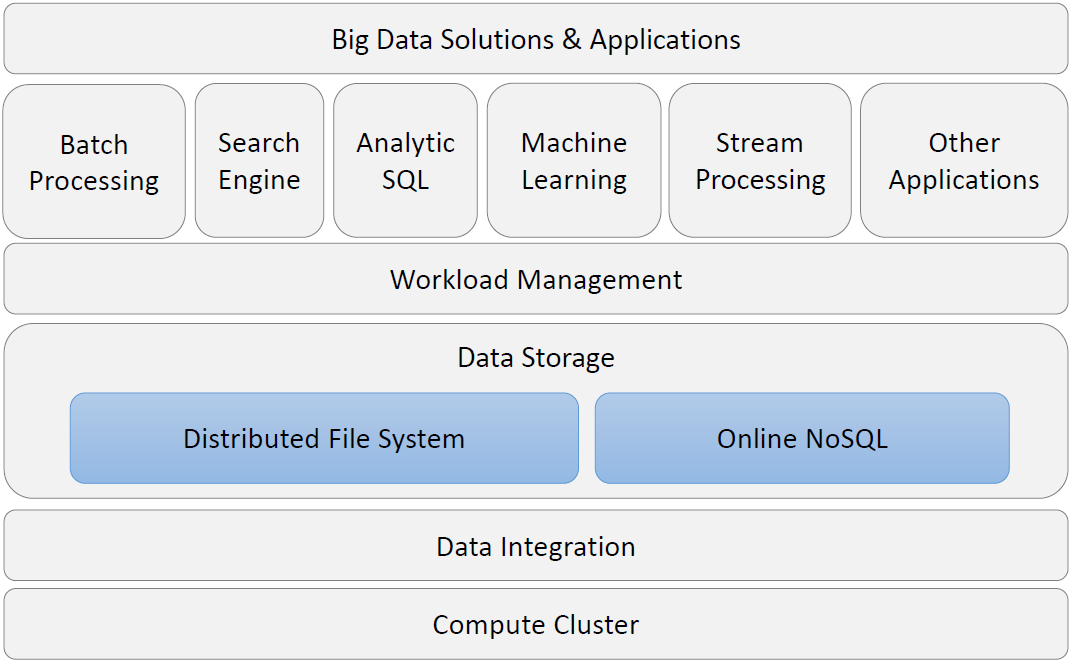
1.Big Data Engineering for Analytics
Data type: big data, fast data, dark data, thick data
1.1 Distributed and Parallel computing
Distributed System A distributed system is one in which components located at networked computers communicate and coordinate their actions only by passing messages. Distributed Transaction Distributed Shared Memory (DSM) Distributed File System (DFS)
Concurrency Control https://www.slideshare.net/wahabtl/chapter-12-transactions-and-concurrency-control Distributed Computing VS Parallel Computing Systems ● In parallel computing, all processors may have access to a shared memory to exchange information between processors.[18] ● In distributed computing, each processor has its own private memory (distributed memory). Information is exchanged by passing messages between the processors. https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Distributed_computing
Parallel computing is subset of concurrency computing There are various different ways of accomplishing concurrency. One of them is parallelism–having multiple CPUs working on the different tasks at the same time. But that’s not the only way. Another is by task switching, which works like this: Task A works up to a certain point, then the CPU working on it stops and switches over to task B, works on it for a while, and then switches back to task A. If the time slices are small enough, it may appear to the user that both things are being run in parallel, even though they’re actually being processed in serial by a multitasking CPU. –https://softwareengineering.stackexchange.com/questions/190719/the-difference-between-concurrent-and-parallel-execution
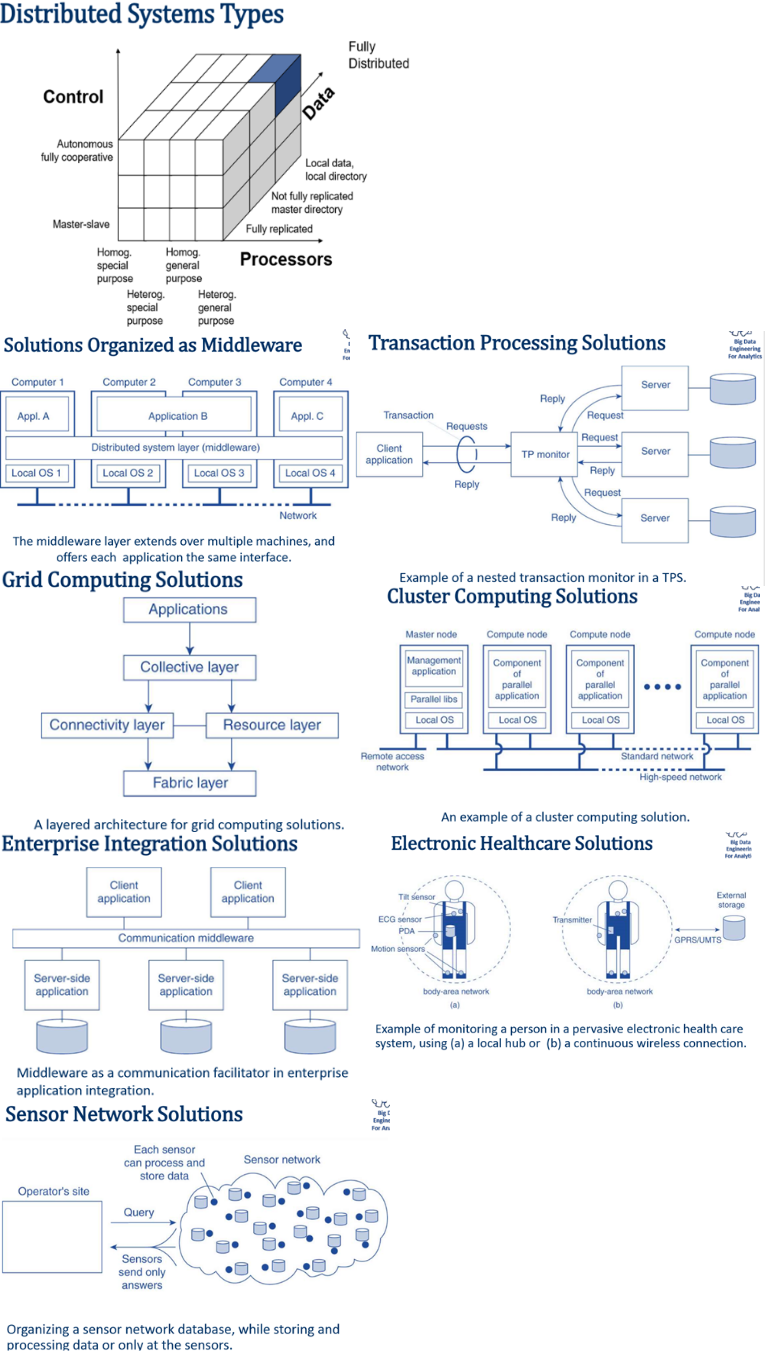
Distributed system Architecture style A style reflects the basic principle that is followed in organizing the interaction between the software components comprising a distributed system. Examples: •Layered architectures •Multi-Tiered architectures •Object-based architectures •Data-centered architectures •Event-based architectures
1.2 Hadoop
Hadoop (HDFS+MapReduce) => specify hadoop map-reduce or map-reduce for short http://ercoppa.github.io/HadoopInternals/HadoopArchitectureOverview.html Rack awareness https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Z7XUVQjI2EE Rack is basically collection of some machines which are physically placed close and are connected to same network switch Hadoop ecosystem refers to the various components of the Apache Hadoop software library, as well as to the accessories and tools provided by the Apache Software Foundation for these types of software projects, and to the ways that they work together.
| Data Processing type | solution | |—|—| | Batch processing | Apache Hadoop(hadoop map reduce) Spark is more efficient compare to hadoop Map reduce | | Realtime processing | storm(distributed and fault-tolerant realtime computation),Storm does not run on Hadoop clusters but uses Zookeeper and its own minion worker to manage its processes. Stormcan read and write files to HDFS. | https://www.dezyre.com/article/spark-vs-hadoop-vs-storm/145 Hadoop(Apache hadoop map reduce) is not designed for real time processing but for batch processing, https://www.ethz.ch/content/dam/ethz/special-interest/gess/computational-social-science-dam/documents/education/Spring2015/datascience/real-time-data-analytics.pdf
Big Data defines a situation in which data sets have grown to such enormous sizes that conventional information technologies can no longer effectively handle either the size of the data set or the scale and growth of the data set. 1.Understand the growth of Big Data and need for a scalable processing framework. 2.Use distributed and shared memory architecture. 3.Understand the various data storage options, choose an appropriate storage model based on the application requirements. 4.Perform Data manipulation and querying on Big Data solutions dealing with high volume using NoSQL. 5.Gain expertise with the fault-tolerant and computing framework for processing Big Data. 6.Understand the distributed computing essentials, storage needs, and relevant architectural mechanism in processing large amounts of structured and unstructured data. 7.Understand various in memory, batch processing and machine learning algorithms to perform analytics.
hadoop ecosystem

Distributions Cloudera, Hortonworks, MapR, Amazon Elastic MapReduce
Hadoop Solution Examples • Extract/Transform/Load (ETL) • Text mining • Index building • Graph creation and analysis • Pattern recognition • Collaborative filtering • Prediction models • Sentiment analysis • Risk assessment • Log processing • Recommendation systems • Business intelligence/data warehousing • Video and image analysis • Archiving
https://subscription.packtpub.com/book/big_data_and_business_intelligence/9781784396688
Hadoop MapReduce
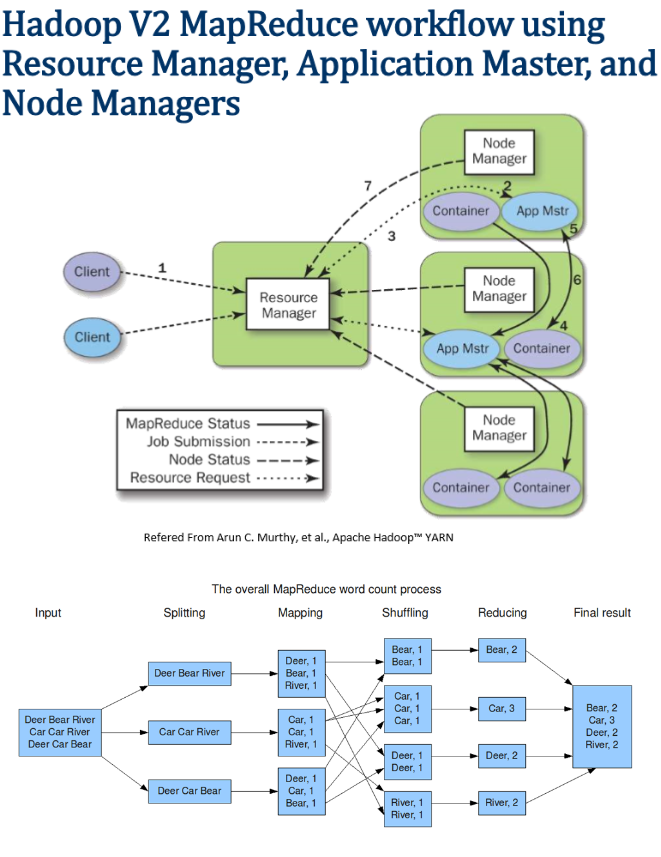
2 Components
Fundamentals of distributed and parallel computing platforms for building Big Data Solutions. Data Source==Ingestion(ETL)== ==>Data Storage ==Computing and Analytics(Query/Compute/Processing(batch process/streaming/machine learning) ==Report/Presentation(visualization dashboard or other forms)
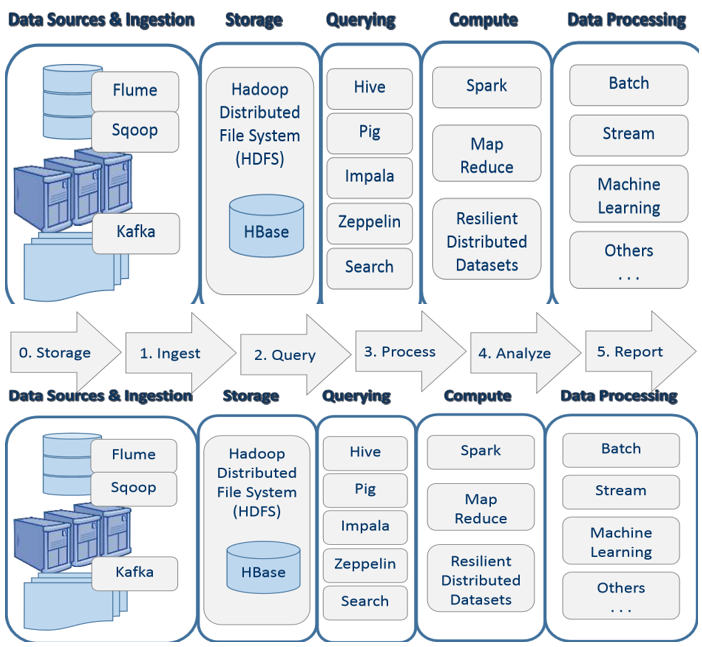
2.1 Data Source
Structured, semi-structured, unstructured, polymorphic data Big Data are large corpse of datasets with characteristics such as volume, variety, velocity, veracity and value.
2.2 Data Ingestion
Discusses the fundamentals of data ingestion, patterns used and tools available.
Process Stages: Input=>Filter=>Enrich=>Process=>Segregate=>Output
step 1. Input: Discover and fetch the data for ingestion. The discovery of data may be from File System, messaging queues, web services, sensors, databases or even the outputs of other ingestion apps. step 2. Filter: Analyse the raw data and identify the interesting subset. The filter stage is typically used for quality control or to simply sample the dataset or parse the data. step 3. Enrich: Plug in the missing pieces in the data. This stage often involves talking to external data sources to plug in the missing data attributes. Data may be transformed from a specific form into a form to make it suitable for downstream processes. step 4. Process – This stage is meant to do some lightweight processing to either further enrich the event or transform the event from one form into another. The process stage usually computes using the existing attributes of the data and at times using external systems. step 5. Segregate – Often times before the data is given to downstream systems, it makes sense to bundle similar data sets together. While this stage may not always be necessary for compaction, segregation does make sense most of the time. step 6. Output – Outputs are almost always mirrors of inputs in terms of what they can do and are as essential as inputs. While the input stage requires fetching the data, the output stage requires resting the data – either on durable storage systems or other processing systems.
Ingestion types and tools
| Objective | Tools | Solution Characteristics | Details |
|---|---|---|---|
| Handling large data volume | Apache Flume;Apache Storm;Apache Spark | Data extraction with load balancing using a distributed solution or a cluster of nodes. | Apache Flume is useful in processing log-data. Apache Storm is desirable for operations monitoring and Apache Spark for streaming data, graph processing and machine-learning |
| Messaging for distributed ingestion | Apache Kafka | Messaging system should ensure scalable and reliable communication across nodes involved in data-ingestion. | LinkedIn makes use of Apache Kafka to achieve fast communication between the cluster-nodes. |
| Real-time or near realtime ingestion | Apache Storm, Apache Spark | Data-ingestion process should be able to handle highfrequency of incoming or streaming data. | NA |
| Batch-mode ingestion | Apache Sqoop;Apache Kafka;Apache Chukwa | Ability to ingest data in bulkmode. | Apache Chukwa process data in batch-mode and are useful when data needs to be ingested at an interval of few minutes/hours/days. |
| Detecting incremental data | DataBus, Infosphere and Goldengate | Ability to handle structured and unstructured data, lowlatency. | Databus from LinkedIn is a distributed solution that provides a timeline-consistent stream of change capture events for a database. – Infosphere and Goldengate are Data Integrators |
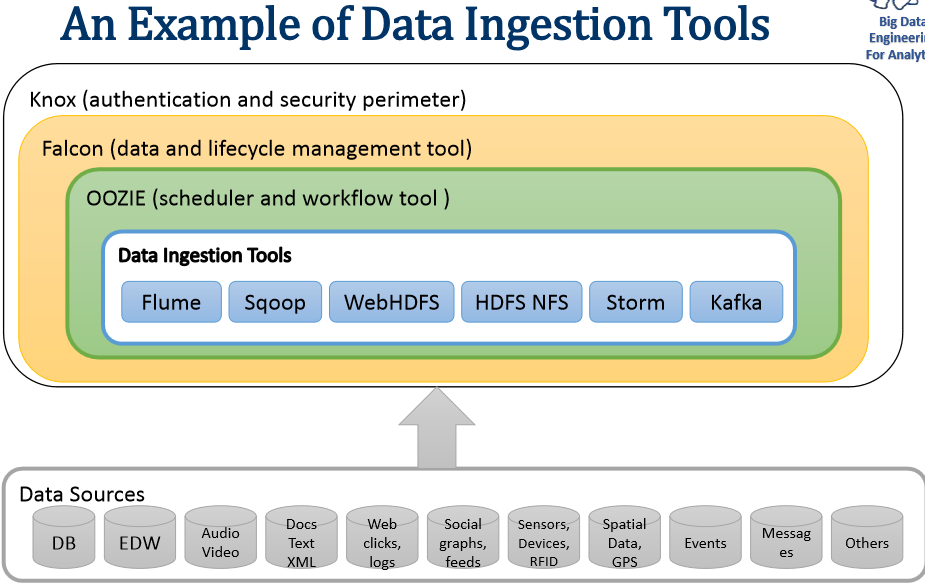
example: Sqoop & Sqoop V2: Using hadoop MapReduce Sqoop helps to move data between hadoop and other databases and it can transfer data in parallel for performance.
Flume: Flume helps to collect data from a variety of sources, like logs, jms, Directory etc. Multiple flume agents can be configured to collect high volume of data. It scales horizontally.
Ingestion Patterns
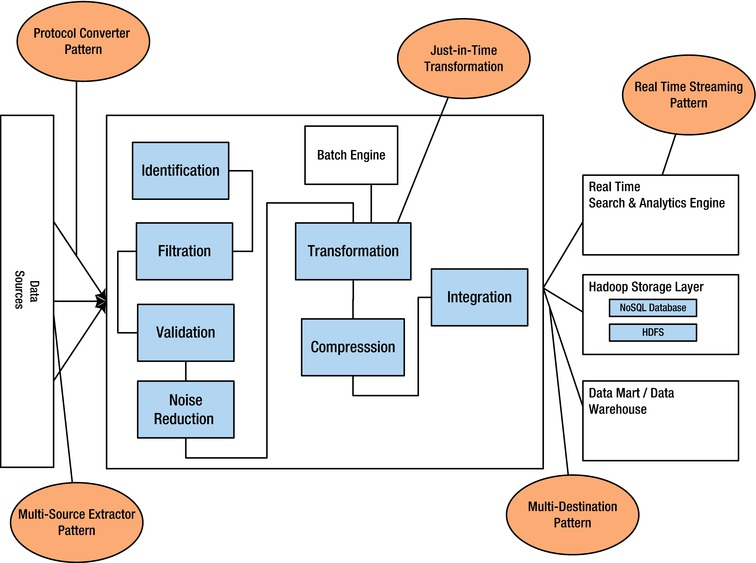
https://link.springer.com/chapter/10.1007/978-1-4302-6293-0_3 • Multisource Extractor Pattern: An approach to ingest multiple data source types in an efficient manner. • Protocol Converter Pattern: Employs a protocol mediator to provide abstraction for the incoming data from the different protocol layers. • Multi-destination Pattern: Used in a scenario where the ingestion layer has to transport the data to multiple storage components like DFS, data marts, or real-time analytics engines. • Just-in-Time Transformation Pattern: Large quantities of unstructured data can be uploaded in a batch mode using traditional ETL (extract, transfer and load) tools and methods. Data is transformed only when required to save compute time. • Real-Time Streaming patterns: Real-time ingestion and analysis of the in-streaming data is required for instant analysis of data.
2.3 Data Storage
Design features of the scalable, fault-tolerant, cost-efficient storage for Big Data.
HDFS - Distributed File System
Naming: add hostname to file names,mouting remote directories to local ones, all files in the system belong to a single namespace. Cache: memory/disk; writing policy; cache consistency Availability: replica Scalability Semantics
HDFS shares many common features with other distributed file systems while supporting some important differences. One significant difference is HDFS’s write-once-read-many model that relaxes concurrency control requirements, simplifies data coherency, and enables high-throughput access. https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/hdfs_design.html A comic-like explanation of HDFS https://docs.google.com/file/d/0B-zw6KHOtbT4MmRkZWJjYzEtYjI3Ni00NTFjLWE0OGItYTU5OGMxYjc0N2M1/edit?pli=1
NameNode: meta information about files and blocks DataNode: files and blocks http://hadoopinrealworld.com/namenode-and-datanode/ http://stackoverflow.com/questions/13577767/file-path-in-hdfs
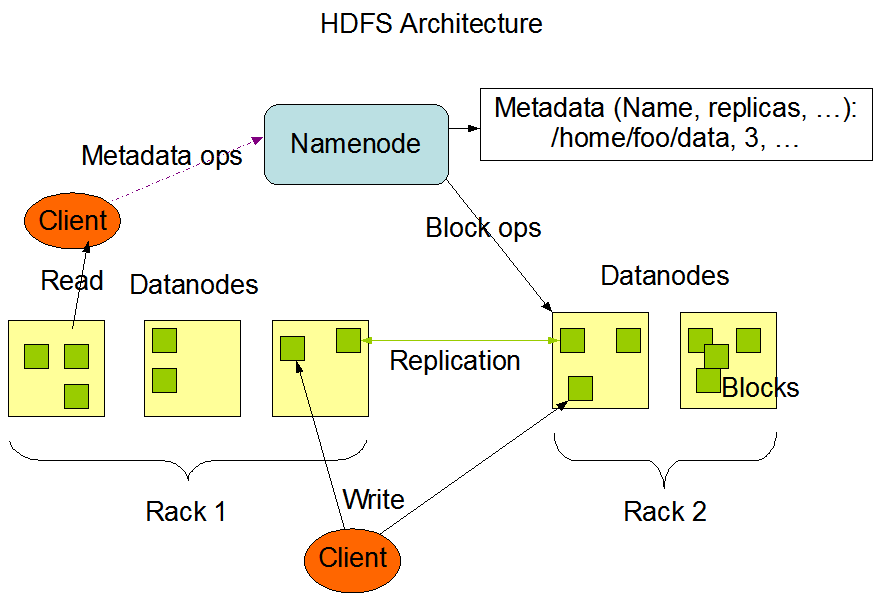
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/r1.2.1/hdfs_design.html
HBASE-NoSQL
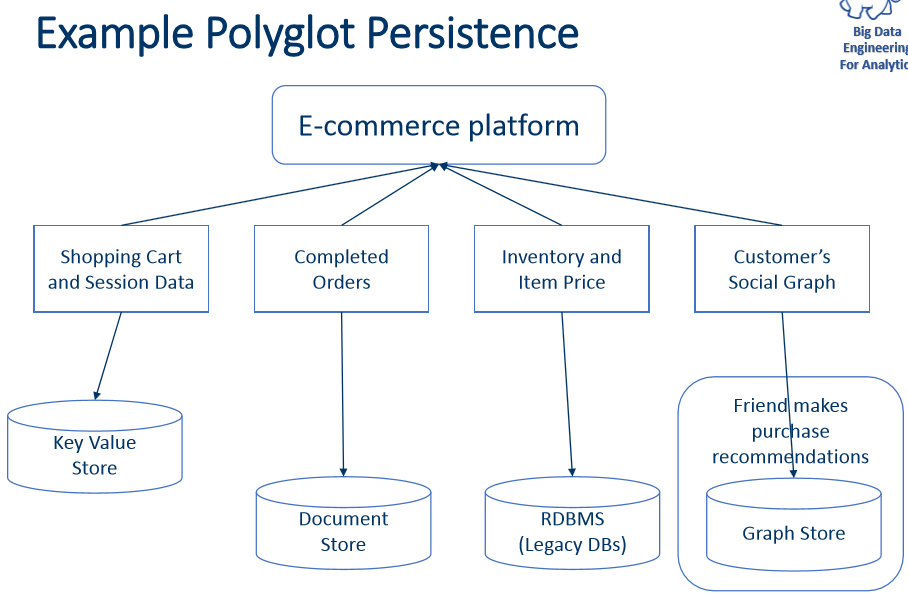
NonSQL->NoRel->NoSQL->NewSQL RDMS: provided successful persistence, concurrency control, and an integration mechanism, but has disadvantage of : declarative, expensive when scaling, impedance mismatch between the relational model and the in-memory data structures.(ORM) Why NoSQL: 1, Exponential growth of data generated by new systems and users 2, Increasing interdependence and complexity of data but hard to achieve ACID in distributed databases, BASE(Basically Available, soft State, Eventual consistency) instead Storage structures and information retrieval on distributed Big Data platforms using NoSQL. Computational Engine: Computational components responsible for scheduling, distributing, and monitoring applications consisting of types of tasks across computing cluster.
ACID Sharding and Replication
| Pattern | Product | Description | Typical uses |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key-value store | Redis | A simple way to associate a large data file with a simple text string | Dictionary, image store, document/file store, query cache, lookup tables |
| Graph store | neo4j;flockDB;InfiniteGraphy | A way to store nodes and arcs of a graph | Social network queries, friend-of-friends queries, inference, rules system, and pattern matching |
| Column family (Bigtable) store | HBase;bigtable(google) | A way to store sparse matrix data using a row and a column as the key | Web crawling, large sparsely populated tables, highly-adaptable systems, systems that have high variance |
| Document store | MongoDB | A way to store tree-structured hierarchical information in a single unit | Any data that has a natural container structure including office documents, sales orders, invoices, product descriptions, forms, and web pages; popular in publishing, document exchange, and document search |
•Projects where RDBMS SQL is ideal: logical related discrete data requirements which can be identified up-front data integrity is essential standards-based proven technology with good developer experience and support. •Projects where NoSQL is ideal: unrelated, indeterminate or evolving data requirements simpler or looser project objectives, able to start coding immediately speed and scalability is imperative.
Benchmark postgresql vs mongodb: https://www.sisense.com/blog/postgres-vs-mongodb-for-storing-json-data/ Why We Moved From NoSQL MongoDB to PostgreSQL https://dzone.com/articles/why-we-moved-from-nosql-mongodb-to-postgresql
Sample case:
| HDFS | HBase |
|---|---|
| HDFS is a Java-based file system utilized for storing large data sets. | HBase is a Java based Not Only SQL database |
| HDFS has a rigid architecture that does not allow changes. It doesn’t facilitate dynamic storage. | HBase allows for dynamic changes and can be utilized for standalone applications. |
| HDFS is ideally suited for write-once and read-many times use cases | HBase is ideally suited for random write and read of data that is stored in HDFS. |
HBASE Architecture
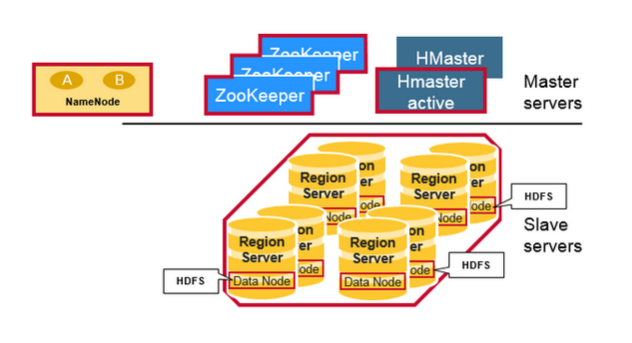
https://mapr.com/blog/in-depth-look-hbase-architecture/
2.4 Data Analytics
Query
Impala Hive
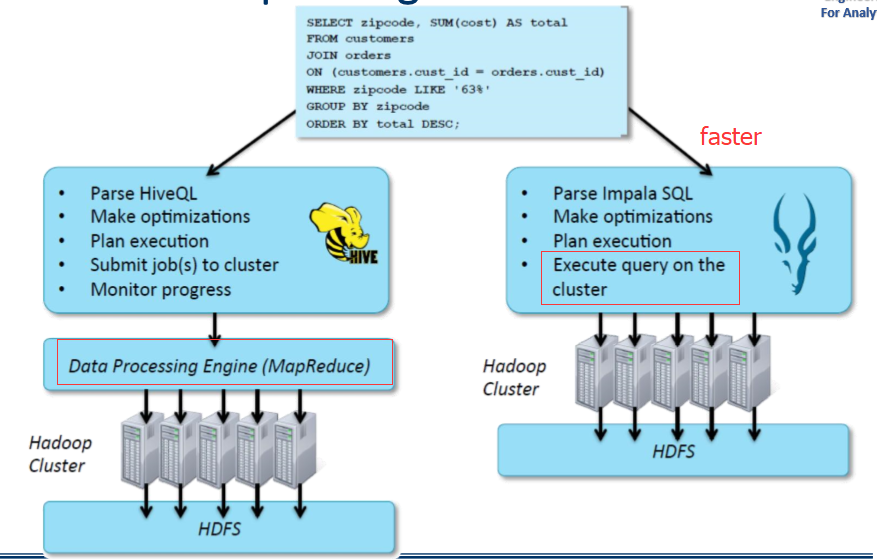
Computing cluster and Analytics
High-performance & Highavailability Computing Systems MapReduce, Apache YARN, Apache Spark……
Analytics: Introduction to use the distributed Big Data platforms for analytics problem solving. Computing Cluster: Architecting the distributed Big Data engineering solutions on cluster computing platform designed to be fast and general-purpose. Parallel Computing: Using functional programming frameworks and the resilient distributed dataset(RDD) inside a distributed shell for solving different types of analytics problems.
Categories :
- Descriptive Analytics What was the sales volume over the past 12 months? What is the number of support calls received as categorized by severity and geographic location? What is the monthly commission earned by each sales agent?
- Diagnostic Analytics Why were Q2 sales less than Q1 sales? Why have there been more support calls originating from the Eastern region than from the Western region? Why was there an increase in patient re-admission rates over the past three months?
- Predictive Analytics What are the chances that a customer will default on a loan if they have missed a monthly payment? What will be the patient survival rate if Drug B is administered instead of Drug A? If a customer has purchased Products A and B, what are the chances that they will also purchase Product C?
- Prescriptive Analytics Prescriptive analytics build upon the results of predictive analytics by prescribing actions that should be taken. The focus is not only on which prescribed option is best to follow, but why.
Major Types Of Clusters:
• Storage Clusters Allows the servers to simultaneously read and write to a single shared file system Simplifies storage administration, supports a cluster-wide file system and simplifies backup and disaster recovery. • High-availability Clusters Provide continuous availability of services by eliminating single points of failure Maintains data integrity and node failures are transparent to external world • Load-balancing Clusters Dispatch network service requests to multiple cluster nodes to balance the request load Provides cost-effective scalability, detects the failure and redirects requests to other cluster nodes. • High-performance Clusters Perform concurrent calculations, allow applications to work in parallel, and enhances performance Referred to as computational clusters
1) Batch Processing Apache Yarn(MapReduce V2) works on the philosophy that moving computation is cheaper than moving data. https://chongyaorobin.wordpress.com/2015/07/01/step-by-step-of-installing-singlenode-yarn-on-ubuntu/ http://backtobazics.com/big-data/setup-multi-node-hadoop-2-6-0-cluster-with-yarn/ Apache Spark (rdd, sql)
MapReduce 2 vs YARN applications https://stackoverflow.com/questions/31044575/mapreduce-2-vs-yarn-applications
You cannot compare Yarn and Spark directly per say. Yarn is a distributed container manager, like Mesos for example, whereas Spark is a data processing tool. Spark can run on Yarn, the same way Hadoop Map Reduce can run on Yarn. It just happens that Hadoop Map Reduce is a feature that ships with Yarn, when Spark is not. –https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29568533/what-is-the-difference-between-yarn-and-spark-processing-engine-based-on-real-ti
https://hadoop.apache.org/docs/current/hadoop-yarn/hadoop-yarn-site/YARN.html
https://backtobazics.com/big-data/spark/understanding-apache-spark-architecture/
Spark vs MapReduce(v1) https://www.quora.com/Apache-Spark/What-is-the-difference-in-idea-design-and-code-between-Apache-Spark-and-Apache-Hadoop
2) Streaming
3) Machine Learning
todo
Storm https://hortonworks.com/apache/storm Kafka https://hortonworks.com/apache/kafka/ Zookeeper https://hortonworks.com/apache/zookeeper/
class notes: Amazon EMR https://aws.amazon.com/emr/ Hadoop(HDFS) vs. RDBMS https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/hadoop-vs-rdbms-thiensi-le hbase vs rdbms sql nosql https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/documentdb/documentdb-nosql-vs-sql Traditional Business Intelligence VS Big Data Technology https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/traditional-business-intelligence-vs-big-data-steven-murhula processing type: http://searchdatamanagement.techtarget.com/feature/Understanding-and-comparing-six-types-of-processing-systems http://www.datasciencecentral.com/profiles/blogs/batch-vs-real-time-data-processing HIVE VS Relational Database- cannot update at row level http://stackoverflow.com/questions/17810537/how-to-delete-and-update-a-record-in-hive
**Hadoop distribution Cloudera vs Hortonworks vs MapR: Comparing Hadoop Distributions https://wiki.apache.org/hadoop/Distributions%20and%20Commercial%20Support
https://www.cloudera.com/more/about/faqs.html https://www.cloudera.com/documentation/enterprise/latest/topics/cdh_intro.html http://tecadmin.net/hadoop-commands-to-manage-files-on-hdfs/# https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/HDP2/HDP-2.4.3/bk_installing_manually_book/content/start_stop_restart_hue.html
How To Setup Multi Node Hadoop 2 (YARN) Cluster http://arturmkrtchyan.com/how-to-setup-multi-node-hadoop-2-yarn-cluster https://github.com/lyhistory/reference-apps
Building a real time, solr-powered recommendation engine https://www.slideshare.net/treygrainger/building-a-real-time-solrpowered-recommendation-engine
hadoop -> hdfs (NameNode DataNode) http://spark.apache.org/examples.html http://www.cnblogs.com/laov/p/3433994.html http://f.dataguru.cn/thread-539253-1-1.html http://blog.csdn.net/sunrising_hill/article/details/53559398 http://www.cnblogs.com/forget-me-not/archive/2016/07/27/5710122.html http://blog.csdn.net/yangjl38/article/details/7595465
**Spark 大数据实战高手进阶之路:Machine Learning on Spark彻底揭秘学习编程拼图理论的框架整理 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1084717
Spark的RDD原理以及2.0特性的介绍 www.open-open.com/lib/view/open1463655510676.html http://www.dataguru.cn/article-9353-1.html Installing and Running Spark on YARN http://dmtolpeko.com/2015/02/06/installing-and-running-spark-on-yarn/ http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/running-on-yarn.html https://nofluffjuststuff.com/blog/mark_johnson/2016/02/5_steps_to_get_started_running_spark_on_yarn_with_a_hadoop_cluster https://www.gitbook.com/book/jaceklaskowski/mastering-apache-spark/details http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/running-on-yarn.html https://chongyaorobin.wordpress.com/2015/07/01/step-by-step-of-installing-apache-spark-on-apache-hadoop/ http://freecontent.manning.com/wp-content/uploads/how-to-start-developing-spark-applications-in-eclipse.pdf https://www.quora.com/How-do-I-set-up-Apache-Spark-with-Yarn-Cluster http://www.cnblogs.com/BYRans/p/5889374.html submit jobs http://spark.apache.org/docs/latest/submitting-applications.html https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/HDP2/HDP-2.3.0/bk_spark-quickstart/content/run_spark_pi.html https://github.com/apache/spark/tree/98ede49496d0d7b4724085083d4f24436b92a7bf/examples/src/main/scala/org/apache/spark/examples/mllib
Scala Tutorial 01 (download + test run the Scala Eclipse plugin) https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=sj53BGwFs9U Learning Scala? Learn the Fundamentals First! https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ugHsIj60VfQ How to use Apache ZooKeeper zkCli Command Line Interface https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6jAVjiAo8cU HBase keeps doing SIMPLE authentication stackoverflow.com/questions/21338874/hbase-keeps-doing-simple-authentication
Apache Spark vs. MapReduce https://dzone.com/articles/apache-spark-introduction-and-its-comparison-to-ma Five things you need to know about Hadoop v. Apache Spark https://www.infoworld.com/article/3014440/big-data/five-things-you-need-to-know-about-hadoop-v-apache-spark.html
Why Apache Spark is a Crossover Hit for Data Scientists blog.cloudera.com/blog/2014/03/why-apache-spark-is-a-crossover-hit-for-data-scientists/
Spark Tips Spark shell Related: #1 cannot load library into class declaration, solution: scala> :paste // Entering paste mode (ctrl-D to finish) Sacla related: PARALLEL COLLECTIONS http://docs.scala-lang.org/overviews/parallel-collections/overview.html
org.apache.spark.sql.AnalysisException Exception when joining DataFrames try not to join two dataframe with the same column name https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/SPARK-10925
Caused by: java.lang.ClassCastException check whether you are using the wrong column index
Scala Scala is one of the hottest modern programming languages. It is the Cadillac of programming languages. It is not only powerful but also a beautiful language. Spark is written in Scala, but it supports multiple programming languages, including Scala, Java, Python, and R. Scala is a great language for developing big data applications. It provides a number of benefits. First, a developer can achieve a significant productivity jump by using Scala. Second, it helps developers write robust code with reduced bugs. Third, Spark is written in Scala, so Scala is a natural fit for developing Spark applications. Functional programming is a programming style that uses functions as a building block and avoids mutable variables, loops, and other imperative control structures. It treats computation as an evaluation of mathematical functions, where the output of a function depends only on the arguments to the function. A program is composed of such functions. In addition, functions are first-class citizens in a functional programming language. First, functional programming provides a tremendous boost in developer productivity. It enables you to solve a problem with fewer lines of code compared to imperative languages. Second, functional programming makes it easier to write concurrent or multithreaded applications. The ability to write multi-threaded applications has become very important with the advent of multi-CPU or multi-core computers. Third, functional programming helps you to write robust code. It helps you avoid common programming errors. Finally, functional programming languages make it easier to write elegant code, which is easy to read, understand, and reason about. A properly written functional code looks beautiful; it is not complex or messy. You get immense joy and satisfaction from your code. Functional Programming
- is composed of ‘Functions’ - First-class citizens: Composable, No Side Effects, Simple
- has immutable data structure
- is expression language Function types:
- Methods
- Local Functions
- High-order methods http://fruzenshtein.com/scala-higher-order-anonymous-functions/
- Function Literals
- Closures class singleton case class case statement Map, Map and flatMap in Scala http://www.brunton-spall.co.uk/post/2011/12/02/map-map-and-flatmap-in-scala/ https://twitter.github.io/scala_school/ http://spark.apache.org/examples.html https://github.com/apache/spark/tree/master/examples learn scala https://www.scala-exercises.org/ page rank https://github.com/eBay/Spark/blob/master/examples/src/main/scala/org/apache/spark/examples/SparkPageRank.scala
mapPartitions vs map vs flatmap http://blog.csdn.net/lsshlsw/article/details/48627737 http://lxw1234.com/archives/2015/07/348.htm
https://databricks.com/blog/2016/07/14/a-tale-of-three-apache-spark-apis-rdds-dataframes-and-datasets.html http://www.brunton-spall.co.uk/post/2011/12/02/map-map-and-flatmap-in-scala/
Apache Spark快速入门 https://www.iteblog.com/archives/1410.html dataframe nested value http://stackoverflow.com/questions/37391241/how-to-explode-columns/37392793#37392793 json in dataframe http://xinhstechblog.blogspot.sg/2015/06/reading-json-data-in-spark-dataframes.html scala json http://stackoverflow.com/questions/31852602/scala-play-json-how-to-read-a-single-element-from-a-element-in-an-array
Data mining A Programmer’s Guide to Data Mining http://guidetodatamining.com https://legacy.gitbook.com/book/wizardforcel/guide-to-data-mining/details https://legacy.gitbook.com/@wizardforcel
Machine Learning /docs/software/bigdata/machinelearning
Deep Learning How To Develop and Evaluate Large Deep Learning Models with Keras on Amazon Web Services machinelearningmastery.com/develop-evaluate-large-deep-learning-models-keras-amazon-web-services/
Keras:基于Theano和TensorFlow的深度学习库 https://keras-cn.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
https://github.com/aaxwaz/NUS_ISS_DeepLearningWorkshop
机器学习(Machine Learning)&深度学习(Deep Learning)资料 https://ask.julyedu.com/article/58
Risk Management 大数据之风控 中国风控之蛮荒,正如金融危机前的美国… http://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?__biz=MzIxNjM3MDc4Mg==&mid=2247484694&idx=1&sn=f8f867ea55d5d4ed8a3feba95260efad&chksm=978b5e27a0fcd731fef42c96bdd7aa634b1c7ace41362df580391890237ff4c9179176b0e744&mpshare=1&scene=1&srcid=0413s4Xtcc8iNxgk78kfrXrn#rd http://v2.shendunfengkong.com/
https://spark-summit.org/east-2016/events/realtime-risk-management-using-kafka-python-and-spark-streaming/
https://databricks.com
京东基于Spark的风控系统架构实践和技术细节 www.infoq.com/cn/articles/jingdong-risk-control-system-architecture-based-on-spark https://www.slideshare.net/SparkSummit/realtime-risk-management-using-kafka-python-and-spark-streaming-by-nick-evans
Setup hortonwork cluster (spark standalone clusters) in local Apache Ambari Installation https://docs.hortonworks.com/HDPDocuments/Ambari-2.6.1.5/bk_ambari-installation/content/ch_Getting_Ready.html
What is the difference between using Ambari for HDP and not using it in Hortonworks? https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-using-Ambari-for-HDP-and-not-using-it-in-Hortonworks Ambari and HDP Installation: Quick Start for new Virtual Machine Users https://community.hortonworks.com/articles/69385/ambari-and-hdp-installation-quick-start-for-new-vi.html