回目录 《spring分布式微服务入门》
我们今天来梳理归纳一下java的开发框架,首先为什么需要框架?
- 节约成本
不可能所有东西都从零造起,成本太高,spring融合了市场上大部分的开源项目,可以直接‘免费’利用
- 安全考虑
当前网络环境复杂,攻击无处不在,成熟的框架已经被主流公司接受使用,很多坑已经被前人踩过,站在巨人的肩膀上是明智之选,不用交额外的智商税
- 业务发展
spring boot不只是框架,还是spring cloud的一部分,spring cloud是微服务架构的一套完整是有序框架集合, spring是建筑材料,spring boot是脚手架,spring cloud就是行业规范,采用行业规范的开发模式有利于IT更好的服务business和业务拓展
# 1. Overview
# 1.1 SOA?微服务?
我们常说用spring boot构建微服务,又说spring cloud构建微服务,他们到底是什么关系?
引用我在微服务架构一章中关于微服务的解释:
首先微服务是啥,微服务首先是一种架构思想, 首先最初的很多产品都是单体monolithic架构,所有的服务都紧紧耦合在一个解决方案中,难以扩展,只能通过加cpu加内存的方式扩展,举例一个电商平台, 刚开始所有功能都放在一个解决方案,比如托管在Apache的一个war或者托管在iis的一个.net mvc程序, 随着项目的发展,团队的壮大,单体会变得庞大而难以维护,我们需要将功能拆分开,比如商家系统、买家系统、管理后台系统等,面向业务或者叫服务切分,分而治之,这种粒度的就是SOA架构, 其显著缺点: 1.从技术的角度,其实业务的切分在技术层面上仍然会有大面积的重叠,因此如果业务切割的不好,形成各种依赖,有可能在修改时牵一发而动全身 2.从业务角度来说,由于是业务的切分,所以当需要发展新的业务时就需要重新构建一个完全新的服务,不利于基于业务创新和发现 所以引入微服务的概念,微服务进一步将服务自底向上或自上到下做更细的切分,最下面是基础系统服务(短信、邮件、存储、缓存、消息推送等),中间是共享服务(支付系统、订单系统、仓储系统等), 最上面则是业务层(零售系统、团购系统、采购系统),比如我们要加一个闪购业务也是很轻松的,不用从底到上再来一遍,只需要基于基础服务和共享服务做业务开发
# 1.2 SpringBoot SpringCloud
Rod Johnson创建的开源框架interface21是 Spring的前身,随着spring从小框架发展为大而全的企业级框架,spring对市面上主流的开源软件都有了对应的组件支持, 人们发现使用spring项目开发变得难用,往往需要引入很多配置,难以维护容易出错,spring因此冠名配置地狱;
Spring boot是基于spring抽象出来的开发框架,是快速开发的scaffold脚手架,spring boot丧心病狂的运用依赖注入DI的思想,配置文件可以auto config,用户只需要定义好需要的bean, spring boot的大容器会进行管理,丰富的starter让开发者可以集中精力在业务逻辑上而不是依赖的配置管理;
依赖注入的思想简单来说就比如小孩要从冰箱拿吃的,但是不应该自己拿,应该交由家长来处理,因为小孩可能会忘记关冰箱门,可能会打乱冰箱里面其他东西,总之小孩这个组件应该只关心自己的事情,不要做这些大人才能做好的事情, 所以从冰箱拿东西吃要交由家长处理,在spring boot中,小孩可以采用构造函数注入或者setter based如autowired方式来使用家长组件;
spring-cloud是一套完整的微服务解决方案,是一系列框架的有序集合,提供了分布式的各种解决方案: 服务开发(springBoot spring springMVC)、服务配置中心(SpringCloudConfig Chef)、服务发现(eureka zookeeper)、服务调用(rest rpc)、负载均衡(ribbon nginx)、服务熔断器、服务监控、服务部署(docker kubernetes)、消息队列(kafka rabbitmq)
所以可见一个个具体的微服务(这里说的微服务就是具体的一个个应用了)是用spring boot开发,spring cloud又提供了服务配置中心、服务注册发现等所谓微服务治理的解决方案
1.spring boot是一个快速开发框架,应该说是spring系列的集大成者。我们可以简单的把spring boot理解成是一个快速开发的脚手架。 2.微服务往往是指Spring Cloud,微服务是一个框架。 3.如果把基于微服务架构的软件比作是一个大厦,钢筋混凝土结构就是spring cloud,而砖头瓦块等就是spring boot。微服务的一个一个服务是用spring boot开发的,spring cloud提供服务注册与发现、负载均衡、API网管、熔断路由、配置中心等框架性服务,当然一个完整的微服务系统有很多其他的内容,例如服务拆分、监控、限流降级等等。
dubbo常常拿来跟spring cloud对比,实际目前已经不具有可比性了,Dubbo现在只是一款高性能的Java RPC框架,只能跟spring cloud集合中的服务调用部分REST RPC做对比
spring cloud alibaba是spring cloud的其中一个微服务解决方案
# 2. Spring Framework
https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/current/spring-framework-reference/ Project generator https://start.spring.io/ https://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring/spring_quick_guide.htm https://docs.spring.io/spring/docs/5.1.6.RELEASE/spring-framework-reference/ (spring boot 2.1.4 depend on spring 5.1.6)
# architecture
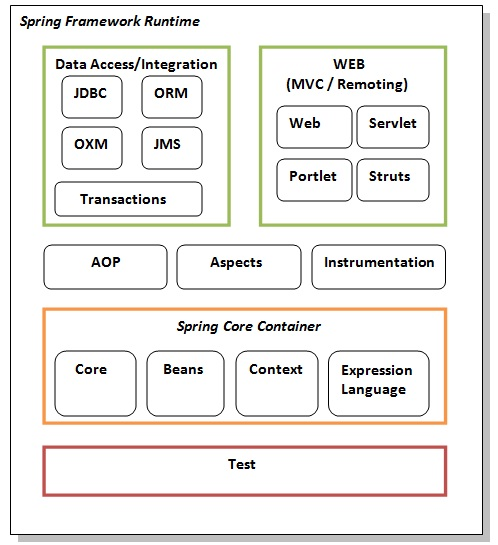
# Beans
Spring uses the class name and converts the first letter to lowercase.
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-bean-names
# Autowired
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-autowire
# Spring AOP
# 代理
动态代理 静态代理 cglib 通过使用proxy设计模式 远程调用看起来像本地调用 增强类 如mybatis,fastclassbyspringcglib
保存生成的动态代理类或者增强类
@EnableAsync
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.setProperty(DebuggingClassWriter.DEBUG_LOCATION_PROPERTY,"C:\\Workspace\\debug");
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
# Spring MVC
spring mvc 处理流程源码解析 (opens new window)
# 3.SpringBoot Framework
While the Spring framework focuses on providing flexibility to you, Spring Boot aims to shorten the code length and provide you with the easiest way to develop a web application. With annotation configuration and default codes, Spring Boot shortens the time involved in developing an application. https://www.tutorialspoint.com/spring_boot/index.htm
https://spring.io/tools3/sts/all
guides: https://spring.io/guides#gs https://spring.io/guides/gs/spring-boot/ Starters samples code: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.4.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/#using-boot-starter https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/tree/master/spring-boot-samples Docs: https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/2.1.4.RELEASE/reference/htmlsingle/ Unit test: https://stackabuse.com/how-to-test-a-spring-boot-application/ https://docs.spring.io/spring-boot/docs/current/reference/html/boot-features-testing.html
Spring Boot中如何干掉过多的if else! https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/Uf8KGTbNcuDtwIlpMJnaXg
Spring boot web default web server: Asp.net default is IIS Express, how about spring boot web? Tomcat vs. Jetty vs. Undertow: Comparison of Spring Boot Embedded Servlet Containers https://examples.javacodegeeks.com/enterprise-java/spring/tomcat-vs-jetty-vs-undertow-comparison-of-spring-boot-embedded-servlet-containers/
# 3.1 Plugins
** spring-boot-maven-plugin
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>${spring-boot-maven-plugin.version}</version>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
这个plugin很重要,其中的repackage是把java程序打包成为executable程序,否则就只是普通的jar包(纠正:实际测试即使没用这个plugin,pom parent继承了org.springframework.boot,一样可以生成可执行程序,原因见后面关于这个包的解释),不能直接执行,比如hello world,需要javac之后生成的class,用java *.class才能执行,而且如果java程序比较负责,依赖了外部的包,还要给出classpath或libpath,极其麻烦,maven本身就是包管理器,最基本的职责就是mvn package打成普通的jar包,然后mvn install到本地.m2 repository,然后mvn deploy到远程的repository,当需要运行的时候就是用前面提到的java命令执行,当然也可以直接用mvn执行,好处是mvn会自动去.m2下面找到依赖的包, mvn exec:java -Dexec.mainClass="com.example.Main" -Dexec.args="arg0 arg1",可以看到mvn实际也就是调用java命令 首先使用这个plugin的情况下,正常的mvn clean package,生成XXX-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar和XXX-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar.origninal: 可以重命名一下orignial为jar,反编译对比下:
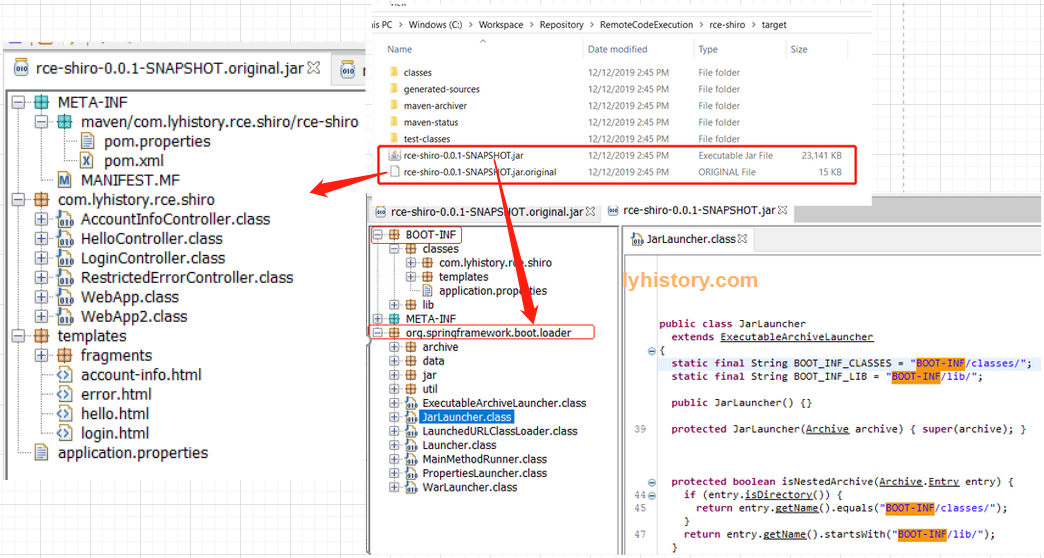
对比可以看到,普通的jar包里面的东西被再次包入了BOOT-INF,然后增加了一个org.springframework.boot.loader的启动包 执行方法: project里:mvn spring-boot:run 打成包后:java -server -jar XXXX.jar --spring.config.location=/config/
这里居然还有个比较傻逼的比较 https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-run-maven-vs-executable-jar 有点意思,还有人这么较真
然后我好奇测试了下mvn最原始的打包plugin,看打成一个fat jar会如何
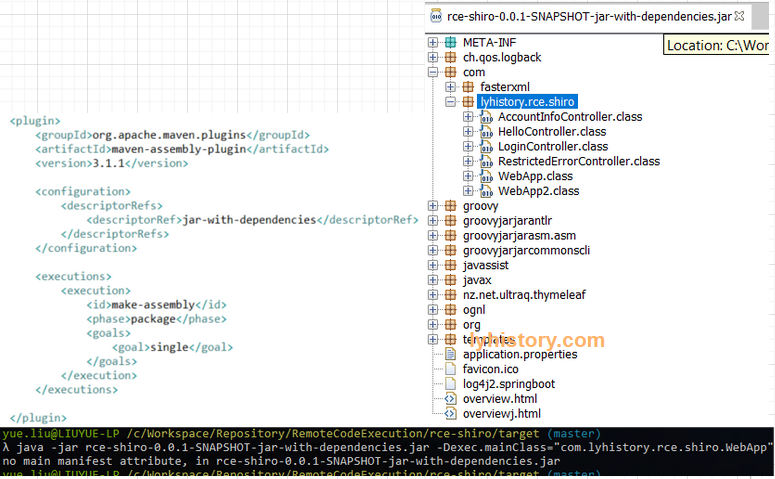 无法运行,估计是缺少springboot的上下文,spring boot的程序自然真正的入口应该是spring boot那个loader,加了annotation的那个所谓的入口main实际只是为spring boot loader准备的入口;
无法运行,估计是缺少springboot的上下文,spring boot的程序自然真正的入口应该是spring boot那个loader,加了annotation的那个所谓的入口main实际只是为spring boot loader准备的入口;
** maven-enforcer-plugin 这个是用来检查依赖问题的 mvn enforcer:enforce
# 3.2 Dependencies
Parent org.springframework.boot https://www.baeldung.com/spring-boot-dependency-management-custom-parent
继承两种方式: 直接写在parent里面; 写在dependencymanagement里面
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>1.5.6.RELEASE</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
如果没有继承org.springframework.boot,如果有多个入口方法,在pom中指定:
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<mainClass>com.lyhistory.rce.shiro.WebApp</mainClass>
</configuration>
<executions>
<execution>
<goals>
<goal>repackage</goal>
</goals>
</execution>
</executions>
</plugin>
如果继承org.springframework.boot,如果有多个入口方法,就多一种方式,在pom中指定:
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>1.5.9.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<properties>
<start-class>com.xx.xx</start-class>
</properties>
# 3.3 Integration
# 3.3.1 redis
@Autowired Private RedisTemplate redisTemplate; https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/issues/7238
一文搞定 Spring Data Redis 详解及实战 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1349818 SpringBoot下Redis相关配置是如何被初始化的 https://my.oschina.net/u/3866531/blog/1858069
Which type of injection?? 深度解析SpringBoot2.x整合Spring-Data-Redis https://www.itcodemonkey.com/article/13627.html
# 3.3.2 Shiro
# more
Thymeleaf https://www.baeldung.com/thymeleaf-in-spring-mvc
# 4. Spring Cloud
spring cloud定义了接口标准,然后各家各组件做了不同实现; (opens new window)
# 从总体上看:
- 从入口开始,DNS动态解析 - -> 机房内负载均衡(LVS+Keepalived) 动静分离可以放这里做,
静态找FastDFS集群(便宜)或cdn服务(贵); 动态则进入下面流量网关
LVS的virtual ip概念,大概是一个数据包发送给192.168.1.1这个服务器,但是负载均衡给了192.168.1.2这个服务器,按照TCP协议,参考我在network的讲解,2这个服务器应该拒绝这个包,因此才引入了VIP的概念;
然后进入流量网关(强调性能)=路由+waf+负载 不是用纯的nginx,一般是用基于netty的nginx做负载均衡,拦截无效非法流量/定向流量分发(挡爬虫、攻击、频控),此处可以放WAF Kona Openresty(nginx+lua) 定向流量分发(一致性哈希) 数亿万个文件 item.jd.com/1234.html hash(1234) mod 服务器个数 引入流量倾斜问题,秒杀(水平扩展热门产品所在的服务器)
然后进入业务网关(强调功能) 一般是基于filter的Netfix zuul和spring cloud gateway,权限认证比如spring security+jwt或者CAS也可以放这里
netty的性能比filter高,所以一般nginx放前面,zuul放后面,当然zuul和spring cloud gateway也可以作为流量网关;
最后到具体微服务内部 基于servlet的springmvc(内置tomcat服务器); 更高性能的基于netty的spring reactive webflux(内置netty服务器); 页面渲染有 Thymleaf Eniov FreeMaker JSON; 微服务内部一般都有Acurator用于上报健康信息给比如springcloud admin; 微服务之间调用:先通过服务治理的注册中心获取服务列表到本地 =>经过断路器用hystrix,sentinel(限流,服务降级)
hystrix 服务降级(从try catch升级为面向切面编程AOP ,比如redis连不上降级查数据库)熔断 隔离(线程池[远程服务]/信号量[本地服务] 线程池之间隔离) =>经过负载均衡用netflix ribbon或springcloud loadbanlancer, =>最后通过封装的http或者tcp client端调用远程服务,一般用Feigin或者其底层的restTemplate,
open-feign可以识别spring-mvc接口,直接调用接口就可以调用对应的服务;
feign必须在代码里显示写出调用哪一个服务才能调用;
服务治理 springcloud admin; 服务注册中心eureka nacos zookeeper
前面网关部分,假如业务网关有多个节点,流量网关的nginx可以通过访问注册中心获得业务网关列表,从而对业务网关进行负载均衡;然后业务网关访问注册中心可以获取对应的微服务;当然所有的业务网关和微服务都是注册到注册中心的; 企业消息总线springcloud bus,kafka
- 分布式事务及微服务之间链路 => 先走分布式事务alibaba seata => 再连接微服务链路追踪 springcloud-sleuth,zokin,skvwalking => 最后获取分布式锁 zookeeper acurator,redlock
# 从厂家看:
- netflix全家桶:
全局外部流量入口:zuul 动态路由 Hystrix熔断降级 微服务内部负载均衡:feign https://blog.csdn.net/zhou920786312/article/details/84982290 feign和ribbon都属于客户端负载均衡(正向代理,当然这里意图并不是说要隐藏客户端,而是反而客户端通过使用feignClient,feiginclient调用微服务B[多个节点在注册中心注册为B服务],从而隐藏具体的调用过程,比如怎么动态选择哪个节点的B服务,通过什么协议等等),nginx属于服务端负载均衡(反向代理),nginx不易于剔除非健康节点;
- spring cloud alibaba全家桶: https://github.com/alibaba/spring-cloud-alibaba
spring cloud gateway 网关代替zuul+hystrix,既有路由又有熔断降级
nacos代替了spring boot的properties或者yml配置,并且可以用于dns注册和rpc服务的注册和服务发现;
Feign 默认采用http,用于微服务的数据共享,微服务可以像调用自己的服务一样调用其他微服务提供的服务,类似于dubbo等rpc框架(rpc+动态代理)
bpm-business process management比如工单流程等: activiti or flowable
Spring Cloud 万字总结,真不错! https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/YGtKoKBE1jxFaEUpEFSaLg
Azure Spring Cloud workshop https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/learn/modules/azure-spring-cloud-workshop/
https://github.com/macrozheng/mall https://github.com/zhangdaiscott/jeecg-boot
https://github.com/ZhongFuCheng3y/msc-Demo https://github.com/forezp/SpringCloudLearning https://github.com/zhoutaoo/SpringCloud
todo: Mvc Thymeleaf Realm
# 5. Versions Compatibility
# 5.1 Spring VS Spring Integration VS Spring Boot VS 3rd-party clients
3rd-party
通常是Apache library
Spring 集成了3rd party,比如 spring kafka,spring data redis,相当于在相应的3rd party,kafka-clients,redis的lettuce、jedis等基础上提供了统一的接口和规范,provides a "template" as a high-level abstraction,helps you apply core Spring concepts (dependency injection and declarative),如果直接使用3rd-party,我们需要自定义@ConfigurationProperties来管理配置,以及@Configuration来定义比如kafkaProuducer等bean,从而使用autowired注入(在spring boot中,注入配置和定义bean都是在spring-boot-autoconfigure)
例如:
spring kafka 提供了 kafkaTemplate和KafkaListener,
替代了kafka-clients的producer和consumer实际上通过pom dependency hierarchy可以看到spring-kafka是依赖于kafka-clients的,只需要引入spring-kafka即可 https://www.baeldung.com/spring-kafka但是有些时候不仅需要引用spring提供的lib,还需要引用3rd party lib,比如使用spring data redis也需要自己引入lettuce或者jedis https://www.baeldung.com/spring-data-redis-tutorial
这个时候经常就会因为 spring data redis版本和三方包版本不同有冲突,这种情况下使用spring boot就可以解决这个烦恼,spring boot提供的starter帮我们引用好了相应版本的spring data redis以及 lettuce和jedis
using spring: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.data</groupId> <artifactId>spring-data-redis</artifactId> <version>2.3.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>redis.clients</groupId> <artifactId>jedis</artifactId> <version>3.3.0</version> <type>jar</type> </dependency> using spring boot: <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-data-redis</artifactId> <version>2.3.3.RELEASE</version> </dependency>Spring Integration
based on Spring, Extends the Spring programming model to support the well-known Enterprise Integration Patterns.
https://spring.io/projects/spring-integration
Spring boot
如前面所说提供starter,集成了3rd party,所有的starter在这里
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-boot/tree/main/spring-boot-project/spring-boot-starters
# 5.2 Compatibility Troubleshooting
general
查看release note,比如
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61118552/zookeeper-3-5-x-backwards-compability-with-zookeeper-3-4-x-clients
- 3.4.x clients compatible with 3.5.x server
- 3.4.x and 3.5.x clients can be mixed on 3.5 server
- 3.5.x clients incompatible with 3.4 server
kafka
Kafka is tested against the Zookeeper version it comes with.
If you want to upgrade, you'll need to verify Zookeeper itself is backwards compatible with older clients/protocols that Kafka may use.
https://github.com/apache/kafka/search?q=zookeeper+version&type=commits
https://archive.apache.org/dist/kafka/1.1.0/RELEASE_NOTES.html
curator
curator-recipies 2.12.0=>
curator-framework 2.12.0=>
curator-client 2.12.0=>
zookeeper 3.4.8
使用 springfox2.9.2,升级springboot从2.0.5到2.4.5,遇到错误:
Description: An attempt was made to call a method that does not exist. The attempt was made from the following location: org.springframework.hateoas.server.core.DelegatingLinkRelationProvider.<init>(DelegatingLinkRelationProvider.java:36) The following method did not exist: org.springframework.plugin.core.PluginRegistry.of([Lorg/springframework/plugin/core/Plugin;)Lorg/springframework/plugin/core/PluginRegistry; The method's class, org.springframework.plugin.core.PluginRegistry, is available from the following locations: jar:file:/C:/Users/yue.liu/.m2/repository/org/springframework/plugin/spring-plugin-core/1.2.0.RELEASE/spring-plugin-core-1.2.0.RELEASE.jar!/org/springframework/plugin/core/PluginRegistry.class The class hierarchy was loaded from the following locations: org.springframework.plugin.core.PluginRegistry: file:/C:/Users/yue.liu/.m2/repository/org/springframework/plugin/spring-plugin-core/1.2.0.RELEASE/spring-plugin-core-1.2.0.RELEASE.jar Action: Correct the classpath of your application so that it contains a single, compatible version of org.springframework.plugin.core.PluginRegistryspring-boot-starter-data-rest => spring-data-rest-webmvc => spring-data-rest-core => spring-plugin-core
springfox-swagger2 => spring-plugin-core
https://github.com/springfox/springfox/issues/3052
https://github.com/springfox/springfox/releases
springfox 3.0: Requires SpringBoot 2.2+ (not tested with earlier versions)
# 5.3 3rd-party&wrapper: kafka
# Client & Sever
直接使用3rd-party
<dependency> <groupId>org.apache.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>kafka-clients</artifactId> <version>2.2.0</version> </dependency>版本
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Compatibility+Matrix
https://www.confluent.io/blog/upgrading-apache-kafka-clients-just-got-easier/
Bidirectional Client Compatibility--- KIP-35 enabled clients: any version (Release: Broker protocol - 0.10.0, Java clients - 0.10.2)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/55691662/determine-the-kafka-client-compatibility-with-kafka-broker/67463949#67463949
# Client & Client Wrapper
使用 Spring-Kafka(spring-kafka自身依赖于kafka-clients)
https://docs.spring.io/spring-kafka/reference/html/#introduction
If you are not using Spring Boot, declare the
spring-kafkajar as a dependency in your project.<dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId> <version>2.7.0</version> </dependency>When using Spring Boot, (and you haven’t used start.spring.io to create your project), omit the version and Boot will automatically bring in the correct version that is compatible with your Boot version:
<parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version> </parent> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId> <artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId> </dependency>版本
https://spring.io/projects/spring-kafka
# 5.4 3rd-party&wrapper: Redis
https://github.com/spring-projects/spring-data-redis/issues/2061
# Client & Server
直接使用3rd-party lettuce / jedis
版本
查看release note
Redis 2.6+ up to Redis 6.x. In terms of Java runtime, Lettuce requires at least Java 8 and works with Java 16. It is tested continuously against the latest Redis source-build.
https://github.com/lettuce-io/lettuce-core/releases
# Client & Client Wrapper
使用
spring-boot-starter-data-redis(自动引入spring-data-redis 和lettuce和jedis)
版本
https://search.maven.org/artifact/org.springframework.boot/spring-boot-starter-data-redis/2.4.5/jar
spring-boot-starter-data-redis 2.4.5
=> spring-data-redis 2.4.8
=> lettuce 6.0.4.RELEASE
ref 为什么说 Java 程序员到了必须掌握 Spring Boot 的时候? (opens new window) 聊一聊Spring中的代理 (opens new window) Spring Cloud (opens new window) spring boot 和微服务的关系? (opens new window) 重新理解微服务 (opens new window) 架构设计漫步:从单体架构、SOA到微服务 (opens new window) Microservices (opens new window)