回目录 《kafka》
cloud DMS PAAS VS original opensource KAFKA? EXAMPLE: huawei DMS
1. Basic concepts
-
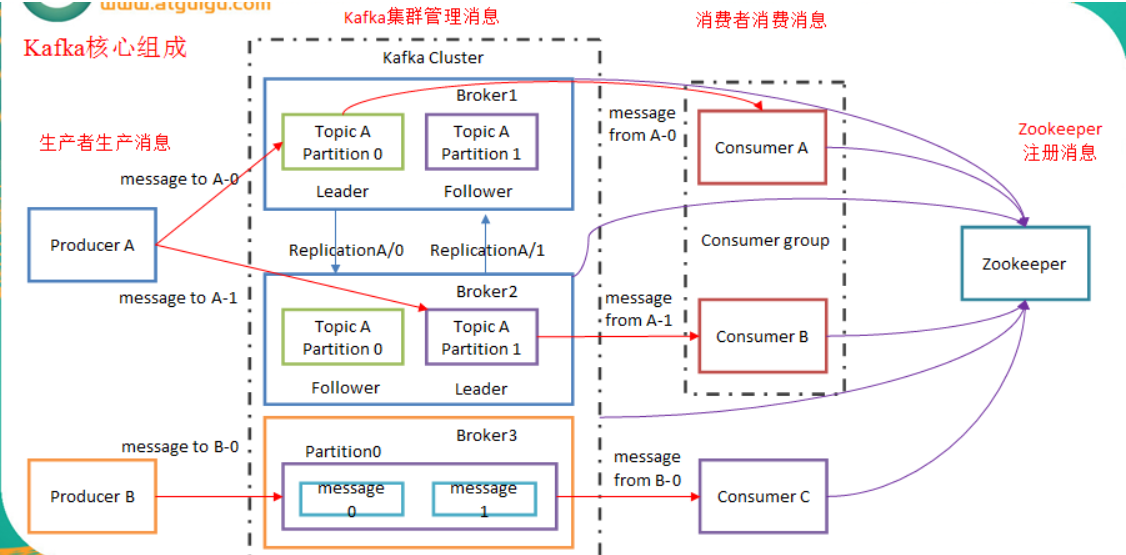
zookeeper: kafka 通过 zookeeper 来存储集群的 meta 信息。
-
broker: kafka 集群中包含的服务器。Each server acts as a leader for some of its partitions and a follower for others so load is well balanced within the cluster.
Kafka service = kafka broker, kafka cluster=multiple instances of kafka broker
-
controller: kafka 集群中的其中一个服务器,用来进行 leader election 以及 各种 failover。
-
producer: 消息生产者,发布消息到 kafka 集群的终端或服务。
-
consumer: 从 kafka 集群中消费消息的终端或服务。
- Topics & logs (Logical concept):
每条发布到 kafka 集群的消息属于的类别,即 kafka 是面向 topic 的。
- LEO:: log end offset offset+1
- ISR:: in-sync replicas
- internal topic:
consumer_offsets __transaction_offsets
key: <consumer_group>,<topic>,<partition> value: <offset>,<partition_leader_epoch>,<metadata>,<timestamp>
-
Partition (Physical concept): 是物理上的概念,每个 topic 包含一个或多个 partition。kafka 分配的单位是 partition。
Ordering (global order == one partition only)
Each partition is a totally ordered log, but there is no global ordering between partitions (other than perhaps some wall-clock time you might include in your messages). The assignment of the messages to a particular partition is controllable by the writer, with most users choosing to partition by some kind of key (e.g. user id). Partitioning allows log appends to occur without co-ordination between shards and allows the throughput of the system to scale linearly with the Kafka cluster size.
-
replica:partition 的副本,保障 partition 的高可用。
high watermark: indicated the offset of messages that are fully replicated, while the end-of-log offset might be larger if there are newly appended records to the leader partition which are not replicated yet.
-
leader:replica 中的一个角色, producer 和 consumer 只跟 leader 交互。(In Kafka 2.3 and older, you can only consume from the leader – this is by design. Replication is for fault-tolerance only.Since Kafka 2.4, it is possible to configure consumers to read from the closest replica. This may help improve latency, and also decrease network costs if using the cloud.)
Leader = topic leader = leader of replicas
-
follower:replica 中的一个角色,从 leader 中复制数据。
- Consumer group:
high-level consumer API 中,每个 consumer 都属于一个 consumer group,每条消息只能被 consumer group 中的一个 Consumer 消费,但可以被多个 consumer group 消费。
- consumer group leader:
is one of the consumer in a consumer group. - consumer coordinator(client side): each kafkaconsumer instance has a private member of consumer coordinator
- group coordinator(server side): is nothing but one of the brokers which receives heartbeats (or polling for messages) from all consumers of a consumer group. Every consumer group has a group coordinator. If a consumer stops sending heartbeats, the coordinator will trigger a rebalance.
- consumer group leader:
-
subscribe mode VS assign mode
先来看一段话
By having a notion of parallelism—the partition—within the topics, Kafka is able to provide both ordering guarantees and load balancing over a pool of consumer processes. This is achieved by assigning the partitions in the topic to the consumers in the consumer group so that **each partition is consumed by exactly one consumer in the group. **By doing this we ensure that the consumer is the only reader of that partition and consumes the data in order. Since there are many partitions this still balances the load over many consumer instances. **Note however that there cannot be more consumer instances in a consumer group than partitions. **
If we add more consumers to a single group with a single topic than we have partitions, some of the consumers will be idle and get no messages at all.
注意到这句话:however that there cannot be more consumer instances in a consumer group than partitions.
实际上这个是指的是assign mode下,同一个consumer group不能多个consumer来assign到同一个partition:
Properties props = new Properties(); props.put(ConsumerConfig.GROUP_ID_CONFIG, "MyConsumerGroup"); props.put("enable.auto.commit", "false"); consumer = new KafkaConsumer<>(props); TopicPartition partition0 = new TopicPartition("mytopic", 0); consumer.assign(Arrays.asList(partition0)); ConsumerRecords<Integer, String> records = consumer.poll(1000);如果一个consumer group启动多个consumer都选择这种assign模式,那么就会有问题,因为
It is important to recall that Kafka keeps one offset per [consumer-group, topic, partition]. That is the reason.
就是kafka自动维护的__consumer_offset是按照[consumer-group, topic, partition]来的[但是这里已经置为false了,所以应该没有问题,如果是true就有问题了,多个consumer读写同一个[consumer-group, topic, partition]就会有冲突]
而如果是使用subscribe mode,就会自动进行rebalance,如果同一个consumer group中的instance多于partition,那么没有问题,大不了consumer就idle或standby而已
Overview:



zookeeper 存储结构


图中不同topic的不同的partition可能位于同一个kafka broker或者不同的kafka broker,具体在哪里,完全可以去每个kafka节点下面寻找,路径:
/kafka/kafka-logs/<TOPIC-PARTITION>
2. Quick Start 安装配置
Quick start https://kafka.apache.org/quickstart
2.1 安装 install kafka
------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Creating a User for Kafka
------------------------------------------------------------------------
sudo useradd kafka -m
sudo passwd kafka
for ubuntu: sudo adduser kafka sudo
for centos: sudo usermod -aG wheel kafka
su -l kafka
------------------------------------------------------------------------
-- Downloading and Extracting the Kafka Binaries
------------------------------------------------------------------------
mkdir ~/Downloads
curl "https://www.apache.org/dist/kafka/2.1.1/kafka_2.11-2.1.1.tgz" -o ~/Downloads/kafka.tgz
mkdir ~/kafka && cd ~/kafka
tar -xvzf ~/Downloads/kafka.tgz --strip 1 (We specify the --strip 1 flag to ensure that the archive’s contents are extracted in ~/kafka/ itself and not in another directory (such as ~/kafka/kafka_2.11-2.1.1/) inside of it)
------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Configuring the Kafka Server
------------------------------------------------------------------------
vim ~/kafka/config/server.properties:
# The id of the broker. This must be set to a unique integer for each broker.
broker.id=0
port=9092
host.name=X.X.X.48
advertised.host.name=X.X.X.48
advertised.port=9092
delete.topic.enable = true
log.retention.hours=168
log.dirs=/opt/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/kafka-logs
#外置zookeeper
zookeeper.connect=1.1.1.1:2181,1.1.1.2:2181,1.1.1.3:2181
------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Option 1: Creating Systemd Unit Files and Starting the Kafka Server
------------------------------------------------------------------------
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/zookeeper.service
[Unit]
Requires=network.target remote-fs.target
After=network.target remote-fs.target
[Service]
Type=simple
User=kafka
ExecStart=/home/kafka/kafka/bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh /home/kafka/kafka/config/zookeeper.properties
ExecStop=/home/kafka/kafka/bin/zookeeper-server-stop.sh
Restart=on-abnormal
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
The [Unit] section specifies that Zookeeper requires networking and the filesystem to be ready before it can start.
The [Service] section specifies that systemd should use the zookeeper-server-start.sh and zookeeper-server-stop.sh shell files for starting and stopping the service. It also specifies that Zookeeper should be restarted automatically if it exits abnormally.
sudo vim /etc/systemd/system/kafka.service
[Unit]
Requires=zookeeper.service
After=zookeeper.service
[Service]
Type=simple
User=kafka
ExecStart=/bin/sh -c '/home/kafka/kafka/bin/kafka-server-start.sh /home/kafka/kafka/config/server.properties > /home/kafka/kafka/kafka.log 2>&1'
ExecStop=/home/kafka/kafka/bin/kafka-server-stop.sh
Restart=on-abnormal
[Install]
WantedBy=multi-user.target
The [Unit] section specifies that this unit file depends on zookeeper.service. This will ensure that zookeeper gets started automatically when the kafka service starts.
The [Service] section specifies that systemd should use the kafka-server-start.sh and kafka-server-stop.sh shell files for starting and stopping the service. It also specifies that Kafka should be restarted automatically if it exits abnormally.
sudo systemctl start kafka
sudo journalctl -u kafka
sudo systemctl enable kafka
------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Option 2: 编写启动脚本
------------------------------------------------------------------------
readonly PROGNAME=$(basename $0)
readonly PROGDIR=$(readlink -m $(dirname $0))
# source env
L_INVOCATION_DIR="$(pwd)"
L_CMD_DIR="/opt/scripts"
if [ "${L_INVOCATION_DIR}" != "${L_CMD_DIR}" ]; then
pushd ${L_CMD_DIR} &> /dev/null
fi
#source ../set_env.sh
#--------------- Function Definition ---------------#
showUsage() {
echo "Usage:"
echo "$0 kafka start|kill"
echo ""
echo "--start or -b: Start kafka"
echo "--kill or -k: Stop kafka"
}
#--------------- Main ---------------#
# Parse arguments
while [ "${1:0:1}" == "-" ]; do
case $1 in
--start)
L_FLAG="B"
;;
--kill)
L_FLAG="K"
;;
--status)
L_FLAG="S"
;;
*)
echo "Unknown option: $1"
echo ""
showUsage
echo ""
exit 1
;;
esac
shift
done
L_RETURN_FLAG=0 # 0 for success while 99 for failure
KAFKA_HOME=/opt/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/bin
ZK_CLUSTER=$HOST1:2181,$HOST2:2181,$HOST3:2181
pushd ${KAFKA_HOME} &>/dev/null
if [ "$L_FLAG" == "B" ]; then
echo "Starting kafka service..."
./kafka-server-start.sh -daemon ../config/server.properties
elif
echo "Stopping kafka service..."
./kafka-server-stop.sh -daemon ../config/server.properties
elif [ "$L_FLAG" == "S" ]; then
echo "Checking kafka status..."
arr=(${ZK_CLUSTER//","/ })
echo "${arr[@]}"
for ZK_NODE in "${arr[@]}";
do
echo "ZK_NODE: $ZK_NODE"
./zookeeper-shell.sh $ZK_NODE ls /brokers/ids
exit_code=$?
echo $exit_code
if [ "$exit_code" = "0" ]; then
exit 1
fi
done
fi
exit $L_RETURN_FLAG
注意:
如果是使用云上的DMS,zookeeper是不开放的,所以查询节点可以换用:
kafka/bin/kafka-broker-api-versions.sh --bootstrap-server "xxxx" | awk '/id/{print $1}'
------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Restricting the Kafka User as a security precaution.
------------------------------------------------------------------------
This step in the prerequisite disables sudo access for the kafka user
for ubuntu:
sudo deluser kafka sudo
for centos:
sudo gpasswd -d kafka wheel
sudo passwd kafka -l (对应unlock:sudo passwd kafka -u)
sudo su - kafka
2.2 Config
https://kafka.apache.org/26/documentation/
https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/installation/configuration
2.2.1 Broker/Server Config
通用配置
############################# Server Basics #############################
# The id of the broker. This must be set to a unique integer for each broker.
broker.id=0
############################# Socket Server Settings #############################
port=9092
host.name=X.X.X.48
advertised.host.name=X.X.X.48
advertised.port=9092
listeners = PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092
#advertised.listeners=PLAINTEXT://your.host.name:9092 //This is the metadata that’s passed back to clients.
listener.security.protocol.map=PLAINTEXT:PLAINTEXT,SSL:SSL,SASL_PLAINTEXT:SASL_PLAINTEXT,SASL_SSL:SASL_SSL
#Kafka brokers communicate between themselves, usually on the internal network (e.g., Docker network, AWS VPC, etc.). To define which listener to use, specify:
inter.broker.listener.name //https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-103%3A+Separation+of+Internal+and+External+traffic
You need to set advertised.listeners (or KAFKA_ADVERTISED_LISTENERS if you’re using Docker images) to the external address (host/IP) so that clients can correctly connect to it. Otherwise, they’ll try to connect to the internal host address—and if that’s not reachable, then problems ensue.
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42998859/kafka-server-configuration-listeners-vs-advertised-listeners
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-103%3A+Separation+of+Internal+and+External+traffic
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-291%3A+Separating+controller+connections+and+requests+from+the+data+plane
############################# Group Coordinator Settings #############################
# The following configuration specifies the time, in milliseconds, that the GroupCoordinator will delay the initial consumer rebalance.
# The rebalance will be further delayed by the value of group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms as new members join the group, up to a maximum of max.poll.interval.ms.
# The default value for this is 3 seconds.
# We override this to 0 here as it makes for a better out-of-the-box experience for development and testing.
# However, in production environments the default value of 3 seconds is more suitable as this will help to avoid unnecessary, and potentially expensive, rebalances during application startup.
group.initial.rebalance.delay.ms=0
还看到配置 scheduled.rebalance.max.delay.ms,
https://medium.com/streamthoughts/apache-kafka-rebalance-protocol-or-the-magic-behind-your-streams-applications-e94baf68e4f2
但是这好像是confluence提供的产品,并不是kafka默认的
############################# Log Retention Policy #############################
# The minimum age of a log file to be eligible for deletion due to age
log.retention.hours=336
# The maximum size of a log segment file. When this size is reached a new log segment will be created.
#log.segment.bytes=1073741824
log.segment.bytes=2147483647
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/65507232/kafka-log-segment-bytes-vs-log-retention-hours
配置 external zookeeper
kafka配置:
# Zookeeper connection string (see zookeeper docs for details).
# This is a comma separated host:port pairs, each corresponding to a zk
# server. e.g. "127.0.0.1:3000,127.0.0.1:3001,127.0.0.1:3002".
# You can also append an optional chroot string to the urls to specify the
# root directory for all kafka znodes.
zookeeper.connect=1.1.1.1:2181,1.1.1.2:2181,1.1.1.3:2181
# Timeout in ms for connecting to zookeeper
zookeeper.connection.timeout.ms=6000
zookeeper配置:
This example is for a 3 node ensemble:
# The number of milliseconds of each tick
tickTime=2000
# The number of ticks that the initial
# synchronization phase can take
initLimit=10
# The number of ticks that can pass between
# sending a request and getting an acknowledgement
syncLimit=5
# the directory where the snapshot is stored.
# do not use /tmp for storage, /tmp here is just
# example sakes.
dataDir=/zookeeper-3.4.8/zkdata
dataLogDir=/zookeeper-3.4.8/logs
# the port at which the clients will connect
clientPort=2181
server.1=1.1.1.1:2888:3888
server.2=1.1.1.2:2888:3888
server.3=1.1.1.3:2888:3888
SERVER_JVMFLAGS=-Xmx1024m'
listener
关于host
测试 listener工具:
-
kafkacat:
https://github.com/edenhill/kafkacat
https://docs.confluent.io/platform/current/app-development/kafkacat-usage.html
kafkacat -b kafka0:9092 -L -
python scripts
https://github.com/lyhistory/kafka-listeners/blob/master/python/python_kafka_test_client.py
https://www.confluent.io/blog/kafka-client-cannot-connect-to-broker-on-aws-on-docker-etc/
-
nc
nc -vz 1.1.1.1 9092
retention / delete
retention.ms 参数指定消息在 topic 中保留的时间,单位是毫秒。在指定的时间过去后,Kafka 会将该 topic 中旧的消息删除
delete.retention.ms 参数是在消息被删除后,要等待多长时间才能在磁盘上删除该消息的文件
cleanup.policy A string that is either “delete” or “compact” or both. This string designates the retention policy to use on old log segments. The default policy (“delete”) will discard old segments when their retention time or size limit has been reached. The “compact” setting will enable log compaction on the topic.
Type: list Default: delete Valid Values: [compact, delete] Server Default Property: log.cleanup.policy Importance: medium
retention.ms This configuration controls the maximum time we will retain a log before we will discard old log segments to free up space if we are using the “delete” retention policy. This represents an SLA on how soon consumers must read their data. If set to -1, no time limit is applied.
Type: long Default: 604800000 (7 days) Valid Values: [-1,…] Server Default Property: log.retention.ms Importance: medium
delete.retention.ms The amount of time to retain delete tombstone markers for log compacted topics. This setting also gives a bound on the time in which a consumer must complete a read if they begin from offset 0 to ensure that they get a valid snapshot of the final stage (otherwise delete tombstones may be collected before they complete their scan).
Type: long Default: 86400000 (1 day) Valid Values: [0,…] Server Default Property: log.cleaner.delete.retention.ms Importance: medium
kafka至少会保留1个工作segment保存消息。消息量超过单个文件存储大小就会新建segment,比如消息量为2.6GB, 就会建立3个segment。kafka会定时扫描非工作segment,将该文件时间和设置的topic过期时间进行对比,如果发现过期就会将该segment文件(具体包括一个log文件和两个index文件)打上.deleted 的标记: kafka-logs/Topic-1/XXXXX.log.deleted 最后kafka中会有专门的删除日志定时任务过来扫描,发现.deleted文件就会将其从磁盘上删除,释放磁盘空间,至此kafka过期消息删除完成。
log.retention.ms: log.retention.ms parameter (default to 1 week). If set to -1, no time limit is applied.
log.retention.bytes: Its default value is -1, which allows for infinite retention. This means that if you have a topic with 8 partitions, and log.retention.bytes is set to 1 GB, the amount of data retained for the topic will be 8 GB at most. If you have specified both log.retention.bytes and log.retention.ms, messages may be removed when either criterion is met.
log.segment.bytes and log.segment.ms: As messages are produced to the Kafka broker, they are appended to the current log segment for the partition. Once the log segment has reached the size specified by the log.segment.bytes parameter (default 1 GB), the log segment is closed and a new one is opened. Only once a log segment has been closed, it can be considered for expiration (by log.retention.ms or log.retention.bytes).
Another way to control when log segments are closed is by using the log.segment.ms parameter, which specifies the amount of time after which a log segment should be closed. Kafka will close a log segment either when the size limit is reached or when the time limit is reached, whichever comes first.
A smaller log-segment size means that files must be closed and allocated more often, which reduces the overall efficiency of disk writes. Adjusting the size of the log segment can be important if topics have a low produce rate. For example, if a topic receives only 100 megabytes per day of messages, and log.segment.bytes is set to the default, it will take 10 days to fill one segment. As messages cannot be expired until the log segment is closed, if log.retention.ms is set to 1 week, they will actually be up to 17 days of messages retained until the closed segment expires. This is because once the log segment is closed with the current 10 days of messages, that log segment must be retained 7 days before it expires based on the time policy.
log.retention.check.interval.ms:default 5 minutes. So the broker log-segments are checked every 5 minutes to see if they can be deleted according to the retention policies.
topic1 configuration had retention policy set (retention.ms=60000), so if there was at least one existing message in an active segment of topic1, that segment would get closed and deleted if it was idle for long enough. Since log.retention.check.interval.ms is broker configuration, it’s not affected by changes on the topic. Also retention.ms has to pass after the last message is produced to the segment. So after the last message is produced to that segment, segment will be deleted in not less than retention.ms milliseconds and not more than retention.ms+log.retention.check.interval.ms.
So the “segment of just 35 bytes, which contained just one message, was deleted after the minute (maybe a little more)” happened because retention check by chance happened almost immediately after the message was produced to that segment. Broker then had just to wait 60 seconds to be sure no new message will be produced to that segment (in which case deletion would’t happen) and since there was none, it deleted the segment
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41048041/kafka-deletes-segments-even-before-segment-size-is-reached
复制因子 replica factor 详解
很重要,对于普通的topic replica factor来说,replica多一些没有问题,但是对internal topic要特别注意,尤其是对于 __transaction_state来说,如果min.isr设置跟replication.factor设置一样,那么任何一个kafka节点down掉,都会造成无法写入kafka(transactional producer写入会报错 NotEnoughReplicasException)
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47483016/recommended-settings-for-kafka-internal-topics-after-upgrade-to-1-0
############################# Internal Topic Settings #############################
# The replication factor for the group metadata internal topics "__consumer_offsets" and "__transaction_state"
# For anything other than development testing, a value greater than 1 is recommended for to ensure availability such as 3.
offsets.topic.num.partitions = 50 (default)
offsets.topic.replication.factor=3
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=3
transaction.state.log.min.isr=2
kafka-topics.sh -describe --bootstrap-server ip:9092 --topic __consumer_offsets
kafka-topics.sh -describe --bootstrap-server ip:9092 --topic __transaction_state
说明:
-
min.insync.replicas(default value=1) https://accu.org/journals/overload/28/159/kozlovski/ 同时控制external topic 以及internal topic
__consumer_offsets和__transaction_state, -
transaction.state.*只控制
__transaction_state(transaction.state.log.min.isr overriden min.insync.replicas), -
offsets.topic.replication.factor控制offsets topic也就是
__consumer_offsets,必须跟broker个数一致(小于等于,默认值为3,如果是两个节点就不行了,所以不要轻易使用默认值),否则无法启动 -
default.replication.factor控制external topic(有时候称为automatically created topics,手动或自动创建auto.create.topics.enable默认是true)
场景:
-
if living/avaliable brokers < default.replication.factor 无法创建topic,报错:InvalidReplicationFactorException
- if offsets.topic.replication.factor > brokers数量,
kafka client无法启动(无法Discover group coordinator)应该是kafka sever无法正常创建internal topic consumer_offset, kafka server报错:ERROR [KafkaApi-0] Number of alive brokers '2' does not meet the required replication factor '3' for the offsets topic (configured via 'offsets.topic.replication.factor'). This error can be ignored if the cluster is starting up and not all brokers are up yet. (kafka.server.KafkaApis) -
if default.replication.factor==节点数,比如: default.replication.factor=3 这样挂掉任何一个节点client都会报错:
2021-06-08 17:06:01.892 ^[[33m WARN^[[m ^[[35m23610GG^[[m [TEST-MANAGER] ^[[36mk.c.NetworkClient$DefaultMetadataUpdater^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-SZL] 1 partitions have leader brokers without a matching listener, including [T-TEST-1] -
if (live isr 活着的节点中并且是isr的节点数) < transaction.state.log.min.isr:
[2021-06-09 09:31:14,285] ERROR [ReplicaManager broker=0] Error processing append operation on partition __transaction_state-28 (kafka.server.ReplicaManager) org.apache.kafka.common.errors.NotEnoughReplicasException: The size of the current ISR Set(0) is insufficient to satisfy the min.isr requirement of 2 for partition __transaction_state-28注意如果不停掉kafka producer程序,上述日志会快速的在kafka/logs/server.log 中刷入,潜在可能会造成磁盘问题
-
if living/avaliable brokers <min.insync.replicas && producer.properties.acks=all: producer报错 NotEnoughReplicasException
-
if (live isr 活着的节点中并且是isr的节点数) <min.insync.replicas of
__consumer_offsets:kafka consumer client discover group之后无法join group,在revoke之后,rejoining group停顿几分钟后狂刷日志:
2021-06-09 10:17:23.076 ^[[32m INFO^[[m ^[[35m26210GG^[[m [TEST-MANAGER] ^[[36mo.a.k.c.c.i.AbstractCoordinator^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-REALTIME-SZL] Group coordinator XXXX:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null) is unavailable or invalid, will attempt rediscovery 2021-06-09 10:17:23.186 ^[[32m INFO^[[m ^[[35m26210GG^[[m [TEST-MANAGER] ^[[36mordinator$FindCoordinatorResponseHandler^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-REALTIME-SZL] Discovered group coordinator XXXX:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null) 2021-06-09 10:17:23.187 ^[[32m INFO^[[m ^[[35m26210GG^[[m [TEST-MANAGER] ^[[36mo.a.k.c.c.i.AbstractCoordinator^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-REALTIME-SZL] Group coordinator XXXX8:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null) is unavailable or invalid, will attempt rediscovery 2021-06-09 10:17:23.288 ^[[32m INFO^[[m ^[[35m26210GG^[[m [TEST-MANAGER] ^[[36mordinator$FindCoordinatorResponseHandler^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-REALTIME-SZL] Discovered group coordinator XXXX:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null) 2021-06-09 10:17:23.289 ^[[32m INFO^[[m ^[[35m26210GG^[[m [TEST-MANAGER] ^[[36mo.a.k.c.c.i.AbstractCoordinator^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-REALTIME-SZL] (Re-)joining group同时kafka server端狂刷日志:
[2021-06-09 10:18:43,146] INFO [GroupCoordinator 0]: Preparing to rebalance group TEST-REALTIME-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 393 (__consumer_offsets-49) (reaso n: error when storing group assignment during SyncGroup (member: consumer-1-0c90d042-0326-4cf2-a870-bb2ae055d140)) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator) [2021-06-09 10:18:43,349] INFO [GroupCoordinator 0]: Stabilized group TEST-REALTIME-SZL generation 394 (__consumer_offsets-49) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator) [2021-06-09 10:18:43,349] INFO [GroupCoordinator 0]: Assignment received from leader for group TEST-REALTIME-SZL for generation 394 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator) [2021-06-09 10:18:43,349] ERROR [ReplicaManager broker=0] Error processing append operation on partition __consumer_offsets-49 (kafka.server.ReplicaManager) org.apache.kafka.common.errors.NotEnoughReplicasException: The size of the current ISR Set(0) is insufficient to satisfy the min.isr requirement of 2 for partition __consumer_offsets- 49服务端borker节点上topic 正常状态(每个topic的partition的leader和replica状态)应该是:
[2022-03-16 15:55:15,899] TRACE [Controller id=0] Leader imbalance ratio for broker 2 is 0.0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 15:55:15,899] DEBUG [Controller id=0] Topics not in preferred replica for broker 1 Map() (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 15:55:15,899] TRACE [Controller id=0] Leader imbalance ratio for broker 1 is 0.0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 15:55:15,899] DEBUG [Controller id=0] Topics not in preferred replica for broker 0 Map() (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 15:55:15,899] TRACE [Controller id=0] Leader imbalance ratio for broker 0 is 0.0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController)但此时是非正常状态:
failed to complete preferred replica leader election [2022-03-16 10:58:02,837] ERROR [Controller id=1] Error completing preferred replica leader election for partition T-TRADE-1 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) kafka.common.StateChangeFailedException: Failed to elect leader for partition T-TRADE-1 under strategy PreferredReplicaPartitionLeaderElectionStrategy at kafka.controller.PartitionStateMachine.$anonfun$doElectLeaderForPartitions$9(PartitionStateMachine.scala:390) at scala.collection.mutable.ResizableArray.foreach(ResizableArray.scala:62) at scala.collection.mutable.ResizableArray.foreach$(ResizableArray.scala:55) at scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer.foreach(ArrayBuffer.scala:49) at kafka.controller.PartitionStateMachine.doElectLeaderForPartitions(PartitionStateMachine.scala:388) at kafka.controller.PartitionStateMachine.electLeaderForPartitions(PartitionStateMachine.scala:315) at kafka.controller.PartitionStateMachine.doHandleStateChanges(PartitionStateMachine.scala:225) at kafka.controller.PartitionStateMachine.handleStateChanges(PartitionStateMachine.scala:141) at kafka.controller.KafkaController.kafka$controller$KafkaController$$onPreferredReplicaElection(KafkaController.scala:649) at kafka.controller.KafkaController.$anonfun$checkAndTriggerAutoLeaderRebalance$6(KafkaController.scala:1008) at scala.collection.immutable.Map$Map3.foreach(Map.scala:195) at kafka.controller.KafkaController.kafka$controller$KafkaController$$checkAndTriggerAutoLeaderRebalance(KafkaController.scala:989) at kafka.controller.KafkaController$AutoPreferredReplicaLeaderElection$.process(KafkaController.scala:1020) at kafka.controller.ControllerEventManager$ControllerEventThread.$anonfun$doWork$1(ControllerEventManager.scala:94) at scala.runtime.java8.JFunction0$mcV$sp.apply(JFunction0$mcV$sp.java:23) at kafka.metrics.KafkaTimer.time(KafkaTimer.scala:31) at kafka.controller.ControllerEventManager$ControllerEventThread.doWork(ControllerEventManager.scala:94) at kafka.utils.ShutdownableThread.run(ShutdownableThread.scala:82) [2022-03-16 10:58:02,837] WARN [Controller id=1] Partition T-TEST-SNP-2 failed to complete preferred replica leader election to 2. Leader is still 0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 10:58:02,837] WARN [Controller id=1] Partition T-TEST-0 failed to complete preferred replica leader election to 2. Leader is still 0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 10:58:02,838] INFO [Controller id=1] Partition T-TEST2-SNP-2 completed preferred replica leader election. New leader is 2 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) [2022-03-16 10:58:02,838] WARN [Controller id=1] Partition T-TEST2-1 failed to complete preferred replica leader election to 2. Leader is still 0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController) - 丢数据:min.insync.replicas=2 && unclean.leader.election.enable=true (It is default false) https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57277370/min-insync-replicas-vs-unclean-leader-election
log dir不要用/tmp
Consumer相关
Producer相关
2.2.2 Client Config
Consumer相关
Producer相关
2.3 GUI & Commands
- GUI:
- KafkaEsque https://kafka.esque.at
- https://github.com/airbnb/kafkat
- 命令:
/bin/*.sh - 单机命令 –broker-list
- 集群命令 –bootstrap-server
2.3.1 单机本地调试 Local
Start zookeeper
bin/zookeeper-server-start.sh config/zookeeper.properties
Start kafka server
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server.properties
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server-1.properties &
bin/kafka-server-start.sh config/server-2.properties &
config/server-1.properties:
broker.id=1
listeners=PLAINTEXT://:9093
log.dirs=/tmp/kafka-logs-1
Create topic
bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --replication-factor 3 --partitions 1 --topic my-replicated-topic
bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic mytopic
#You can use kafka-topics.sh to see how the Kafka topic is laid out among the Kafka brokers. The ---describe will show partitions, ISRs, and broker partition leadership.
[test@localhost kafka_2.12-2.2.0]$ bin/kafka-topics.sh --describe --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic my-replicated-topic
OpenJDK 64-Bit Server VM warning: If the number of processors is expected to increase from one, then you should configure the number of parallel GC threads appropriately using -XX:ParallelGCThreads=N
Topic:my-replicated-topic PartitionCount:1 ReplicationFactor:3 Configs:segment.bytes=1073741824
Topic: my-replicated-topic Partition: 0 Leader: 1 Replicas: 1,2,0 Isr: 1,2,0
Reassign Partition
kafka-reassign-partitions.sh
-- 1.generate current assignment
kafka-reassign-partitions --zookeeper hostname:port --topics-to-move-json-file topics to move.json --broker-list broker 1, broker 2 --generate
-- 2.modify and apply
kafka-reassign-partitions --zookeeper hostname:port --reassignment-json-file reassignment configuration.json --bootstrap-server hostname:port --execute
-- 3.verify
kafka-reassign-partitions --zookeeper hostname:port --reassignment-json-file reassignment configuration.json --bootstrap-server hostname:port --verify
Produce
bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic my-replicated-topic
# for test
bin/kafka-verifiable-producer.sh --topic consumer-tutorial --max-messages 200000 --broker-list localhost:9092
Consume
bin/kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper localhost:2181
bin/kafka-topics.sh --describe --zookeeper localhost:2181 --topic "ngs.svl.20220519.fib.result"
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --from-beginning --topic my-replicated-topic
bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server <你的kafka配置> --topic T-RISK --partition 0 --offset 3350 --max-messages 1
kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic first_topic --formatter kafka.tools.DefaultMessageFormatter --property print.timestamp=true --property print.key=true --property print.value=true --from-beginning
More properties are available such as:
print.partition
print.offset
print.headers
key.separator
line.separator
headers.separator
#inspect partition assignments and consumption progress
bin/kafka-consumer-groups.sh --new-consumer --describe --group consumer-tutorial-group --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
=>
shows all the partitions assigned within the consumer group, which consumer instance owns it, and the last committed offset (reported here as the “current offset”). The lag of a partition is the difference between the log end offset and the last committed offset.
#count total messages for a topic:
kafka-console-consumer.sh \
--from-beginning \
--bootstrap-server <BROKER:PORT> \
--property print.key=true \
--property print.value=false \
--property print.partition \
--topic <TOPIC_NAME> | tail -n 10|grep "Msg Count="
$ kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.GetOffsetShell \
--broker-list <HOST1:PORT,HOST2:PORT> \
--topic <TOPIC_NAME>
kafka-run-class.sh kafka.admin.ConsumerGroupCommand \
--group <GROUP_NAME> \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 \
--describe
kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.ConsumerOffsetChecker \
--topic <TOPIC_NAME> \
--zookeeper localhost:2181 \
--group <GROUP_NAME>
#!/usr/bin/bash
# Copyright (c) 2016 AsiaInvestment Pte. Ltd. Singapore
# All rights reserved.
BOOTS_STRAP_SERVER=127.0.0.1:9092
ZK_SERVER=127.0.0.1:2181
pushd /kafka_2.12-2.2.0/bin &>/dev/null
echo "#################################"
echo "### TOPICS"
echo "#################################"
topics=(`./kafka-topics.sh --list --zookeeper $ZK_SERVER | grep -v grep | awk '{print $1}'`)
for topic in ${topics[@]}
do
./kafka-topics.sh --describe --bootstrap-server $BOOTS_STRAP_SERVER --topic $topic
done
echo "#################################"
echo "### CONSUMER GROUP"
echo "#################################"
consumer_groups=(`./kafka-consumer-groups.sh --list --bootstrap-server $BOOTS_STRAP_SERVER | grep -v grep | awk '{print $1}'`)
for group in ${consumer_groups[@]}
do
echo " >>>group:$group<<<"
./kafka-consumer-groups.sh --describe --group $group --bootstrap-server $BOOTS_STRAP_SERVER
done
popd &>/dev/null
dump log
./kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.DumpLogSegments --deep-iteration --print-data-log --files /tmp/kafka-logs/mftp1-0/00000000000000000000.log
describe
/bin/kafka-configs.sh --describe --bootstrap-server "192.168.250.11:9092" --all --entity-type "brokers" --entity-name "0"
2.3.2 虚拟机远程调试 Remote
VM Host only mode
systemctl stop firewalld
Test from windows bat
.\kafka-console-producer.bat --broker-list x.x.x.x:9092 --topic test
C:\Workspace\Temp\kafka_2.12-2.2.1\bin\windows> .\kafka-console-consumer.bat --bootstrap-server x.x.x.x:9092 --from-beginning --topic test
Test from windows with python
pip install python-kafka
#python NO brokeravaialble
producer = KafkaProducer(bootstrap_servers=['x.x.x.x:9092'], api_version=(0,10))
#assert type(value_bytes) in (bytes, bytearray, memoryview, type(None)) AssertionError
producer.send('test', 'hi'.encode('utf-8'))

Failed on VM NAT mode
Someone succeed: https://boristyukin.com/connecting-to-kafka-on-virtualbox-from-windows/ But keep got: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TimeoutException: Topic not present in metadata after 60000 ms
Port forward: 9092 Changed vm hostname And map on host machine
When producer/consumer accesses the Kafka broker, the Kafka broker returns its host name for data producer or consumer at default settings. So producers/consumers need to resolve broker’s host name to IPAddress. For broker returning an arbitrary host name, use the advertised.listeners settings. listeners vs. advertised.listeners https://stackoverflow.com/questions/42998859/kafka-server-configuration-listeners-vs-advertised-listeners
Turned on log level to DEBUG
May be need to do something like: https://forums.virtualbox.org/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=29990 https://github.com/trivago/gollum/issues/93
Telnet 127.0.0.1/guesthost 9092 WORKS, but it doesn’t mean it can reach to the guest machine, simply because of port forwarding opened 9092 port on host

Final vm workaround (NAT+HOSTONLY) vim /etc/sysconfig/network-scripts/ifcfg-enp0s3
3. 管理维护 Maintain
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#operations
3.1 节点状态
------------------------------------------
--- zookeeper status
------------------------------------------
/zookeeper/bin/zkServer.sh status
------------------------------------------
--- 查看kafka broker节点
------------------------------------------
>/zookeeper/bin/zkCli.sh -server localhost:2181 #Make sure your Broker is already running
#ls /brokers/ids # Gives the list of active brokers
#ls /brokers/topics #Gives the list of topics
#get /brokers/ids/0 #Gives more detailed information of the broker id '0'
3.2 Backup (point-in-time snapshot) & Restore
为什么需要备份?
https://medium.com/@anatolyz/introducing-kafka-backup-9dc0677ea7ee
Replication handles many error cases but by far not all. What about the case that there is a bug in Kafka that deletes old data? What about a misconfiguration of the topic (are you sure, that your value of retention.ms is a millisecond value?)? What about an admin that accidentally deleted the whole Prod Cluster because they thought they were on dev? What about security breaches? If an attacker gets access to your Kafka Management interface, they can do whatever they like.
Of course, this does not matter too much if you are using Kafka to distribute click-streams data for your analytics department and it is tolerable to loose some data. But if you use Kafka as your “central nervous system” for your company and you store your core business data in Kafka you better think about a cold storage backup for your Kafka Cluster.
停机备份
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorials/how-to-back-up-import-and-migrate-your-apache-kafka-data-on-ubuntu-18-04
单机版例子,集群类似,只是需要停掉所有的zookeeper和kafka,然后备份其中一台机器的zookeeper和kafka,然后在所有机器上恢复
sudo -iu kafka
~/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --create --zookeeper localhost:2181 --replication-factor 1 --partitions 1 --topic BackupTopic
echo "Test Message 1" | ~/kafka/bin/kafka-console-producer.sh --broker-list localhost:9092 --topic BackupTopic > /dev/null
~/kafka/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic BackupTopic --from-beginning
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Backing Up the ZooKeeper State Data
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
kafka内置zookeeper:
ZooKeeper stores its data in the directory specified by the dataDir field in the /kafka/config/zookeeper.properties:
dataDir=/tmp/zookeeper
使用外置zookeeper:
/zookeeper/conf/zoo.cfg
dataDir=/opt/zookeeper-3.4.8/zkdata
dataLogDir=/opt/zookeeper-3.4.8/logs
compressed archive files are a better option over regular archive files to save disk space:
tar -czf /opt/kafka_backup/zookeeper-backup.tar.gz /opt/zookeeper-3.4.8/zkdata/*
忽略错误 tar: Removing leading `/' from member names
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Backing Up the Kafka Topics and Messages
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Kafka stores topics, messages, and internal files in the directory that the log.dirs field specifies
/kafka/config/server.properties:
log.dirs=/opt/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/kafka-logs
stop the Kafka service so that the data in the log.dirs directory is in a consistent state when creating the archive with tar
sudo systemctl stop kafka (前面安装时移除了kafka的sudo权限,需要使用其他有sudo权限的非root用户执行)
sudo -iu kafka
tar -czf /opt/kafka_backup/kafka-backup.tar.gz /opt/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/kafka-logs/*
sudo systemctl start kafka (同样切换其他用户)
sudo -iu kafka
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Restoring the ZooKeeper Data & Kafka Data
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
You need to stop the Kafka and ZooKeeper services as a precaution against the data directories receiving invalid data during the restoration process.
sudo systemctl stop kafka
sudo systemctl stop zookeeper
sudo -iu kafka
rm -r /opt/zookeeper-3.4.8/zkdata/*
tar -C /opt/zookeeper-3.4.8/zkdata -xzf /opt/kafka_backup/zookeeper-backup.tar.gz --strip-components 2
(specify the --strip 2 flag to make tar extract the archive’s contents in /tmp/zookeeper/ itself and not in another directory (such as /tmp/zookeeper/tmp/zookeeper/) inside of it.)
rm -r /opt/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/kafka-logs/*
tar -C /opt/kafka_2.12-2.2.0/kafka-logs -xzf /opt/kafka_backup/kafka-backup.tar.gz --strip-components 2
sudo systemctl start kafka
sudo systemctl start zookeeper
sudo -iu kafka
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Verifying the Restoration
-----------------------------------------------------------------------------------
~/kafka/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic BackupTopic --from-beginning
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47791039/backup-restore-kafka-and-zookeeper/48337651
在线备份
Still no. You’re dealing with a distributed system. It’s not magic. Any attempt to trigger a snapshot ‘simultaneously’ across multiple hosts/disks is going to be subject to some small level of timing difference whether those are VMs managed by you in the Cloud or containers in K8s with persistent disks managed by the Cloud provider. It’d probably work in small scale tests, but break under significant production load.
https://www.reddit.com/r/apachekafka/comments/jb400p/kafka_backup_and_recovery/g8vkju7/
https://www.reddit.com/r/apachekafka/comments/g73nk9/how_to_take_full_backupsnapshot_of_kafka/
解决方案:
Support point-in-time backups :
提出需求:https://github.com/itadventurer/kafka-backup/issues/52
解决方案:
1)当前版本在一定场景下可以使用:
- Let Kafka Backup running in the background
- Kafka Backup writes data continuously in the background to the file system
kill -9Kafka Backup as soon as it is “finished”, i.e. it finished writing your data. This should be promptly after you finished producing data- move the data of Kafka Backup to your new destination.
需要用到kafka自带的connect-standalone.sh 所以要配置环境变量
export PATH=$PATH:~/kafka/bin
backup:
sudo env "PATH=$PATH" backup-standalone.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --target-dir /path/to/backup/dir --topics 'topic1,topic2'
~/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --delete --topic topic1
~/kafka/bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --delete --topic 'topic.*'
restore:
restore-standalone.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --target-dir /path/to/backup/dir --topics 'topic1,topic2'
~/kafka/bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic BackupTopic --from-beginning
2)新增的支持 https://github.com/itadventurer/kafka-backup/pull/99 但是没有发布
https://www.confluent.io/blog/3-ways-prepare-disaster-recovery-multi-datacenter-apache-kafka-deployments/
3.3 re-partition?
注意:改变partition数量不会重新动态分配/迁移现有数据
Alter:
bin/kafka-topics.sh –bootstrap-server broker_host:port –alter –topic my_topic_name
–partitions 40
kafka-reassign-partitions命令是针对Partition进行重新分配,而不能将整个Topic的数据重新均衡到所有的Partition中。
https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000011721643
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1349448
Be aware that one use case for partitions is to semantically partition data, and adding partitions doesn’t change the partitioning of existing data so this may disturb consumers if they rely on that partition. That is if data is partitioned by hash(key) % number_of_partitions then this partitioning will potentially be shuffled by adding partitions but Kafka will not attempt to automatically redistribute data in any way.
3.4 工具/日志排查
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#monitoring
系统排查
$ jps
17303 Jps
29819 Kafka
$ ll /proc/29819/fd
日志位置
-
/kafka/logs
controller.log.2021-03-01-00 kafka集群选举出的Controller负责通信 server.log.2021-03-01-00 具体负责某个partition replica的leader的日志以及负责某个consumer group的group coordinator日志 state-change.log.2021-03-01 记录topic partition的online offline等状态信息
kafkaServer.out跟server.log一样,只是会定期archive到server.log
-
/kafka/kafka-logs
__consumer_offsets-0/
__transaction_state-0/
[TOPIC]-[PARTITION]/
kafka server端日志解析
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- create/delete topic, from controller.log
1)这个是命令创建的
./kafka-topics.sh --create --bootstrap-server $KFK_CLUSTER --replication-factor 2 --partitions 3 --topic T-XXX
replica是2,所以对应两个broker,所以后面还要选一个prefer replica作为leader
[2021-04-14 11:04:11,239] INFO [Controller id=0] New topics: [Set(T-XXX)], deleted topics: [Set()], new partition replica assignment [Map(T-XXX-2 -> Vector(3, 0), T-XXX-1 -> Vector(0, 1), T-XXX-0 -> Vector(1, 3))] (kafka.controller.KafkaController)
--- elect TOPIC-PARTITION replica leader
INFO [Controller id=0] Partition T-XXX-2 completed preferred replica leader election. New leader is 3 (kafka.controller.KafkaController)
2)下面这个内部topic是何时被创建的(更准确的应该是说其各个分区是何时创建的)
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/19958
__consumer_offsets创建的时机有很多种,主要包括:
broker响应FindCoordinatorRequest请求时
broker响应MetadataRequest显式请求__consumer_offsets元数据时
其中以第一种最为常见,而第一种时机的表现形式可能有很多,比如用户启动了一个消费者组(下称consumer group)进行消费或调用kafka-consumer-groups --describe等
注意,各自分区都是对应到一个broker,所以consumer group也就是直接对应到了相应的broker(group coordinator)
[2021-04-14 11:14:20,601] INFO [Controller id=0] New topics: [Set(__consumer_offsets)], deleted topics: [Set()], new partition replica assignment [Map(__consumer_offsets-22 -> Vector(3), __consumer_offsets-30 -> Vector(1), __consumer_offsets-8 -> Vector(0), __consumer_offsets-21 -> Vector(1), __co
对应到项目代码应该就是消费组 consumer group启动的时候
3)这个是代码创建的:
auto.create.topics.enable=true,代码读取T-XXX-SNP就会创建:
SNP就是我们后面会提到的所谓自己维护的增量快照
默认用了1个replica,所以直接就对应某个broker
[2021-04-14 11:14:27,347] INFO [Controller id=0] New topics: [Set(T-XXX-SNP)], deleted topics: [Set()], new partition replica assignment [Map(T-sss-SNP-2 -> Vector(3), T-XXX-SNP-1 -> Vector(1), T-XXX-SNP-0 -> Vector(0))] (kafka.controller.KafkaController)
[2021-04-14 11:14:27,347] INFO [Controller id=0] New partition creation callback for T-XXX-SNP-2,T-XXX-SNP-1,T-XXX-SNP-0 (kafka.controller.KafkaController)
最后变成一张broker map:
[2021-04-14 11:18:36,979] DEBUG [Controller id=0] Preferred replicas by broker Map(1 -> Map(T-JOB-SNP-0 -> Vector(1), __consumer_offsets-27 -> Vector(1), T-TEST-1 -> Vector(1, 0), __transaction_state-2 -> Vector(1, 3), __transaction_state-20 -> Vector(1, 3), __consumer_offsets-33 -> Vector(1), T-DBMS-SNP-0 -> Vector(1), T-CAPTURE-0 -> Vector(1, 0), __consumer_offsets-36 -> Vector(1), __transaction_state-29 -> Vector(1, 0), __consumer_offsets-42 -> Vector(1), __consumer_offsets-3 -> Vector(1), __consumer_offsets-18 -> Vector(1), __transaction_state-38 -> Vector(1, 3), T-TEST-SNP-2 -> Vector(1, 3), T-MEMBER-1 -> Vector(1, 0), __consumer_offsets-15 -> Vector(1), __consumer_offsets-24 -> Vector(1), T-EOD-1 -> Vector(1, 0), T-QUOTATION-2 -> Vector(1, 0), __transaction_state-14 -> Vector(1, 3), __transaction_state-44 -> Vector(1, 3), T-RISK-0 -> Vector(1, 3), T-RISK-SNP-2 -> Vector(1), __transaction_state-32 -> Vector(1, 3), __consumer_offsets-48 -> Vector(1), T-CAPTURE-SNP-1 -> Vector(1), T-TEST-0 -> Vector(1, 0), T-EOD-SNP-1 -> Vector(1), __transaction_state-17 -> Vector(1, 0), __transaction_state-23 -> Vector(1, 0), __transaction_state-47 -> Vector(1, 0), __consumer_offsets-6 -> Vector(1), T-QUOTATION-SNP-1 -> Vector(1), __transaction_state-26 -> Vector(1, 3), T-JOB-2 -> Vector(1, 0), __transaction_state-5 -> Vector(1, 0), __transaction_state-8 -> Vector(1, 3)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- elect Controller from controller.log
[2021-04-14 10:53:31,013] DEBUG [Controller id=1] Broker 0 has been elected as the controller, so stopping the election process. (kafka.controller.KafkaController)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- rebalance by group coordinator broker 3,from server.log or kafkaServer.out
[2021-04-15 08:24:20,809] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Preparing to rebalance group XXXX-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 0 (__consumer_offsets-28) (reason: Adding new member consumer-1-11aac9d7-8a72-44fe-bf5c-0519941bbb6a) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:20,811] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Stabilized group XXX-SZL generation 1 (__consumer_offsets-28) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:20,823] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Assignment received from leader for group XXXX-SZL for generation 1 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:22,543] INFO [TransactionCoordinator id=3] Initialized transactionalId XXX-TID-0 with producerId 1004 and producer epoch 1 on partition __transaction_state-15 (kafka.coordinator.transaction.TransactionCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:23,957] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Preparing to rebalance group XXXX-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 0 (__consumer_offsets-49) (reason: Adding new member consumer-1-416c9379-0f89-48f4-b125-eadf648d57c7) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:23,959] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Stabilized group XXXXE-SZL generation 1 (__consumer_offsets-49) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:23,972] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Assignment received from leader for group XXX-SZL for generation 1 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-15 08:24:25,524] INFO [TransactionCoordinator id=3] Initialized transactionalId XXXX-TID-0 with producerId 1005 and producer epoch 1 on partition __transaction_state-18 (kafka.coordinator.transaction.TransactionCoordinator)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- closed kafka client, from server.log or kafkaServer.out
[2021-04-16 17:51:05,705] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Member consumer-1-416c9379-0f89-48f4-b125-eadf648d57c7 in group TEST-REALTIME-SZL has failed, removing it from the group (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-16 17:51:05,707] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Preparing to rebalance group TEST-REALTIME-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 1 (__consumer_offsets-49) (reason: removing member consumer-1-416c9379-0f89-48f4-b125-eadf648d57c7 on heartbeat expiration) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
客户端consumer group所有的consumer都停掉了,所以是empty,然后整个group宣布dead
[2021-04-16 17:51:05,707] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]: Group XXX-SZL with generation 2 is now empty (__consumer_offsets-49) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2021-04-16 17:53:56,956] INFO [GroupMetadataManager brokerId=3] Group XXX-SZL transitioned to Dead in generation 2 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupMetadataManager)
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
---shutdown kafka borker 3, from server.log or kafkaServer.out
[2021-04-15 08:59:31,965] INFO Terminating process due to signal SIGTERM (org.apache.kafka.common.utils.LoggingSignalHandler)
[2021-04-15 08:59:31,973] INFO [KafkaServer id=3] shutting down (kafka.server.KafkaServer)
[2021-04-15 08:59:31,977] INFO [KafkaServer id=3] Starting controlled shutdown (kafka.server.KafkaServer)
[2021-04-15 08:59:32,066] INFO [ReplicaFetcherManager on broker 3] Removed fetcher for partitions Set(__transaction_state-45, __transaction_state-27, __transaction_state-9, T-XXX-2, T-XXX-1, __transaction_state-39, __transaction_state-36, ...... __transaction_state-0) (kafka.server.ReplicaFetcherManager)
--------------------------------------------------------
--- consumer subscribe topic 引起的rebalance
[2022-03-12 18:33:00,630] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Preparing to rebalance group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 0 (__consumer_offsets-43)
(reason: Adding new member consumer-2-808a151c-06dd-4df8-83fc-8b1b15a53a4d) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:33:00,631] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Stabilized group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL generation 1 (__consumer_offsets-43) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:33:00,634] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Assignment received from leader for group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL for generation 1 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
-----------------------------------------------------
--- consumer removed
[2022-03-12 18:41:58,862] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Member consumer-2-808a151c-06dd-4df8-83fc-8b1b15a53a4d in group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL has failed, removing it from the group (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:41:58,862] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Preparing to rebalance group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 1 (__consumer_offsets-43)
(reason: removing member consumer-2-808a151c-06dd-4df8-83fc-8b1b15a53a4d on heartbeat expiration) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:41:58,863] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL with generation 2 is now empty (__consumer_offsets-43) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:43:22,158] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Preparing to rebalance group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 2 (__consumer_offsets-43)
(reason: Adding new member consumer-2-aedafa05-22cb-4130-8e91-927c99f3fd06) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:43:22,159] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Stabilized group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL generation 3 (__consumer_offsets-43) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:43:22,162] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Assignment received from leader for group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL for generation 3 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:46:57,292] INFO [GroupMetadataManager brokerId=3] Removed 0 expired offsets in 0 milliseconds. (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupMetadataManager)
[2022-03-12 18:54:50,418] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Member consumer-2-aedafa05-22cb-4130-8e91-927c99f3fd06 in group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL has failed, removing it from the group (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:54:50,418] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Preparing to rebalance group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 3 (__consumer_offsets-43) (reason: removing member consumer-2-aedafa05-22cb-4130-8e91-927c99f3fd06 on heartbeat expiration) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:54:50,418] INFO [GroupCoordinator 3]:
Group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL with generation 4 is now empty (__consumer_offsets-43) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
[2022-03-12 18:56:57,292] INFO [GroupMetadataManager brokerId=3]
Group TEST-TRADEFRONT-SZL transitioned to Dead in generation 4 (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupMetadataManager)
Reasons:
A consumer left the group (clean shut down)
A consumer seems to be dead in the view of Kafka
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54183045/unexpected-failing-rebalancing-of-consumers
----Shrinking ISR from
代表有broker节点失联或挂掉
----Expanding ISR from
代码broker节点恢复或新增节点
----Will not attempt to authenticate using SASL (unknown error)
kafka server端无法连接zookeeper或者连接异常
kafka client端日志解析
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- metadata
this.kafkaConsumer.partitionsFor(context.getConfig().getTaskTopic())
=>
2021-04-01 14:37:00.622 INFO 32380GG [main] o.a.k.c.Metadata : Cluster ID: uEekh0baSnKon5ENwtY9dg
consumer.endOffsets(Collections.singleton(topicPartition)).get(topicPartition)
=>
2021-04-01 14:37:51.146 INFO 32380GG [RKER-RECOVERY-2] o.a.k.c.Metadata : Cluster ID: uEekh0baSnKon5ENwtY9dg
或
2021-03-27 15:40:29 395-[org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata.update(Metadata.java:365)]-[INFO] Cluster ID: pjnHKkklRtuSQjVDsUbgVw
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- subscribe to topic or to topic|partition
this.kafkaConsumer.subscribe(Collections.singleton(context.getConfig().getTaskTopic()), new SimpleWorkBalancer(context.getRestorer(), this::removeWorker, this::addWorker));
=>
2021-04-01 14:37:00.639 INFO 32380GG [main] o.a.k.c.c.KafkaConsumer : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=XXXX-SZL] Subscribed to topic(s): T-XXXX
consumer.assign(Collections.singleton(topicPartition));
=>
2021-04-01 14:38:09.783 INFO 32380GG [RKER-RECOVERY-2] o.a.k.c.c.KafkaConsumer : [Consumer clientId=consumer-2, groupId=RESTORE-1] Subscribed to partition(s): T-XXXX-SNP-1
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- Discover group
consumer.poll(Duration.ofMillis(10_000L));
=>
如果是assign mode,如果前面没有调用endOffsets之类获取metadata,此时会打印(估计跟consumer.seek(topicPartition, checkpointOffset);有关,当然如果之前调用过就会在调用时打印,此时不会打印):
2021-04-01 15:56:50.755 INFO 22064GG [RKER-RECOVERY-1] o.a.k.c.Metadata : Cluster ID: uEekh0baSnKon5ENwtY9dg
然后打印
2021-04-01 14:37:40.379 INFO 32380GG [XXXX-MANAGER] ordinator$FindCoordinatorResponseHandler : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=XXX-SZL] Discovered group coordinator 1.1.1.1:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null)
2021-04-01 14:38:41.369 INFO 32380GG [RKER-RECOVERY-2] ordinator$FindCoordinatorResponseHandler : [Consumer clientId=consumer-2, groupId=RESTORE-1] Discovered group coordinator 1.1.1.1:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null)
如果触发了rebalance,则接着打印
2021-03-31 08:59:01.727 INFO 20080GG [XXX-MANAGER] o.a.k.c.c.i.AbstractCoordinator : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-PRICEENGINE-SZL] (Re-)joining group
2021-03-31 08:59:01.904 INFO 20080GG [XXX-MANAGER] o.a.k.c.c.i.AbstractCoordinator : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-PRICEENGINE-SZL] (Re-)joining group
2021-03-31 08:59:04.122 INFO 20080GG [XXX-MANAGER] o.a.k.c.c.i.AbstractCoordinator$1 : [Consumer clientId=consumer-1, groupId=TEST-PRICEENGINE-SZL] Successfully joined group with generation 10
---------------------------------------------------------------------------
--- todo
Leader imbalance ratio for broker 3 is 0.0
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/57475580/whats-the-difference-between-kafka-preferred-replica-election-sh-and-auto-leade
kafka 常见异常Exceptions
Kafka常见错误整理 https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/article/1508919
--- NotEnoughReplicasException
The size of the current ISR Set(0) is insufficient to satisfy the min.isr requirement
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/62770272/notenoughreplicasexception-the-size-of-the-current-isr-set2-is-insufficient-t
例如:对于producer来说就是
The size of the current ISR Set(0) is insufficient to satisfy the min.isr requirement of 2 for partition __transaction_state-
对应client端的错误日志为:
java.lang.reflect.UndeclaredThrowableException: null
Caused by: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TimeoutException: Timeout expired while initializing transactional state in 60000ms.
--- LEADER_NOT_AVAILABLE:
topic 可能不存在,kafka api默认会自动创建
--- offset commit failed on partition this is not the correct coordinator
--- Offset commit failed on partition xxx at offset 957: The coordinator is not aware of this member
https://www.cnblogs.com/chuijingjing/p/12797035.html
--- topic not presetn in metadata after 6000ms
partition 可能不存在或者是其他问题,比如
https://blog.csdn.net/bay_bai/article/details/104799498
https://github.com/wurstmeister/kafka-docker/issues/553
--- Connection to node -1 could not be established. Broker may not be available.
listener设置不对
https://blog.csdn.net/Mr_hou2016/article/details/79484032
--- Connection to node -2 could not be established. Broker may not be available.
--- org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TimeoutException: Failed to get offsets by times in 30000ms
endOffsets()->fetchOffsetsByTimes
--- UNKNOWN_MEMBER_ID
Attempt to heartbeat failed for since member id consumer-1-c4ff67d3-b776-4994-9179-4a19f9ff87a6 is not valid
可能1:如果当前 group 的状态为 Dead,则说明对应的 group 不再可用,或者已经由其它 GroupCoordinator 实例管理,直接响应 UNKNOWN_MEMBER_ID 错误,消费者可以再次请求获取新接管的 GroupCoordinator 实例所在的位置信息。
可能2:消费者会在轮询获取消息或提交偏移量时发送心跳,如果消费者停止发送心跳的时间足够长,会话就会过期,组协调器认为它已经死亡,就会触发一次再均衡,至于原因,有可能是:
一般来说producer的生产消息的逻辑速度都会比consumer的消费消息的逻辑速度快,当producer在短时间内产生大量的数据丢进kafka的broker里面时,可能出现类似错误:Offset commit failed on partition : The coordinator is not aware of this member.
1) kafka的consumer会从broker里面取出一批数据,给消费线程进行消费;
2) 由于取出的一批消息数量太大,consumer在session.timeout.ms时间之内没有消费完成;
3) consumer coordinator 会由于没有接受到心跳而挂掉;
4) 由于自动提交offset失败,reblance之后又重新消费之前的一批数据(offset提交失败),恶性循环,越积越多;
- https://www.cnblogs.com/chuijingjing/p/12797035.html
--- Group coordinator is unavailable or invalid
Group coordinator x.x.x.x:9092 (id: 2147483647 rack: null) is unavailable or invalid, will attempt rediscovery
--- CommitFailedException
If a simple consumer(assign mode) tries to commit offsets with a group id which matches an active consumer group, the coordinator will reject the commit (which will result in a CommitFailedException). However, there won’t be any errors if another simple consumer instance shares the same group id.
--- INVALID_FETCH_SESSION_EPOCH.
Node 1 was unable to process the fetch request with (sessionId=1972558084, epoch=904746): INVALID_FETCH_SESSION_EPOCH.
--- UnkownProducerIdException
基本原因就是producer创建后超过 retention expire 过期时间或者大小,所以被清理,kafka服务端向客户端报错后会立即重新注册该producer,所以最好的处理办法是callback中重试
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61084031/how-to-handle-unkownproduceridexception/69999568#69999568
2021-11-16 09:08:29.206 [31mERROR[m [35m5527GG[m [ad | producer-1] [36mo.a.k.c.p.i.Sender[m : [Producer clientId=producer-1] The broker returned org.apache.kafka.common.errors.UnknownProducerIdException: This exception is raised by the broker if it could not locate the producer metadata associated with the producerId in question. This could happen if, for instance, the producer's records were deleted because their retention time had elapsed. Once the last records of the producerId are removed, the producer's metadata is removed from the broker, and future appends by the producer will return this exception. for topic-partition T-TEST-1 at offset -1. This indicates data loss on the broker, and should be investigated.
2021-11-16 09:08:29.207 [32m INFO[m [35m5527GG[m [ad | producer-1] [36mo.a.k.c.p.i.TransactionManager[m : [Producer clientId=producer-1] ProducerId set to -1 with epoch -1
2021-11-16 09:08:29.219 [32m INFO[m [35m5527GG[m [ad | producer-1] [36mo.a.k.c.p.i.TransactionManager[m : [Producer clientId=producer-1] ProducerId set to 35804 with epoch 0
kafka-log-dirs.sh
./bin/kafka-log-dirs.sh --describe --bootstrap-server hostname:port --broker-list broker 1, broker 2 --topic-list topic 1, topic 2
kafka-dump-log.sh
KAFKA Internal consumer topic log:
./bin/kafka-dump-log.sh --files ./kafka-logs/T-TOPIC-1/00000000000000000192.log --print-data-log
kafka-console-consumer.sh
KAFKA Internal offset topic: __consumer_offsets:
#Create consumer config
echo "exclude.internal.topics=false" > /tmp/consumer.config
#Consume all offsets
./kafka-console-consumer.sh --consumer.config /tmp/consumer.config \
--formatter "kafka.coordinator.group.GroupMetadataManager\$OffsetsMessageFormatter" \
--bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --topic __consumer_offsets --from-beginning
KAFKA Internal transaction log:
暂时没找到方法看,参考
You can look to source code of
TransactionLogMessageParserclass insidekafka/tools/DumpLogSegments.scalafile as an example. It usesreadTxnRecordValuefunction fromTransactionLogclass. The first argument for this function could be retrieved viareadTxnRecordKeyfunction of the same class.https://stackoverflow.com/questions/47670477/reading-data-from-transaction-state-topic-in-kafka-0-11-0-1
KAFKA Internal transaction topic: __transaction_state
echo "exclude.internal.topics=false" > consumer.config
./bin/kafka-console-consumer.sh --consumer.config consumer.config --formatter "kafka.coordinator.transaction.TransactionLog\$TransactionLogMessageFormatter" --bootstrap-server x.x.x.x:9092,X.X.X.46:9092,X.X.X.47:9092 --topic __transaction_state --from-beginning
3.5 Performance metric monitoring
Benchmarking Apache Kafka: 2 Million Writes Per Second (On Three Cheap Machines)
Monitoring Kafka performance metrics
scripting approach to run performance tests
4. Exactly-Once 一致性语义
4.1 Exactly-Once-Message-Processing
there are only two hard problems in distributed systems:
- Guaranteed order of messages
- Exactly-once delivery
https://www.confluent.io/online-talk/introducing-exactly-once-semantics-in-apache-kafka/
https://www.confluent.io/blog/transactions-apache-kafka/
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-98+-+Exactly+Once+Delivery+and+Transactional+Messaging
https://blog.csdn.net/alex_xfboy/article/details/82988259
KIP-129: Streams Exactly-Once Semantics https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-129%3A+Streams+Exactly-Once+Semantics
重点:
-
Producer:
开启幂等enable.idempotence和事务 transactional.id,并维护offset
-
Consumer:
设置isolation.level=read_committed(配合事务型Producer)
-
跟 kafka borker交互:
consumer根据kafka broker的rebalance来为每个partition创建producer,事务型 producer通过initTransaction操作来fence zombie(仍然是依靠kafka broker),从而屏蔽掉其他过时的producer(rebalance过程中被收回了partition的consumer之前所创建的producer)消费消息的可能性,然后consumer可以放心的restore
The first generation of stream processing applications could tolerate inaccurate processing. For instance, applications which consumed a stream of web page impressions and produced aggregate counts of views per web page could tolerate some error in the counts.
However, the demand for stream processing applications with stronger semantics has grown along with the popularity of these applications. For instance, some financial institutions use stream processing applications to process debits and credits on user accounts. In these situations, there is no tolerance for errors in processing: we need every message to be processed exactly once, without exception.
从某个Topic的某个Partition的数据流看 atomic read-process-write pattern(对于使用kafka stream 的应用来说就是 consume-transform-produce):
More formally, if a stream processing application consumes message A and produces message B such that B = F(A), then exactly once processing means that A is considered consumed if and only if B is successfully produced, and vice versa.
message A will be considered consumed from topic-partition tp0 only when its offset X is marked as consumed. Marking an offset as consumed is called committing an offset. In Kafka, we record offset commits by writing to an internal Kafka topic called the offsets topic. A message is considered consumed only when its offset is committed to the offsets topic
Thus since an offset commit is just another write to a Kafka topic, and since a message is considered consumed only when its offset is committed, atomic writes across multiple topics and partitions also enable atomic read-process-write cycles: the commit of the offset X to the offsets topic and the write of message B to tp1 will be part of a single transaction, and hence atomic.
设计:
每个application订阅一个主题,创建一个KafkaConsumer,发生rebalance之后根据分配的partition,每个partition都创建一个Transactional KafkaProducer
1.上游KafkaProducer:
-
保证不会重复发送:
1) retry 重发场景:The producer.send() could result in duplicate writes of message B due to internal retries.
解决方法:This is addressed by the idempotent producer: enable.idempotence=true
2) Reprocessing may happen if the stream processing application crashes after writing B but before marking A as consumed. Thus when it resumes, it will consume A again and write B again, causing a duplicate.
解决方法:使用transaction,将 write B和mark A consumed(self main consumer offset on kafka topic partition)作为一个transaction
3) 挂起后又恢复场景,applications will crash or—worse!—temporarily lose connectivity to the rest of the system. Typically, new instances are automatically started to replace the ones which were deemed lost. Through this process, we may have multiple instances processing the same input topics and writing to the same output topics, causing duplicate outputs and violating the exactly once processing semantics. We call this the problem of “zombie instances.”
比如Producer发送Kafka消息(commitTransaction之前)突然挂起,然后transaction.id被新起的Producer占用,当之前的Producer又恢复的时候再commitTransaction会被Fence屏蔽掉,并且KafkaConsumer的read_committed隔离级别也可以保证不读取这些尚未提交的事务消息(The Kafka consumer will only deliver transactional messages to the application if the transaction was actually committed. Put another way, the consumer will not deliver transactional messages which are part of an open transaction, and nor will it deliver messages which are part of an aborted transaction.
when using a Kafka consumer to consume messages from a topic, an application will not know whether these messages were written as part of a transaction, and so they do not know when transactions start or end.
In short: Kafka guarantees that a consumer will eventually deliver only non-transactional messages or committed transactional messages. It will withhold messages from open transactions and filter out messages from aborted transactions.)
解决方法:通过 transaction.id 进行 zombie Fence
4)consumer group中多个服务发生rebalance后重启的场景:服务A处理Paritition 0和1,然后服务B进入引起rebalance,分配结果为B接管Partition 0,当B创建KafkaProducer处理partition 0时,首先要定位到partition 0之前被处理到哪里了,这种场景仍然是先使用 Transaction.id进行zombie fence,以防服务A的处理Partition 0的kafkaproducer还在工作(比如使用了disruptor有ringbuffer缓存,即使没有用disruptor这种东西,由于A和B是两个独立的进程,B也无法保证A的kafka producer没有继续再处理某条消息,所以先小人后君子),然后才读取offset,定位到之前A在Partition 0成功提交的最后一条消息(换句话就是被zombie fence之前成功的最后一条消息)
-
保证不漏发:
- KafkaProducer需要使用幂等性,并且千万不要设置 ETRIES_CONFIG = “retries”,使用默认的Integer.MAX_VALUE
- 首先上游不要漏掉处理某个信息,此时如果上游的角色就是kafkaConsumer,问题进一步分解为:
- 上游不要漏掉某条kafka消息,这个完全由kafka保证
- 收到kafka消息后,处理到发送给下游的过程不要“漏”,即这个过程要保证鲁棒性和一致性
- 其次处理完后调用kafkaProducer接口send给下游,这个调用完全是kafka来保证不会漏
2.下游KafkaConsumer:
-
保证不要重复处理:
-
默认这个是由kafka offset来控制,_consumer_offset,但是在某些场景下使用 _consumer_offset 会有问题:
比如KafkaConsumer处理数据的过程包括作为KafkaProducer继续往下游发送消息,那么可以通过KafkaProducer的transaction处理,同时发送一个增量快照保存起当前的offset,这样就可以脱离开系统默认的__consumer_offset
-
另外一个比较隐含的场景就是上游出了问题,参考上游的场景3)和4)
-
-
保证不要丢失消息:
1)不要使用 auto commit,因为调用poll之后,消息offset可能已经被自动提交,但是此时如果没有处理完程序崩溃,再启动就会丢失消息;
而是采用 atomic read-process-write模型,将write和Mark read作为一个transaction,这样不会出现前面的: 消息被标记为已读,但是还没处理完程序崩溃,重启之后丢失的问题;
2)一旦producer成功将事务型的消息或非事务型的消息发送给了kafka(成功调用send api或commit transaction),接下来就是kafka的集群来保证消息不会丢掉了(比如关于replication high watermark)
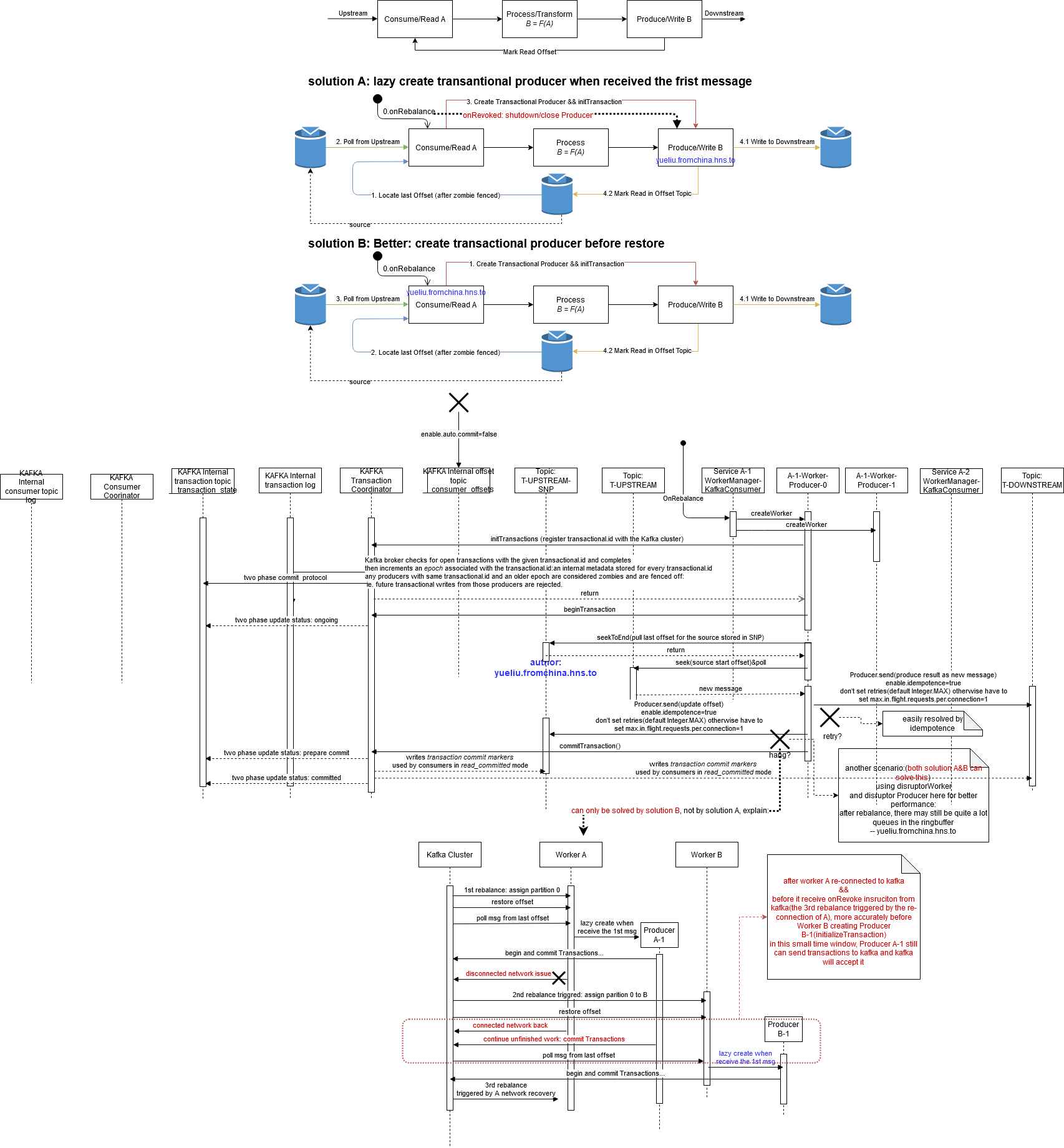
如图中所示,solution A不完美,因为解决不了服务A因为网络跟kafka集群断开又恢复的场景下有可能在极短的时间窗口发生的重复消费问题,solution B是最完美的设计,充分利用了kafka的exactly once能力

详细解读参考:
- Consumer Indepth 跳转至 深入Kafka Consumer消费者解析
- Producer Indepth 跳转至 深入Kafka Producer生产者解析
4.2 Exactly-Once-Stream-Processsing
or stream processing applications built using Kafka’s Streams API, we leverage the fact that the source of truth for the state store and the input offsets are Kafka topics. Hence we can transparently fold this data into transactions that atomically write to multiple partitions, and thus provide the exactly-once guarantee for streams across the read-process-write operations.
processing.guarantee=exactly_once
Note that exactly-once semantics is guaranteed within the scope of Kafka Streams’ internal processing only; for example, if the event streaming app written in Streams makes an RPC call to update some remote stores, or if it uses a customized client to directly read or write to a Kafka topic, the resulting side effects would not be guaranteed exactly once.
详细解读参考: 深入Kafka Stream
5. 集成开发
apache-kafka
org.apache.kafka.kafka-client
https://docs.confluent.io/clients-kafka-java/current/overview.html
https://www.baeldung.com/kafka-exactly-once
https://kafka.apache.org/20/javadoc/org/apache/kafka/clients/producer/KafkaProducer.html
https://dzone.com/articles/kafka-producer-and-consumer-example
默认配置:
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation.html#configuration https://kafka.apache.org/22/javadoc/org/apache/kafka/clients/consumer/ConsumerConfig.html
springboot spring-kafka
https://www.baeldung.com/spring-kafka
org.springframework.kafka包含:
- spring-context
- spring-messaging
- spring-tx
- spring-retry
- kafka-clients
6. Diving into Kafka 设计内幕
理想情况下,我们使用类似kafka这样成熟的产品,一般只需要将kafka当做黑盒,然后通过kafka开放的API来达到跟kafka交互的exactly-once,但实际上为了更好的理解或者有时候kafka本身的很多细节也会影响到使用性能甚至是可用性,我们常常还是要打开黑盒,进入其代码内部或者阅读其代码设计文档
Sourcecodes
Kafka Client sourcecode in Java
kafka Server sourcecode in Scala
KAFKA PROTOCOL GUIDE https://kafka.apache.org/protocol#The_Messages_WriteTxnMarkers Difference between kafka batch and kafka request https://stackoverflow.com/questions/74088393/difference-between-kafka-batch-and-kafka-request
leader epoch & high watermark
Kafka is a highly available, persistent, durable system where every message written to a partition is persisted and replicated some number of times (we will call it n). As a result, Kafka can tolerate n-1 broker failures, meaning that a partition is available as long as there is at least one broker available. Kafka’s replication protocol guarantees that once a message has been written successfully to the leader replica, it will be replicated to all available replicas.
https://rongxinblog.wordpress.com/2016/07/29/kafka-high-watermark/
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-101+-+Alter+Replication+Protocol+to+use+Leader+Epoch+rather+than+High+Watermark+for+Truncation Kafka数据丢失及最新改进策略 http://lday.me/2017/10/08/0014_kafka_data_loss_and_new_mechanism/ kafka ISR设计及水印与leader epoch副本同步机制深入剖析-kafka 商业环境实战 https://juejin.im/post/5bf6b0acf265da612d18e931 leader epoch与watermark https://www.cnblogs.com/huxi2b/p/7453543.html High watermark If you want to improve the reliability of the data, set the request.required.acks = -1, but also min.insync.replicas this parameter (which can be set in the broker or topic level) to achieve maximum effectiveness. https://medium.com/@mukeshkumar_46704/in-depth-kafka-message-queue-principles-of-high-reliability-42e464e66172
副本 replication 等细节
https://www.cnblogs.com/luozhiyun/p/12079527.html
Consumer coordinator & Group coordinator & Rebalance
https://matt33.com/2017/10/22/consumer-join-group/
https://cloud.tencent.com/developer/news/19958
While the old consumer depended on Zookeeper for group management, the new consumer uses a group coordination protocol built into Kafka itself. For each group, one of the brokers is selected as the group coordinator. The coordinator is responsible for managing the state of the group. Its main job is to mediate partition assignment when new members arrive, old members depart, and when topic metadata changes. The act of reassigning partitions is known as rebalancing the group.
https://www.confluent.io/blog/tutorial-getting-started-with-the-new-apache-kafka-0-9-consumer-client/
keyword:
-
GroupCoordinator 服务端 borker(Kafka 会依据请求的 group 的 ID 查找对应 offset topic [consumer_offsets?]分区 leader 副本所在的 broker 节点:
每个 Group 都会选择一个 Coordinator 来完成自己组内各 Partition 的 Offset 信息,选择的规则如下: 1. 计算 Group 对应在 __consumer_offsets
上的Partition 2. 根据对应的Partition寻找该Partition的leader所对应的Broker,该Broker上的Group Coordinator即就是该Group的Coordinator) -
ConsumerCoordinator
-
Consumer leader/follower 第一个申请加入group的consumer作为leader,在服务端确定好分区分配策略之后,具体执行分区分配的工作则交由 leader 消费者负责,并在完成分区分配之后将分配结果反馈给服务端
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Kafka+Client-side+Assignment+Proposal
https://www.zhenchao.org/2019/06/25/kafka/kafka-group-coordinator/
在 kafka-0.10 版本,Kafka 在服务端引入了组协调器(GroupCoordinator),每个 Kafka Server 启动时都会创建一个 GroupCoordinator 实例,用于管理部分消费者组和该消费者组下的每个消费者的消费偏移量。同时在客户端引入了消费者协调器(ConsumerCoordinator),实例化一个消费者就会实例化一个 ConsumerCoordinator 对象,ConsumerCoordinator 负责同一个消费者组下各消费者与服务端的 GroupCoordinator 进行通信。
客户端-消费者协调器(ConsumerCoordinator)
To control this assignment, users can either write an implementation of the PartitionAssignor interface or use one of the three provided implementations (configured through the partition.assignment.strategy config):
RangeAssignor: For each topic, divide its partitions by the number of consumers subscribed to it and assign X to each (lexicographically sorted) consumer. If it does not evenly divide, the first consumers will have more partitions.RoundRobinAssignor: Assign all partitions from all the subscribed topics to each consumer sequentially, one by one.StickyAssignor: Assign partitions so that they are distributed as evenly as possible. During rebalances, partitions stay with their previously assigned consumers as much as possible.
Additionally, the PartitionAssignor interface exposes a metadata() method. Every consumer in the group can use this method to send generic metadata about itself to the broker when joining a group. Once a rebalance is in the works, every consumer’s metadata is propagated to the group leader. This enables the leader to make a well-informed decision about assigning partitions (e.g., by considering a consumer application’s datacenter rack).
public class KafkaConsumer<K, V> implements Consumer<K, V> {
private final ConsumerCoordinator coordinator;
}
public final class ConsumerCoordinator extends AbstractCoordinator {
private final List<PartitionAssignor> assignors;
private final OffsetCommitCallback defaultOffsetCommitCallback;
private final SubscriptionState subscriptions;
private final ConsumerInterceptors<?, ?> interceptors;
private boolean isLeader = false;
private MetadataSnapshot metadataSnapshot;
private MetadataSnapshot assignmentSnapshot;
省略了部分代码....
}
public abstract class AbstractCoordinator implements Closeable {
private enum MemberState {
UNJOINED, // the client is not part of a group
REBALANCING, // the client has begun rebalancing
STABLE, // the client has joined and is sending heartbeats
}
private final Heartbeat heartbeat;
protected final ConsumerNetworkClient client;
private HeartbeatThread heartbeatThread = null;
private MemberState state = MemberState.UNJOINED;
private RequestFuture<ByteBuffer> joinFuture = null;
省略了部分代码....
}
ConsumerCoordinator 是 KafkaConsumer 的一个私有的成员变量,因此 ConsumerCoordinator 中存储的信息也只有与之对应的消费者可见,不同消费者之间是看不到彼此的 ConsumerCoordinator 中的信息的。
ConsumerCoordinator 的作用:
- 处理更新消费者缓存的 Metadata 请求
- 向组协调器发起加入消费者组的请求
- 对本消费者加入消费者前后的相应处理
- 请求离开消费者组(例如当消费者取消订阅时)
- 向组协调器发送提交偏移量的请求
- 通过一个定时的心跳检测任务来让组协调器感知自己的运行状态
- Leader消费者的 ConsumerCoordinator 还负责执行分区的分配,一个消费者组中消费者 leader 由组协调器选出,leader 消费者的 ConsumerCoordinator 负责消费者与分区的分配,然后把分配结果发送给组协调器,然后组协调器再把分配结果返回给其他消费者的消费者协调器,这样减轻了服务端的负担
ConsumerCoordinator 实现上述功能的组件是 ConsumerCoordinator 类的私有成员或者是其父类的私有成员:

服务端-组协调器(GroupCoordinator)
class GroupCoordinator(
val brokerId: Int, // 所属的 broker 节点的 ID
val groupConfig: GroupConfig, // Group 配置对象,记录了 group 中 session 过期的最小时长和最大时长,即超时时长的合法区间
val offsetConfig: OffsetConfig, // 记录 OffsetMetadata 相关的配置项
val groupManager: GroupMetadataManager, // 负责管理 group 元数据以及对应的 offset 信息
val heartbeatPurgatory: DelayedOperationPurgatory[DelayedHeartbeat], // 管理 DelayedHeartbeat 延时任务的炼狱
val joinPurgatory: DelayedOperationPurgatory[DelayedJoin], // 管理 DelayedJoin 延时任务的炼狱
time: Time) extends Logging {
/** 标识当前 GroupCoordinator 实例是否启动 */
private val isActive = new AtomicBoolean(false)
// ... 省略方法定义
}
其中 GroupMetadataManager 类主要用于管理消费者 group 的元数据信息和 offset 相关信息
Kafka 服务在启动时针对每一个 broker 节点都会创建一个 GroupCoordinator 实例,并调用 GroupCoordinator#startup 方法启动运行。GroupCoordinator 在启动时主要是调用了 GroupMetadataManager#enableMetadataExpiration 方法启动 delete-expired-group-metadata 定时任务
定时任务 delete-expired-group-metadata 的主要作用在于从 group 的元数据信息中移除那些已经过期的 topic 分区对应的 offset 元数据,并将这些元数据以消息的形式记录到 offset topic 中,具体执行流程如下:
1.依据当前时间戳计算并获取已经过期的 topic 分区对应的 offset 元数据信息;
2.将状态为 Empty 且名下记录的所有 offset 元数据都已经过期的 group 切换成 Dead 状态;
3.如果 group 已经失效,则从 GroupCoordinator 本地移除对应的元数据信息,并与步骤 1 中获取到的 offset 元数据信息一起封装成消息记录到 offset topic 中。
具体逻辑由 GroupMetadataManager#cleanupGroupMetadata 方法实现
GroupState 特质定义了 group 的状态,并由 GroupCoordinator 进行维护。围绕 GroupState 特质,Kafka 实现了 5 个样例对象,分别用于描述 group 的 5 种状态:
PreparingRebalance :表示 group 正在准备执行分区再分配操作。
AwaitingSync :表示 group 正在等待 leader 消费者的分区分配结果,新版本已更名为 CompletingRebalance。
Stable :表示 group 处于正常运行状态。
Dead :表示 group 名下已经没有消费者,且对应的元数据已经(或正在)被删除。
Empty :表示 group 名下已经没有消费者,并且正在等待记录的所有 offset 元数据过期。
GroupCoordinator 的作用:
- 负责对其管理的组员(消费者)提交的相关请求进行处理
- 与消费者之间建立连接,并从与之连接的消费者之间选出一个 leader
- 当 leader 分配好消费者与分区的订阅关系后,会把结果发送给组协调器,组协调器再把结果返回给各个消费者
- 管理与之连接的消费者的消费偏移量的提交,将每个消费者的消费偏移量保存到kafka的内部主题中
- 通过心跳检测消费者与自己的连接状态
- 启动组协调器的时候创建一个定时任务,用于清理过期的消费组元数据以及过去的消费偏移量信息
GroupCoordinator 依赖的组件及其作用:

- KafkaConfig:实例化 OffsetConfig 和 GroupConfig
- ZkUtils:分消费者分配组协调器时从Zookeeper获取内部主题的分区元数据信息。
- GroupMetadataManager:负责管理 GroupMetadata以及消费偏移量的提交,并提供了一系列的组管理的方法供组协调器调用。GroupMetadataManager 不仅把 GroupMetadata 写到kafka内部主题中,而且还在内存中缓存了一份GroupMetadata,其中包括了组员(消费者)的元数据信息,例如消费者的 memberId、leaderId、分区分配关系,状态元数据等。状态元数据可以是以下五种状态:
- PreparingRebalance:消费组准备进行平衡操作
- AwaitingSync:等待leader消费者将分区分配关系发送给组协调器
- Stable:消费者正常运行状态,心跳检测正常
- Dead:处于该状态的消费组没有任何消费者成员,且元数据信息也已经被删除
- Empty:处于该状态的消费组没有任何消费者成员,但元数据信息也没有被删除,知道所有消费者对应的消费偏移量元数据信息过期。
- ReplicaManager:GroupMetadataManager需要把消费组元数据信息以及消费者提交的已消费偏移量信息写入 Kafka 内部主题中,对内部主题的操作与对其他主题的操作一样,先通过 ReplicaManager 将消息写入 leader 副本,ReplicaManager 负责 leader 副本与其他副本的管理。
- DelayedJoin:延迟操作类,用于监视处理所有消费组成员与组协调器之间的心跳超时
- GroupConfig:定义了组成员与组协调器之间session超时时间配置
消费者协调器和组协调器的交互 -(核心 rebalance)
https://chrzaszcz.dev/2019/06/kafka-rebalancing/
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-429%3A+Kafka+Consumer+Incremental+Rebalance+Protocol
https://www.slideshare.net/ConfluentInc/the-silver-bullet-for-endless-rebalancing

(1) 心跳
消费者协调器通过和组协调器发送心跳来维持它们和群组的从属关系以及它们对分区的所有权关系。只要消费者以正常的时间间隔发送心跳,就被认为是活跃的,说明它还在读取分区里的消息。消费者会在轮询获取消息或提交偏移量时发送心跳。
如果消费者停止发送心跳的时间足够长,会话就会过期,组协调器认为它已经死亡,就会触发一次再均衡。
在 0.10 版本里,心跳任务由一个独立的心跳线程来执行,可以在轮询获取消息的空档发送心跳。这样一来,发送心跳的频率(也就是组协调器群检测消费者运行状态的时间)与消息轮询的频率(由处理消息所花费的时间来确定)之间就是相互独立的。在0.10 版本的 Kafka 里,可以指定消费者在离开群组并触发再均衡之前可以有多长时间不进行消息轮询,这样可以避免出现活锁(livelock),比如有时候应用程序并没有崩溃,只是由于某些原因导致无法正常运行。这个配置与 session.timeout.ms 是相互独立的,后者用于控制检测消费者发生崩溃的时间和停止发送心跳的时间。
(2) 分区再均衡
发生分区再均衡的3种情况:
- 一个新的消费者加入群组时,它读取的是原本由其他消费者读取的消息。
- 当一个消费者被关闭或发生崩溃时,它就离开群组,原本由它读取的分区将由群组里的其他消费者来读取。如果一个消费者主动离开消费组,消费者会通知组协调器它将要离开群组,组协调器会立即触发一次再均衡,尽量降低处理停顿。如果一个消费者意外发生崩溃,没有通知组协调器就停止读取消息,组协调器会等待几秒钟,确认它死亡了才会触发再均衡。在这几秒钟时间里,死掉的消费者不会读取分区里的消息。
- 在主题发生变化时,比如管理员添加了新的分区,会发生分区重分配。
分区的所有权从一个消费者转移到另一个消费者,这样的行为被称为分区再均衡。再均衡非常重要,它为消费者群组带来了高可用性和伸缩性(我们可以放心地添加或移除消费者),不过在正常情况下,我们并不希望发生这样的行为。在再均衡期间,消费者无法读取消息,造成整个群组一小段时间的不可用。另外,当分区被重新分配给另一个消费者时,消费者当前的读取状态会丢失,它有可能还需要去刷新缓存,在它重新恢复状态之前会拖慢应用程序。
(3) leader 消费者分配分区的策略
当消费者要加入群组时,它会向群组协调器发送一个 JoinGroup 请求。第一个加入群组的消费者将成为leader消费者。leader消费者从组协调器那里获得群组的成员列表(列表中包含了所有最近发送过心跳的消费者,它们被认为是活跃的),并负责给每一个消费者分配分区。
每个消费者的消费者协调器在向组协调器请求加入组时,都会把自己支持的分区分配策略报告给组协调器(轮询或者是按跨度分配或者其他),组协调器选出该消费组下所有消费者都支持的的分区分配策略发送给leader消费者,leader消费者根据这个分区分配策略进行分配。
完毕之后,leader消费者把分配情况列表发送给组协调器,消费者协调器再把这些信息发送给所有消费者。每个消费者只能看到自己的分配信息,只有leader消费者知道群组里所有消费者的分配信息。这个过程会在每次再均衡时重复发生。
(4) 消费者入组过程
-
消费者创建后,消费者协调器会选择一个负载较小的节点,向该节点发送寻找组协调器的请求
-
KafkaApis 处理请求,调用返回组协调器所在的节点,过程如下:
def partitionFor(group: String): Int = groupManager.partitionFor(group)
https://github.com/a0x8o/kafka/blob/master/core/src/main/scala/kafka/coordinator/group/GroupCoordinator.scala
=>
groupId的哈希值的绝对值对 __consumer_offset 这个topic的partition的个数(默认50)取余 得到一个分区的id
def partitionFor(groupId: String): Int = Utils.abs(groupId.hashCode) % groupMetadataTopicPartitionCount
https://github.com/a0x8o/kafka/blob/master/core/src/main/scala/kafka/coordinator/group/GroupMetadataManager.scala
=>
该分区的leader副本所在的节点就是组协调器所在的节点,该消费组的元数据信息以及消费者消费偏移量信息都会写到__consumer_offset的这个分区中
-
找到组协调器后,消费者协调器申请加入消费组,发送 JoinGroupRequest请求
-
KafkaApis 调用 handleJoinGroup() 方法处理请求
- 把消费者注册到消费组中
- 把消费者的clientId与一个UUID值生成一个memberId分配给消费者
- 构造器该消费者的MemberMetadata信息
- 把该消费者的MemberMetadata信息注册到GroupMetadata中
- 第一个加入组的消费者将成为leader
-
把处理JoinGroupRequest请求的结果返回给消费者
-
加入组成功后,进行分区再均衡
kafka idempotent 原理
http://matt33.com/2018/10/24/kafka-idempotent/
kafka Transaction 原理 Transaction Coordinator and Transaction Log
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-98+-+Exactly+Once+Delivery+and+Transactional+Messaging
The components introduced with the transactions API in Kafka 0.11.0 are the Transaction Coordinator and the Transaction Log on the right hand side of the diagram above.
The transaction coordinator is a module running inside every Kafka broker. The transaction log is an internal kafka topic. Each coordinator owns some subset of the partitions in the transaction log, ie. the partitions for which its broker is the leader.
Every transactional.id is mapped to a specific partition of the transaction log through a simple hashing function. This means that exactly one coordinator owns a given transactional.id.
This way, we leverage Kafka’s rock solid replication protocol and leader election processes to ensure that the transaction coordinator is always available and all transaction state is stored durably.
It is worth noting that the transaction log just stores the latest state of a transaction and not the actual messages in the transaction. The messages are stored solely in the actual topic-partitions. The transaction could be in various states like “Ongoing,” “Prepare commit,” and “Completed.” It is this state and associated metadata that is stored in the transaction log.

data flow
A: the producer and transaction coordinator interaction
When executing transactions, the producer makes requests to the transaction coordinator at the following points:
- The initTransactions API registers a transactional.id with the coordinator. At this point, the coordinator closes any pending transactions with that transactional.id and bumps the epoch to fence out zombies. This happens only once per producer session.
- When the producer is about to send data to a partition for the first time in a transaction, the partition is registered with the coordinator first.
- When the application calls commitTransaction or abortTransaction, a request is sent to the coordinator to begin the two phase commit protocol.
B: the coordinator and transaction log interaction
As the transaction progresses, the producer sends the requests above to update the state of the transaction on the coordinator. The transaction coordinator keeps the state of each transaction it owns in memory, and also writes that state to the transaction log (which is replicated three ways and hence is durable).
The transaction coordinator is the only component to read and write from the transaction log. If a given broker fails, a new coordinator is elected as the leader for the transaction log partitions the dead broker owned, and it reads the messages from the incoming partitions to rebuild its in-memory state for the transactions in those partitions.
C: the producer writing data to target topic-partitions
After registering new partitions in a transaction with the coordinator, the producer sends data to the actual partitions as normal. This is exactly the same producer.send flow, but with some extra validation to ensure that the producer isn’t fenced.
D: the coordinator to topic-partition interaction
After the producer initiates a commit (or an abort), the coordinator begins the two phase commit protocol.
In the first phase, the coordinator updates its internal state to “prepare_commit” and updates this state in the transaction log. Once this is done the transaction is guaranteed to be committed no matter what.
The coordinator then begins phase 2, where it writes transaction commit markers to the topic-partitions which are part of the transaction.
These transaction markers are not exposed to applications, but are used by consumers in read_committed mode to filter out messages from aborted transactions and to not return messages which are part of open transactions (i.e., those which are in the log but don’t have a transaction marker associated with them).
Once the markers are written, the transaction coordinator marks the transaction as “complete” and the producer can start the next transaction.
Performance of the transactional producer
Let’s turn our attention to how transactions perform.
First, transactions cause only moderate write amplification. The additional writes are due to:
- For each transaction, we have had additional RPCs to register the partitions with the coordinator. These are batched, so we have fewer RPCs than there are partitions in the transaction.
- When completing a transaction, one transaction marker has to be written to each partition participating in the transaction. Again, the transaction coordinator batches all markers bound for the same broker in a single RPC, so we save the RPC overhead there. But we cannot avoid one additional write to each partition in the transaction.
- Finally, we write state changes to the transaction log. This includes a write for each batch of partitions added to the transaction, the “prepare_commit” state, and the “complete_commit” state.
As we can see the overhead is independent of the number of messages written as part of a transaction. So the key to having higher throughput is to include a larger number of messages per transaction.
In practice, for a producer producing 1KB records at maximum throughput, committing messages every 100ms results in only a 3% degradation in throughput. Smaller messages or shorter transaction commit intervals would result in more severe degradation.
The main tradeoff when increasing the transaction duration is that it increases end-to-end latency. Recall that a consumer reading transactional messages will not deliver messages which are part of open transactions. So the longer the interval between commits, the longer consuming applications will have to wait, increasing the end-to-end latency.
Performance of the transactional consumer
The transactional consumer is much simpler than the producer, since all it needs to do is:
- Filter out messages belonging to aborted transactions.
- Not return transactional messages which are part of open transactions.
As such, the transactional consumer shows no degradation in throughput when reading transactional messages in read_committed mode. The main reason for this is that we preserve zero copy reads when reading transactional messages.
Further, the consumer does not need to any buffering to wait for transactions to complete. Instead, the broker does not allow it to advance to offsets which include open transactions.
[main] [org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.TransactionManager : [Producer clientId=producer-1, transactionalId=TID-PARTITION-0] ProducerId set to -1 with epoch -1
[ad | producer-1] [org.apache.kafka.clients.Metadata : Cluster ID: uEekh0baSnKon5ENwtY9dg
[ad | producer-1] [org.apache.kafka.clients.producer.internals.TransactionManager : [Producer clientId=producer-1, transactionalId=TID-PARTITION-0] ProducerId set to 16871 with epoch 85
之前一直困惑于这个 -1 -1,不过因为这三条log全部是org.apache.kafka的,所以刚开始抱着完全信任kafka的想法就先放一边了,后来忍不住大概debug进去瞅了下,确认是kafka正常的设计,第一条log直接就能debug到,step into initTransactions很容易看到,所以意思是默认就会先初始化一个-1 -1,我估计是先给个负值的epoch,等到完全注册好才给后面那个正数的epoch,是合理的,不然还没有注册好事务型的producer,直接给一个合法的epoch,会影响到现在正常工作的其他producer(比如万一因为问题这个新的producer初始化失败也不会影响到/zombie fence使用相同Transaction.id的其他producer)
NIO Selector
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/46185430/kafka-source-understanding-the-semantics-of-selector-poll
Log Compaction
https://kafka.apache.org/22/documentation/#compaction Kafka技术内幕-日志压缩 https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000005312891
Note however that there cannot be more consumer instances(task) in a consumer group than partitions. https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-28+-+Add+a+processor+client
Kafka Fetch Session剖析
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54823733/kafka-invalid-fetch-session-epoch https://www.cnblogs.com/smartloli/p/14352489.html
对于客户端来说,什么时候一个分区会被包含到增量的拉取请求中:
Client通知Broker,分区的maxBytes,fetchOffset,LogStartOffset改变了; 分区在之前的增量拉取会话中不存在,Client想要增加这个分区,从而来拉取新的分区; 分区在增量拉取会话中,Client要删除。 对于服务端来说,增量分区包含到增量的拉取响应中:
Broker通知Client分区的HighWaterMark或者brokerLogStartOffset改变了; 分区有新的数据
Nodes expansion
https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/#basic_ops_cluster_expansion
注意,kafka是不可以动态扩增的,一旦配置好并且开启n个节点,第一个consumer接入的时候就会创建50个partition的__consumer_offsets并且在n个节点上平均分配,第一个producer接入的时候会创建50个__transaction_state并且在n个节点上平均分配,创建的外部topic也同样平均分配在n个节点上,如果扩增node到n+1,并不会自动的重新分配,需要手动migration;
另外n最好是等于replica factor的设置,低于replica factor无法正常启动工作,高于replica factor则会造成节点浪费,比如
replica factor=2,启动3个node,那么就出现比如 __consumer_offsets_49的replica分布在node 1和2上,所以min.isr=1的情况下只支持node1和2只能挂掉一个,同理其他的分布在node1和node3,node2和node3上,所以总的来说,只能挂掉3个节点的一个,假设挂掉两个node1和2,node3上有replica的topic没问题,但是__consumer_offsets_49显然就挂了
kafka offset not increase by 1?
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54636524/kafka-streams-does-not-increment-offset-by-1-when-producing-to-topic
https://issues.apache.org/jira/browse/KAFKA-6607
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/54544074/how-to-make-restart-able-producer
https://github.com/confluentinc/confluent-kafka-go/issues/195
clean up
__consumer_offsets https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41429053/how-to-change-consumer-offsets-cleanup-plicy-to-delete-from-compact
kafka的日志模块
https://www.cnblogs.com/boanxin/p/13466209.html https://www.applenice.net/2020/05/31/Kafka-Notes-06/
7. Troubleshooting 踩过的坑
Caused by: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.InvalidReplicationFactorException: Replication factor is below 1 or larger than the number of available brokers.
配置
offsets.topic.replication.factor=3
min.insync.replicas=1
transaction.state.log.replication.factor=3
transaction.state.log.min.isr=1
default.replication.factor=3
一个节点挂了,然后启动kafka client(并且此时topic还未创建),报错
Error starting ApplicationContext. To display the conditions report re-run your application with 'debug' enabled.
2022-06-27 06:20:09.825 [31mERROR[m [35m2506GG[m [main] [36mo.s.b.SpringApplication[m : Application run failed
org.apache.kafka.common.KafkaException: Unexpected error fetching metadata for topic T-TEST
at org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.internals.Fetcher.getTopicMetadata(Fetcher.java:327)
at org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer.partitionsFor(KafkaConsumer.java:1803)
at org.apache.kafka.clients.consumer.KafkaConsumer.partitionsFor(KafkaConsumer.java:1771)
....
at org.springframework.boot.loader.MainMethodRunner.run(MainMethodRunner.java:49)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.Launcher.launch(Launcher.java:108)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.Launcher.launch(Launcher.java:58)
at org.springframework.boot.loader.JarLauncher.main(JarLauncher.java:88)
Caused by: org.apache.kafka.common.errors.InvalidReplicationFactorException: Replication factor is below 1 or larger than the number of available brokers.
很正常,因为创建topic需要活着的节点>=replication.factor,对应这段代码是在请求 getTopicMetadata 触发kafka服务端创建topic
@Override
public List<PartitionInfo> partitionsFor(String topic, Duration timeout) {
acquireAndEnsureOpen();
try {
Cluster cluster = this.metadata.fetch();
List<PartitionInfo> parts = cluster.partitionsForTopic(topic);
if (!parts.isEmpty())
return parts;
Timer timer = time.timer(timeout);
Map<String, List<PartitionInfo>> topicMetadata = fetcher.getTopicMetadata(
new MetadataRequest.Builder(Collections.singletonList(topic), true), timer);
return topicMetadata.get(topic);
} finally {
release();
}
}
auto.create.topics.enable
MetadataRequest auto create kafka topic InvalidReplicationFactorException
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/KIP-361%3A+Add+Consumer+Configuration+to+Disable+Auto+Topic+Creation
然后还有一个kafka client程序也是类似问题,只不过这个程序使用了多个topic: Topic1 Topic2,Topic1事先已经创建了所以没有问题,在请求 Topic2的 metadata的时候(endoffset)也是自动创建失败产生类似报错
Fatal error during KafkaServer startup. Prepare to shutdown (kafka.server.KafkaServer)
[2019-05-07 21:45:48,648] ERROR [KafkaServer id=0] Fatal error during KafkaServer startup. Prepare to shutdown (kafka.server.KafkaServer)
org.apache.kafka.common.KafkaException: Failed to acquire lock on file .lock in /tmp/kafka-logs. A Kafka instance in another process or thread is using this directory.
UNKOWN_PRDOCUER_ID
got error produce response with correlation id on topic-partition UNKOWN_PRDOCUER_ID
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/51036351/kafka-unknown-producer-id-exception
基本上就是因为过期了
log.retention.hours=720
transactional.id.expiration.ms=2073600000
kafka segment.bytes different for each topic
修改了其中一个broker节点的config,忘记同步到所有的节点
无法删除topic
bin/kafka-topics.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092 --delete --topic T-*
可以通过zookeeper删除
bin/kafka-topics.sh --zookeeper localhost:2181 --delete --topic T-.*
删除topic后无法创建,提示已存在,但是找不到 org.apache.kafka.common.errors.TopicExistsException
是zookeeper跟kafka数据不一致,
./bin/zookeeper-shell.sh :2181 get /brokers/topics
或者
bin/zookeeper-shell.sh localhost:2181
ls /brokers/topics
ls /admin/delete_topics
会看到很多topic存在这里
直接通过命令delete,或者更简单的通过删除 ../zookeeper/logs/version-2/ 和 ../zookeeper/zkdata/version-2/
rm -rf ../zookeeper/zkdata/version-2/*
rm -rf ../zookeeper/logs/version-2/*
rm -rf kafka-logs/*
rm -rf logs/*
时钟漂移
client端日志 2022-03-14 09:00:56.202 ^[[32m INFO^[[m ^[[35m16686GG^[[m [JOB-MANAGER] ^[[36mordinator$FindCoordinatorResponseHandler^[[m : [Consumer clientId=consumer-2, groupId=TEST-SZL] Discovered group coordinator HOST2:9092 (id: 2147483646 rack: null) 但是在机器HOST2上没有找到对应时间段日志,最后发现 HOST2比HOST1和3时钟快了几分钟,对应kafka日志刚好是四分钟[2022-03-14 09:04:23,689] [2022-03-14 09:04:23,689] INFO [GroupCoordinator 1]: Preparing to rebalance group TEST-SZL in state PreparingRebalance with old generation 0 (__consumer_offsets-43) (reason: Adding new member consumer-2-ab88af5d-b206-48fb-a38b-ead5e50ad76e) (kafka.coordinator.group.GroupCoordinator)
Kafka 节点挂掉
解决方法:
- Upgrade the JDK to version 1.8.0_192 or later.
- Adjust the garbage collection strategy from G1 to CMS.
Appendix
Reference
-
kafka原理
-
kafka架构/工作方式 http://www.linkedkeeper.com/detail/blog.action?bid=1016 https://www.cnblogs.com/qiu-hua/p/13388326.html https://blog.csdn.net/qq_37095882/article/details/81024048
Kafka 数据可靠性深度解读
https://www.infoq.cn/article/depth-interpretation-of-kafka-data-reliability 震惊了!原来这才是kafka!
https://www.jianshu.com/p/d3e963ff8b70
-
kafka stream
https://github.com/confluentinc/kafka-streams-examples/tree/4.0.0-post
https://www.confluent.io/blog/building-a-microservices-ecosystem-with-kafka-streams-and-ksql/ https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p9wcx3aTjuo http://benstopford.com/uploads/CraftMeetup.pdf https://kafka.apache.org/documentation/streams/developer-guide/interactive-queries.html Designing Event-Driven Systems Concepts and Patterns for Streaming Services with Apache Kafka –Ben Stopford
Building Event Driven Services with Apache Kafka and Kafka Streams by Ben Stopford
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/40274884/is-kafka-stream-statestore-global-over-all-instances-or-just-local https://stackoverflow.com/questions/52488070/difference-between-ktable-and-local-store https://stackoverflow.com/questions/50741186/how-to-filter-out-unnecessary-records-before-materializing-globalktable/50752095#50752095 https://github.com/confluentinc/kafka-streams-examples/issues/126
-
Consumer
consumer group: https://www.oreilly.com/library/view/kafka-the-definitive/9781491936153/ch04.html https://www.confluent.io/blog/apache-kafka-data-access-semantics-consumers-and-membership
Kafka Consumer设计解析 http://www.jasongj.com/2015/08/09/KafkaColumn4/
kafka9重复消费问题解决
https://blog.csdn.net/u011637069/article/details/72899915
-
other detail
partition message ordering: https://stackoverflow.com/questions/29820384/apache-kafka-order-of-messages-with-multiple-partitions
一文看懂Kafka消息格式的演变
https://blog.csdn.net/u013256816/article/details/80300225
consuming and then producing messages based on what you consumed https://stackoverflow.com/questions/45195010/meaning-of-sendoffsetstotransaction-in-kafka-0-11
seek seekToEnd
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/48395934/how-to-get-last-committed-offset-from-read-committed-kafka-consumer
assign() vs subscribe()
-
-
Dev doc
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/apache_kafka/apache_kafka_quick_guide.htm
https://kafka.apache.org/20/javadoc/org/apache/kafka/clients/
-
best practice
https://go.streamsets.com/wc-guide-best-practices-for-simplifying-apache-kafka.html?assetpushed=guide-simplifying-apache-kafka
https://www.digitalocean.com/community/tutorial_collections/how-to-install-apache-kafka
-
use case
Kafka实现淘宝亿万级数据统计 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/58747239
How Netflix Handles Data Streams Up to 8M Events/sec
如何使用Kafka Streams构建广告消耗预测系统 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s?spm=a2c4e.11153940.blogcont270421.21.7d142e7catwiNO&__biz=MzU1NDA4NjU2MA==&mid=2247486752&idx=1&sn=e9e789c18a6801af12db4c97dcb098e5&chksm=fbe9b4efcc9e3df9cb7d8f666335ed669a7339b27663fc223e5aacfbfa5d2d7404b431b3937d&scene=27#wechat_redirect https://medium.com/@Pinterest_Engineering/using-kafka-streams-api-for-predictive-budgeting-9f58d206c996
Twitter
Twitter is an online social networking service that provides a platform to send and receive user tweets. Registered users can read and post tweets, but unregistered users can only read tweets. Twitter uses Storm-Kafka as a part of their stream processing infrastructure.
LinkedIn
Apache Kafka is used at LinkedIn for activity stream data and operational metrics. Kafka mes-saging system helps LinkedIn with various products like LinkedIn Newsfeed, LinkedIn Today for online message consumption and in addition to offline analytics systems like Hadoop. Kafka’s strong durability is also one of the key factors in connection with LinkedIn.
Netflix
Netflix is an American multinational provider of on-demand Internet streaming media. Netflix uses Kafka for real-time monitoring and event processing.
Mozilla
Mozilla is a free-software community, created in 1998 by members of Netscape. Kafka will soon be replacing a part of Mozilla current production system to collect performance and usage data from the end-user’s browser for projects like Telemetry, Test Pilot, etc.
Oracle
Oracle provides native connectivity to Kafka from its Enterprise Service Bus product called OSB (Oracle Service Bus) which allows developers to leverage OSB built-in mediation capabilities to implement staged data pipelines.
https://www.bilibili.com/read/cv24831491/#/
-
products https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/Ecosystem
schema registry https://docs.confluent.io/current/schema-registry/schema_registry_tutorial.html
-
Cheatsheet https://gist.github.com/filipefigcorreia/3db4c7e525581553e17442792a2e7489
-
related https://medium.com/eleven-labs/cqrs-pattern-c1d6f8517314 https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/cqrs https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/azure/architecture/patterns/materialized-view
https://cwiki.apache.org/confluence/display/KAFKA/A+Guide+To+The+Kafka+Protocol
Presentaion 《Introduction to kafka》
1.Basic Concepts What’s Kafka Why use Kafka How it works 2.Exactly once Semantics
What’s Kafka
Apache Kafka is a community distributed streaming platform capable of handling trillions of events a day. Initially conceived as a messaging queue, Kafka is based on an abstraction of a distributed commit log. Since being created and open sourced by LinkedIn in 2011, Kafka has quickly evolved from messaging queue to a full-fledged event streaming platform.
Why use Kafka
Microservice and kafka already became a de-facto industry standard
1. basicaly kafka is a messaging system, compare to other messaging middleware like the one I used before called rabbit mq, with rabbit mq you can only process once, after consuming the message, it’s removed from the queue. kafka provides durable storage of messages, sometimes kafka is used as a kind of database. and now kafka has evolved from messaging queue to full-fleged event streaming platform, we’re not using the streaming feature, so today the topic only cover messaging queue.
2. why do we use kafka

Let’s have a look at architecuture diagram next slides microservices approach vs traditional approach, in traditional approach, application stack multiple layers and compononets together as a single unit. we can see microservice segregates functionalities into a set of autonamous services,so the circle connecting microservices is message queue system. there are some advantages for microservice approach, there is no single point of failure, one service broke down doesn’t impact other services; its easier to scale up, all these services are deployed independently, esier to identify the bottle neck and scale up; from developer standpoint, it can save a lot of time troubleshooting the microservices compared to debug into the traditional application, micorservice is designed based on single reponsiblity principle, you can find the paticular service responsible for the cause straightforward.
3.

kafka works like this: producers publish message to the topics on brokers, the consumers subscribe to the topic will continously poll from the brokers. in the middle is the brokers, we have 4 brokers, each broker represents one instance of the kafka server, we have 2 topics allocated on the brokers: topic 1 and topic 2, topic 1 have 2 paritions, topic 2 have 1 parition, each topic has two replications, to publish a message, the producers has to specify 3 params: the topic name, which partition and the message itself, the messsage will be published on to leader partition, and the followers will replicate from leader,
consumers can join in the same group by config the same application id, each one partition can be consumed by consumers from different consumer group, but one partition can only be consumed by one consumer in the same consumer group, in another word, consumers in the same consumer group load balance the topic partitions, consumers from different consumer group are idenpendent from each other.
4. one critical concerns is how do we achieve exactly once semantics, how do we guarantee there is no missing or duplicated messages, there is a misconception that develop using kafka API will inherently has the capbility to achieve exactly once senmantics, truth is we have to design properly. to discuss this concern, let’s look at a typical application.
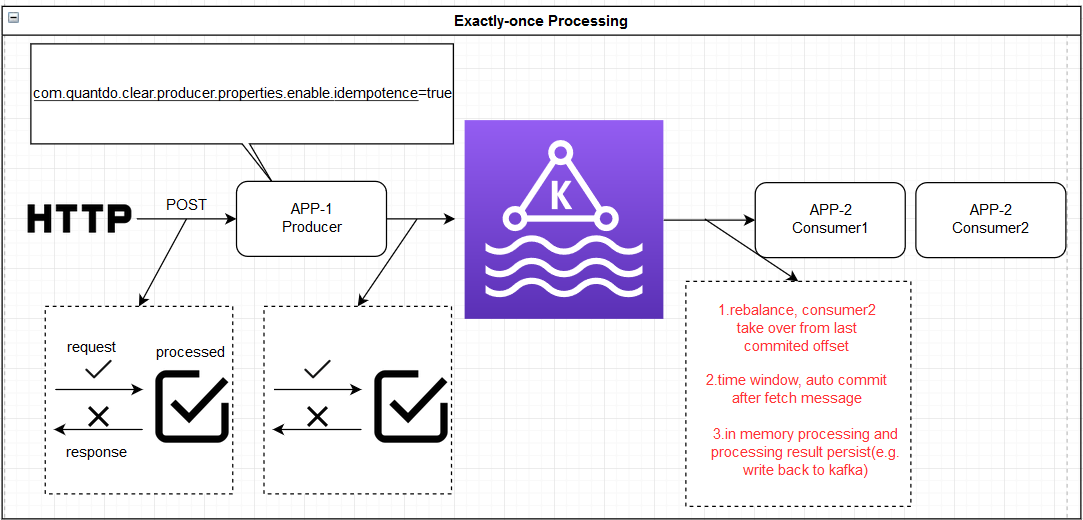
we post a message to APP-1, APP-1 extract the data,transform and produce the message to kafka, APP-2 will consume the message. very simple but it can go wrong from many aspects. first, the http call, when we make a http post, it may happen that APP-1 recevied the post data and processed, but somehow failed to return the reposonse back to the http client due to may be network issue, so the http client side will be timeout, normally the http client library will retry for this secnario, if the network recovered, APP-1 will recevie duplicated message, in this case from my own experience, what we would do is that we use redis on APP-1 to check duplication. the same may happen when APP-1 publish message to kafka, good news is that in the latest kafka version, it already help us handled this secnario, all we need to do is simply config enable idempotence to be ture. go on the consumer side, unfortunately, consumer side is too much complicated, there is no easy way to solve it, before further discuss, let me clarify the verb ‘processing’, there are mainly two types of processing: in-memory processing, the other type is data persist(for example store into database, write to kafka), if it’s purly in-memory processing there is nothing to worry about, whenever it’s broken, so I’m talking about type 2, , let’s assume processing here means write to kafka.

Transactional delivery allows producers to send data to multiple partitions such that either all messages are successfully delivered, or none of them are.
1) Producer However, idempotent producers don’t provide guarantees for writes across multiple TopicPartitions. For this, one needs stronger transactional guarantees, ie. the ability to write to several TopicPartitions atomically. By atomically, we mean the ability to commit a set of messages across TopicPartitions as a unit: either all messages are committed, or none of them are. 2) Consumer maintain offset Refer to https://kafka.apache.org/0102/javadoc/index.html?org/apache/kafka/clients/consumer/KafkaConsumer.html By default, kafka help maintains consumer offset in topic called “__consumer_offset”, whenever the consumer dies and restart or failover to another consumer in the same consumer group, it will continue from last committed offset.For example, we have two consumers A and B in one consumer group, if A crashed, B will take over A and continue from where A left over(from last committed offset), sounds good? Actually no, here is why? there are two ways to commit offset: Automatically commit when receive the record by calling poll()[Let’s say, you call poll each 10 ms, and set commit-interval to 100ms. Thus, in every 10th call to poll will commit (and this commit covers all messages from the last 10 poll calls).], the problem with this way is that the consumer may fail process the offset has already advanced(If auto-commit is enabled for the Kafka consumer, the event processor might already have commited the event offset and fail before finishing the event. The consumer must commit the event manually after all relevant sub-processes have completed.), the other way is manually commit after process the record, this method is still problematic as the consumer may crashed after processing the record(calculating some results and send it to the downstream consumers/send to kafka) but before sending the commit to the kafka broker.
**snapshot and recovery **
When the rebalance happen, for the example when a consumer crashed, the other consumer will take over the partition and continue from last committed offset, but hold on, what about the context, I mean the states stored in the memory, how do we recover the states. So what we can do is that we reprocessing the partition from the beginning, but the problem is message processing is time consuming, and when the partition grows fast, there are too many messages, reprocessing the partition may take a long time. So what we can improve is that we add a checkpoint to take snapshot of the memory state, we call it checkpoint, so when rebalance happens, we can recover from the latest checkpoint instead of beginning, so this will improve the performance, save time for recovery. By design, the new xxx system process records from kafka one by one in sequence, during the data processing, the consumer generated many in memory results, for example currentPosition for each positionAccount, we want to have snapshot of the result from time to time, so in the case of recovery, the consumer can recover from snapshot, save a lot computing power to re-calculate the result. By the way, Kafka do support stateful operation with kafka stream state store, but that’s mainly for aggregation operation, so in our framework we didn’t take advantage of it
业务流水线假设为: 微服务A->微服务B->微服务C
微服务B处理完来自微服务A的某条kafka信息,然后需要往下游也就是微服务C发送kafka消息SendKafkaMsg_InfoToC()时,同时会保存此时处理的来自微服务A的消息的offset SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset(),我们成为增量快照, SendKafkaMsg_InfoToC()和SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset()可以作为一个事务一起提交, 这种情况下,增量快照保存的是一个offset,假设此时服务B挂掉,重启后,B会寻找offset,然后从头开始恢复内存状态,直到这个offset,恢复区段为【0, offset】;
为了更快的恢复,我们不想每次从0开始恢复,所以引入全量快照SendKafkaMsg_SaveMemory(),保存此时的内存状态,并且全量快照中还要保存此时对应的来自微服务A的消息的offset,也就是说这是处理完第几条消息之后的内存状态, 增量快照中保存了两个信息:全量快照的位置和恢复区段的终止位置即offsetEND, 然后根据全量快照的位置,再去取出全量快照,全量快照中保存了当时的内存信息以及恢复区段的起始位置即offsetSTART, 所以恢复时先找到增量快照,然后根据增量快照存的位置信息找到全量快照,恢复内存,剩下的一点差异再通过恢复区段【offsetSTART,offsetEND】,恢复到服务B挂掉之前的完整内存状态;
注意一点,跟前面的“SendKafkaMsg_InfoToC()和SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset()可以作为一个事务一起提交”不同, SendKafkaMsg_SaveMemory()不能跟SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset()为一个事务一起提交,因为这两个是有前后依赖的,因为增量快照SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset()还需要保存全量快照的位置信息,而全量快照SendKafkaMsg_SaveMemory() 本身发送给Kafka是异步操作,回调中才能拿到自己的位置信息,所以无法作为同一个事务一起提交,所以只能等异步回调之后拿到全量的位置再存到增量快照SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset()或者另一种做法是将全量快照的位置先存在内存中,增量快照SendKafkaMsg_SaveOffset()在下一次提交, 即使挂掉也影响不大,大不了从头开始或者从更早的全量快照开始恢复;
因此就可以理解下图:
