1.Overview
The EOS operating system promises to allow developers to build decentralized applications - similar to Ethereum - that can be commercially scalable. The software includes “accounts, authentication, databases, asynchronous communication, and the scheduling of applications across many CPU cores or clusters,” according to the white paper. https://cointelegraph.com/news/moment-of-truth-for-eos-whats-next-for-4-bln-eosio-following-launch-of-v10
1.1 Useful links
https://www.eosdocs.io/dappdevelopment/ C++ online: https://en.cppreference.com/w/cpp/language/auto
https://eostoolkit.io/home http://status-eos.io http://eosnetworkmonitor.io
Blogs https://eos.io https://eos.io/faq https://block.one Documents https://github.com/EOSIO/Documentation https://github.com/EOSIO/Documentation/blob/master/TechnicalWhitePaper.md https://gallery.mailchimp.com/bdd950af20d4497861945b8b5/files/6699b0fa-4880-4f7a-9674-cb0d14a0f973/LedgerIntel_EOS_Report.pdf
Coding resource https://developers.eos.io/ https://steemit.com/cryptocurrency/@sheldonhuang/eos https://eosindex.io/posts https://github.com/EOS-Nation/Awesome-EOS https://github.com/eoscostarica/eos-contracts
Info 超越白皮书2 EOS主网上线前夕的实测分析与技术建议 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/r1il4FMy11A8GDZuZ92DLg https://eoslaomao.com EOS 101: Getting started with EOS https://hackernoon.com/eos-101-getting-started-with-eos-part-1-ab0324c233e0
Explorer https://scaneos.io/ BP NODES https://www.eoscout.com Singapore Node: https://meet.one https://mainnet-sg.meet.one/v1/chain/get_info
当你说智能合约,你说的到底是什么(EOS篇) https://m.8btc.com/eos-smart-contract?from=singlemessage
EOS生态网站收集整理 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/35049606
2. Get started
2.1 Overview
https://developers.eos.io/eosio-nodeos/docs/overview-1
2.2 Use docker
DEV: docker pull eosio/eos-dev
PRD: docker pull eosio/eos
sudo docker run --rm --name eosio -d -p 8888:8888 -p 9876:9876 -v /tmp/work:/work -v /tmp/eosio:/mnt/dev/data eosio/eos-dev /bin/bash -c "nodeos -e -p eosio --plugin eosio::wallet_api_plugin --plugin eosio::wallet_plugin --plugin eosio::producer_plugin --plugin eosio::history_plugin --plugin eosio::chain_api_plugin --plugin eosio::history_api_plugin --plugin eosio::http_plugin -d /mnt/dev/data --http-server-address=0.0.0.0:8888 --access-control-allow-origin=* --contracts-console"
sudo docker exec -it eosio /bin/bash
sudo docker logs --tail 10 eosio
http://192.168.1.199:8888/v1/chain/get_info
alias cleos='docker exec eosio /opt/eosio/bin/cleos --wallet-url http://localhost:8888'
alias cleos='sudo docker exec eosio /opt/eosio/bin/cleos --wallet-url http://localhost:8888'
cleos --help
sudo docker stop eosio
2.3 Build EOS
use https://developers.eos.io/eosio-nodeos/docs/autobuild-script
git clone https://github.com/EOSIO/eos --recursive
cd eos
./eosio_build.sh
To verify your installation run the following commands:
export PATH=${HOME}/opt/mongodb/bin:$PATH
/home/blockchain/opt/mongodb/bin/mongod -f /home/blockchain/opt/mongodb/mongod.conf &
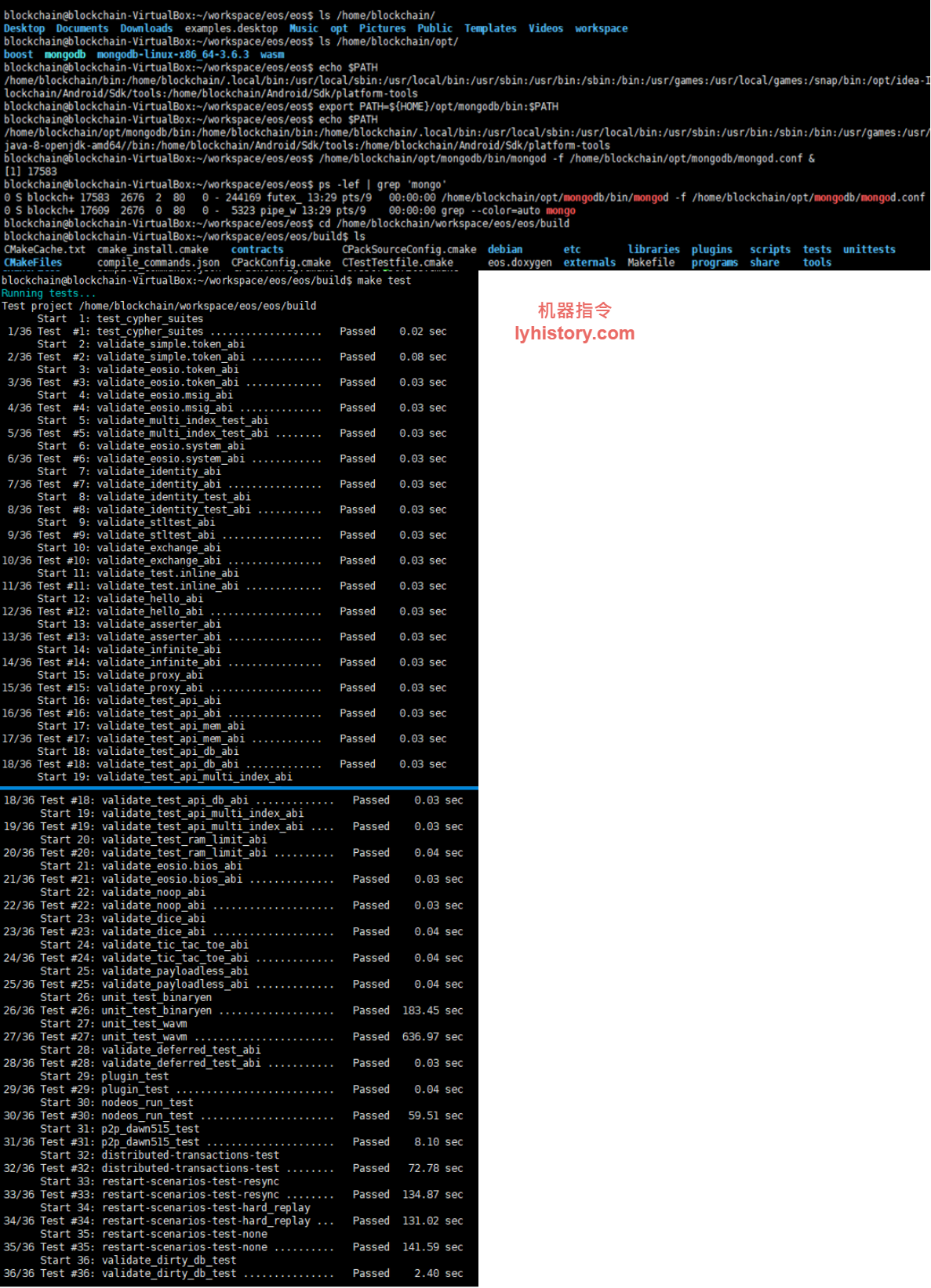
cd /home/blockchain/workspace/eos/eos/build; make test
For more information:
EOSIO website: https://eos.io
EOSIO Telegram channel @ https://t.me/EOSProject
EOSIO resources: https://eos.io/resources/
EOSIO Stack Exchange: https://eosio.stackexchange.com
EOSIO wiki: https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/wiki
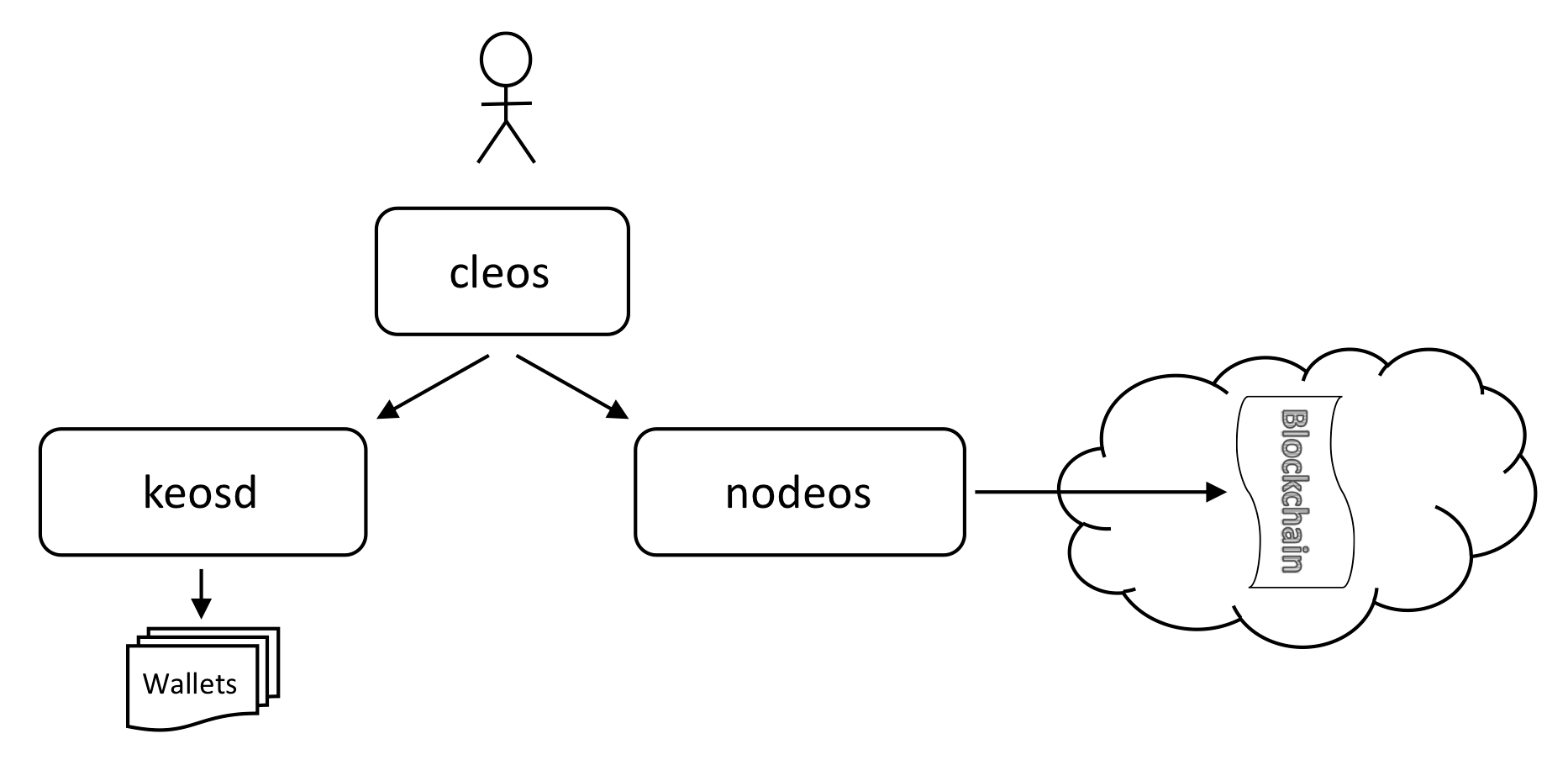
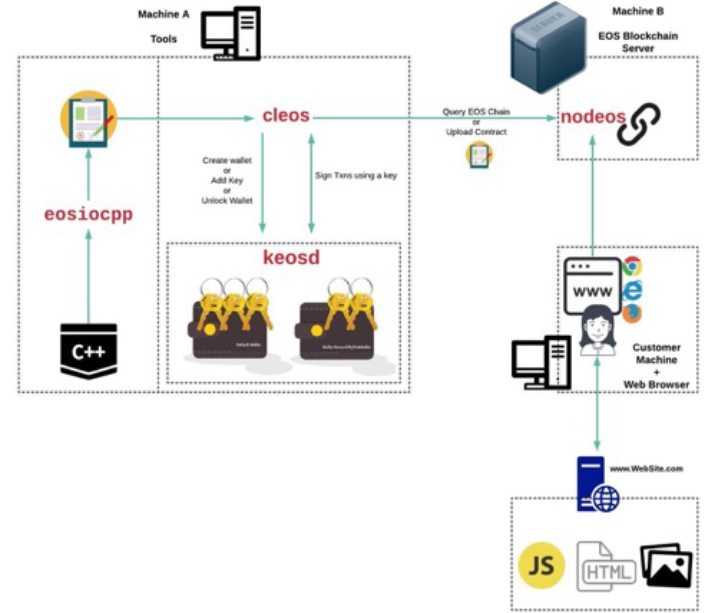
2.4 CLEOS KEOSD NODEOS
2.4.1 Comprehensive Guide to Accounts & Wallets
Wallet(Password) Keys(PrivateKey Public Key) Account (Permission: Owner, Active)
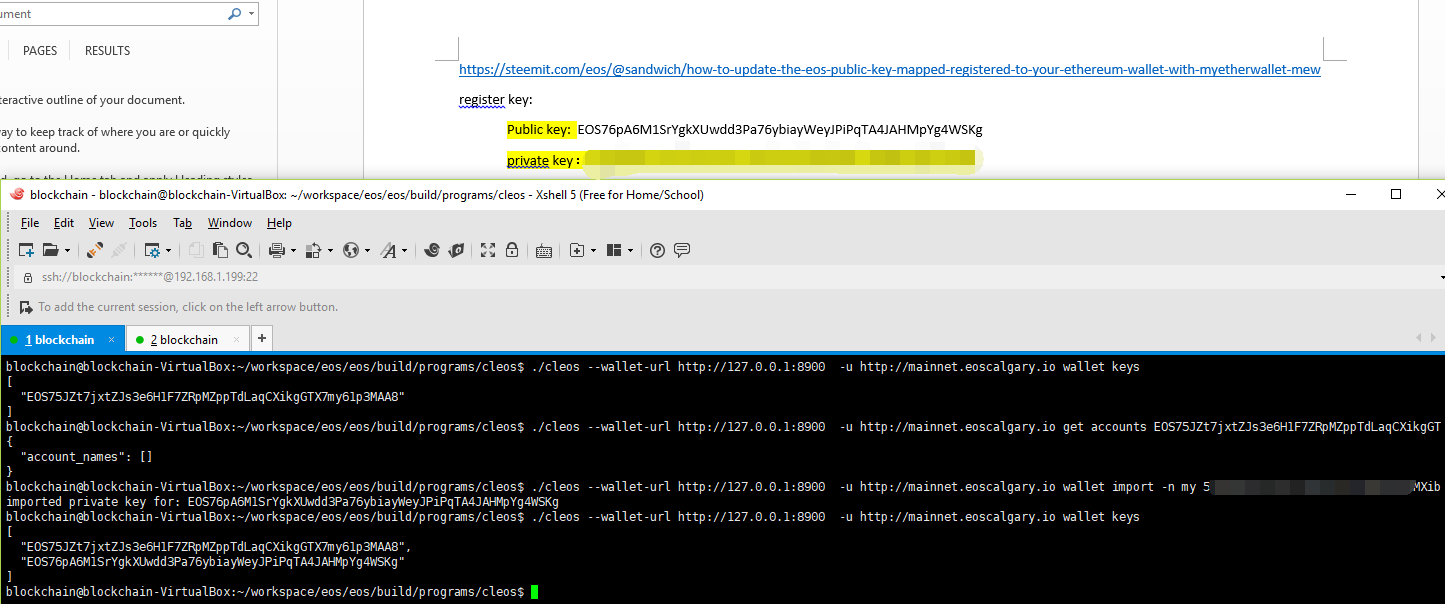
Change ownership https://medium.com/@cc32d9/changing-the-private-key-for-an-eos-account-58a79dc385cd
method: 5分钟学会注册EOS主网账户、投票和发币 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/37891815 https://my.oschina.net/lizongyue/blog/1827882 http://liyuechun.org/2018/04/19/eos-cleos/ https://eosfans.io/topics/561
Querstion: https://eosio.stackexchange.com/questions/598/what-is-the-difference-between-cleos-create-account-and-cleos-system-newaccount provided keys, permissions, and delays do not satisfy declared authorizations https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/issues/4154
Related: https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/issues/3001 https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/wiki/Tutorial-Getting-Started-With-Contracts#loading-the-bios-contract
~/workspace/eos/eos/build/programs/cleos/cleos
2.5 Smart Contract and more
https://developers.eos.io/eosio-nodeos/docs/testnets
https://developers.eos.io/eosio-cpp/docs/introduction-to-smart-contracts
3. Eco System
3.1 premium name
Intro: Name Bidding and Premium Names on EOS https://steemit.com/eos/@genereos/name-bidding-and-premium-names-on-eos https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=lduNqCIKbR8
Method: https://eosio.stackexchange.com/questions/738/need-help-name-bidding-on-premium-names cleos -u https://user-api.eoseoul.io:443 system bidnameinfo hello
EOS-3.0时代开启的世界 账户名竞拍篇 https://www.weibo.com/ttarticle/p/show?id=2309404253659679620837#interest
multisig https://steemit.com/eos/@genereos/eos-multisig-tutorial
4. Walkthrough
4.1 prepare
4.1.1 virtualbox
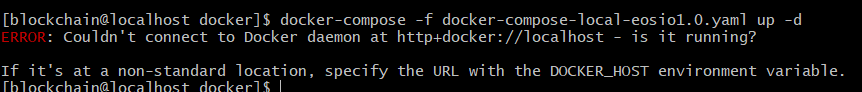
docker/docker composer
Create volumes/ pull docker image: eos-dev tags1.0.8
sudo docker pull eosio/eos-dev:v1.0.8
sudo docker pull eosio/eos-dev:v1.1.2
sudo docker tag eosio/eos-dev:v1.1.2 eosio/eos-dev:latest
https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/centos/#set-up-the-repository https://docs.docker.com/compose/install/#install-compose https://docs.docker.com/storage/volumes/#choose-the–v-or—mount-flag https://hub.docker.com/r/eosio/eos-dev/tags/
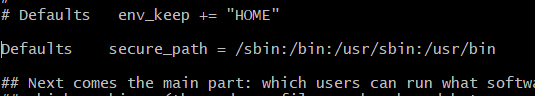
?#issues: sudoers reset
sudo vi /etc/sudoers https://superuser.com/questions/548508/why-cant-i-sudo-some-commands-e-g-vim
4.1.2 sourcecode and ide
https://code.visualstudio.com 安装C/C++扩展 https://marketplace.visualstudio.com/items?itemName=ms-vscode.cpptools
https://github.com/EOSIO/eos
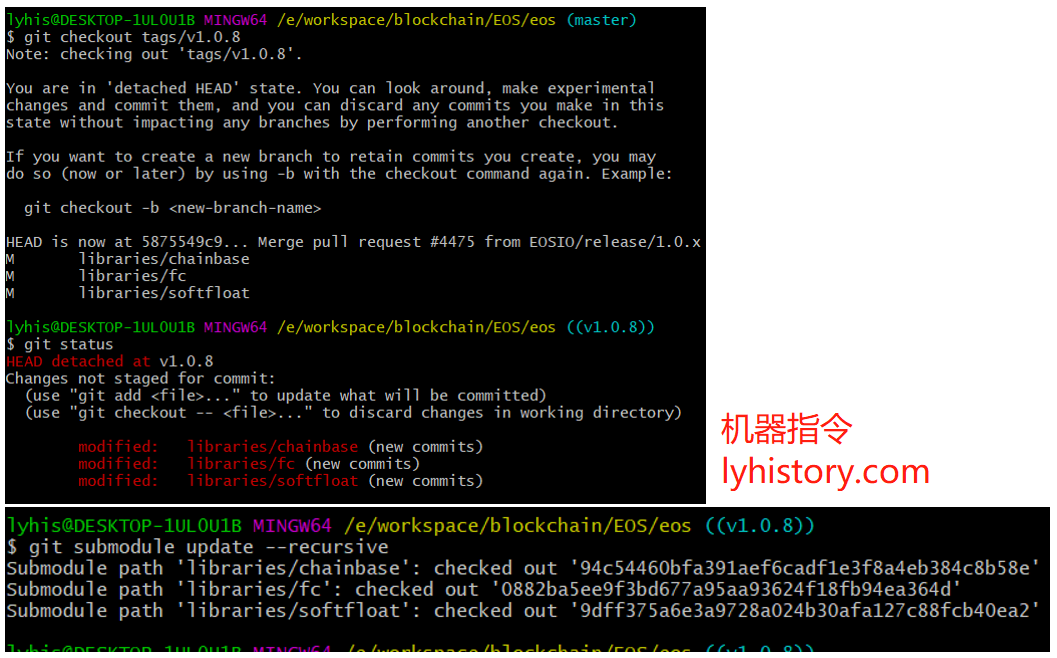
git clone https://github.com/EOSIO/eos --recursive
git checkout tags/v1.0.8
git submodule update --recursive
4.2 基本概念
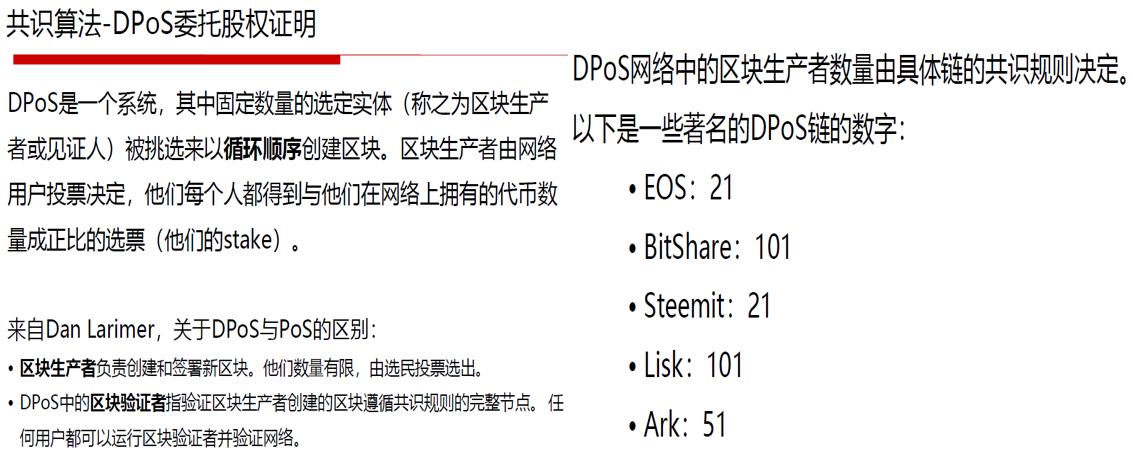
4.2.1 Dpos
Understanding Blockchain Fundamentals, Part 3: Delegated Proof of Stake https://medium.com/loom-network/understanding-blockchain-fundamentals-part-3-delegated-proof-of-stake-b385a6b92ef https://steemit.com/dpos/@dantheman/dpos-consensus-algorithm-this-missing-white-paper 解读BM视频里说的「DPOS BFT混合共识」 https://www.soniubi.com/blog/13376.html DPOS BFT— Pipelined Byzantine Fault Tolerance https://medium.com/eosio/dpos-bft-pipelined-byzantine-fault-tolerance-8a0634a270ba EOS: Explanation of DPoS+BFT w/ Daniel Larimer https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Xs1dyZFhIr4
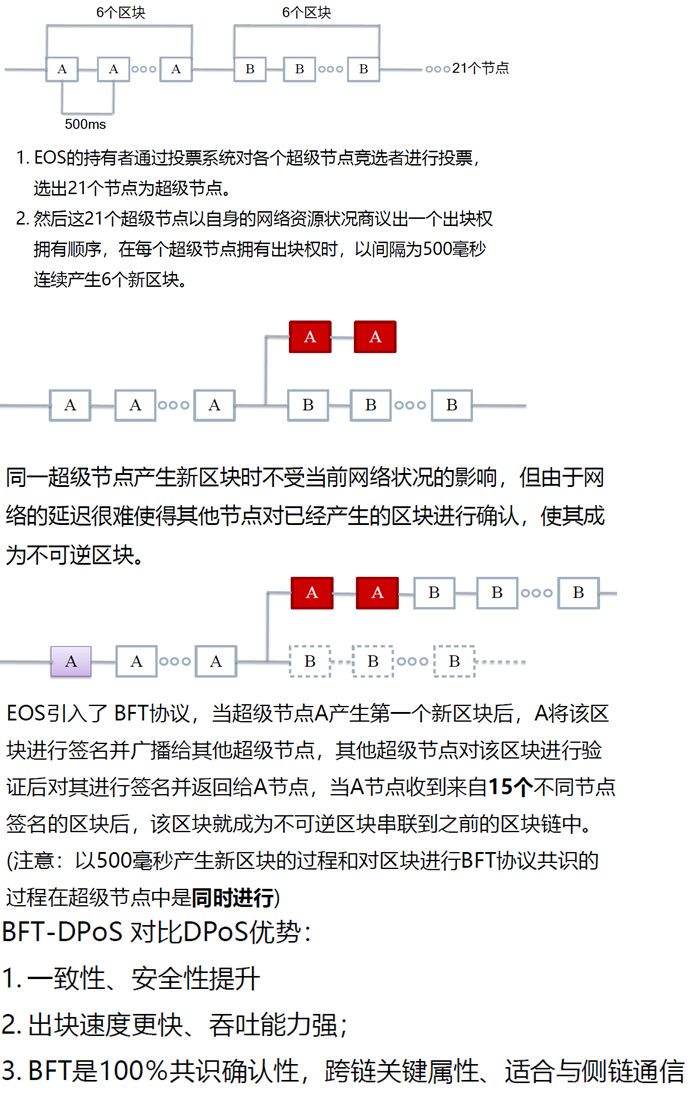
Dpos+bft
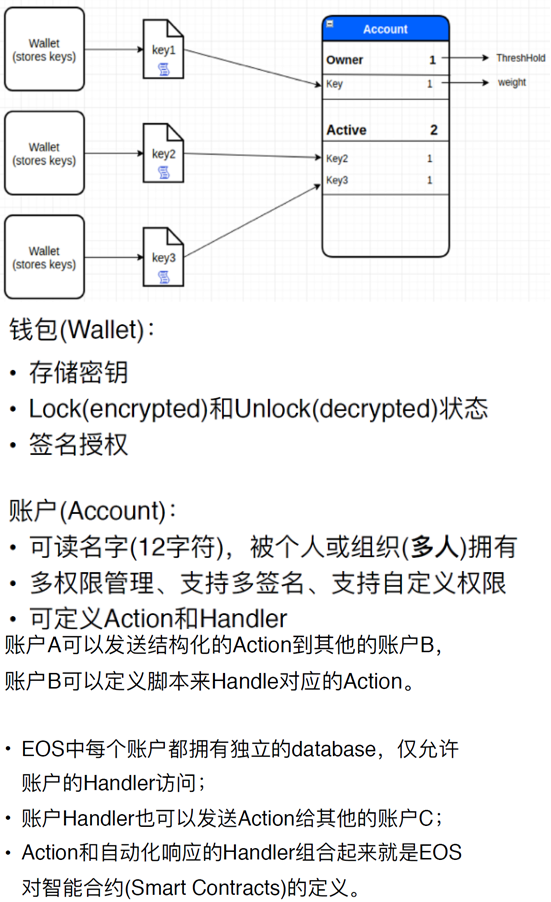
4.2.2 账户体系与安全设计
https://hackernoon.com/eos-101-getting-started-with-eos-part-2-2afbce4a8a05 EOS智能合约和虚拟机分析 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/iRs-ku21jOsXeMOxheb6bw
账户权限管理,action handler
被盗账户恢复

虚拟机环境
EVM LLVM WebAssembly
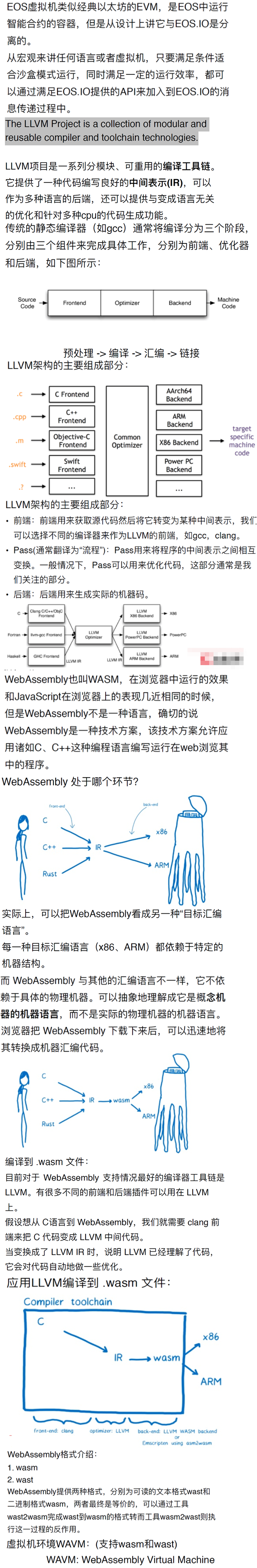
4.3 核心框架/源码剖析
| EOS源码框架剖析第二篇 | 源码整体脉络梳理中篇 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzU1NDc2MzA2OA==&mid=2247483761&idx=1&sn=0cfd55dbc416c4df33f5c28c34ed7849&chksm=fbdfd722cca85e34d8f9fd93ff81ef531a15bb40895b5a895ef2ae2a3358c0fb0efd5a41dd42&scene=21#wechat_redirect |
Ecc: https://github.com/EOSIO/eosjs-ecc
4.3.1 编译模块

4.3.2 主程序模块

4.3.3 依赖库模块

4.3.4 插件模块

4.3.5 智能合约模块

4.3.6 测试模块

4.3.7 docker定制模块

4.3.8 文档说明模块
4.4 EOS单节点测试网络
https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/04
● eosio/builder : 包含编译eos的所有依赖库,是eos编译的一个完整环境,这样开发者就无需安装各种工具和依赖库,准备eos的编译环境了。 ● eosio/eos : 主网节点使用,比较轻量级,镜像中不包含编译智能合约的依赖库。 ● eosio/eos-dev : 适用于开发者的定制环境,其中包含编译智能合约需要的相关工具和依赖库。
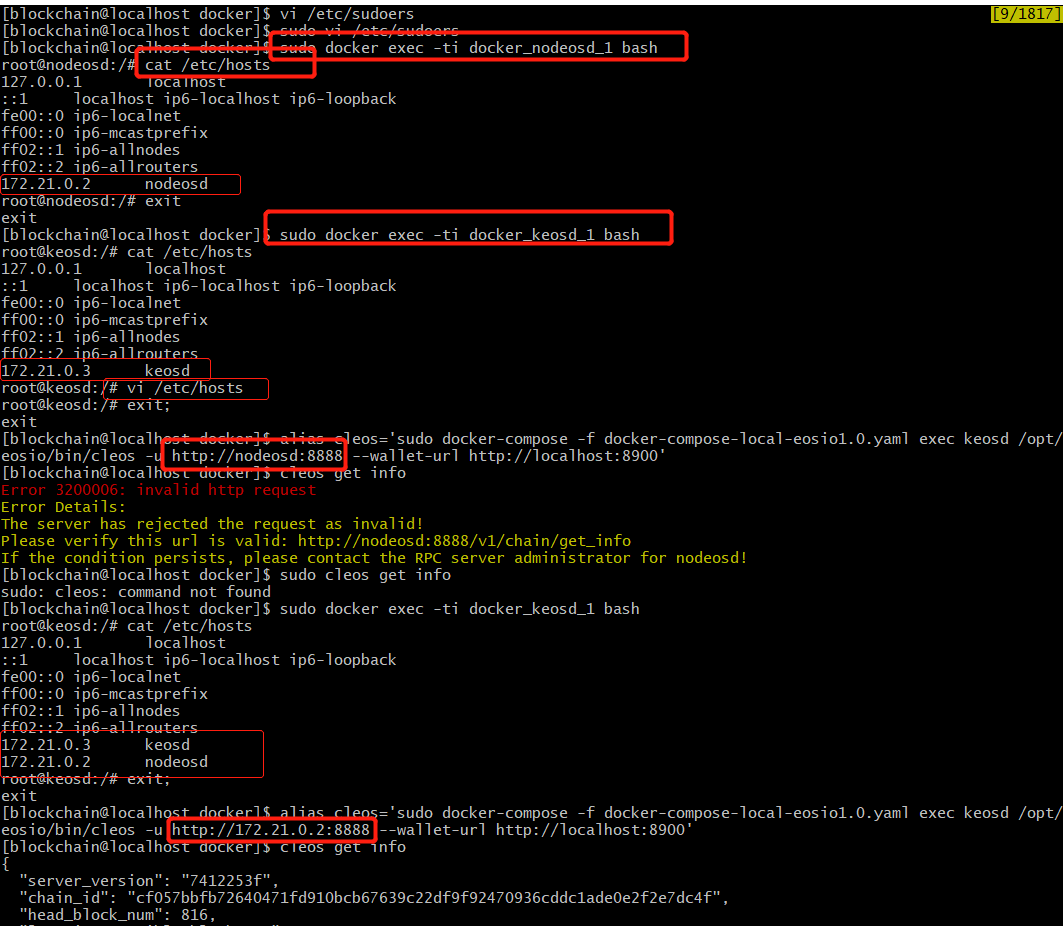
Hostname works on version eos-dev1.0.8, not working on eos-dev1.1.2
4.5 数据存储
https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/06
API https://eosio-cpp.readme.io/docs/multi-index-table-tutorial
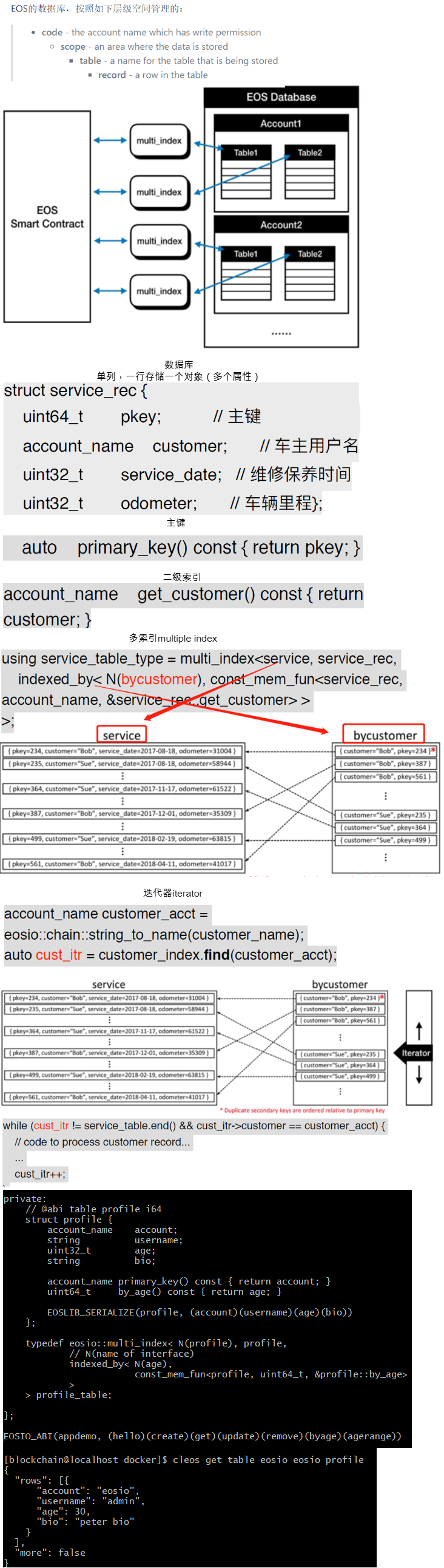
Rerference https://medium.com/@bytemaster/eosio-development-update-272198df22c1 https://developers.eos.io/eosio-cpp/docs/file-structure https://developers.eos.io/eosio-cpp/reference#multi-index https://eosfans.io/topics/410 http://www.codeblogbt.com/archives/155917 https://medium.com/fueled-engineering/exploring-the-eos-multi-index-database-557769b1b7a6
4.6 智能合约入门
https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/05 https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/07
Eosipcpp,abi

李嘉图合约(The Ricardian Contract) https://www.jianshu.com/p/3b45c92e86af https://www.jianshu.com/p/f95c845416d7
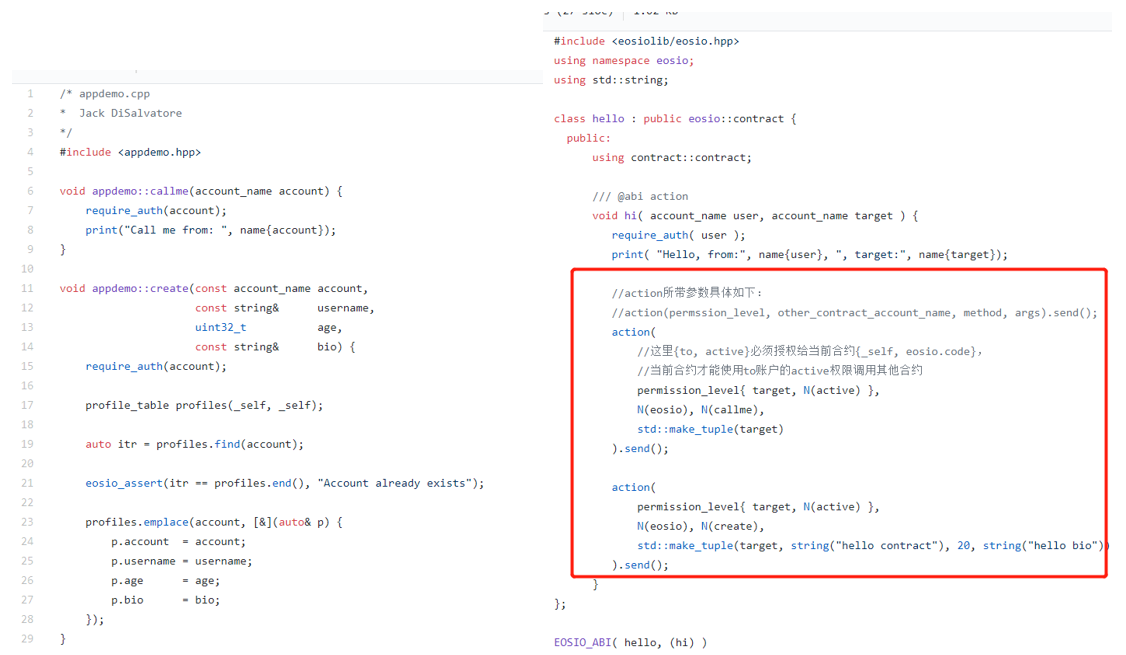
合约间调用和权限控制 Refer:
- EOS 合约调用(视频):https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E3Tx2DseLGE&feature=youtu.be&t=1h03m50s
- 合约调用权限管理:https://blog.csdn.net/itleaks/article/details/80535318 https://www.jianshu.com/p/8bd118dc865b
Transaction Inline Deferred(queue)
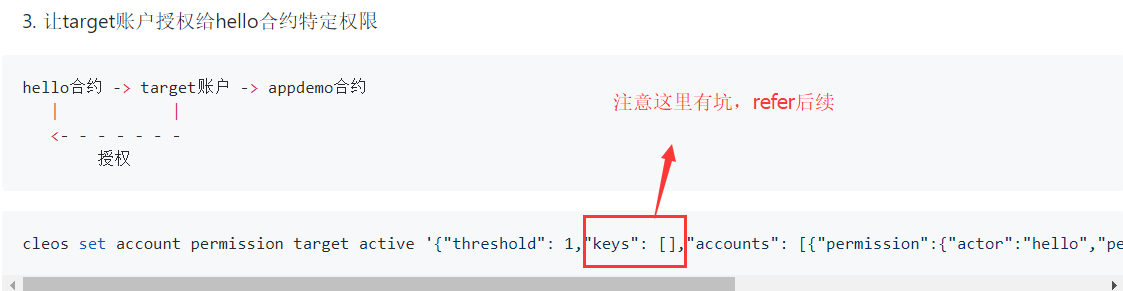
3090003 unsatisfied_authorization: provided keys, permissions, and delays do not satisfy de clared authorizations transaction declares authority ‘{“actor”:”target”,”permission”:”active”}’, but does not have signatures for it under a provided delay of 0 ms, provided permissions [{“actor”:”hello”,”p ermission”:”eosio.code”}], and provided keys [] {“auth”:{“actor”:”target”,”permission”:”active”},”provided_delay”:0,”provided_permission s”:[{“actor”:”hello”,”permission”:”eosio.code”}],”provided_keys”:[],”delay_max_limit_ms”:388 8000000} thread-0 authorization_manager.cpp:409 check_authorization
{"_pending_console_output.str()":"Hello, from:caller, target:target"}
thread-0 apply_context.cpp:62 exec_one
Debug

合约例子 Sourcecode: eos.io/eos/contracts https://developers.eos.io/eosio-cpp/docs/hello-world Understanding The eosio.token Contract https://medium.com/coinmonks/understanding-the-eosio-token-contract-87466b9fdca9
Reference https://github.com/nsjames/Scatter-Tutorials/blob/master/basics.md https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=EbWDHrm2ETY https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PamSV-WGcZo https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=E3Tx2DseLGE&feature=youtu.be&t=1h03m50s
4.7 eosjs
https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/08
Centos:
curl –silent –location https://rpm.nodesource.com/setup_10.x | sudo bash -
sudo yum -y install nodejs
[blockchain@localhost docker]$ node -v
v10.9.0
[blockchain@localhost docker]$ npm -v
6.2.0
Win10: https://chocolatey.org/packages/nodejs
Set process env https://www.jb51.net/article/126838.htm
how to set account permission by eosjs https://github.com/EOSIO/eosjs/issues/305
Failed: 1)Eos.transaction pushtransaction 2)getTableRows
Reference:
- eosjs github: https://github.com/EOSIO/eosjs
- eosjs API: https://github.com/EOSIO/eosjs-api/blob/master/docs/api.md#eos–object
- nodeos API: https://developers.eos.io/eosio-nodeos/reference
- eosjs API demos: https://medium.com/coinmonks/how-to-use-eosjs-api-1-770b037b22ad
4.8 Dapp demo - Oasis
https://infinitexlabs.com/eos-development-tutorial-part-1/ https://infinitexlabs.com/eos-development-tutorial-part-2/
https://github.com/oasis-eos https://github.com/dabdevelop/playerone https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/09 https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/10 https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/11 https://github.com/shanlusun/blockchain/tree/master/eos/12
dapp framework
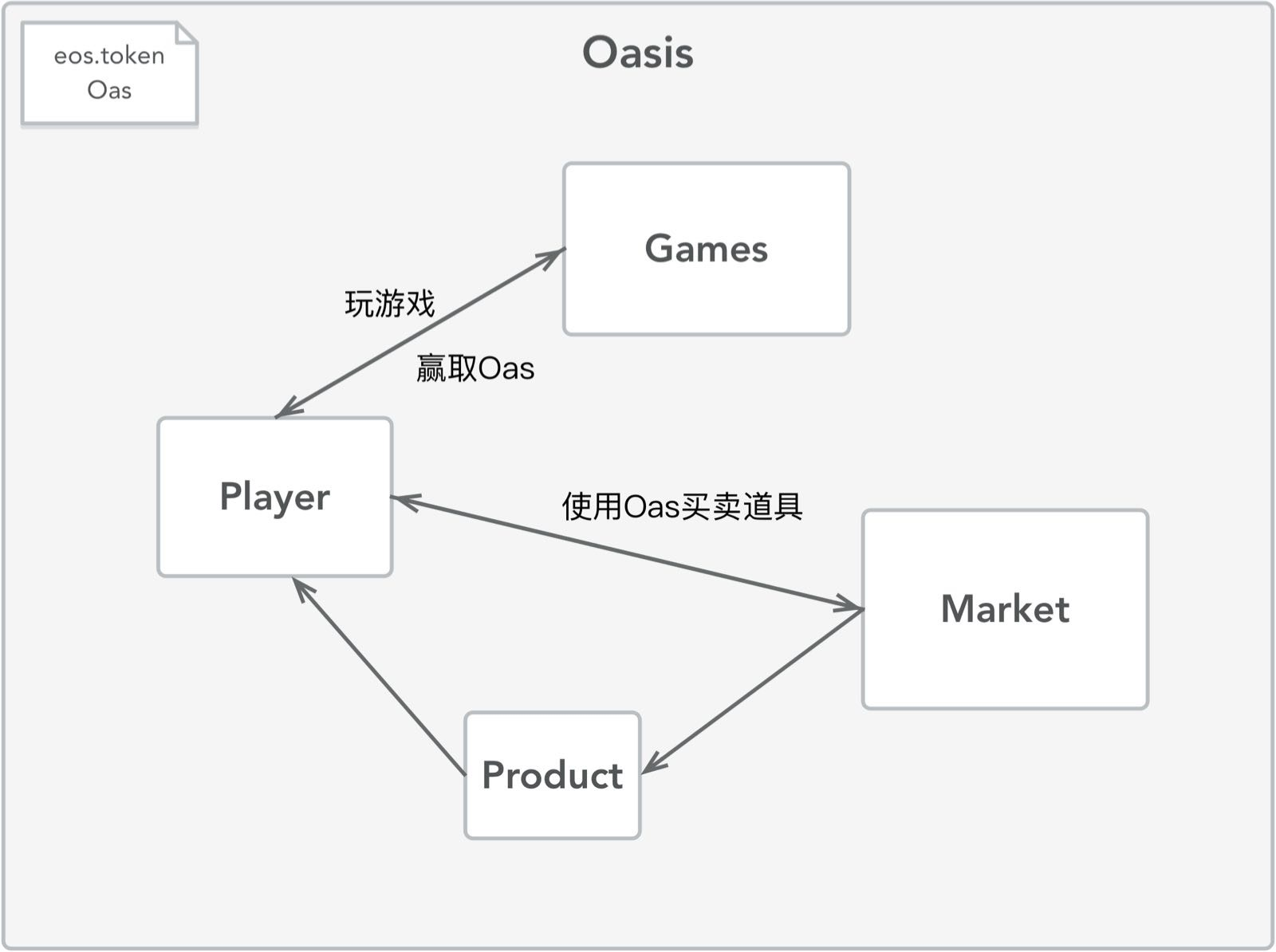
 Oasis
● Player
● Market
● Product (Extend Item)
● Game
● eosio.token OAS
Oasis
● Player
● Market
● Product (Extend Item)
● Game
● eosio.token OAS
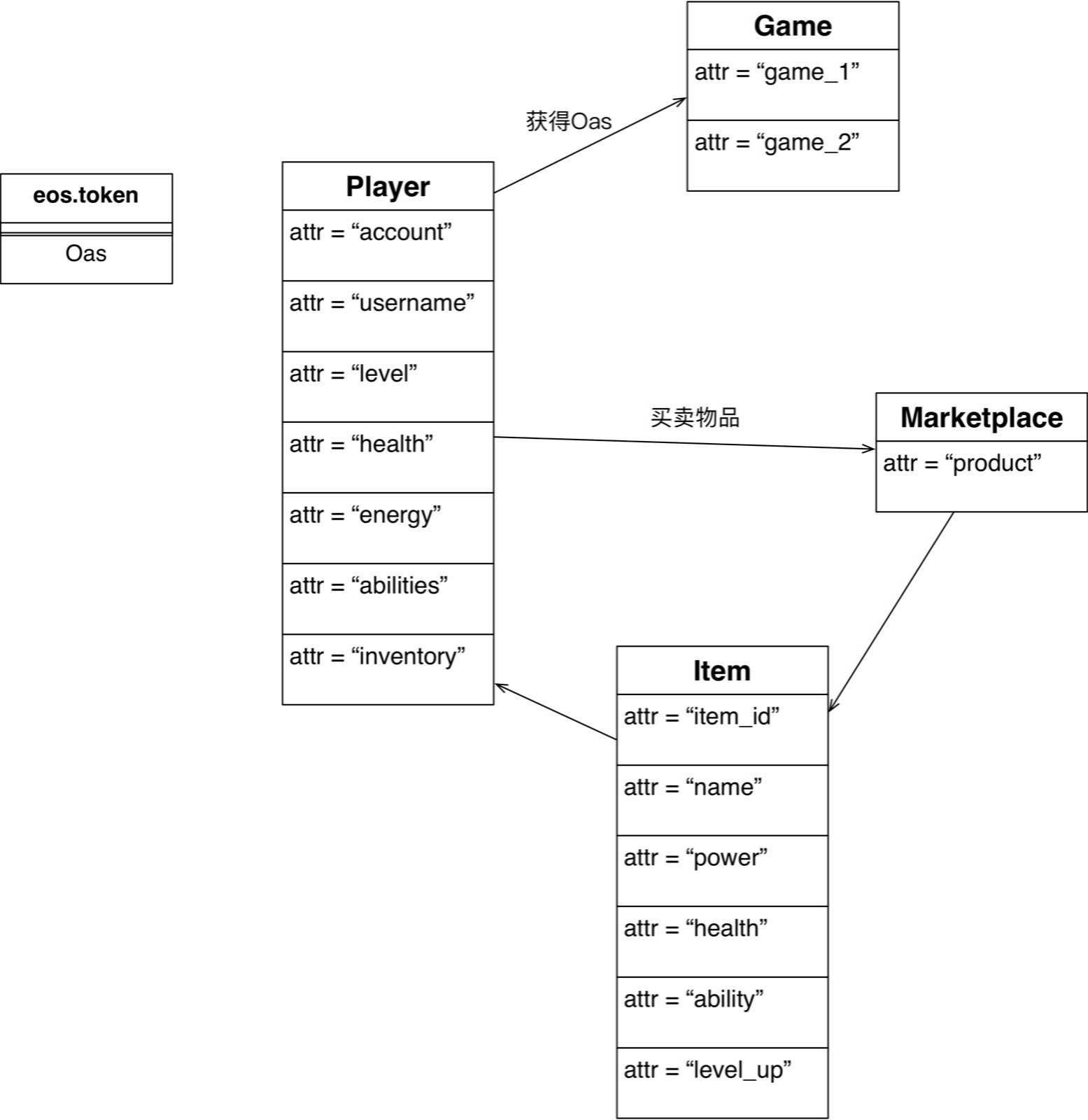
注意:我们这里使用的eosio.token代码与eos源码中的eosio.token代码不同,已经做了多处修改和调整。修改的原因是:源码原生eosio.token为系统代码,不能通过eosiocpp工具生成完整的abi文件,原生eosio.token需要使用cmake编译产生对应abi文件,因此也可以选择直接使用eos源码原生的eosio.token合约的abi。参考文献2 https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/issues/3471 https://github.com/EOSIO/eos/issues/4636
Buy product https://developers.eos.io/eosio-cleos/reference#cleos-set-account
cleos set account permission player1 active ‘{“threshold”: 1,”keys”: [],”accounts”: [{“permission”:{“actor”:”market”,”permission”:”eosio.code”},”weight”:1}]}’ owner -p player1@owner
cleos set account permission player1 active '{"threshold": 1,"keys": [{"key": "EOS8LiH1sqRAvkMaeWKQe5mQrvDz1Be1HKcar8EmejpahvSncBne2","weight": 1}],"accounts": [{"permission":{"actor":"market","permission":"eosio.code"},"weight":1}]}' owner -p player1@owner
[blockchain@localhost docker]$ cleos get account player1 -j
{
"account_name": "player1",
"head_block_num": 10242,
"head_block_time": "2018-08-23T05:33:17.500",
"privileged": false,
"last_code_update": "1970-01-01T00:00:00.000",
"created": "2018-08-23T04:49:4WP.500",
"ram_quota": -1,
"net_weight": -1,
"cpu_weight": -1,
"net_limit": {
"used": -1,
"available": -1,
"max": -1
},
"cpu_limit": {
"used": -1,
"available": -1,
"max": -1
},
"ram_usage": 3649,
"permissions": [{
"perm_name": "active",
"parent": "owner",
"required_auth": {
"threshold": 1,
"keys": [{
"key": "EOS8LiH1sqRAvkMaeWKQe5mQrvDz1Be1HKcar8EmejpahvSncBne2",
"weight": 1
}
],
"accounts": [{
"permission": {
"actor": "market",
"permission": "eosio.code"
},
"weight": 1
}
],
"waits": []
}
},{
"perm_name": "owner",
"parent": "",
"required_auth": {
"threshold": 1,
"keys": [{
"key": "EOS8LiH1sqRAvkMaeWKQe5mQrvDz1Be1HKcar8EmejpahvSncBne2",
"weight": 1
}
],
"accounts": [],
"waits": []
}
}
],
"total_resources": null,
"self_delegated_bandwidth": null,
"refund_request": null,
"voter_info": null
}
Test:
If we change
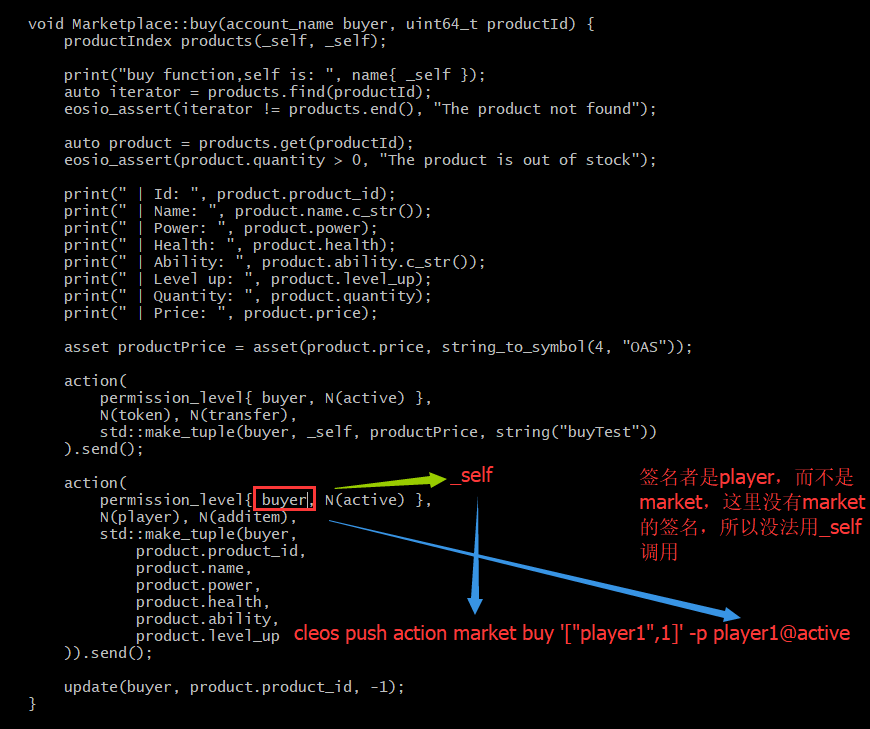
771055ms thread-0 http_plugin.cpp:405 handle_exception ] FC Exception encountered while processing chain.push_transaction 771055ms thread-0 http_plugin.cpp:406 handle_exception ] Exception Details: 3090003 unsa tisfied_authorization: provided keys, permissions, and delays do not satisfy declared authorizations transaction declares authority ‘{“actor”:”market”,”permission”:”active”}’, but does not have signatures for it under a provided delay of 0 ms, provided permissions [{“actor”:”market”,”permission”:”eosio.code” }], and provided keys [] {“auth”:{“actor”:”market”,”permission”:”active”},”provided_delay”:0,”provided_permissions”:[{“actor” :”market”,”permission”:”eosio.code”}],”provided_keys”:[],”delay_max_limit_ms”:3888000000} thread-0 authorization_manager.cpp:409 check_authorization
{"_pending_console_output.str()":"buy function,self is: market | Id: 1 | Name: magic ball | Power: 1 20 | Health: 10 | Ability: see the future | Level up: 3 | Quantity: 10 | Price: 150"}
thread-0 apply_context.cpp:62 exec_one
Please note that this will work because market@active in real env, need sign of market the account owner, because in testing env, we have already imported all related keys and unlocked wallet: cleos push action player additem ‘{“account”:”player”,”purchased_item”:{“item_id”:1,”name”:”knife”,”power”:50,”health”:300,”ability”:”heal fast”,”level_up”:0}}’ -p market@active
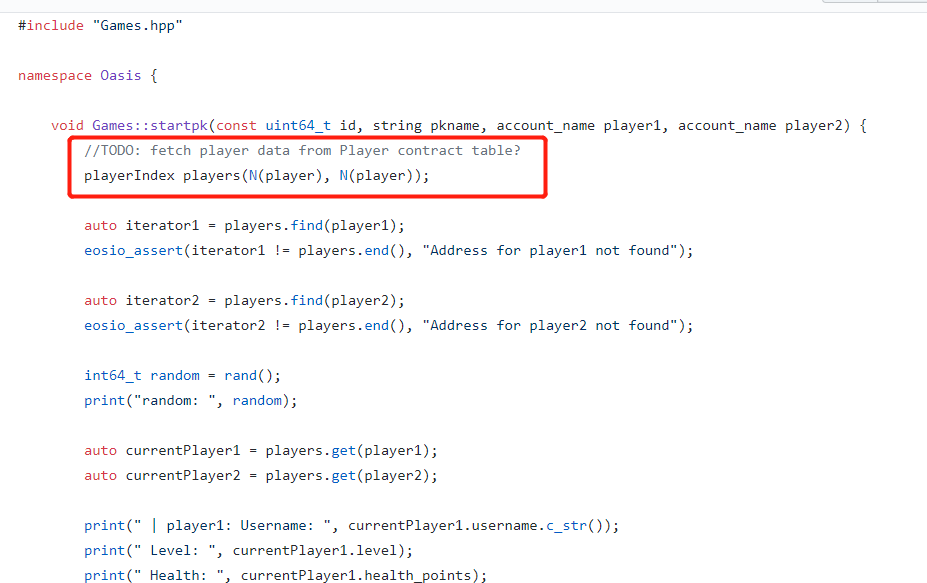
访问其他合约的table数据
4.9 Q&A
1.关于合约间调用权限控制的问题 http://www.chinahadoop.cn/course/1161/thread/2200
以最近的这个eos ram漏洞为例子,http://www.cocoachina.com/blockchain/20180802/2442WP.html
1. 先不说例子,假设正常的合约C1和C2, 当eos账号A1 调用C1的某个方法M1,而M1又会调用C2的M2方法,然后如果A1事先没有授权C1 eosio.code权限,那么C1是无法"传递"A1的权限到C2的M2的,调用会失败,对吧
2. 再说上面的例子,require_recipient是不是相对于一个特殊的授权方式?只要有这个,C1的transfer就可以用A1的权限去调用C2的transfer,假设A1在调用C1的transfer时授权权限owner,岂不是说C1可以拿着A1 owner的权限做任何事情?
3.没有理解文中的这句话“并且我们发现, 只要维持这个数据结构占据的字节不变,这个窃取的RAM在komo合约中是可以一直使用的。”
5. Diving in
https://www.reddit.com/r/eos/comments/8rmbw4/everything_eos_click_here_to_get_started/ https://eosfans.io/
eos 内存交易的漏洞和套利方法 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/38579278
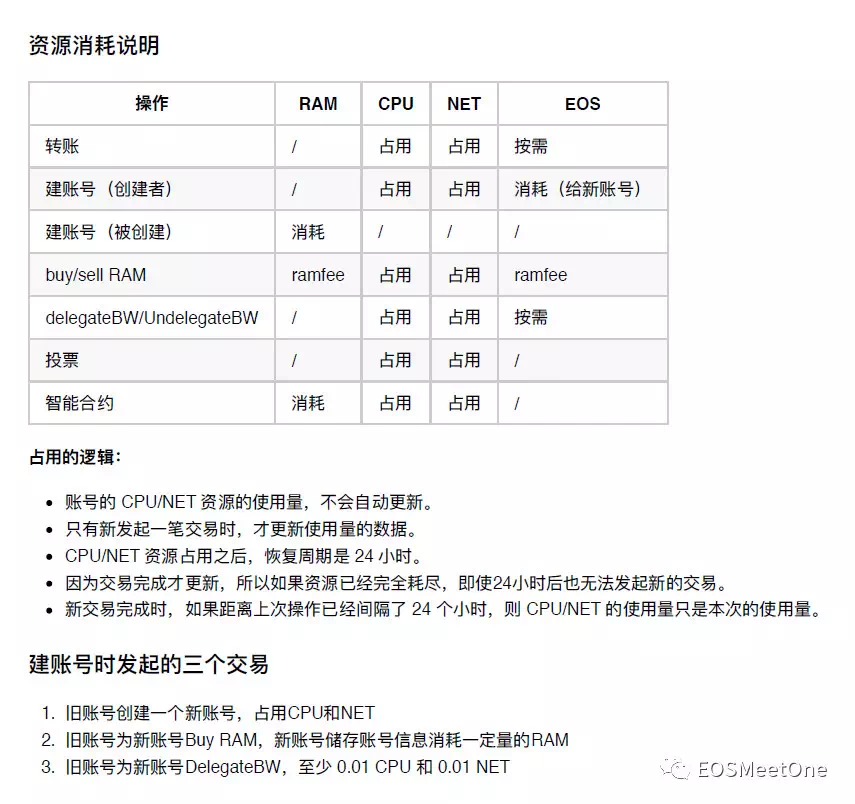
6. Trouble shooting
response_content_length >= 0: Invalid content-length response https://www.bcskill.com/index.php/archives/268.html
7. Theory
WP. White paper Learning EOS.IO Technical White Paper v2
«DPOS Consensus Algorithm - The Missing White Paper» https://steemit.com/dpos/@dantheman/dpos-consensus-algorithm-this-missing-white-paper
WP.1 Requirements for Blockchain Applications
Support Millions of Users Free Usage Easy Upgrades and Bug Recovery Low Latency Sequential Performance Parallel Performance
WP.2 Consensus Algorithm (BFT-DPOS)
Token holders, block producers, blocks are produced in rounds of 126 (6 blocks each, times 21 producers) Byzantine Fault Tolerance is added to traditional DPOS by allowing all producers to sign all blocks so long as no producer signs two blocks with the same timestamp or the same block height. Once 15 producers have signed a block the block is deemed irreversible. Any byzantine producer would have to generate cryptographic evidence of their treason by signing two blocks with the same timestamp or blockheight. Under this model a irreversible consensus should be reachable within 1 second.
Transaction Confirmation
Transaction as Proof of Stake (TaPoS) The EOS.IO software requires every transaction to include part of the hash of a recent block header. This hash serves two purposes:
- prevents a replay of a transaction on forks that do not include the referenced block;
- and signals the network that a particular user and their stake are on a specific fork.
WP.3 Accounts
The account creator must reserve the RAM required to store the new account until the new account stakes tokens to reserve its own RAM application developers will pay the nominal cost of account creation to sign up a new user.there is no need to create accounts for users already signed up by another application. Actions & Handlers To support parallel execution, each account can also define any number of scopes within their database. The block producers will schedule transaction in such a way that there is no conflict over memory access to scopes and therefore they can be executed in parallel. Role Based Permission Management EOS.IO software allows accounts to define what combination of keys and/or accounts can send a particular Action type to another account. For example, it is possible to have one key for a user’s social media account and another for access to the exchange. It is even possible to give other accounts permission to act on behalf of a user’s account without assigning them keys. Named Permission Levels Another example is the Steem blockchain which has three hard-coded named permission levels: owner, active, and posting. The posting permission can only perform social actions such as voting and posting, while the active permission can do everything except change the owner. The owner permission is meant for cold storage and is able to do everything. The EOS.IO software generalizes this concept by allowing each account holder to define their own hierarchy as well as the grouping of actions.
Permission Mapping
mapping between a contract/action or contract of any other account and their own Named Permission Level. For example, an account holder could map the account holder’s social media application to the account holder’s “Friend” permission group. With this mapping, any friend could post as the account holder on the account holder’s social media. Even though they would post as the account holder, they would still use their own keys to sign the Action. This means it is always possible to identify which friends used the account and in what way.
Evaluating Permissions
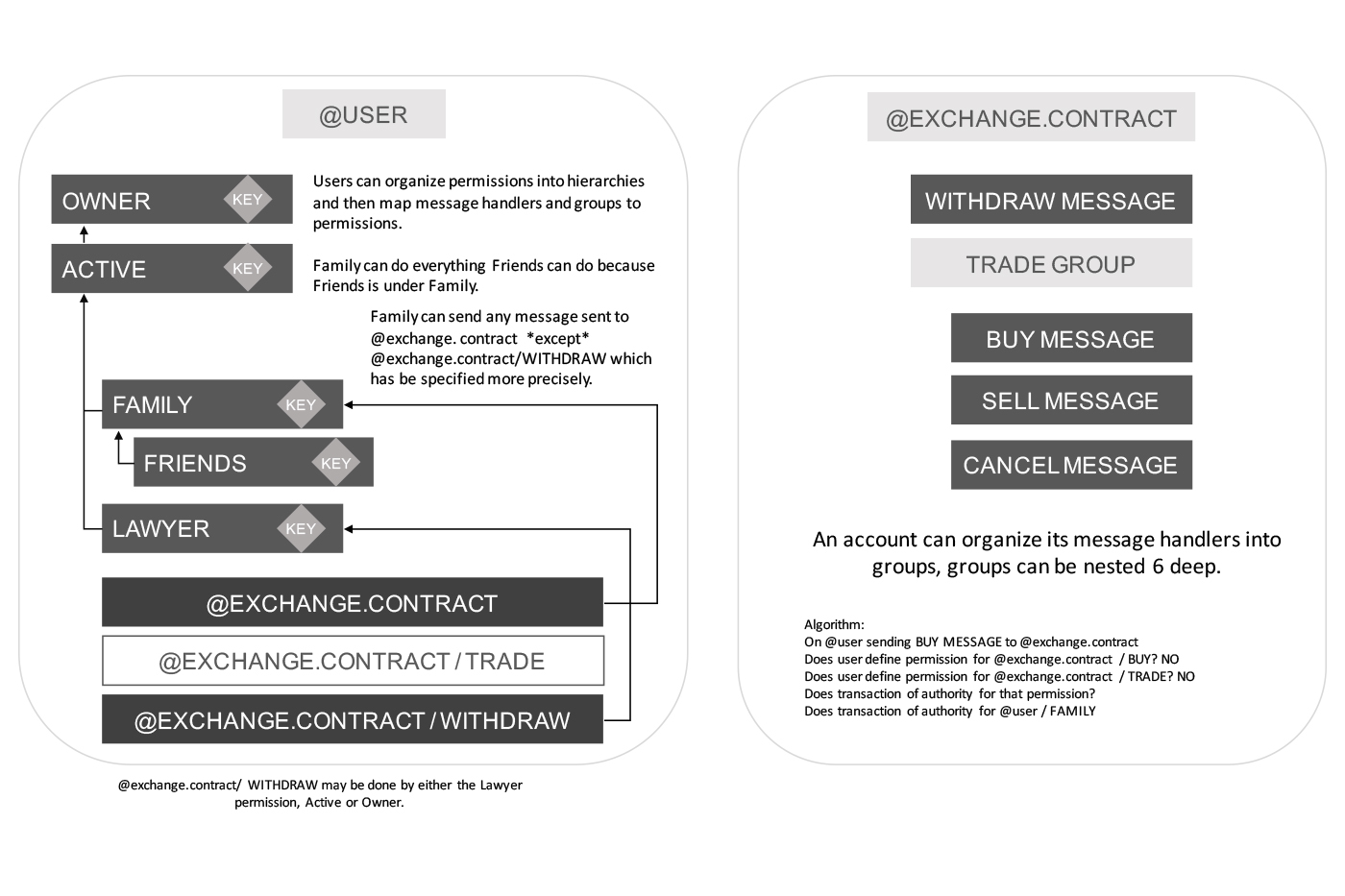
Default Permission Groups Owner Active
Parallel Evaluation of Permissions The permission evaluation process is “read-only” and changes to permissions made by transactions do not take effect until the end of a block. This means that all keys and permission evaluation for all transactions can be executed in parallel. When replaying the blockchain to regenerate the deterministic state from the log of Actions there is no need to evaluate the permissions again. The fact that a transaction is included in a known good block is sufficient to skip this step. This dramatically reduces the computational load associated with replaying an ever growing blockchain. Actions with Mandatory Delay Notify user when the action been broadcasted, recovery process. The required delay depends upon how sensitive an operation is. Paying for a coffee might have no delay and be irreversible in seconds, while buying a house may require a 72 hour clearing period. Transferring an entire account to new control may take up to 30 days. The exact delays are chosen by application developers and users. Recovery from Stolen Keys Owner, The account recovery partner, multi-factor authentication
WP.4 Deterministic Parallel Execution of Applications
Deterministic / reproducible, shard

Minimizing Communication Latency
Read-Only Action Handlers Some accounts may be able to process an Action on a pass/fail basis without modifying their internal state. If this is the case, then these handlers can be executed in parallel so long as only read-only Action handlers for a particular account are included in one or more shards within a particular cycle.
Atomic Transactions with Multiple Accounts Sometimes it is desirable to ensure that Actions are delivered to and accepted by multiple accounts atomically. In this case both Actions are placed in one transaction and both accounts will be assigned the same shard and the Actions applied sequentially.
Partial Evaluation of Blockchain State An exchange application developer runs full nodes for the purpose of displaying the exchange state to its users. This exchange application has no need for the state associated with social media applications. EOS.IO software allows any full node to pick any subset of applications to run. Actions delivered to other applications are safely ignored if your application never depends upon the state of another contract.
Subjective Best Effort Scheduling 自主最优调度
WASM Deferred Transactions
Context Free Actions A Context Free Action involves computations that depend only on transaction data, but not upon the blockchain state.
WP.5 Token Model and Resource Usage
instantaneous usage and long-term usage Action log Snapshots of the blockchain’s state
All blockchains are resource constrained and require a system to prevent abuse. Bandwidth and Log Storage (Disk); Computation and Computational Backlog (CPU); State Storage (RAM).
Adopting the EOS.IO software on a launched blockchain means bandwidth and computational capacity are allocated on a fractional reserve basis because they are transient (unused capacity cannot be saved for future use). The algorithm used by EOS.IO software is similar to the algorithm used by Steem to rate-limit bandwidth usage.
Objective and Subjective Measurements Receiver Pays A launched blockchain that uses the EOS.IO software does not require its users to pay the blockchain directly for its use and therefore does not constrain or prevent a business from determining its own monetization strategy for its products. While it is true that the receiver can pay, EOS.IO enables the sender to pay for bandwidth, computation, and storage. This empowers application developers to pick the method that is best for their application. In many cases sender-pays significantly reduces complexity for application developers who do not want to implement their own rationing system. Application developers can delegate bandwidth and computation to their users and then let the “sender pays” model enforce the usage. From the perspective of the end user it is free, but from the perspective of the blockchain it is sender-pays. Delegating Capacity delegate or rent such unconsumed bandwidth to others; the block producers running EOS.IO software on such blockchain will recognize this delegation of capacity and allocate bandwidth accordingly. Separating Transaction costs from Token Value If an application owner holds a relevant number of tokens on a blockchain adopting EOS.IO software, then the application can run indefinitely within a fixed state and bandwidth usage.
A blockchain using EOS.IO software also awards block producers tokens every time they produce a block. The value of the tokens will impact the amount of bandwidth, storage, and computation a producer can afford to purchase; this model naturally leverages rising token values to increase network performance.
State Storage Costs While bandwidth and computation can be delegated, storage of application state will require an application developer to hold tokens until that state is deleted. If state is never deleted, then the tokens are effectively removed from circulation. Block Rewards
total annual increase in token supply does not exceed 5%. Worker Proposal System The system contracts that implement Worker Proposals may not be in place at initial launch in June 2018, but the funding mechanism will. It will begin to accumulate funds at the same time block producer awards start. Since the Worker Proposal System will be implemented in WASM it can be added at a later date without a fork.
WP.6 Governance
Freezing Accounts Changing Account Code Constitution Upgrading the Protocol & Constitution Emergency Changes
WP.7 Scripts & Virtual Machines
Schema Defined Actions Schema Defined Database Generic Multi Index Database API Separating Authentication from Application
Validating that an Action is internally consistent; Validating that all preconditions are valid; Modifying the application state.
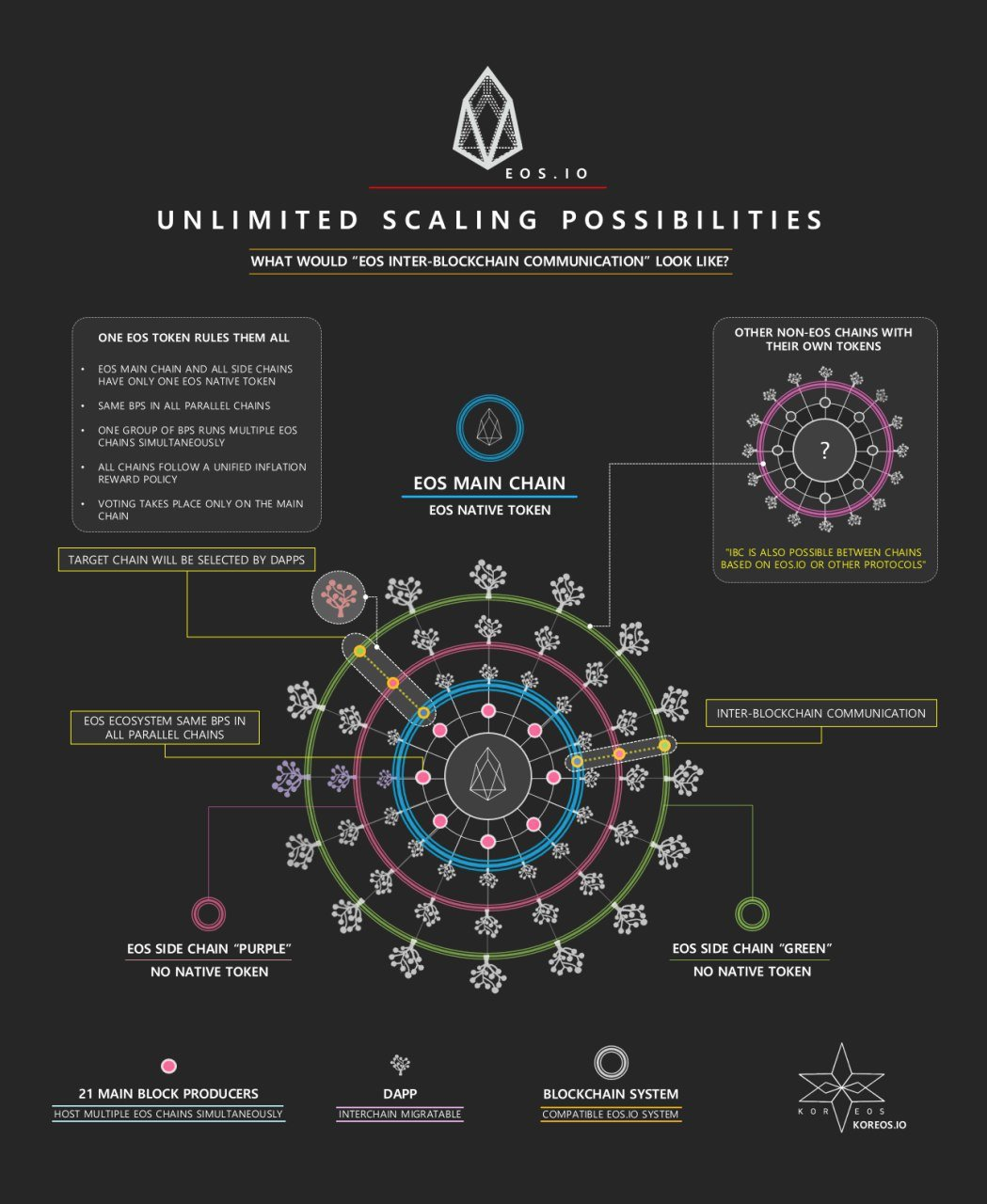
WP.8 Inter Blockchain Communication
proof of Action existence and proof of Action sequence
Merkle Proofs for Light Client Validation (LCV)
Latency of Interchain Communication
Proof of Completeness Segregated Witness
