可以把Http请求映射到不同的Servlet实例上。所以,在Servlet时代(structs时代)的web.xml中,会有很多的项配置。 SpringMVC的改变: SpringMVC也是Servlet的实现,只不过SpringMVC增加了一个DispatchServlet,所有的http请求都是映射到这个Servlet上,请求进入到这个Servlet中之后,就算进入到了框架之中了,由这个Servlet来统一的分配http请求到各个Controller
https://blog.csdn.net/achenyuan/article/details/77246395
Tomcat连接器(Connector)是处理请求的主要组件,它负责接收请求,创建Request和Response对象用于和前端进行数据的交换;然后分配线程让Servlet容器来处理这个请求,并把产生的Request和Response对象传给Servlet容器。当Engine处理完请求后,也会通过Connector将结果返回给请求端。即Connector进行请求的调度和控制。 根据协议的不同,可以分为Http Connector和AJP Connector, Tomcat处理连接请求的模式: BIO:阻塞模型 NIO:非阻塞模型 ,好像servlet3.0之后的版本都是采用NIO模式,比如tomcat7应该用的是3.1版本 APR: 高性能,可扩展的模式,Tomcat8版本默认模式 https://www.jianshu.com/p/c4fab2a30c3a
比如spring mvc程序开启,默认tomcat会开启10个线程,如果并发请求大于10个,则创建新线程名字大概是http-nio-(nio就是说当前tomcat的连接模式是非阻塞的),最多限制貌似是200
servlet让客户端和服务器端不仅仅是进行简单的静态资源传输, 它可以实现动态的资源和一些复杂的业务逻辑。
我们使用的spring mvc和后面的springboot,都是基于dispatcherServlet来调用的
Tomcat,Nio和Servlet的一些笔记
https://blog.csdn.net/zzzgd_666/article/details/92078433
servlet filter拦截器
这里稍微扩展下,在关于shiro讲解的一文中也提到有个坑,就是自定义shiro拦截器如果交给spring IOC容器管理,会注册到servlet的filter中,脱离了shiro的控制,从而导致servlet直接过滤掉,不交给shiro处理, shiro对servlet的filter进行了扩展/继承,所以我们实现的shiro拦截器本身也是继承自servlet拦截器,web容器接收到http 请求,转交给servlet,servlet的拦截器生效,filter之后再internal dofilter转交给shiro;
.NET中对应的servlet概念是?
Microsoft® ASP.NET does not provide a direct equivalent to the servlet class.
Instead, there are two basic alternatives.
The first alternative, which is used by the Java Language Conversion Assistant (JLCA), is to encapsulate the functionality of a servlet in the codebehind of a non-graphical ASP.NET page.
The other alternative is to create a new HttpHandler and direct a URL request to a specified class. The HTTPHandler is actually closer to the new Filter functionality in the servlet specification.
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/dotnet/articles/aa478987(v=msdn.10)?redirectedfrom=MSDN
可以看到的是servlet并不只是一个web概念,它在non-graphical的环境一样工作, 比如一个很常见的shiro登录组件也是基于servlet,当然了shiro增加了其他特性比如利用built-in enterprise session management从而还支持非servlet/web环境, 而.NET对应于web环境引入了httphandler,非web环境用了其他的方式;
tomcat vs netty, 既然前面说了tomcat也支持nio,比如现在spring mvc很多默认的tomcat版本就是采用了nio,为什么说基于nio的netty'性能更高?
Netty和Tomcat最大的区别就在于通信协议,Tomcat是基于Http协议的,他的实质是一个基于http协议的web容器,但是Netty不一样,他能通过编程自定义各种协议,因为netty能够通过codec自己来编码/解码字节流,完成类似redis访问的功能,这就是netty和tomcat最大的不同。
有人说netty的性能就一定比tomcat性能高,其实不然,tomcat从6.x开始就支持了nio模式,并且后续还有arp模式——一种通过jni调用apache网络库的模式,相比于旧的bio模式,并发性能得到了很大提高,特别是arp模式,而netty是否比tomcat性能更高,则要取决于netty程序作者的技术实力了。
https://www.cnblogs.com/pangguoming/p/9353536.html
https://www.iteye.com/problems/92400
由此,又产生另外一个问题:tomcat 源码为啥不采用netty 处理并发?
tomcat 内部的connector 是基于JDK NIO处理并发请求的,既然netty 性能稳定性远超JDK NIO,为什么不采用netty代替JDK NIO?
因为servlet规范,tomcat要实现servlet规范所以不能最大发挥NIO的特性,servlet3.0之前完全是同步阻塞模型,在read http body 以及 response的情况下,即使tomcat选择 NIO的 connector也是模拟阻塞的行为,因为servlet规范规定的就是这样。
netty不用遵循servlet规范,可以最大化发挥NIO的特性,性能更高一些。但对于多数业务来讲tomcat的connector已经足够了。
https://www.zhihu.com/question/53498767
具体的NIO参考《java基础》关于IO-BIO-NIO-多路复用部分讲解;
# 基础
JavaWeb——Servlet(全网最详细教程包括Servlet源码分析) (opens new window)
# Servlet生命周期
1,初始化阶段:调用init()方法:
init 方法被设计成只调用一次。它在第一次创建 Servlet 时被调用,在后续每次用户请求时不再调用;
Servlet 创建于用户第一次调用对应于该 Servlet 的 URL 时,但是您也可以指定 Servlet 在服务器第一次启动时被加载。
当第一个用户调用某一个 Servlet 时,就会创建一个该Servlet 实例,init() 方法简单地创建或加载一些数据,这些数据将被用于 Servlet 的整个生命周期。
2,响应客户请求阶段:调用service()方法
每一个用户请求都会产生一个新的线程,每次服务器接收到一个 Servlet 请求时,服务器会产生一个新的线程并调用服务; service() 方法检查 HTTP 请求类型(GET、POST、PUT、DELETE 等),并在适当的时候调用 doGet、doPost、doPut,doDelete 等方法。
3,终止阶段:调用destroy()方法
# Servlet的单例多线程安全
Java里有个API叫做ThreadLocal,spring单例模式下用它来切换不同线程之间的参数。用ThreadLocal是为了保证线程安全,实际上ThreadLoacal的key就是当前线程的Thread实例。单例模式下,spring把每个线程可能存在线程安全问题的参数值放进了ThreadLocal。这样虽然是一个实例在操作,但是不同线程下的数据互相之间都是隔离的,因为运行时创建和销毁的bean大大减少了,所以大多数场景下这种方式对内存资源的消耗较少,而且并发越高优势越明显。
单例:Servlet只在用户第一次请求时被实例化,并且是单例的,在服务器重启或关闭时才会被销毁。
多线程:当请求到达时,Servlet容器(Tomcat...)通过线程池中可用的线程给请求者并执行Service方法,每个线程执行一个单一的 Servlet 实例的 service() 方法
有人说单例处理多线程会有性能问题,因为并发请求肯定要排队,其实未必,很多高并发的框架都是单例模式;
有人提出了实例池,但是我没有找到太多信息,仅供参考:
Servlet thread pool vs Servlet instance pool: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7826452/servlet-thread-pool-vs-servlet-instance-pool-by-the-web-container Servlet的单例模式的理解 https://www.breakyizhan.com/java/5016.html
# 线程模型
Thread per connection
Thread per request
Servlet线程模型与异步请求 (opens new window) Servlet与多线程的关系是什么? (opens new window) servlet单实例多线程模式 (opens new window)
# HandlerInterceptors vs. Filters in Spring MVC
Interceptors operate at the controller level, while Filters operate at the servlet level. This means that Interceptors have access to the controller and can modify the model and view, while Filters do not have access to the controller and can only modify the request and response. https://www.baeldung.com/spring-mvc-handlerinterceptor-vs-filter
# 应用
spring boot supports
Spring Boot supports the following embedded servlet containers:
You can also deploy Spring Boot applications to any Servlet 3.1+ compatible container.
https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/htmlsingle/#getting-started-system-requirements-servlet-containers
| Name | Servlet Version |
|---|---|
| Tomcat 9.0 | 4.0 |
| Jetty 9.4 | 3.1 |
| Undertow 2.0 | 4.0 |
spring boot Framework支持的三种环境:
# 源码解读
springmvc request参数解析@RequestBody和Controller方法调用
///
org.apache.catalina.core;
public final class ApplicationFilterChain implements FilterChain {
doFilter=>
internalDoFilter=>
servlet.service(request, response);
org.springframework.web.servlet
public class DispatcherServlet extends FrameworkServlet {
service
doPost=>
processRequest=>
doService=>
doDispatch=>
mv = ha.handle(processedRequest, response, mappedHandler.getHandler());
## processedRequest
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation
public class RequestMappingHandlerAdapter extends AbstractHandlerMethodAdapter
implements BeanFactoryAware, InitializingBean {
handleInternal
=>mav = invokeHandlerMethod(request, response, handlerMethod);
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation
public class ServletInvocableHandlerMethod extends InvocableHandlerMethod {
invokeAndHandle=>
Object returnValue = invokeForRequest(webRequest, mavContainer, providedArgs);
org.springframework.web.method.support
public class InvocableHandlerMethod extends HandlerMethod {
public Object invokeForRequest(NativeWebRequest request, @Nullable ModelAndViewContainer mavContainer,
Object... providedArgs) throws Exception {
Object[] args = getMethodArgumentValues(request, mavContainer, providedArgs);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Invoking '" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(), getBeanType()) +
"' with arguments " + Arrays.toString(args));
}
Object returnValue = doInvoke(args);
if (logger.isTraceEnabled()) {
logger.trace("Method [" + ClassUtils.getQualifiedMethodName(getMethod(), getBeanType()) +
"] returned [" + returnValue + "]");
}
return returnValue;
}
## getMethodArgumentValues 解析参数
org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.method.annotation
public class RequestResponseBodyMethodProcessor extends AbstractMessageConverterMethodProcessor {
resolveArgument
## doInvoke 调用Controller方法
# web server VS servlet container
A Servlet Container is a Web Server that must be able to run Java Servlets.
Web Server, on the other hand, is a broader term including all software running and communicating through HTTP protocol.
ref
https://www.w3cschool.cn/servlet/servlet-life-cycle.html
https://blog.csdn.net/u010763324/article/details/80747559 Servlet的多线程和线程安全 https://www.cnblogs.com/binyue/p/4513577.html