回目录 《硬件基础与物联网IOT》
WARNING
Safety first! Safety first!
Please be careful when working with high voltage. Seriously, it may shock you or even take your life. If you’re NOT 100% sure what you are doing, do yourself a favor and don’t touch anything. Ask someone who knows!
# 集成电路基础
In the early 1970s, two American companies, Intel and Texas Instruments, introduced microprocessors and microcontrollers to the world. These companies envisioned a future dominated by single-chip integrated computers.
the microcontroller system accepts at least one input, performs some action on that input, and prodces one or more outputs. The inputs and outputs of a microcontroller system are voltages that we can use to determine the state of external devices. The microcontroller reads the voltages from an input device and uses this information to decide on the correct voltage to output.
A microcontroller system is embedded in an integrated circuit (IC). A typical microcontroller includes a processor, program memory, RAM, input/output pins, and more on a single chip.
Microcontrollers can be used to control a wide variety of electronic devices. They are perfect for applications requiring multiple repetitive operations or high-speed computations. Here’s a list of some devices that a microcontroller could be used to control:
- Computers
- Computer peripherals
- Telephone systems
- Home appliances
- Industrial equipment
- Security systems
- Sensors and sensor arrays
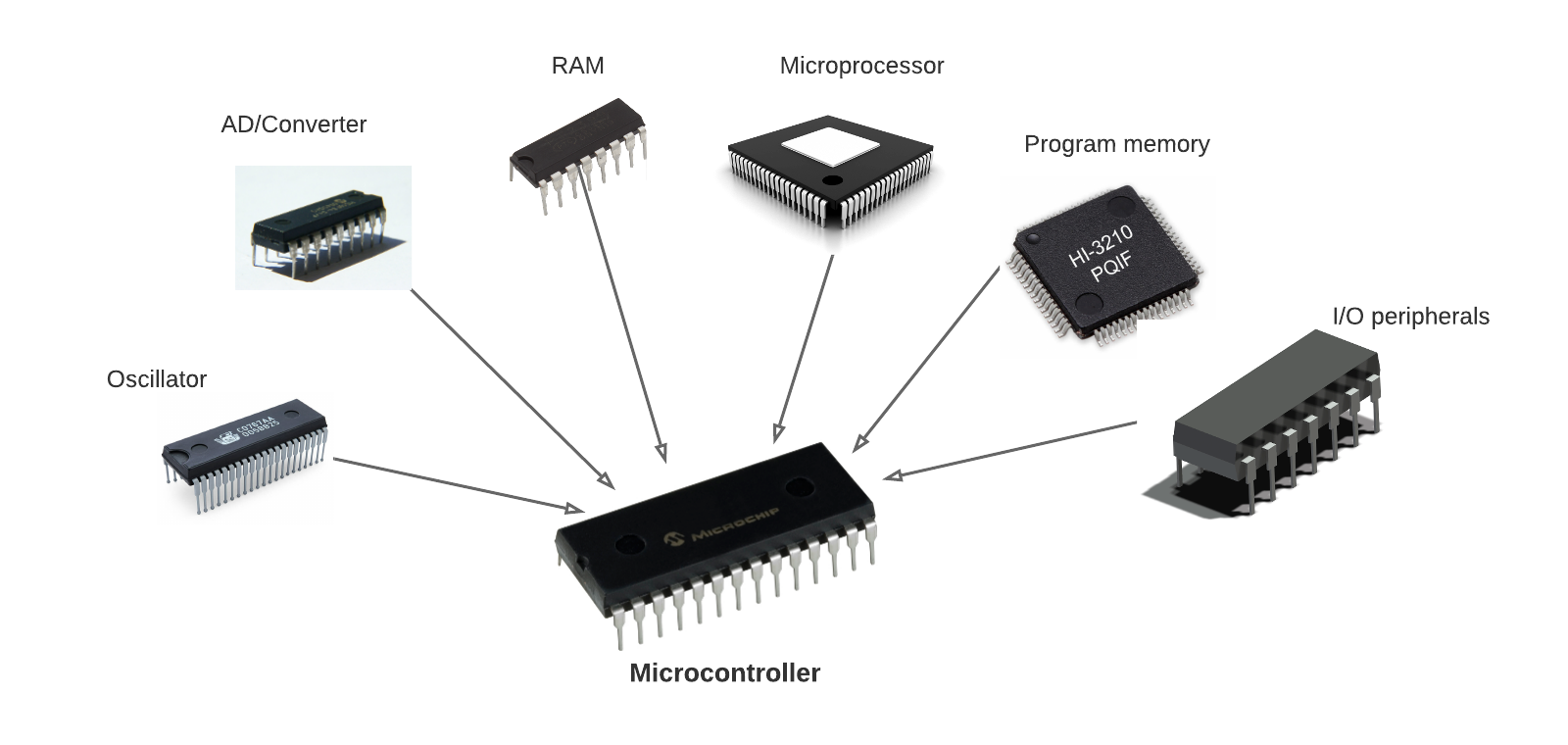
# 基本概念
- 半导体(semiconductor)指常温下导电性能介于导体与绝缘体之间的材料 48页PPT,看懂芯片半导体基础! (opens new window) 半导体在最原始的时候是一种材料,比如硅。后来使用这些半导体材料制作了集成电路,又将集成电路封装成芯片。但是半导体这个名字一直保留着,所以我们通常把这些统统以半导体这三个字代替。 半导体(材料)=》芯片(组成)+其他电子元器件=》集成电路 二极管和晶闸管 transistor是半导体器件,电阻电容不是 Is transistor the only electronic component on a CPU? (opens new window) The processors (C.P.U) only contains transistors. But it doesn't means they only made up of only transistors, but they are made up of transistors, diodes, capacitors, resistors and etc.. Here transistor also plays a role of resistor, capacitor, diodes and etc… That's why we need only transistors. Processor are made up of millions or billions transistors ( transistors also plays a role of resistors , capacitors, diode and etc..) for switching so that it can process the input and give desired output. Some electrical properties also added to the processor by photolithography Technique.
- 印刷电路板 PCB-Printed Circuit Board 是芯片IC的载体
- 电子元器件 Electronic Components 是电子电路中的基本元素,通常是个别封装,并具有两个或以上的引线或金属接点。电子元件须相互连接以构成一个具有特定功能的电子电路,例如:放大器、无线电接收机、振荡器等,连接电子元件常见的方式之一是焊接到印刷电路板上。电子元件也许是单独的封装(电阻器、电容器、电感器、晶体管、二极管等),或是各种不同复杂度的群组,例如:集成电路(运算放大器、排阻、逻辑门等)。
- 逻辑门电路
逻辑门(Logic Gates)是在集成电路(Integrated Circuit)上的基本组件;
最常用的集成门电路有
- TTL系列集成逻辑门
- CMOS系列集成逻辑门 两大类。就其功能而言,常用的有与门、或门、非门、与非门、或非门、与或非门、异或门以及集电极开路(OC)门、三态(TS)门等 在数字电路中,所谓“门”就是只能实现基本逻辑关系的电路。最基本的逻辑关系是与、或、非,最基本的逻辑门是与门、或门和非门。逻辑门可以用电阻、电容、二极管、三极管等分立原件构成,成为分立元件门。也可以将门电路的所有器件及连接导线制作在同一块半导体基片上,构成集成逻辑门电路 集成电路按照单位芯片面积集成门电路的个数,分为:
- 小规模集成电路(SSI)
- 中规模集成电路(MSI)
- 大规模集成电路(LSI)
- 超大规模集成电路(VLSI) 从制造工艺上来看,数字集成电路可分为:
- 双极型集成电路
- 单极型集成电路
- 集成电路 IC-Integrated Circuit 又称 芯片 Integrated Circuit Chip, an integrated circuit or monolithic integrated circuit (also referred to as an IC, a chip, or a microchip) is a set of electronic circuits on one small flat piece (or "chip") of semiconductor material, usually silicon.
- 可编程逻辑器件(英语:Programmable Logic Device,缩写为PLD) 是一种电子零件、电子组件,简而言之也是一种集成电路、芯片。PLD芯片属于数字类型的电路芯片,而非模拟或混合信号(同时具有数字电路与模拟电路)芯片。 PLD与一般数字芯片不同的是:PLD内部的数字电路可以在出厂后才规划决定,有些类型的PLD也允许在规划决定后再次进行变更、改变,而一般数字芯片在出厂前就已经决定其内部电路,无法在出厂后再次改变,事实上与一般的模拟芯片、混合信号芯片一样,在出厂后就无法再对其内部电路进行调修。
- 可编程逻辑控制器 Programmable Controllers / PLC-programmable logic controller is an industrial computer that has been ruggedized and adapted for the control of manufacturing processes, such as assembly lines, machines, robotic devices, or any activity that requires high reliability, ease of programming, and process fault diagnosis. 一种具有微处理器的数字电子设备,用于自动化控制的数位逻辑控制器,可以将控制指令随时载入记忆体内储存与执行。可程式控制器由内部CPU,指令及资料记忆体、输入输出单元、电源模组、数位类比等单元所模组化组合成。PLC可接收(输入)及发送(输出)多种型态的电气或电子讯号,并使用他们来控制或监督几乎所有种类的机械与电气系统。 现在工业上使用可程式逻辑控制器已经相当接近于一台轻巧型电脑所构成,甚至已经出现整合个人电脑(采用嵌入式作业系统)与PLC结合架构的可程式自动化控制器(Programmable Automation Controller,简称PAC),能透过数位或类比输入/输出模组控制机器设备、制造处理流程及其他控制模组的电子系统 最初的可编程序逻辑控制器只有电路逻辑控制的功能,所以被命名为可程式逻辑控制器,后来随着不断的发展,这些当初功能简单的计算机模块已经有了包括逻辑控制,时序控制、模拟控制、多机通信等许多的功能,名称也改为可程式控制器(Programmable Controller),但是由于它的简写也是PC与个人电脑(Personal Computer)的简写相冲突,也由于多年来的使用习惯,人们还是经常使用可程式逻辑控制器这一称呼,并在术语中仍沿用PLC这一缩写
- 单片机/单片微型计算机 Single Chip Microcomputer,它是把中央处理器(Central Process Unit;CPU)的频率与规格做适当缩减,并将内存(memory)、计数器(Timer)、USB、A/D转换、UART、PLC、DMA等周边接口,甚至LCD驱动电路都整合在单一芯片上,形成芯片级的计算机,为不同的应用场合做不同组合控制 单片机是一种芯片IC;
- CPU MCU MPU
中央处理器(CPU)是电脑中的核心配件,其功能主要是解释计算机指令以及处理计算机软件中的数据。中央处理器主要包括两个部分,即控制器、运算器,其中还包括高速缓冲存储器及实现它们之间联系的数据、控制的总线。处理器架构设计的迭代更新以及集成电路工艺的不断提升促使CPU不断发展完善,从最初专用于数学计算到广泛应用于通用计算,从4位到8位、16位、32位处理器,最后到64位处理器,从各厂商互不兼容到不同指令集架构规范的出现,CPU 自诞生以来一直在飞速发展。
In the earlier days, a processor (or central processing unit: CPU) consisted of a number of IC chips, though the advancements in chip scaling technologies soon enabled all necessary components to be packed onto a single semiconductor chip, leading to the birth of the microprocessor.
CPU逐渐发展出来三个分枝:
一个是DSP(Digital Signal Processing/Processor,数字信号处理),
另外两个是MCU(Micro Control Unit,微控制器单元)和MPU(Micro Processor Unit,微处理器单元)。
开发板DEVELOPMENT BOARD -- Two basic processing platforms for implementing embedded systems:
- MCU-Microcontroller Unit - Arduinos These devices have varying amounts of integrated Flash (<= 2MB) and RAM (<= 1MB), and are designed to run bare-metal code or a real-time operating system (RTOS), like FreeRTOS. An example of an MCU based system is most Arduinos(ATmega328 8-bit Microcontroller) 新款MCU EFM32和EFM8功能升级,加速物联网产品原型设计 (opens new window)
- MPU- microprocessor unit - Raspberry PI The second is the Linux-capable Microprocessor Unit (MPU). An MPU typically does not have embedded Flash and RAM — at least on the same die. an example of an MPU based system is the Raspberry PI(RP2040). The fundamental difference between MCU/RTOS and MPU/Linux systems is the memory architecture and the amount of memory in the system. http://bec-systems.com/site/1540/microcontroller-mcu-or-microprocessor-mpu
# 概念对比
# microprocessor(in personal computer) VS microcontroller
The main processor in a desktop computer or laptop will be a microprocessor. But the computer may have microcontrollers as well, to perform peripheral functions.
The main difference between a microprocessor and microcontroller, is that microprocessors generally don’t have much memory inside the chip, except for perhaps cache memory, since these systems generally have GBs of RAM and that is too much to put on a processor chip. Microcontrollers generally have both their program and data memory on chip, but it is in the range of KBs and perhaps MBs at the most.
Another major difference between the two is microcontrollers have way more peripherals on chip than a microprocessor. Serial interfaces like UART, I2C, SPI, CAN, LIN, USB etc., along with parallel I/O ports, ADC(s), DAC(s), comparators, timer/counters, and DMA. A microprocessor used in a desktop or laptop will a PCI interface, memory interface, and possibly a graphics co-processor and interface.
So if a desktop of laptop PC needs some of the serial interfaces listed above, it will require extra components. About a year ago, I wrote code for a “USB bridge” for a ARM Cortex-M0+ microcontroller. It connects to the main processor via USB, and provides virtual I/O ports, I2C, and SPI interfaces. Inside the microprocessor, calls to drivers for these peripherals are sent to the USB bridge instead. It’s going into production this year inside laptops from one of the major laptop vendors.
# embedded operating system vs microcontroller
嵌入式系统,就是,在其它电子产品或设备中,加入(嵌入)一个小小的"计算机"。目的是为了,人机交互、采集传感器数据、处理数据、控制执行机构和通信。这些是"计算机"擅长的。这个小小的"计算机",就是嵌入式系统。它由各种"单片机"或叫微控制器再加上其它外围电路组成。
An embedded system is a microprocessor- or microcontroller-based system of hardware and software designed to perform dedicated functions within a larger mechanical or electrical system.
At the heart of most embedded systems there is a microcontroller or microprocessor running the application. Embedded systems are generally more basic and rudimentary than microcontrollers since they often do not have logic to run the system.
Let’s go back to the Lego analogy for a second. The Legos, when put together, create a larger more complete system. Each Lego however has a specific task and use case. The embedded systems are typically told what to do by the CPU or Central Processing Unit of a computer. When the CPU tells an embedded system to do something the CPU generally communicates with a microcontroller that is part of the embedded system. Think of the microcontroller as the brains of the embedded system. Once the CPU tells the microcontroller to do something the microcontroller then directs the components of the embedded system to execute its specific tasks.
# 可编程芯片和不可编程的芯片有什么区别:
单片机MCU是软编程,可编程逻辑芯片PLD是硬编程。
MCU 中是电路已经固定,它的编程是只能做固有的几十条指令的动作。而且是一条条的执行。
PLD 中电路未定,它的编程是电路的编程,也就是电路模块的设计。模块间是并行式的。
MCU中的资源固定,比如某型号只有一个定时器,一个IO中断。程序只是控制这些。
PLD 中电路未定,想做成几个定时器,或中断,或PWM输出,或别的什么模块。由程序决定。
MCU就像是火车只能在建好的铁轨上跑。
PLD就是飞机可以随便飞。或者说像72变的孙悟空,能变成火车跑,也能变成飞机飞。
# PLC vs 单片机
PLC技术采用单片机技术,但 PLC技术并非单片机技术的延伸。此处我们若将单片机比作一张白纸, PLC是已绘制在白纸上的表格,那么使用单片机技术就像在白纸上写字,用 pcl技术就是填写表格,而用单片机技术则是填写表格。因此,掌握两种技巧,相当于学习在一张白纸上书写、看表格、填表。
# PLC vs 嵌入式
嵌入式系统从广义上讲凡是以应用为中心,软硬件可裁减的的控制系统都可以叫做嵌入式系统,它包括的范围更为广阔,他包括PLC和单片机,不过现代人很多把嵌入式理解为嵌入式操作系统,嵌入式操作系统有嵌入式window CE,或者Linux系统等,我们可以把操作系统嵌入到存储器里,可以实现更为强大的功能,比如可以PDA、手机等。
To make a generalization… All PLCs are embedded systems, but not all embedded systems are PLCs.
A PLC is a readymade embedded system that can be deployed “in situ” meaning in to an end application with very little engineering overheads. The application design engineer(s) don't have to worry about the power requirement, or yes withstanding industrial conditions such as extended temperature ranges or EMI RFI noise. They can straight away concentrate on meeting the requirements of the end application. The I/O points on a PLC are already protected. The PLC takes a microcontroller … builds a set of peripherals around it and then offers all of it to the outside world … with the appropriate protection circuitry for the I/o pins in place of course. It does this by having a special type of high level programming language that lets you build applications quickly without having to be bothered about nitty gritty of microcontroller programming such as how the microcontroller communicates with its peripherals or how it manages memory. In a sense it adds a layer of abstraction in the same way for example as a PC allows you to create programs without having to bother about the low level bios calls or managing access to storage media such as hard drives.
An embedded systems design engineer, on the other hand, is dealing directly with the hardware and all the issues that go with it….such as for example managing power requirements, managing the current sourcing / sinking capacity of i/o pins, what bus to use for peripherals communication, or how much non-volatile memory to allocate and so on.
So there is a price trade-off for the extra features you get with PLCs, making them more expensive than the embedded counterparts. Initial cost of deploying an embedded system would be very high compared to a PLC, going down as quantities increase and vise versa for PLCs. So clearly a PLC cannot be a solution in a price sensitive application… automobiles for example
Likewise an embedded system would not be a good solution where a quick turnaround time is a criterion ….. such as a proof of concept for automation of a material handling application
Typical examples where PLCs make them a good choice:
Car wash automation Material handling over conveyor belts in a plant Robotic arms handling radioactive waste Laser cutting machines Washing machines Elevators Pouch filling machines Mail sorting system in a postal department. Gravimetric batching control system All of the above can indeed be realized with embedded systems. Typical examples where it makes more sense to use them would be:
Automotive electronics such as Engine control units, Anti lock braking, cabin climate control etc. Pouch filling machines UPS or power management systems Data loggers for physical parameters such as temperature, pressure, flow, liquid level etc in chemical plants. Protection equipment for HV transformers Static and dynamic weighing applications. Solar inverters Fuel dispensers Communication equipment such as gateways, routers and converter In conclusion, I should mention one major difference between these two. The application program of an embedded system cannot be reprogrammed or modified in a short time in the same way it can be done for a PLC.
# 可编程逻辑控制器(PLC)和分散式控制系统(DCS)
# 上电启动过程
电脑及微型电脑启动过程 Booting process of a computer : When the computer is turned on it starts execution from the ROM (BIOS) that in turn located the Disk connected to the computer, then the MBR (Master boor record) of the Disk is loaded, the MBR located the disk partition where the OS is installed, then the OS is loaded in the RAM, then the computers completes its booting process.
单片机 加电后,先运行芯片内部固有程序(这个程序是用户访问不到也改写不了的),即启动代码 bootloader。启动代码程序建立完运行环境后,会去读串口状态,就是用户下载程序用到的各个端口,判断用户是否正在使用端口准备下载程序,如果是,就按用户要求,把用户程序下载到指定地址上。 如果不是,就跳转到已经下载过的用户程序入口,从而把芯片控制权交给用户程序。如果是新的芯片还没有下载过,那么就停留在读取串口状态的循环中。 启动代码通常都烧写在flash中,它是系统一上电就执行的一段程序,它运行在任何用户C代码之前。上电后,arm处理器处于arm态,运行于管理模式,同时系统所有中断被禁止,PC到地址0处取指令执行。
四种Bootloader程序安全机制设计 (opens new window)
# 编程区别
Microcontroller 不能运行操作系统,所以需要烧录程序到 flash memory 或 ROM; 对于个人电脑,ROM存储BIOS,硬盘存储操作系统,编译程序是跑在操作系统上甚至是操作系统之上的虚拟机如JVM里,所以不存在烧录; 所以对于集成了 Microcontroller 的 无操作系统的Arduino 来说就是只能烧录程序,而对于像树莓派这种集成了 Microprocessor 的微型电脑来说可以跑操作系统;
分类一:
- Controller programming:
- Microcontroller (Arduino, STM32) programming using C, Mostly required to unplug Microcontroller from circuit for programming (but Some burning devices have ability to Program Microcontroller in circuit programming like Pik kit) 程序烧录到flash内存 or ROM;
- PLC programming using Ladder Logic, Proggramming of PLC is in form of symbols & blocks of I/Os, just connect and compile PLC的程序下载到PLC硬件里去,最老的方式叫“烧录”,那时候通讯和软件还极不发达,只能靠写入芯片的方法来做。现在可能单片机还有这种说法。现在的PLC是由很多芯片组成的一个硬件系统加上复杂的软件系统来组成的,通讯是现在PLC的必备能力,因此,可能很多朋友对于“烧录”这个词比较陌生了。
- Microprocessor (with GPIO),
- ROS
- Interface/Client development: Winforms/WPF/WinUI, HTML frameworks, HMI, Android/iOS
- Server/Backend programming: APIs, Networked servers, SCADA (application), data collection, databases
分类二:
- ICP(In Circuit Programing)在电路编程 使用对应厂家的软件以及仿真器都可以烧录程序,目前主流的有Jtag(Joint Test Action Group)以及SWD(Serial Wire Debug)接口。而ICP编程就是以SWD接口进行的。 执行ICP功能,仅需要3个引脚RESET、ICPDA、ICPCK。RESET用于进入或退出ICP模式,ICPDA为数据输入输出脚,ICPCK为编程时钟输入脚。用户需要在系统板上预留VDD、GND以及这三个脚。
- ISP(In System Programing)在系统编程 目标芯片使用USB/UART/SPI/I²C/RS-485/CAN周边接口的LDROM引导代码去更新晶片内部APROM、数据闪存(DataFlash)和用户配置字(Config)
- IAP(In applicating Programing)在应用编程 IAP就是通过软件实现在线电擦除和编程的方法。IAP技术是从结构上将Flash存储器映射为两个存储体,当运行一个存储体上的用户程序时,可对另一个存储体重新编程,之后将程序从一个存储体转向另一个。
# 1.Fundamentals
Electronics Foundations: https://www.linkedin.com/learning/electronics-foundations-fundamentals
# 公式
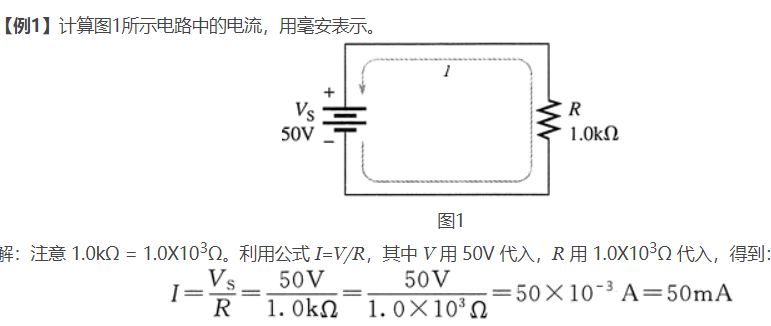
欧姆公式
http://www.54benniao.com/view/28.html
 https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/78519916
https://zhidao.baidu.com/question/78519916
# 电子元器件 Electronic Components
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Electronic_symbol
R 电阻:
色环图
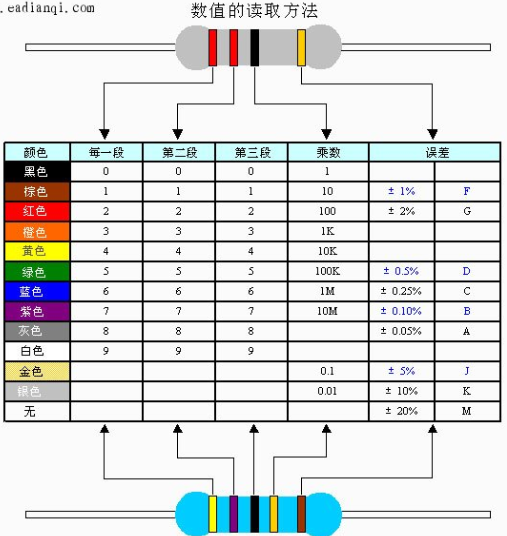 快速:两个红色 220欧, 一个红色 10k,一个黄一个紫色 4.7k,没有比较亮的颜色(棕黑黑) 1k
快速:两个红色 220欧, 一个红色 10k,一个黄一个紫色 4.7k,没有比较亮的颜色(棕黑黑) 1k
LED 长正短负
C 电容
铜线/杜邦线能通过的最大电流
模拟引脚(analog) 频率HZ 周期(微秒) 100Hz不是直接等于多少毫秒的问题;它是交流电频率与周期的关系,并且是倒数关系:周期T=1/100=0.01秒=10毫秒。
1.杜邦线 dupont line 贴片元件的焊接教程 - 拖焊技巧 http://www.elecfans.com/article/89/140/2012/20120522273004.html Solderless Breadboard http://www.petervis.com/Raspberry_PI/Solderless_Breadboard/Solderless_Breadboard.html spring clips 弹簧卡子 copper strips 铜带 multimeter 万用表 jumper 跳线 rail 引脚
power regulator oxidation semiconductor transistor 晶体管 MB102 Breadboard Power Supply Module 3.3V 5V http://www.petervis.com/Raspberry_PI/Breadboard_Power_Supply/YwRobot_Breadboard_Power_Supply.html http://www.petervis.com/Raspberry_PI/Breadboard_Power_Supply/Breadboard_Power_Supply.html Provide two different voltages on the two supply lines of the breadboard as needed.However, you should be careful about on which side of the breadboard the module been attached. Check that is minus (-) really is on the blue line and plus (+) on the red line, otherwise it may cause the circuit arrangement evil confusing! Specifications: jumper adjustable output voltage: 3.3V and / or 5V DC – directly on the breadboard additional: 2x 3.3V and 2x 5V plug connections on top USB connector power supply connector (input voltage 6.5V – 12V DC, already tested with 6V) maximum output current: 700mA status LED on/off switch suitable breadboard types: MB-102, ZY-60 dimensions: 52mm x 34mm 可编程逻辑电源/新能源MEMS/传感技术测量仪表嵌入式技术制造/封装模拟技术连接器EMC/EMI设计光电显示存储技术EDA/IC设计处理器/DSP接口/总线/驱动控制/MCURF/无线
引脚高低电平 内部拉起?拉电流弱 外部:接电阻,又5v引脚供电,又称低电平控制/负极控制,灌电流强
# PCB-Printed Circuit Board 印制电路板 - 芯片的载体
PCB类型,如何通过板子画出电路图? 电路板上如何区分交流直流
如何用万用表测找出电路板的坏的地方?电容爆炸? https://www.elecfans.com/d/1695230.html http://news.eeworld.com.cn/Test_and_measurement/ic521913.html https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ejDGCiJ-aVs
http://news.eeworld.com.cn/Test_and_measurement/ic514591.html 1、看元件的状态 拿到一块出故障的电路板,首先观察电路板有没有明显的元件损坏,如电解电容烧毁和鼓胀、电阻烧坏以及功率器件的烧损等。
2、看电路板的焊接 如印制电路板有没有变形翘曲;有没有焊点脱落、明显虚焊;电路板覆铜皮有没有翘起、烧糊变黑。
3、观察元件的插件 如集成电路、二极管、电路板电源变压器等方向有没插错。
4、电阻电容电感的简单测试 使用万用表对量程内的电阻、电容、电感等可怀疑元件进行简单的测试,测试有否电阻阻值变大、电容短路、开路和容值变化、电感短路和开路等现象。
5、上电测试 经过上述简单观察和测试后,无法排除故障,可进行上电测试。首先测试电路板供电是否正常。如电路板的交流电源是否异常、稳压器输出是否异常、开关电源输出和波形是否异常等
6、刷程序 对于有单片机、DSP、CPLD等可编程元件,可考虑重新刷一遍程序,排除程序运行异常造成的电路故障。
# 工具
# 仿真
https://wokwi.com https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/p4YQnxKWCcFlrLxXrPqMmw
# 做图
Electronic design automation (EDA), also referred to as electronic computer-aided design (ECAD), is a category of software tools for designing electronic systems such as integrated circuits and printed circuit boards.
- Fritzing
- custom parts: https://fritzing.org/learning/tutorials/creating-custom-parts https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0RDrw8WvYNQ
- kicad https://forum.kicad.info/t/reproducing-a-pcb-from-scanned-image-bmp-jpg-etc/12106
- online tool
- https://www.circuito.io/app
- https://www.circuit-diagram.org/editor/
- https://qucs.sourceforge.net/
PCD打板:
- 立创eda
- Altium Designer
牛逼,自己设计芯片:
https://xie.infoq.cn/article/30387388381a0d915b2494f91 https://bbs.hassbian.com/thread-11256-1-1.html
# Prototype
- 初级: 电路积木 中小学电学实验箱 接线柱。配合U形导线,快速搭建电路
- 初级: 电路实验箱 接线柱:香蕉头,和电路积木类似,直接插入就能完成电路连接
- 中级:面包板+导线组合 专用的导线或用杜邦线
- 高级:万用板/洞洞板 学校和工厂更常用,需要焊接,可靠性比面包板高很多
- 高级:PCB打样 PCB Gerber https://www.proto-electronics.com/blog/gerber-files-what-are-they Prototype PCB online (opens new window) jlcpcb.com
# iot apps
blynk.io
# 工作室 ELECTRONICS WORK BENCH
https://www.circuitbasics.com/how-to-build-an-electronics-work-bench/
# 通信协议
逼真动画展示I2C、SPI、UART的通信过程 (opens new window)
硬件接口:
- Serial port 串口 即 COM口(communication port)
In strict theory, any port using serial communications (almost any modern bus - including USB, which stands for "Universal Serial Bus") is a "serial port". The term "serial port" simply means that the data is transferred one bit at a time over a single signal path. However, in most cases, when people refer to "the serial port", they actually refer to a port that complies to RS232.
串口的硬件实现主要有两种:D型9针插头(DB9)和 4针杜邦头
- UART接口: 通用异步收发器(UniversalAsynchronous Receiver/Transmitter),UART是串口收发的逻辑电路,这部分可以独立成芯片,也可以作为模块嵌入到其他芯片里,单片机、SOC、PC里都会有UART模块; UART是通用异步收发传输器,它是完成一个特定的功能的硬件,它本身不是协议。它的最基本功能,是串行数据和并行数据之间的转换。计算机中的数据以Byte为基本单位,对一个Byte的存取是并行的,即同时取得/写入8个bit。而串行通信,则需要将这个Byte"打碎",按照时间顺序来收发以实现串行。它是设备间进行异步通信的关键模块,UART负责处理数据总线和串行口之间的串/并、并/串转换,并规定了帧格式;通信双方只要采用相同的帧格式和波特率,就能在未共享时钟信号的情况下,仅用两根信号线(Rx 和Tx)就可以完成通信过程,因此也称为异步串行通信; 在嵌入式里面说的串口,一般是指UART口; 针脚:UART有4个pin(VCC、GND、RX、TX),用的是TTL电平,低电平为0(0V),高电平为1(3.3V或以上)。
- I2C接口 I2C接口包括时钟线(SCL)和数据线(SDA)。这两条线都是漏极开路或者集电极开路结构,使用时需要外加上拉电阻,可以挂载多个设备。每个设备都有自己的地址,主机通过不同地址来选中不同的设备。 针脚:SCL/SDA
- SPI Serial Peripheral interface,顾名思义就是串行外围设备接口,是Motorola首先在其MC68HCXX系列处理器上定义的。SPI总线是微控制器四线的外部总线(相对于内部总线)。与IIC不同,SPI没有明文标准,只是一种事实标准,对通信操作的实现只作一般的抽象描述,芯片厂商与驱动开发者通过data sheets和application notes沟通实现上的细节。
- CAN
- USB口: 通用串行总线,和串口完全是两个概念。虽然也是串行方式通信,但由于USB的通信时序和信号电平都和串口完全不同(串口通常都是采用RS232标准,而USB不是),因此和串口没有任何关系。USB是高速的通信接口,用于PC连接各种外设,U盘、键鼠、移动硬盘、当然也包括"USB转串口"的模块。(USB转串口模块,就是USB接口的UART模块)
- 并口 并行接口,简称并口。并口采用的是25针D形接头。所谓“并行”,是指8位数据同时通过并行线进行传送,这样数据传送速度大大提高,但并行传送的线路长度受到限制,因为长度增加,干扰就会增加,数据也就容易出错,目前,并行接口主要作为打印机端口等。
digital logic 电平标准/电气协议(逻辑电平的表示方式):
- TTL 低电平为0,高电平为1(电平信号)
- RS232 正电平为0,负电平为1(电平信号) RS-232接口连接器使用型号为DB-25的25芯插头座。一些设备与PC机连接的RS-232接口,因为不使用对方的传送控制信号,只需三条接口线,即RXD、TXD、GND,所以采用DB-9的9芯插头座,传输线采用屏蔽双绞线。
- RS-485、RS-422 与RS-232类似,但是采用差分信号逻辑,更适合长距离、高速传输。
Hard resetting via RTS pin https://electronicsinnovation.com/hard-resetting-via-rts-pin-fixed-explained/
# 常用芯片-模块
# 数模转换 ADC
microprocesser 完全是 digital device, can only understand digital signals, 所以连接一些模拟信号类型的传感器等设备就需要 microcontroller 进行AD转换, 然后也有很多终端设备需要接受模拟信号,比如老式的CRT TV,所以microcontroller又需要将digital signals模拟成 analog output输出给这些设备;
Analog (Analog Voltage Signal)-to-Digital(Digital Signal) Converter,常称ADC, 是指将连续变量的模拟信号转换为离散的数字信号的器件,比如将模温度感器产生的电信号转为控制芯片能处理的数字信号0101,这样ADC就建立了模拟世界的传感器和数字世界的信号处理与数据转换的联系。 解释 (opens new window)
DAC 数模转换
Arduino 本身已经带有ADC和DAC(PWM),可以进行 analog的读写和digital的读写 (opens new window) 但是raspberry pi没有(不能直接读analog,可以模拟写),所以连接模拟信号传感器的时候需要跟ADC一起工作
# 串口ttl转usb
convert from uart to USB
cp210X ch9102 TTL - Transistor-Transistor Logic,晶体管晶体管逻辑电路
从稳定性来看,ft3232 > cp210X(cp2102) > ch340(ch340K)
cp2102 CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Drivers (opens new window)
ch9102
windows驱动,device manager=》Ports(COM&LPT)
# RFID模块
RC522和PN532的区别 协议支持的类型PN比RC系列更多,PN支持NFC协议,RC主要是ISO14443A/B
# 常用芯片-单片机
RP2040 vs STM32 vs ESP32 vs ESP8266 (opens new window)
Common tips 1.install correct drive 2.cannot find serial port Change the usb cable 3.Upload speed 波特率 Device Manager Port(Com and LRT) USB-SERIAL CH340/341 (pre-install successful, install ' 驱动精灵' and connect USB will auto detect drive) 芯片类型 STC90C5XX 晶振频率 调整波特率一超时 -- 改用低速下载
:atmel,stc,pic,avr,凌阳,80C51,arm
https://hackaday.io/
http://www.yeelink.net/
http://www.elecfans.com/
http://www.robotsky.com/
PCB 入门教程 http://dword1511.info/dword/gswpcb_zhcn/ news: http://www.guancha.cn/Industry/2015_12_09_344069.shtml
Tools http://fritzing.org
NodeMcu vs Esp32 vs esp8266 (opens new window)
"NodeMcu" is the name of a firmware originally for the ESP8266 microcontroller, with support for the ESP32 microcontroller added more recently, that allows you to program these microcontrollers using the Lua programming language.
In the early days of the hobbyist community's adoption of the ESP8266, ESP8266 development boards were marketed with the name NodeMcu and the term "NodeMcu" started to be associated more with the hardware than the firmware. It is common for people with no interest in the Lua programming language to buy "NodeMcu" boards and program them with the Arduino IDE, which erases the NodeMcu firmware from the board. To make things more confusing, multiple companies marketed boards with the name "NodeMcu", but with small hardware differences. Over time, the NodeMcu boards became less popular in the Arduino world because the similarly priced WeMos D1 Mini came out with the same functionality, but in a smaller form factor. Now, the "NodeMcu" name is being used to market ESP32 boards as well.
ESP32 is the name of a microcontroller made by Espressif. You will find this microcontroller on a variety of development boards, in a variety of forms. You can also purchase the ESP32 module, without the support components provided by the development boards.
ESP8266 is the name of a microcontroller made by Espressif. You will find this microcontroller on a variety of development boards, in a variety of forms. You can also purchase the ESP8266 module, without the support components provided by the development boards.
# Espressif ESP*** Based Development Board
what's wrrom wrover... (opens new window) wroom mini wrover pico (opens new window)
品牌 lolin lilygo
Esp32 vs esp8266 https://makeradvisor.com/esp32-vs-esp8266/ M5stack https://docs.m5stack.com/#/en/core/basic M5stickC https://docs.m5stack.com/#/zh_CN/core/m5stickc https://docs.m5stack.com/#/zh_CN/quick_start/m5stickc/m5stickc_quick_start_with_arduino_Windows https://github.com/m5stack/M5StickC/tree/master https://www.hackster.io/herbert-stiebritz/very-simple-m5stickc-clock-08275b
https://docs.platformio.org/en/latest/boards/espressif32/m5stick-c.html
esp8266 A Beginner's Guide to the ESP8266 https://tttapa.github.io/ESP8266/Chap01%20-%20ESP8266.html esp8266 esp-12 https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=8J7zflVO8K0
ESP32 ESP8266 ESP8266真会是Arduino Killer么? https://blog.csdn.net/eezata/article/details/49884179 https://esp32.com/viewtopic.php?t=86 Arduino for esp32&esp8266开发环境搭建 https://www.jianshu.com/p/8088d461fd11
- ESP32-S2 is a highly integrated, low-power, single-core Wi-Fi microcontroller designed to be secure and cost-effective, with a high performance and a rich set of IO capabilities.
- ESP32-S3 is a dual-core XTensa LX7 MCU, capable of running at 240 MHz. Apart from its 512 KB of internal SRAM, it also comes with integrated 2.4 GHz, 802.11 b/g/n WiFi and Bluetooth 5 (LE) connectivity that provides long-range support. It has 45 programmable GPIOs and supports a rich set of peripherals. ESP32-S3 supports larger, high-speed octal SPI flash, and PSRAM with configurable data and instruction cache.
- ESP32-C3 is a cost-effective RISC-V MCU with Wi-Fi and Bluetooth 5 (LE) connectivity for secure IoT applications.
# NodeMCU
NodeMCU is an open source Lua based firmware for the ESP32 and ESP8266 WiFi SOC from Espressif and uses an on-module flash-based SPIFFS file system. NodeMCU is implemented in C and is layered on the Espressif ESP-IDF.
official site: http://www.nodemcu.com forum: http://bbs.nodemcu.com/ source code: https://github.com/nodemcu
Setup: download: http://yunpan.cn/c3qQbdCTK7dtb 访问密码 ef05 win7 users may need cp2102 usb to uart bridge controller driver, CP210x USB to UART Bridge VCP Drivers https://www.silabs.com/products/mcu/Pages/USBtoUARTBridgeVCPDrivers.aspx
NodeMCU Amica Driver: https://www.silabs.com/products/development-tools/software/usb-to-uart-bridge-vcp-drivers Sample: WebServer https://www.teachmemicro.com/simple-nodemcu-web-server/ MessageQueue-PubSub https://www.losant.com/blog/getting-started-with-platformio-esp8266-nodemcu https://github.com/Losant/losant-mqtt-arduino/blob/master/examples/esp8266/esp8266.ino
nodemcu是基于8266,nodemcu32是基于 esp32?
# Raspberry Pi RP2040
# 51单片机和STM32单片机的区别
51单片机是对所有兼容Intel8031指令系统的单片机的统称,这一系列的单片机的始祖是Intel的8031单片机,后来随着flash ROM技术的发展,8031单片机取得了长足的进展成为了应用最广泛的8bit单片机之一,他的代表型号就是ATMEL公司的AT89系列。
STM32单片机则是ST(意法半导体)公司使用arm公司的cortex-M3为核心生产的32bit系列的单片机,他的内部资源(寄存器和外设功能)较8051、AVR和PIC都要多的多,基本上接近于计算机的CPU了,适用于手机、路由器等等。
# 操作系统
- FreeRTOS is a real-time operating system kernel for embedded devices that has been ported to 35 microcontroller platforms.
- Home Assistant Operating System Home Assistant Operating System uses Docker as Container engine. It by default deploys the Home Assistant Supervisor as a container. Home Assistant Supervisor in turn uses the Docker container engine to control Home Assistant Core and Add-Ons in separate containers. Home Assistant Operating System is not based on a regular Linux distribution like Ubuntu. It is built using Buildroot and it is optimized to run Home Assistant. It targets single board compute (SBC) devices like the Raspberry Pi or ODROID but also supports x86-64 systems with UEFI. https://github.com/home-assistant/operating-system 微信公众号 (opens new window)
# 云平台
Arduino IoT Cloud、Blynk
# 框架
单片机编程为啥要有框架? https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/8UTXyJpNqNmDWRzORihO2g
FastBee开源物联网平台: 演示地址:https://iot.fastbee.cn/ 账号密码:fastbee/123456 获取源码: https://github.com/kerwincui/FastBee
# 简单案例
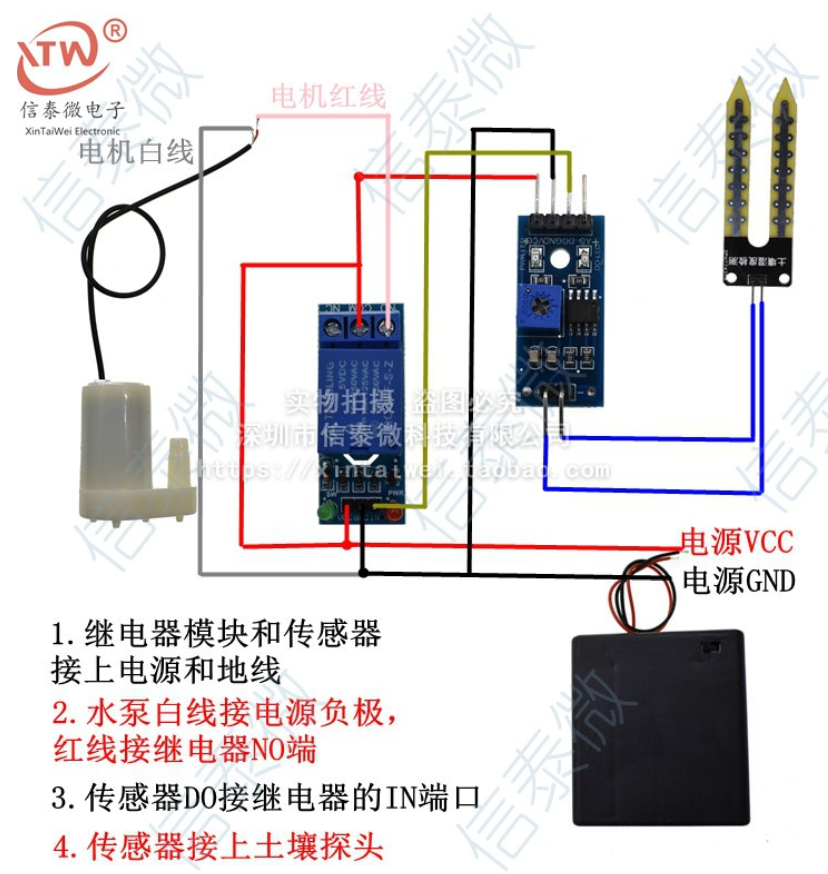
# 物联网 IOT
what? The Internet of Things - IOT is the network of physical objects - devices, vehicles, buildings and other items embedded with electronics, software, sensors, and network connectivity - that enables these objects to collect and exchange data. A global infrastructure for the information society, enabling advanced services by interconnecting(physical and virtual) things based on existing and evolving interoperable information and communication technologies. Pervasive computing+Networking
when we talk about IOT, what's in/ comes to your mind? question marks? circuit board. collect data,visualize data,analysis data,perform actions show business case: self-driven car / robot arm automation now we talk about smart city, smart nation, but from my point of view, these ideas are somehow unrealistic for now. but smart home and smart factory are relatively much more easy to achieve. At least, machines can take over such kind of tedious jobs like : https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzA3OTM2NDM2Mw==&mid=2649732684&idx=5&sn=37c3be90ebcf347d9e637066c57aed8b&scene=0#rd someone may feel worried that our jobs may be taken over by machines, but think in this way, we humans can spend more time on tasks require more creative energy.
Why? this concept came out many years ago, why iot is rising today, why now: http://iotindiamag.com/2016/08/10-reasons-iot-rising-today/ sensors developing fast, and getting cheaper https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/iot-business-boost-economy-next-decades-posted-success-scodiero?articleId=8372849347531761698 show raspberry pi & arduino price comparison main stream with these, you can quickly build up your prototype from scratch. comparison: raspberry is a computer looks not like a computer microcomputer, just like your smart phone, besides standard inputs like keysroke/camera/your voice/GPS singal/Radio singal, it also can read from all kinds of sensors it's cheap and full functional, but the downside is it's a single computer,the kernel is a microprocessor, but aruino: controller board, an old fashioned feature phone without os. Microcontrollers are designed to perform specific tasks. Specific means applications where the relationship of input and output is defined. for example, the drone, quadrocopter, 6 channles, yaw, rotate, forward/backward... fly control is a microcontroller https://www.quora.com/How-feasible-is-it-to-use-a-Raspberry-Pi-as-the-control-system-on-an-autonomously-flying-quadcopter http://www.engineersgarage.com/tutorials/difference-between-microprocessor-and-microcontroller
How? I will show you a video https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0kzjqBacF1k https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=onZ4KMM94yI because we can do it? that's not enough, why we build it? back to 'auto driven car', shared economy
if the car hit someone or another car, who will be responsible for it? programmer? liabilities must be clear. right? agree?
business value, security, risks emerged
how are we going to build IOT system. I would like to introduce some tools here. raspberry pi&arduino facilitate us play with IOT.
tools facilitate your iot development python script i2tool https://www.shodan.io/
The last job on Earth: imagining a fully automated world – video https://www.theguardian.com/sustainable-business/video/2016/feb/17/last-job-on-earth-automation-robots-unemployment-animation-video
LPWAN+CNN低功耗加卷积网络 https://www.matchx.io/getstarted/
IoT Live Demo: 100.000 Connected Cars With Kubernetes, Kafka, MQTT, TensorFlow https://dzone.com/articles/iot-live-demo-100000-connected-cars-with-kubernete
# 厂商
长江智动 http://www.cjmcu.com/
# ref:
单片机里的程序是如何运行的? (opens new window) https://www.cnblogs.com/hyper99
Blogs&Forum https://www.teachmemicro.com/tutorials/
废物利用:改造旧充电宝 https://ezo.biz/Technolog/fix-powerbank.html 树莓派UPS:用充电宝改造的不间断电源 https://www.quwj.com/2018/12/13/ups-for-raspberry-pi.html
微雪学堂 http://www.waveshare.net/study/portal.php 物联网快速开发(基础篇) http://edu.csdn.net/course/detail/923 DemoBoard 开发板专题: raspberrypi 树莓派 https://www.raspberrypi.org/ https://www.pretzellogix.net/2015/01/14/the-best-raspberry-pi-starter-kits-compared-and-reviewed/ https://learn.adafruit.com/category/learn-raspberry-pi nodemcu http://www.nodemcu.com/ http://www.doit.am/ http://www.doit.am/ Microduino https://www.microduino.cc/ http://www.leiphone.com/tag/Microduino http://www.geekpark.net/topics/212704 arduino https://www.arduino.cc/ http://www.leiphone.com/tag/arduino TinyDuino
物联网工具 https://www.relayr.io/ http://nodered.org/ http://thethingsystem.com/
Shopping: http://www.ickey.cn/
开源工具: https://processing.org/tutorials/electronics/ http://www.datamation.com/open-source/35-open-source-tools-for-the-internet-of-things-1.html
产品: http://www.faxsun.com/ http://skyworksas.com/eedu/
http://36kr.com/p/5038505.html http://www.leiphone.com/news/201509/vp9Fi4Oeuwgx0CU6.html
单片机入门 http://www.elecfans.com/soft/33/2012/20120821285311.html 51、AVR、PIC、MSP430、ARM、DSP http://www.eeskill.com/article/index/id/20643 51单片机 vs 8051 ESP8266 http://www.esp8266.com/ nodemcu based on ESP8266 Arduino 与树莓派 Raspberry P http://www.zhihu.com/question/20755144 https://www.quora.com/What-can-the-Arduino-do-that-the-Raspberry-Pi-cant-and-vice-versa arduino or 8051 https://www.quora.com/Which-is-better-arduino-or-8051-microcontroller
http://www.elecfans.com/zhuanti/DIY_Robot.html http://www.leiphone.com/news/201501/iSmdLPJvuDFiJuVF.html http://www.instructables.com/contest/robotics2015/
MEETINGS: http://solidcon.com/internet-of-things-2015/public/schedule/detail/40797
automated dinosaur game bot https://www.reddit.com/r/arduino/comments/c5o4kf/i_made_an_automated_dinosaur_game_bot/ LDR sensor 光敏电阻
https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/fsCQdJOYUs0BcjfSUmvJvg
为了实现上网自由,我做了一个多功能串口服务器 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/_5b4g5MvrqcCJaA6NyeB8A