回目录 《架构》
# Where are we?
以java开发举例:
- 第一层 操作系统
- 第二层 开源的openjdk或收费的jdk 包含jvm虚拟机 java security math等基础包
- 第三层 公司或个人基于java开发的类库中间件产品包括服务端产品以及客户端框架等等,甚至有如spring cloud一条龙全家桶
- 第四层 架构师基于选择的技术栈设计的特定业务运行的底层框架或者引擎或者核心代码,比如基于kafka构建的消息队列处理引擎
- 第五层 普通开发者基于核心引擎框架开发业务代码
理想情况下大家各司其职,上一层通过文档理解下一层的思想,但是实际很骨感:
- 第二层 遇到过openjdk security padding的错误,跟其他机器的padding策略不一致,造成无法tls握手成功
- 第三层 比如kafka的文档相对完善但是有些部分并不友好,有时候也需要稍微扒一下源码加深理解,还有些文档相当不友好比如Disruptor不断的强调其单线程的设计思想,如果不看源码我还以为默认就是single writer mode,结果默认是multiple producers+lock strategy;如果想要深刻理解某些中间件的设计思想比如Disruptor,就需要对第二层用户态的jvm以及更下一层的os操作系统有深刻理解;
- 第四层 架构师如果对第三层理解错误或者不全面会造成写的核心代码出现漏洞,甚至是误以为市面产品达不到要求自己造出更加残缺的轮子难以维护
- 第五层 业务开发,普通开发者日常基本是copy paste的工作模式按照样例进行业务代码开发,如果出现架构师的核心代码缺乏文档或者缺乏示范用例,普通开发者甚至是高级开发者会用错误的方式绕过架构师的设计造成核心代码失效或者业务代码工作但是功能在异常情况下有问题
基本上每一层都是盲人摸象,不同的任务属性或者问题根源决定是否要停留在该层解决,盲人摸象是正常状态,不是轮子的建造者不可能对轮子有完全的了解,黑客关心的是如何在这头大象找到一条路径进入系统并实现权限控制,开发者关心的是这头大象是否能解决核心需求痛点,在实际的过程中不得不跨层研究,但是不能深陷其中,因为不可能重造每个轮子。
我们谈过分布式系统,谈过并发和并行, 也谈过微服务框架和spring cloud微服务框架, 前面说了很多“系统system”、“框架Framework”,现在来站的更高一层谈谈“架构architecture”(跟前面提到第四层架构师的工作不同,这里是更高层次的抽象)
谈到架构默认就是 OOA - object-oriented architecture
面向过程是算法模型,面向对象是交互模型。 面向对象的封装,继承,多态是在架构起到很大作用,按对象和类形成多种设计模式。这是架构的核心。
面向切面 AOP(Aspect-Oriented Programming) complements OOP by enabling modularity of cross-cutting concerns. The Key unit of Modularity(breaking of code into different modules) in Aspect-Oriented Programming is Aspect. one of the major advantages of AOP is that it allows developers to concentrate on business logic. It is more convenient to use because changes need to be done in only one place. Note: Cross cutting concerns are one of the concerns in any application such as logging, security, caching, etc. They are present in one part of the program but they may affect other parts of the program too. AOP is used along with Oop as it also works around classes and objects, etc. We can also say that Oop is a basic term for AOP. Different Frameworks used in Aop are AspectJ, JBoss, and Spring. AOP makes the program loosely coupled. AOP separates business logic from cross-cutting concerns.
# 1. Terminology
architecture VS framework 首先架构跟框架的关系,简单说就是架构是设计蓝图, 框架是摸得到看得到的建筑脚手架和钢筋结构;一个是概念类,一个是实例;
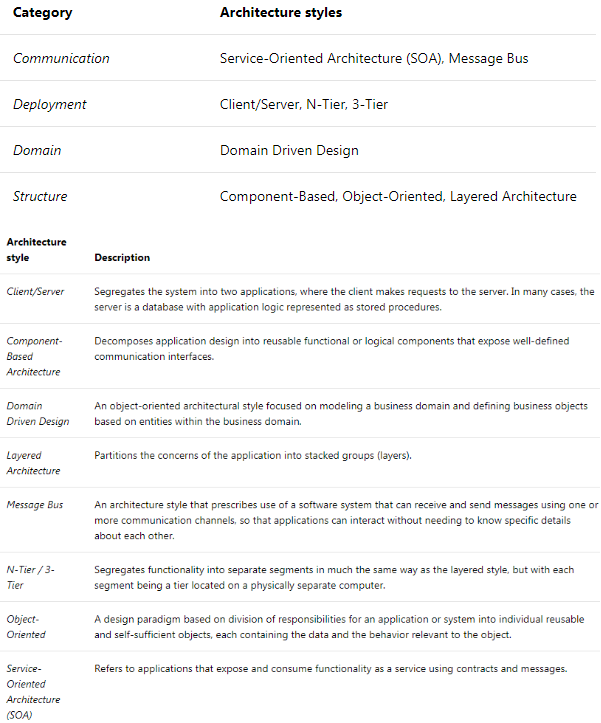
**Architectural Styles vs. Architectural Patterns vs. Design Patterns ** https://herbertograca.com/2017/07/28/architectural-styles-vs-architectural-patterns-vs-design-patterns/
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/4243187/whats-the-difference-between-design-patterns-and-architectural-patterns
patterns vs frameworks Patterns: facilitate reuse of architecture and design in similar contexts Framework: facilitate reuse of detailed design and code in related applications.
Levels of Abstraction--Patterns can be classified by the level of abstraction of the problem they solve: Architecture - organizes a system as a set of communicating subsystems. Design - solves a design problem using a set of communicating design objects Framework - solves a specific domain problem using a set of communicating design patterns. Implementation - solves an implementation problem using platform/language-specific features
# 2. Principles
todo: https://drive.google.com/file/d/0B01BZttEuPVvR2V5QnZXXzlTYUE/view?ths=true
Single-Responsibility Separate of concern (interception,cross-cutting concerns: logging, auditing, access control, validation) High level objects don’t care the detail of lower level objects ( IOC) Liskov substitution principle Open/Closed Principle - programming to an interface - Loose coupling responsibility and segregation
# 3. High level design - Architectural Patterns and Styles
# 3.1 Architecture Style
Microsoft Application Architecture Guide, 2nd Edition https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/msp-n-p/ff650706(v%3dpandp.10)
https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/previous-versions/msp-n-p/ee658117(v=pandp.10)
https://github.com/mspnp
# 3.2 Samples
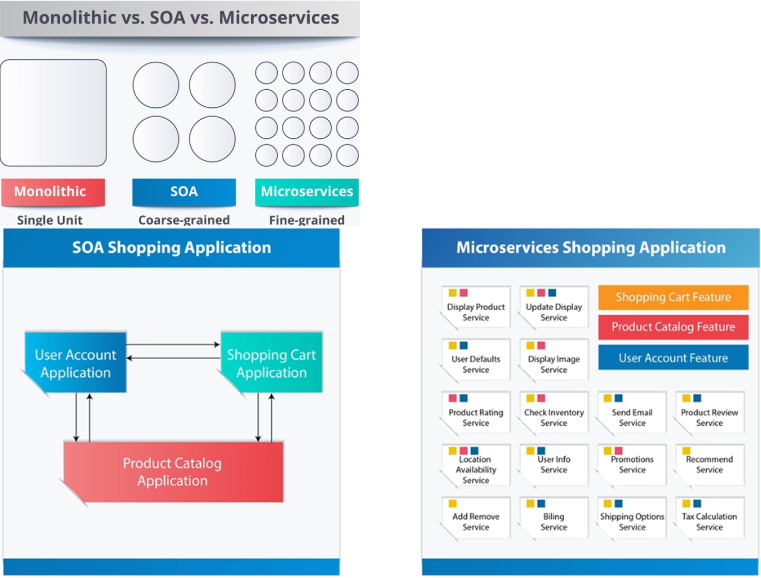
# 3.2.1 SOA VS Microservices
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EpyPFnjue38
# 3.2.2 CQRS - Command-Query Responsibility Segregation
Principle: responsibility and segregation
https://kalele.io/blog-posts/really-simple-cqrs/ https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/cqrs
# 4. Detail design - technical architecture
# 4.1 N-tier
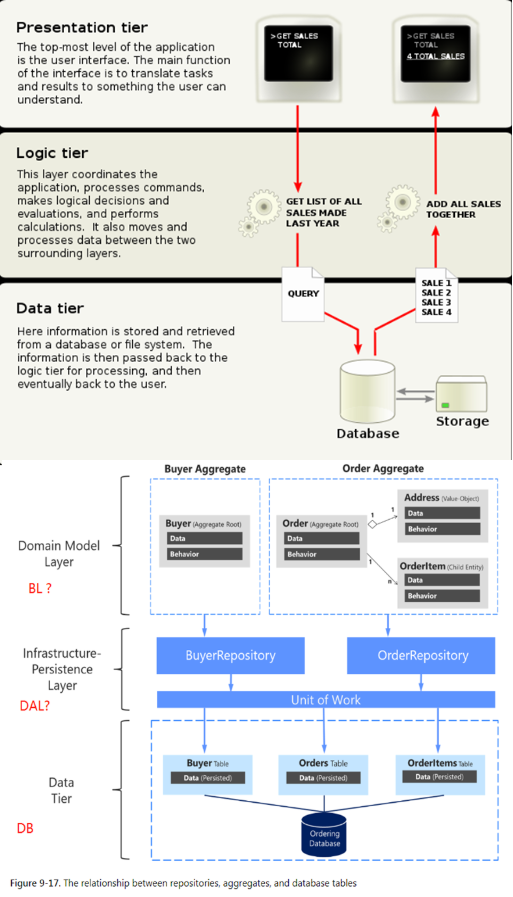
# 4.2 Layer and related concepts
Presentation Layer MVC, Domain Object(Domain objects can have logic (depending on whether you are using domain-driven design or have anemic data model) and they are usually related to the database structure.) Application layer / service layer Business Layer Business Object DTO (DTOs don't have any logic. They only have fields (state). They are used when transferring data from one layer/subsystem to another) Data Access Layer DAO The Data Access Layer(DAL) is the layer of a system that exists between the business logic layer and the persistence / storage layer. A DAL might be a single class, or it might be composed of multiple Data Access Objects(DAOs). It may have a facade over the top for the business layer to talk to, hiding the complexity of the data access logic. It might be a third-party object-relational mapping tool(ORM) such as Hibernate. Persistence Layer ORM(Entity framework) (POCO/entity)
1. MVC framework is for Presentation layer
2. About Persistence layer
a. PL == DAL
b. PL == Storage, BL - DAL - PL
what is the difference between 3 tier architecture and a mvc? https://stackoverflow.com/questions/10739914/what-is-the-difference-between-3-tier-architecture-and-a-mvc
At first glance, the three tiers may seem similar to the model-view-controller (MVC) concept; however, topologically they are different. A fundamental rule in a three tier architecture is the client tier never communicates directly with the data tier; in a three-tier model all communication must pass through the middle tier. Conceptually the three-tier architecture is linear. However, the model-view-controller MVC architecture is triangular: the view sends updates to the controller, the controller updates the model, and the view gets updated directly from the model.
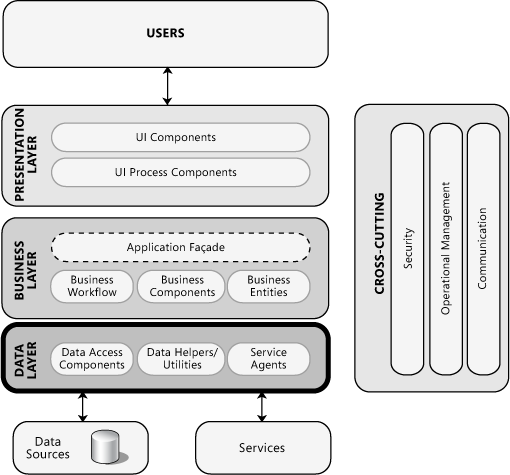
# 4.3 BL/DAL/PL - patterns
Domain layer(Domain Driven Design) Domain Module Pattern Table Module Pattern Transaction Script Pattern
BL/DAL:
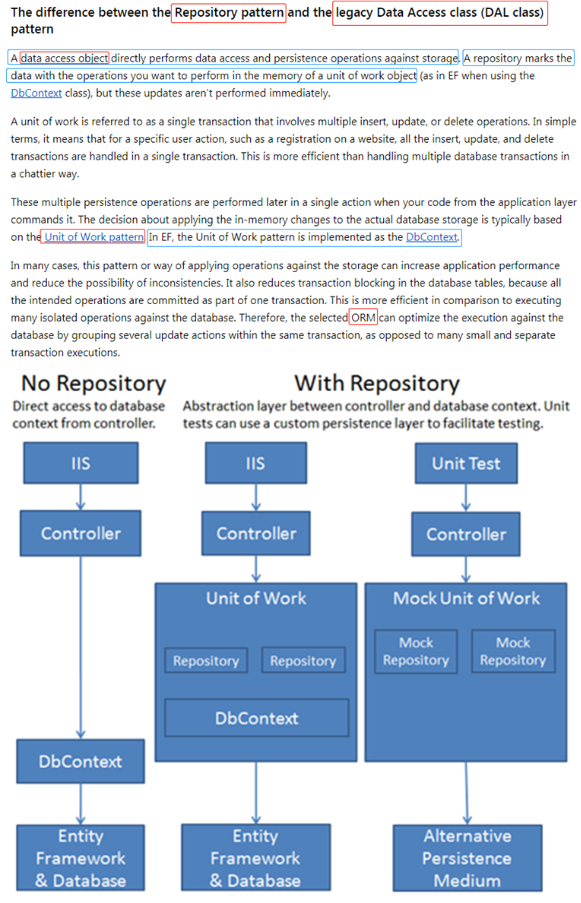
Data Layer: DAO pattern VS Repository(+unitOfWork) pattern
 Key Word: Long connection, short connection, connection pool, connection time out,thread safe
DTO, DAO, Repository, ORM,
leaky abstraction,code duplication,abstraction inversion
Key Word: Long connection, short connection, connection pool, connection time out,thread safe
DTO, DAO, Repository, ORM,
leaky abstraction,code duplication,abstraction inversion
Concerns: resource consuming(frequency of opening/closing connection), too many calculation logic in DB(SP) may cause time out issue, concurrency issue,avoid sharing connections between threads(seems no need to concern this,connection drivers already handle it very well) leaky abstraction(The SQL language abstracts away the procedural steps for querying a database, allowing one to merely define what one wants. But certain SQL queries are thousands of times slower than other logically equivalent queries. On an even higher level of abstraction, ORM systems, which isolate object-oriented code from the implementation of object persistence using a relational database, still force the programmer to think in terms of databases, tables, and native SQL queries as soon as performance of ORM-generated queries becomes a concern.)
Tools: DB Profile, db connector Framework: ORM: ORMLite, Asp.Net Entity Framework, Comparison of object-relational mapping software (opens new window) Common Data Access Layer: ClownFish MySQL Connector/Net (opens new window) Design Guidelines&Patterns: Chapter 8: Data Layer Guidelines (opens new window) Appendix C: Data Access Technology Matrix (opens new window) Writing a Portable Data Access Layer (opens new window) Mapping Objects to Relational Databases: O/R Mapping In Detail (opens new window) Decisions on DAO pattern VS Repository(+unitOfWork) pattern My previous school assignment was using DAO pattern. JSP Servlets send http request, controllers process request, forward to other controllers if needed, controllers call delegates which will invoke relevant services, services call dao(dao interface implemented by daoImpl), dao will do the crud operation. DAO would be considered closer to the database, often table-centric. Repository would be considered closer to the Domain, dealing only in Aggregate Roots. A Repository could be implemented using DAO's, but you wouldn't do the opposite. --quotes from stackoverflow Datalayer Decisions (Repository, DAO, Services) in Domain-Driven-Design Applications (opens new window) DB Features: MongoDB: Support asynchronous connection
references: SQL Server Connection Pooling (ADO.NET) (opens new window) Go's Connection Pool, Retries, and Timeouts (opens new window) ClownFish:比手写代码还快的通用数据访问层 (opens new window) some misunderstanding and arguments: DAO vs ORM(hibernate) pattern (opens new window)
Data Access Layer to Business Layer: Repository Pattern:
Key Focus: 1.Loosely coupled system : components have little or no knowledge about the rest of the components in the application. 2.Ease of maintain Advantage: 1.Different components can be changed in isolation without affecting the rest of the components thus making application easier to maintain. 2.It is more suited to the agile methodology in which changes happen very frequently thus tight coupling will not allow future enhancement. 3.Creating mock tests is easier as the actual objects can be easily replaced with mock objects.
question: repository vs dal/orm ? repository with DDD? repository and business logic ? dbcontext vs repository?
from http://stackoverflow.com/questions/14092234/how-does-the-repository-pattern-differ-from-a-simple-data-access-layer::
Take a look at the "Using the IQueryable interface" section and beyond at Extending and Enhancing the Orders and Registrations Bounded Context. It provides an insightful and balanced discussion of DAO/Repository implementations. As subsequently highlighted by Bob Horn, the Persistence Patterns articles summarises that: [highlight]Basically, the Repository pattern just means putting a façade over your persistence system so that you can shield the rest of your application code from having to know how persistence works.[/highlight] In general I agree with author's statements, but I'd like to add some details Difference between Repository and DAL/ORM that first not only abstracts the persistence mechanism, but also provides collection-like interface for accessing domain objects … andisolates domain objects from details of the database access code: Differences For external layers, such as Business Logic: ● Helps to avoid leaky abstraction. External layers depend on abstraction of Repository, rather than a specific implementation of DAL/ORM. Thus you could avoid all infrastructure and logical dependencies while working with Repository. ● operates with domain objects, rather then a instances of POJO/POCO/DTO ● CRUD operations applied to collection-like interface provided by Repository, rather then specificDAL/ORM methods. For example .net: working with collection that implements IEnumerable, rather then entity-framework context or nhibernate session Similarities Repository contains DAL/ORM underneath and serves same purpose
From msdn
Use a repository to separate the logic that retrieves the data and maps it to the entity model from the business logic that acts on the model. The business logic should be agnostic to the type of data that comprises the data source layer. For example, the data source layer can be a database, a SharePoint list, or a Web service. The repository mediates between the data source layer and the business layers of the application. It queries the data source for the data, maps the data from the data source to a business entity, and persists changes in the business entity to the data source. A repository separates the business logic from the interactions with the underlying data source or Web service. The separation between the data and business tiers has three benefits: ● It centralizes the data logic or Web service access logic. ● It provides a substitution point for the unit tests. ● It provides a flexible architecture that can be adapted as the overall design of the application evolves. There are two ways that the repository can query business entities. It can submit a query object to the client's business logic or it can use methods that specify the business criteria. In the latter case, the repository forms the query on the client's behalf. The repository returns a matching set of entities that satisfy the query. The following diagram shows the interactions of the repository with the client and the data source. Interactions of the repository
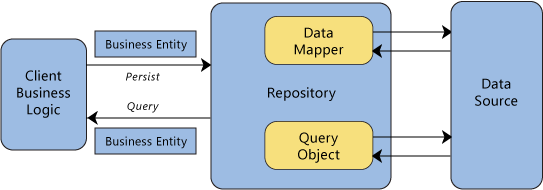 EF/Nhibernate/Dapper already using repository pattern ? http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19796223/repository-vs-service-pattern-in-dal-ef-and-dapper
https://www.codeproject.com/Tips/572761/Generic-repository-pattern-using-EF-with-Dependenc
ORM VS SQL/stored procedures
Repository Pattern VS Sql
Respository Pattern & Unit-of-work Pattern
http://geekswithblogs.net/Aligned/archive/2013/03/12/herersquos-how-the-unit-of-work-is-useful-to-me.aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/dd882510.aspx
http://codetunnel.io/how-to-combine-the-unit-of-work-pattern-and-repository-pattern-in-an-easy-and-intuitive-way/
Unit of Work Concurrency
EF/Nhibernate/Dapper already using repository pattern ? http://stackoverflow.com/questions/19796223/repository-vs-service-pattern-in-dal-ef-and-dapper
https://www.codeproject.com/Tips/572761/Generic-repository-pattern-using-EF-with-Dependenc
ORM VS SQL/stored procedures
Repository Pattern VS Sql
Respository Pattern & Unit-of-work Pattern
http://geekswithblogs.net/Aligned/archive/2013/03/12/herersquos-how-the-unit-of-work-is-useful-to-me.aspx
https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/magazine/dd882510.aspx
http://codetunnel.io/how-to-combine-the-unit-of-work-pattern-and-repository-pattern-in-an-easy-and-intuitive-way/
Unit of Work Concurrency
Generic Unit of Work & (Extensible) Repositories Framework https://genericunitofworkandrepositories.codeplex.com/ Generic Repository and Unit of Work Pattern, Entity Framework, Unit Testing, Autofac IoC Container and ASP.NET MVC http://techbrij.com/generic-repository-unit-of-work-entity-framework-unit-testing-asp-net-mvc The Repository Pattern https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ff649690.aspx Design pattern – Inversion of control and Dependency injection http://www.codeproject.com/Articles/29271/Design-pattern-Inversion-of-control-and-Dependency Say No to the Repository Pattern in your DAL http://tech.pro/blog/1191/say-no-to-the-repository-pattern-in-your-dal https://cockneycoder.wordpress.com/2013/04/07/why-entity-framework-renders-the-repository-pattern-obsolete/
Business Layer - Facade Pattern:
Provide a unified interface to a set of interfaces in a subsystem. Façade defines a higher-level interface that makes the subsystem easier to use.
Sessions in ASP.NET MVC using Dependency Injection Don’t Do Role-Based Authorization Checks; Do Activity-Based Checks
Customer Relationship Management (CRM)
Cross Cutting Layer - AOP
AutoFac/Unity Resolver Container ILifetimescope http://blog.darkthread.net/post-2013-11-03-autofac-notes-3-lifetime-scope.aspx http://www.asp.net/web-api/overview/advanced/dependency-injection
Thinking out of box: DDD + EVENT BUS EVENT HANDLER + REPOSITORY The false myth of encapsulating data access in the DAL db connection long or short? default pool? queue? static class pros&cons (concurrency cache)
**DAL/PL: ** Data Mapper Pattern, ORM Pattern(entity framework or NHibernate), DAO Pattern
**PL/DB: ** ORM (vs Stored Procedure https://rob.conery.io/2015/02/20/its-time-to-get-over-that-stored-procedure-aversion-you-have/) .NET 主流的ORM:https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011676744 Dapper ClownFish:比手写代码还快的通用数据访问层 https://www.cnblogs.com/fish-li/archive/2012/07/17/ClownFish.html#!comments Entity framework (buit on ADO.NET https://stackoverflow.com/questions/22328889/entityframework-vs-pure-ado-net, https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40506382/what-is-the-difference-between-an-orm-and-ado-net)
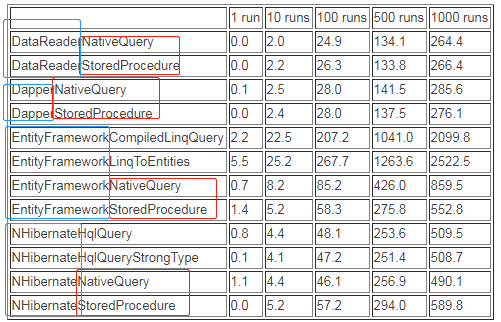
Perfomance DataReaders, Entity Framework, NHibernate and Dapper http://www.luisrocha.net/2011/12/data-access-performance-comparison-in.html https://github.com/lerocha/DotNetDataAccessPerformance/tree/c2a71ede37f3dd9ee437221a84054e504773b626
Refer: Pattern vs Data Mapper Pattern http://www.bradoncode.com/blog/2013/08/repository-vs-domain-model-vs-data.html
Generic repository pattern using EF with Dependency injection https://www.codeproject.com/Tips/572761/Generic-repository-pattern-using-EF-with-Dependenc Designing the infrastructure persistence layer https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/dotnet/standard/microservices-architecture/microservice-ddd-cqrs-patterns/infrastructure-persistence-layer-design DAL、DAO、ORM、Active Record辨析 https://blog.csdn.net/suiye/article/details/7824943
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6732124/difference-between-transfer-objects-and-domain-objects PO, VO, TO, BO, DAO, POJO https://www.programering.com/a/MDM2kjNwATc.html DTO, DAO, and VO in Java https://www.quora.com/What-is-DTO-DAO-and-VO-in-Java
Repository pattern vs DAO pattern 4 Common Mistakes with the Repository Pattern https://programmingwithmosh.com/entity-framework/common-mistakes-with-the-repository-pattern/ Don’t use DAO, use Repository https://thinkinginobjects.com/2012/08/26/dont-use-dao-use-repository/
https://www.thoughtfulcode.com/orm-active-record-vs-data-mapper/ https://social.msdn.microsoft.com/Forums/en-US/aed501f8-d7e4-40d9-8a98-32c5cdc78243/help-with-the-orm-vs-stored-procedures-argument?forum=architecturegeneral https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-pros-and-cons-of-using-SQL-Stored-Procs-versus-ORM-for-database-quering DAO Pattern https://www.baeldung.com/java-dao-pattern
# 4.4 Communication Style
Webservice VS RPC, refer to java实用基础 IPC (microkernel) https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Inter-process_communication
# 5.Network/Physical design
《参考network部分内容》 DMZ区面向公网,核心区托管数据库等重要信息,办公区(公司内网)存放公司重要的内部信息(财务、法律文书、人力资源等),外网和办公区都只能通过DMZ访问核心区数据, 办公区跟外网需要做防火墙、硬盘加密;
# 6.实际经验:架构和框架演进
JAVA架构师学习路线图 (opens new window)
Web framework https://iris-go.com/donate
architect will get evolved along with business growing when critical issues emerge. It's impossible to design an architect which will keep unchanged for example, at the beginning we are limited to one server, some design can not be adopt to such situation which may be time consuming and meaningless. Layered Application Guidelines https://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/ee658109.aspx#ServicesLayers
学习服务端高并发分布式架构演进之路 (opens new window)
How a First Time CTO Can Choose the Right Techstack for Their Startup (opens new window) 
对话独角兽得物(毒)App CTO 陈思淼:组建技术团队的十件事 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/TNgbzCzqSCWy_ZcK_ZZC_w
Why We Leverage Multi-tenancy in Uber’s Microservice Architecture https://eng.uber.com/multitenancy-microservice-architecture/
.NET技术+25台服务器怎样支撑世界第54大网站 https://www.csdn.net/article/2014-07-22/2820774-stackoverflow-update-560m-pageviews-a-month-25-servers
可伸缩性最佳实践:来自eBay的经验 https://kb.cnblogs.com/page/157745/