回目录 《postgresql实用基础》
Arichtecture
https://medium.com/@hnasr/postgresql-process-architecture-f21e16459907#/ Postmaster
1. Setup
1.1 install
| postgresql-client | libraries and client binaries |
|---|---|
| postgresql-server | core database server |
| postgresql-contrib | additional supplied modules |
| postgresql-devel | libraries and headers for C language development |
method1:
sudo yum install -y https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/reporpms/EL-7-x86_64/pgdg-redhat-repo-latest.noarch.rpm
sudo yum install -y postgresql12-server
sudo /usr/pgsql-12/bin/postgresql-12-setup initdb
sudo systemctl enable postgresql-12
sudo systemctl start postgresql-12
method2:
download:
https://www.postgresql.org/download/linux/redhat/
https://yum.postgresql.org/rpmchart/
https://download.postgresql.org/pub/repos/yum/12/redhat/rhel-7.6-x86_64/
postgresql12-libs-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm
postgresql12-contrib-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm
postgresql12-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm
postgresql12-server-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm
yum install ./postgresql12-libs-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm
yum install ./postgresql12-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm
yum install ./postgresql12-contrib-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm -y
yum install ./postgresql12-server-12.7-1PGDG.rhel7.x86_64.rpm -y
folder
vim /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/postgresql.conf vim /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.conf
$ locate bin/postgres
$ /usr/pgsql-12/bin/postgres -V
postgres (PostgreSQL) 12.7
定位配置:
psql
# show config_file;
# show data_directroy;
systemctl status postgresql-12.servcie systemctl edit postgresql-12 sudo vim /usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql-12.service
PostgreSQL 修改数据存储路径:
- method 1: https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/671203356
- method 2: https://blog.csdn.net/aikudexiaohai/article/details/129692013
1.2 client连接
CLI - psql
su - postgres
进入bash,输入
#psql
就进入到plsql命令窗口,执行\l就可以看到所有db
为啥默认角色:postgres呢,执行:
\du
List of roles
Role name | Attributes | Member of
-----------+------------------------------------------------------------+-----------
_gvm | | {dba}
dba | Superuser, No inheritance, Cannot login | {}
postgres | Superuser, Create role, Create DB, Replication, Bypass RLS | {}
可以创建更多角色
sudo -u postgres createuser owning_user
sudo -u postgres createdb -O owning_user dbname
常用命令:
\l \list
\c [DATABASE]
\d
\d TABLE_NAME
\du 查看用户权限
\dx 查看插件
SELECT * FROM pg_extension;
--format output
\x on
解锁 unlock
dbname=# select pid from pg_locks l join pg_class t on l.relation = t.oid where t.relname = 'tablename';
dbname=# SELECT pg_cancel_backend(the id);
SELECT pg_terminate_backend(3567);
select * from pg_stat_activity where pid=3567;
\copy (query) to result.csv csv header
GUI Client
- Offical: Pgadmin 4 https://www.pgadmin.org/download/
- Pgadmin3 LTS by BigSQL (don’t support 11g)
-
DBeaver offline install settings: class name: org.postgresql.Driver template: jdbc:postgresql://{host}:{port}/{database} libraries: add postgres drivers show all databases On the connection, right-click ->
Edit connection->Connection settings-> on the tabbed panel, selectPostgreSQL, check the boxShow all databases.How do you view PostgreSQL messages (such as RAISE NOTICE) in DBeaver? you can use Ctrl+Shif+O or the button Show server output console on the left side of the script window.
Drivers
- C# 连接 PostgreSQL — Npgsql
1.3 Utilities
- pg_ctl pg_ctl status pg_ctl start/stop vs systemctl start/stop postgresql.service
- pg_dump ``` pg_dump -s dbName > db_schema_dump.sql
dump users
pg_dumpall –globals-only –file=globals.sql
| gzip -dc filename.bak.gz | psql -U postgres |
+ pg_basebackup 备份恢复
https://www.cnblogs.com/cqdba/p/15920508.html
+ pgbench 官方压测
### 1.4 Config
#### 理解一下posgresql的用户概念
the `postgres` PostgreSQL user account already exists and is configured to be accessible via `peer` authentication for unix sockets in `pg_hba.conf`
https://www.liquidweb.com/kb/what-is-the-default-password-for-postgresql/
本机如果直接通过plsql连接,可以修改local用户(默认用户postgres):
https://www.hostinger.com/tutorials/how-to-install-postgresql-on-centos-7/
psql -d template1 -c “ALTER USER postgres WITH PASSWORD ‘NewPassword’;”
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18664074/getting-error-peer-authentication-failed-for-user-postgres-when-trying-to-ge
#### 开启远程连接:
https://blog.csdn.net/zhangzeyuaaa/article/details/77941039
step 1:开启监听:
vim /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/postgresql.conf
listen_addresses = ‘*’ # what IP address(es) to listen on;
step 2:修改访问规则, md5方式:
vim /var/lib/pgsql/12/data/pg_hba.conf
host all all 0.0.0.0/0 md5
step 3:md5方式需要设置密码然后再重启: su - postgres $ psql -U postgres -p 5432 postgres=# \password postgres
systemctl restart postgresql-12
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6405127/how-do-i-specify-a-password-to-psql-non-interactively PGPASSWORD=postgres psql –host IP –port 5432 -U postgres -d DBNAME -c “query;” PGPASSWORD=postgres psql –host IP –port 5432 -U postgres -d DBNAME -f file.sql
#### 更改PGDATA位置
systemctl status postgresql-12.service
● postgresql-12.service - PostgreSQL 12 database server Loaded: loaded (/usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql-12.service;
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql-12.service
Location of database directory
Environment=PGDATA=/var/lib/pgsql/12/data/
mkdir pg_data_base #careful, it’s parent folder rsync -av /var/lib/pgsql/12 pg_data_base/
mv /var/lib/pgsql/12/data /var/lib/pgsql/12/data-bk
vi /usr/lib/systemd/system/postgresql-12.service [Service] Environment=PGDATA=/apex/data/pg_data_base/12/data/
systemctl daemon-reload systemctl start postgresql-12.service
sudo -u postgres psql SHOW data_directory;
### Extension
dblink vs postgres_fdw
## 2. Syntax
Assign null or empty ‘’ to numberic, to_number(‘’) throw exception, use if else instead
Bigint default value is NULL not 0
### 2.1 Basic
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/postgresql/index.htm
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/app-psql.html
表空间
postgres=# select * from pg_tablespace; oid | spcname | spcowner | spcacl | spcoptions ——+————+———-+——–+———— 1663 | pg_default | 10 | | 1664 | pg_global | 10 | | (2 rows)
#### System
Oracle rownum / now(), sysdate postgresql: limit / now(), CURRENT_DATE
NULL and empty string:
Assign null or empty ‘’ to numberic, to_number(‘’) throw exception, use if else instead Bigint default value is NULL not 0 Oracle NVL() PGSQL coalesce()
Returning into:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7191902/cannot-select-from-update-returning-clause-in-postgres Oracle: SQL%ROWCOUNT PG: GET DIAGNOSTICS integer_var = ROW_COUNT;
#### Data Format
**varchar to numeric**
‘12.01’::numeric
**Date**
规范数据: SELECT to_char(‘20230308 1:1:1.1’::timestamp, ‘yyyymmdd HH24:MI:SS:MS’); =》 20230308 01:01:01:100 但是注意: SELECT to_timestamp(‘20230308 1:1:1.1’, ‘yyyymmdd HH24:MI:SS:MS’); =》2023-03-08 01:01:01.100 带- 并不是我们想要的格式
select timestamp’20211227’; select to_timestamp(‘2021-12-24 05:00:00’,’yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’); select cast(current_date-interval ‘4 day’+interval ‘5 hour’ as text)::timestamp ‘2013-08-20 14:52:49’::timestamp
to_timestamp(‘20/8/2013 14:52:49’, ‘DD/MM/YYYY hh24:mi:ss’) to_timestamp(‘20/8/2013 14:52:49’, ‘DD/MM/YYYY hh24:mi:ss’)::timestamp to_timestamp(‘20/8/2013 14:52:49’, ‘DD/MM/YYYY hh24:mi:ss’) AT TIME ZONE ‘UTC’
select to_timestamp(epoch_column)::date;
select to_char(current_date-1,’yyyymmdd’); select TO_CHAR(current_date+interval ‘5 hour’,’yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) select TO_CHAR(current_date+interval ‘5 hour’+’4 minute’,’yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) select to_char(current_date - interval ‘1’ month, ‘YYYYMM’);
select extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date-interval ‘5 day’+interval ‘19 hour’+interval ‘1 minute’ as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE ‘SGT’)::int
CURRENT_TIMESTAMP in milliseconds: SELECT (extract(epoch from now())*1000)::bigint;
SELECT * FROM your-table WHERE EXTRACT(MINUTE FROM begin_time) = ‘45’
ORACLE VS POSTGRES
Oracle to_char(param) postgresql to_char(parma1, ‘999’)
Concat Character string connector (||) will fail in postgresql when there is ‘’ or null concat() Format v_sql := format(\(select * from table where col1=%s\),’test’)
Datetime Oracle to_date(str, ‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) Postgresql to_timestamp(str, ‘yyyy-mm-dd hh24:mi:ss’) select extract (day from timestamp ‘2011-01-01 01:01:01’ - timestamp ‘2001-01-01 01:01:01’);
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/functions-formatting.html
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/static/functions-datetime.html
https://thebuild.com/blog/2018/08/07/does-anyone-really-know-what-time-it-is/
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.2/functions-datetime.html
#### Tables and Views
The new query must generate the same columns that were generated by the existing view query (that is, the same column names in the same order and with the same data types) (...)
### 2.2 CRUD
#### update from select subquery
```sql
UPDATE dummy
SET customer=subquery.customer,
address=subquery.address,
partn=subquery.partn
FROM (SELECT address_id, customer, address, partn
FROM /* big hairy SQL */ ...) AS subquery
WHERE dummy.address_id=subquery.address_id;
OR
WITH subquery AS (
SELECT address_id, customer, address, partn
FROM /* big hairy SQL */ ...
)
UPDATE dummy
SET customer = subquery.customer,
address = subquery.address,
partn = subquery.partn
FROM subquery
WHERE dummy.address_id = subquery.address_id;
insert or update if exists:
最简单的思路:
if exists (select * from table where ...) then
update
else
insert
end if;
如果是基于primary key或index可以用 insert on conflict或者upsert:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1109061/insert-on-duplicate-update-in-postgresql/1109198#1109198
Oracle merge into
Pgsql insert into
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.5/static/sql-insert.html
insert into table1 as t1(col1,col2, col3)
select col1, col2,col3
from ( select col1,col2, max(col3) as col3
from table2
where col3 >= date'2012-01-01'
and col3 <date'2013-01-01'
and col1 is not null
and col2 is not null
group by col1, col2 ) a
on conflict(col1, col2) do
update set col3 = excluded.col3,
col2 = case when excluded.col2 is null then t1.col2 else excluded.col2 end
For update
WITH Statement
WITH provides a way to write auxiliary statements for use in a larger query.
WITH moved_rows AS (
DELETE FROM t_bticoin_index
WHERE index_time/1000<=
extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date-interval '7 day' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int
RETURNING index_name,index_value,index_time,server_time
)
INSERT INTO t_bticoin_index_hist
SELECT * FROM moved_rows;
2.3 Functions & Stored Procedure
if condition_1 then
statement_1;
elsif condition_2 then
statement_2
...
elsif condition_n then
statement_n;
else
else-statement;
end if;
Use the right type, character to numeric v_product := to_number(p_walletcode);
Dont use FROM DUAL in procedrue
Json
Json array https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24006291/postgresql-return-result-set-as-json-array/24006432
PostgreSQL Error Codes: array_length(array[1,2,3], 1) https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/static/functions-array.html
Transaction
Cursor: https://www.postgresql.org/docs/11/static/sql-call.html
cannot commit while a subtransaction is active to_json
https://hashrocket.com/blog/posts/faster-json-generation-with-postgresql select row_to_json(t) from ( select id, text from words ) t
Functions
Perform function https://stackoverflow.com/questions/18315633/calling-functions-with-exec-instead-of-select
Dynamic sql https://stackoverflow.com/questions/12780275/dynamic-sql-query-in-postgres execute immediate v_sql into v_count;
Cursor and fetch
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.3/static/sql-fetch.html
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.3/static/plpgsql-cursors.html

Exception handling https://www.postgresql.org/docs/8.2/static/plpgsql-statements.html No data found Select into strict
SELECT * INTO myrec FROM emp WHERE empname = myname;
IF NOT FOUND THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'employee % not found', myname;
END IF;
If the STRICT option is specified, the query must return exactly one row or a run-time error will be reported, either NO_DATA_FOUND (no rows) or TOO_MANY_ROWS (more than one row). You can use an exception block if you wish to catch the error, for example:
BEGIN
SELECT * INTO STRICT myrec FROM emp WHERE empname = myname;
EXCEPTION
WHEN NO_DATA_FOUND THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'employee % not found', myname;
WHEN TOO_MANY_ROWS THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'employee % not unique', myname;
END;
generate time series
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/functions-srf.html
select 'btc',null,extract(epoch FROM index_time::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int,(extract(epoch from now())*1000)::bigint
from generate_series(cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT',
cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT',
interval '1 minutes') as s(index_time)
where index_time not in (select to_timestamp(index_time/1000) from t_bticoin_index_test)
查找缺失数据
SELECT *
FROM generate_series('2022-01-14 12:00:00','2022-01-25 11:19:00',
interval '1 minutes') as s(index_time)
where index_time not in (select to_timestamp(index_time/1000) from t_bticoin_index where index_time/1000>=
extract(epoch FROM cast('2022-01-14 12:00:00' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int);
detect & fill gaps
https://www.jianshu.com/p/890137e60597
update temp_table
set index_value=t2.index_value
from (
with x as (
select
index_time,index_value,
lead(index_time,1,index_time) over(order by index_time) as index_time1
from
(
select index_time,index_value
from temp_table
where index_value is not null
) o
)
select
index_time,index_value,to_timestamp(index_time/1000)
from
(
select temp_table.index_time,x.index_value
from temp_table,x
where temp_table.index_value is null and (temp_table.index_time between x.index_time and x.index_time1)
union all
select index_time,index_value
from temp_table
where index_value is not null
) t1
order by index_time
)as t2
where temp_table.index_time=t2.index_time;
2.4 Trigger
A trigger function is created with the CREATE FUNCTION command, declaring it as a function with no arguments and a return type of trigger (for data change triggers) or event_trigger (for database event triggers). Special local variables named TG_something are automatically defined
A trigger function must return either NULL or a record/row value having exactly the structure of the table the trigger was fired for.
Example 1: Row-level triggers fired BEFORE can return null to signal the trigger manager to skip the rest of the operation for this row (i.e., subsequent triggers are not fired, and the INSERT/UPDATE/DELETE does not occur for this row)
This example trigger ensures that any insert, update or delete of a row in the emp table is recorded (i.e., audited) in the emp_audit table. The current time and user name are stamped into the row, together with the type of operation performed on it.
CREATE TABLE emp (
empname text NOT NULL,
salary integer
);
CREATE TABLE emp_audit(
operation char(1) NOT NULL,
stamp timestamp NOT NULL,
userid text NOT NULL,
empname text NOT NULL,
salary integer
);
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION process_emp_audit() RETURNS TRIGGER AS $emp_audit$
BEGIN
--
-- Create a row in emp_audit to reflect the operation performed on emp,
-- making use of the special variable TG_OP to work out the operation.
--
IF (TG_OP = 'DELETE') THEN
INSERT INTO emp_audit SELECT 'D', now(), user, OLD.*;
ELSIF (TG_OP = 'UPDATE') THEN
INSERT INTO emp_audit SELECT 'U', now(), user, NEW.*;
ELSIF (TG_OP = 'INSERT') THEN
INSERT INTO emp_audit SELECT 'I', now(), user, NEW.*;
END IF;
RETURN NULL; -- result is ignored since this is an AFTER trigger
END;
$emp_audit$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER emp_audit
AFTER INSERT OR UPDATE OR DELETE ON emp
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION process_emp_audit();
Example 2:
If a nonnull value is returned then the operation proceeds with that row value. Returning a row value different from the original value of NEW alters the row that will be inserted or updated. Thus, if the trigger function wants the triggering action to succeed normally without altering the row value, NEW (or a value equal thereto) has to be returned. To alter the row to be stored, it is possible to replace single values directly in NEW and return the modified NEW, or to build a complete new record/row to return. In the case of a before-trigger on DELETE, the returned value has no direct effect, but it has to be nonnull to allow the trigger action to proceed. Note that NEW is null in DELETE triggers, so returning that is usually not sensible. The usual idiom in DELETE triggers is to return OLD.
This example trigger ensures that any time a row is inserted or updated in the table, the current user name and time are stamped into the row. And it checks that an employee’s name is given and that the salary is a positive value.
CREATE TABLE emp (
empname text,
salary integer,
last_date timestamp,
last_user text
);
CREATE FUNCTION emp_stamp() RETURNS trigger AS $emp_stamp$
BEGIN
-- Check that empname and salary are given
IF NEW.empname IS NULL THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION 'empname cannot be null';
END IF;
IF NEW.salary IS NULL THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION '% cannot have null salary', NEW.empname;
END IF;
-- Who works for us when they must pay for it?
IF NEW.salary < 0 THEN
RAISE EXCEPTION '% cannot have a negative salary', NEW.empname;
END IF;
-- Remember who changed the payroll when
NEW.last_date := current_timestamp;
NEW.last_user := current_user;
RETURN NEW;
END;
$emp_stamp$ LANGUAGE plpgsql;
CREATE TRIGGER emp_stamp BEFORE INSERT OR UPDATE ON emp
FOR EACH ROW EXECUTE FUNCTION emp_stamp();
2.5 子表继承
SELECT,UPDATE和DELETE–支持这个”ONLY”符号
Similarly an inheritance link can be removed from a child using the NO INHERIT variant of ALTER TABLE. Dynamically adding and removing inheritance links like this can be useful when the inheritance relationship is being used for table partitioning (see Section 5.9)[https://www.postgresql.org/docs/12/ddl-partitioning.html].
2.6 Partition 分区
Inheritance Partitioning VS postgresl12 原生 built-in Declarative Partitioning https://www.postgresql.org/docs/12/ddl-partitioning.html#DDL-PARTITIONING-USING-INHERITANCE https://www.postgresql.org/docs/12/ddl-partitioning.html#DDL-PARTITIONING-DECLARATIVE
PARTITIONING-DECLARATIVE:
ALTER TABLE measurement DETACH PARTITION measurement_y2006m02;
PARTITIONING-USING-INHERITANCE:
ALTER TABLE measurement_y2006m02 NO INHERIT measurement;
注意,如果创建分区比如 measurement_y2006m02 之前插入的数据是在 父表 measurement里面,查询可以使用 ONLY 关键字
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/plpgsql-trigger.html
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/ddl-partitioning.html
在 PostgreSQL 中,当使用 INHERITS 关键字创建一个表来继承另一个表时,子表会继承父表的列结构(但不包括约束、索引、外键等),并且你可以为子表添加自己的约束。但是,由于 INHERITS 不会自动继承约束,你需要在子表上显式地重新声明这些约束。
然而,对于主键(PRIMARY KEY),情况有点特殊。PostgreSQL 不允许直接在子表上设置与父表相同列的主键约束,因为主键约束本质上是一个唯一约束加上一个非空约束,并且 PostgreSQL 不允许在不同的表上设置跨表的主键约束。但是,你可以通过 UNIQUE 约束和 NOT NULL 约束来模拟主键的行为。
不过,在大多数情况下,如果父表已经有一个主键,并且子表想要使用相同的列作为唯一标识符,那么你可以简单地在子表上设置一个 UNIQUE 约束(尽管这不是严格意义上的主键,因为它不会被自动用作外键引用的目标)。但是,由于你已经知道 id 是自增的,并且父表已经将其作为主键,因此在子表中保持 id 的唯一性(并且不为空)是合理的。
下面是一个例子,展示如何创建一个名为 employees2024 的子表,它继承自 employees 表,并且尝试模拟与 employees 表相同的 PRIMARY KEY、CHECK 和 UNIQUE 约束(注意,PRIMARY KEY 约束在子表中被模拟为 UNIQUE NOT NULL):
sql CREATE TABLE employees2024 ( CHECK (id >= (SELECT MAX(id) FROM employees) + 1) – 这是一个可选的CHECK约束,用于确保子表的id不会与父表冲突(但通常不推荐这样做,因为更好的做法是使用序列或生成器) ) INHERITS (employees);
– 由于我们不能直接继承主键约束,我们在这里添加一个UNIQUE约束来模拟主键的行为 – 注意:这通常不是必需的,因为子表会继承id列,并且由于id是自增的,它自然会在子表中保持唯一 ALTER TABLE employees2024 ADD CONSTRAINT employees2024_pkey UNIQUE (id);
– 如果父表的CHECK和UNIQUE约束对于子表来说也是必要的,你通常不需要再次添加它们, – 因为子表已经继承了这些列的定义,并且可以在需要时依赖父表的约束。 – 但是,如果你想要为子表添加额外的CHECK约束,你可以这样做: ALTER TABLE employees2024 ADD CONSTRAINT employees2024_age_check CHECK (age >= 20); – 例如,只接受20岁及以上的员工
– 注意:由于email在父表中已经是UNIQUE的,并且子表继承了email列, – 因此你不需要(也不能)在子表上再次添加UNIQUE约束到email列, – 因为这将违反UNIQUE约束的定义(即不能有重复的值)。 – 但是,如果你想要对子表的email应用更严格的规则(尽管这通常不是必需的), – 你可能需要考虑使用触发器或更复杂的逻辑。
然而,请注意以下几点:
我添加了一个可选的 CHECK 约束来确保 employees2024 表的 id 不会与 employees 表的 id 冲突。然而,这通常不是一个好主意,因为更好的做法是使用序列或某种形式的ID生成器来确保ID的唯一性和连续性。
我为 id 列添加了一个 UNIQUE 约束来模拟主键的行为。但是,请注意,这实际上是不必要的,因为 id 列在父表中已经是主键,并且子表会继承这个列。在大多数情况下,你可以依赖父表的主键约束来确保 id 的唯一性。
对于 email 列,由于它在父表中已经是 UNIQUE 的,因此你不需要(也不能)在子表上再次添加 UNIQUE 约束。
如果你想要为子表添加额外的 CHECK 约束,你可以像上面那样做。但是,请确保这些约束与父表的约束不冲突,并且它们对于子表来说是有意义的。
自动分区-继承分区
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.pg_auto_insert_TABLE()
RETURNS trigger
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $function$
declare
partition_column_name text ;
strSQL text;
curMM varchar(6);
isExist boolean;
startTime text;
endTime text;
begin
partition_column_name := TG_ARGV[0];
EXECUTE 'SELECT $1.'||partition_column_name INTO strSQL USING NEW;
raise info 'strSQL:%',strSQL;
curMM := to_char(to_timestamp(strSQL::BIGINT/1000), 'YYYYMM');
raise info 'curMM:%',curMM;
select count(*) INTO isExist from pg_class where relname = (TG_RELNAME||'_'||curMM);
IF ( isExist = false ) THEN
startTime := curMM||'01 00:00:00.000';
endTime := to_char(startTime::timestamp + interval '1 month', 'YYYY-MM-DD HH24:MI:SS.MS');
strSQL := 'CREATE TABLE IF NOT EXISTS '||TG_RELNAME||'_'||curMM||
' ( CHECK('||partition_column_name||'>='''|| (extract(epoch FROM startTime::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')*1000)::bigint ||''' AND '
||partition_column_name||'< '''|| (extract(epoch FROM endTime::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')*1000)::bigint ||''' )
) INHERITS ('||TG_RELNAME||') ;';
EXECUTE strSQL;
strSQL := 'CREATE INDEX idx_time_'||curMM||' ON '
||TG_RELNAME||'_'||curMM||' ('||partition_column_name||');';
EXECUTE strSQL;
END IF;
strSQL := 'INSERT INTO '||TG_RELNAME||'_'||curMM||' SELECT $1.*';
EXECUTE strSQL USING NEW;
RETURN NULL;
END;
$function$
;
CREATE TRIGGER insert_TABLE
BEFORE INSERT
ON t_TABLE
FOR EACH ROW
EXECUTE PROCEDURE pg_auto_insert_TABLE('index_time');
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.pg_houseclean()
RETURNS integer
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $function$
declare
result integer;
previous_month varchar;
strSql varchar;
begin
select to_char(current_date - interval '1' month, 'YYYYMM') into previous_month;
strSql :='ALTER TABLE t_TABLE_'||previous_month||' NO INHERIT t_TABLE;';
raise info 'strSQL:%',strSql;
EXECUTE strSql;
select 100 into result;
RETURN result;
END;
$function$
;
2.7 Advanced
index
注意,跟mysql不同,postgresql的索引是schema级别的,不是table级别的,所以虽然是 create index IDX_NAME on TABLE(COLUMN) IDX_NAME也不能重复! Indexes and tables (and views, and sequences, and…) are stored in the pg_class catalog, and they’re unique per schema due to a unique key on it
select * from pg_class c join pg_namespace ns on c.relnamespace = ns.oid where c.relname='idx_time_202204';
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/27306539/at-what-level-do-postgres-index-names-need-to-be-unique
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/61408317/creating-multicolumn-indexes-in-postgresql#/
Temp table
https://github.com/yallie/pg_global_temp_tables

https://stackoverflow.com/questions/41178844/are-temporary-tables-in-postgresql-visible-over-all-client-sessions
Sequence
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/8.2/static/functions-sequence.html
Customized Types
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.6/static/sql-createtype.html
CREATE TYPE “XYZ” AS TABLE OF VARCHAR2(104) in postgresql https://stackoverflow.com/questions/24017175/create-type-xyz-as-table-of-varchar2104-in-postgresql
Array[] as input https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.1/static/arrays.html https://stackoverflow.com/questions/570393/postgres-integer-arrays-as-parameters
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/3660787/how-to-list-custom-types-using-postgres-information-schema
Oracle bulk collect into
Pgsql Offset
/*CREATE TYPE t_my AS (
col1 numeric(16,6),
col2 numeric,
col3 bpchar(36)
);*/
do $$DECLARE
c cursor(os int) for select * from table limit 5 offset os;
r record;
v_name varchar(100)[];
recs t_my[];
BEGIN
select array (select row(0, col, 'aaa') from table1 limit 5 offset 10 ) into recs;
--v_games:= array_to_string(v_name,',');
raise notice '%', recs[1].col1;
END
$$;
Analysis
Window function https://www.postgresql.org/docs/11/static/tutorial-window.html https://gist.github.com/dialogbox/454380d6a68344556350bb8dbf1d64e5
select col1, col2, min(col3) points
from (select t1.col1, t1.col2,
first_value(col3) over w as col3
from table1 t1
where t1.date >= to_date('2018-01-01','yyyy-mm-dd')
and t1.date<to_date('2018-07-01','yyyy-mm-dd')
window w AS(
partition by col1,col2
order by date desc
)
) t group by col1, col2
order by 1,2;
Dynamic cursor
In sp pg_test:
INOUT results refcursor)
results := 'cur';
_query_:=’select * from table’;
perform pg_dyncursor('cur', _query_);
Then in plsql:
Begin
Call pg_test();
End;
FETCH ALL IN cur;
close cur;
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION pg_dyncursor(cursor_name text, query text)
RETURNS void
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $function$
DECLARE
BEGIN
EXECUTE 'DECLARE' || quote_ident(cursor_name) || ' CURSOR WITH HOLD FOR ' || query;
END
$function$
Scheduler
https://github.com/citusdata/pg_cron https://crontab.guru/
SELECT cron.schedule(‘0 2 * * *’, \(TODO\));
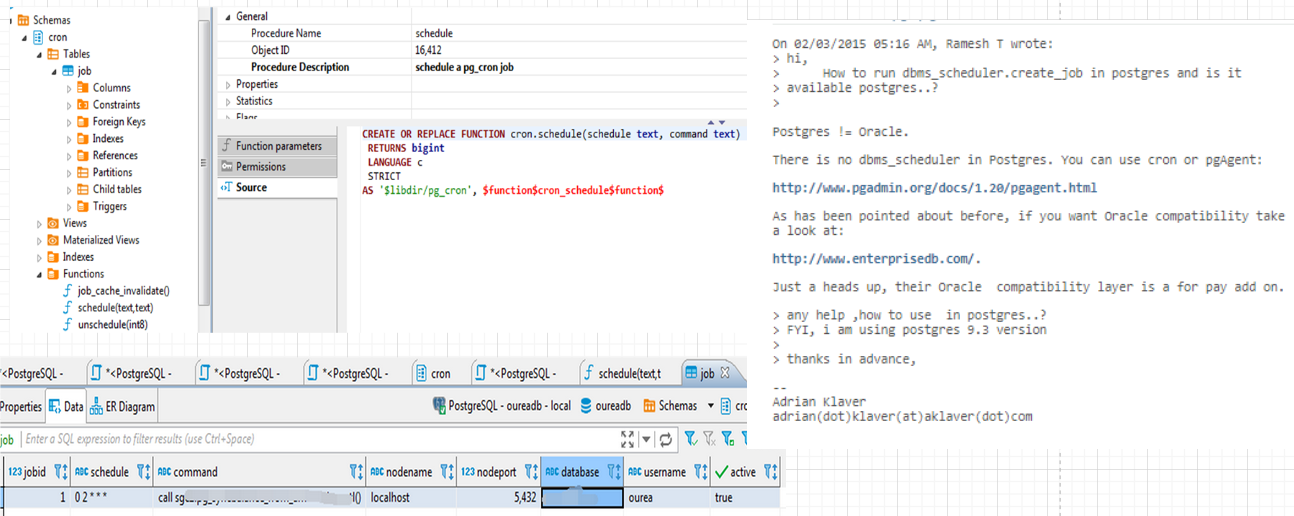 https://www.pgadmin.org/docs/pgadmin3/1.22/pgagent.html
https://www.pgadmin.org/docs/pgadmin3/1.22/pgagent.html
Message Flow / Protocol Flow
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/11/static/protocol-flow.html Simple query: Recommended practice is to code frontends in a state-machine style that will accept any message type at any time that it could make sense, rather than wiring in assumptions about the exact sequence of messages Extended query:
Lock
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/explicit-locking.html
- Table-Level Locks
- Row-Level Locks
- Page-Level Locks
- Deadlocks
- Advisory Locks
System Table
- db: postgres
select * FROM information_schema.triggers SELECT pg_terminate_backend(pg_stat_activity.pid) FROM pg_stat_activity WHERE pg_stat_activity.datname = 'TARGET_DB' -- ← change this to your DB AND pid <> pg_backend_pid(); - db: template0
- db: template1
Gaps between Oracle PLSQL and PostgreSQL
https://github.com/digoal/blog/blob/master/201607/20160714_01.md
https://wiki.postgresql.org/wiki/Oracle_to_Postgres_Conversion
oracle keep dense_rank CHANGE in postgresql
https://www.eversql.com/rank-vs-dense_rank-vs-row_number-in-postgresql/
oracle is record, is table CHANGE in postgresql
type rec_tk is record(
tkno VARCHAR2(100),
cg_zdj number(12, 0) := 0,
cg_jsf number(12, 0) := 0
);
type tklist is table of rec_tk index by binary_integer;
修改为
create type rec_tk as(
tkno VARCHAR(100),
cg_zdj numeric(12,0),
cg_jsf numeric(12,0)
);
#函数外执行创建类型的SQL
create type rec_cjr as(
cjrid varchar(30),
tk rec_tk[]
);
#函数内对table的使用修改为数组的使用,数组的下标从1开始
p_cjrs rec_cjr[];
3. Backup and Restore
full backup restore
make sure all connections to db disconnected or systemctl restart
pg_dump -Fc dbname > outfile psql dbname < infile
pg_dump dbname | gzip > filename.gz createdb dbname gunzip -c filename.gz | psql dbname pg_restore -d dbname /path-to-backup
incremental backup restore
Continuous Archiving and Point-in-Time Recovery (PITR)
4. High Availability
Database servers can work together to allow a second server to take over quickly if the primary server fails (high availability), or to allow several computers to serve the same data (load balancing). Ideally, database servers could work together seamlessly. Web servers serving static web pages can be combined quite easily by merely load-balancing web requests to multiple machines. In fact, read-only database servers can be combined relatively easily too. Unfortunately, most database servers have a read/write mix of requests, and read/write servers are much harder to combine. This is because though read-only data needs to be placed on each server only once, a write to any server has to be propagated to all servers so that future read requests to those servers return consistent results.
This synchronization problem is the fundamental difficulty for servers working together. Because there is no single solution that eliminates the impact of the sync problem for all use cases, there are multiple solutions. Each solution addresses this problem in a different way, and minimizes its impact for a specific workload.
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/high-availability.html
4.1 Replication不同方案:
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/different-replication-solutions.html
- Shared Disk Failover:
Shared hardware functionality is common in network storage devices.
- File System (Block Device) Replication
A modified version of shared hardware functionality
DRBD is a popular file system replication solution for Linux.
- Write-Ahead Log Shipping
A standby server can be implemented using file-based log shipping (Section 26.2) or streaming replication (see Section 26.2.5), or a combination of both. For information on hot standby, see Section 26.5.
- Logical Replication
Allows a database server to send a stream of data modifications to another server. Chapter 30.(Chapter 48
- Trigger-Based Master-Standby Replication
The standby can answer read-only queries while the master server is running. The standby server is ideal for data warehouse queries.Slony-I is an example of this type of replication, with per-table granularity, and support for multiple standby servers. Because it updates the standby server asynchronously (in batches), there is possible data loss during fail over.
- Statement-Based Replication Middleware
ach server operates independently. Read-write queries must be sent to all servers, so that every server receives any changes. But read-only queries can be sent to just one server, allowing the read workload to be distributed among them.Care must also be taken that all transactions either commit or abort on all servers, perhaps using two-phase commit (PREPARE TRANSACTION and COMMIT PREPARED). Pgpool-II and Continuent Tungsten are examples of this type of replication.
- Asynchronous Multimaster Replication
each server works independently, and periodically communicates with the other servers to identify conflicting transactions. The conflicts can be resolved by users or conflict resolution rules. Bucardo is an example of this type of replication.
- Synchronous Multimaster Replication
PostgreSQL does not offer this type of replication
-
Commercial Solutions
-
Data Partitioning
Data partitioning splits tables into data sets. Each set can be modified by only one server. For example, data can be partitioned by offices, e.g., London and Paris,
- Multiple-Server Parallel Query Execution
Many of the above solutions allow multiple servers to handle multiple queries, but none allow a single query to use multiple servers to complete faster. This solution allows multiple servers to work concurrently on a single query. It is usually accomplished by splitting the data among servers and having each server execute its part of the query and return results to a central server where they are combined and returned to the user.
4.2 具体方案1:warm standby or log shipping
Log-Shipping Standby Servers # PostgreSQL and SRE : Log Shipping Replication.
The primary server operates in continuous archiving mode, while each standby server operates in continuous recovery mode, reading the WAL(write ahead logging) files from the primary(Directly moving WAL records from one database server to another is typically described as log shipping).
4.3 具体方案2:hot standby
https://www.postgresql.org/docs/current/hot-standby.html
4.4 具体配置 温备/热备
http://www.mamicode.com/info-detail-2466322.html
5. Integreation - Drivers
download: https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download.html
5.1 Java
pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-jdbc</artifactId>
</dependency>
application.yml:
spring:
##Druid DataSource数据库访问配置
datasource:
#is-dynamic-datasource: true
type: com.alibaba.druid.pool.DruidDataSource
url: jdbc:postgresql://HOST:5432/test
username: postgres
password: postgres
driver-class-name: org.postgresql.Driver
druid:
#连接池配置
#初始化时建立物理连接的个数
initialSize: 1
#最小连接池数量
minIdle: 0
#最大连接池数量
maxActive: 5
#获取连接时最大等待时间,单位毫秒。配置了maxWait之后,缺省启用公平锁,并发效率会有所下降,
#如果需要可以通过配置useUnfairLock属性为true使用非公平锁。
maxWait: 60000
#配置相隔多久进行一次检测(检测可以关闭的空闲连接),此处设置为1分钟检测一次。
timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis: 60000
#一个连接在池中最小生存的时间(ms),此处设置为半小时。
minEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 1800000
#一个连接在池中最大生存的时间(ms),此处设置为7天。
maxEvictableIdleTimeMillis: 25200000
#用来检测连接是否有效的sql; 如果validationQuery为null,testOnBorrow、testOnReturn、testWhileIdle都不会启作用。
validationQuery: SELECT 1 FROM DUAL
#检测连接是否有效的超时时间,默认-1(单位:秒).
validationQueryTimeout: 5
#建议配置为true,不影响性能,并且保证安全性,申请连接的时候检测,如果空闲时间大于timeBetweenEvictionRunsMillis,
#执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效。
testWhileIdle: true
#申请连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能。
testOnBorrow: false
#归还连接时执行validationQuery检测连接是否有效,做了这个配置会降低性能
testOnReturn: false
#是否缓存preparedStatement,也就是PSCache;PSCache对支持游标的数据库性能提升巨大,比如说oracle;
#在mysql5.5以下的版本中没有PSCache功能,建议关闭掉。
poolPreparedStatements: true
#打开PSCache,并且指定每个连接上PSCache的大小
maxPoolPreparedStatementPerConnectionSize: 20
sharePreparedStatements: false
# 通过connectProperties属性来打开mergeSql功能;慢SQL记录
#connectionProperties: druid.stat.mergeSql=true;druid.stat.logSlowSql=true;druid.stat.slowSqlMillis=5000
# 配置监控统计拦截的filters,去掉后监控界面sql无法统计,'wall'用于防火墙
filters: stat,wall,log4j2
#要启用PSCache,必须配置大于0,当大于0时,poolPreparedStatements自动触发修改为true。
#在Druid中,不会存在Oracle下PSCache占用内存过多的问题,可以把这个数值配置大一些,比如说100
#此处默认为-1
maxOpenPreparedStatements: 10
#合并多个DruidDataSource的监控数据
useGlobalDataSourceStat: true
@Service("jdbcService")
public class JdbcServiceImpl implements JdbcService{
private Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(getClass());
@Autowired
public DataSource dataSource;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
private Connection connection;
public Connection getConnection() {
try {
if (connection == null || connection.isClosed()) {
connection = initConnection();
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
logger.error("Initialize connection failed: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
return connection;
}
public Connection initConnection(){
Connection conn = null;
try {
conn = dataSource.getConnection();
conn.setAutoCommit(false);
} catch (SQLException e) {
logger.error("Initialize connection failed: {}", e.getMessage(), e);
}
return conn;
}
@Override
public void savetList(List<Test> list) {
String sql = "insert into t_table(col1,col2) select ?,?,?,? where not exists (select col1 from t_table where col1=?)";
jdbcTemplate.batchUpdate(sql, list, 10000, new ParameterizedPreparedStatementSetter<Test>() {
@Override
public void setValues(java.sql.PreparedStatement ps, Test ac) throws SQLException {
ps.setString(1, ac.getName());
ps.setBigDecimal(2, ac.getValue());
}
});
}
@Override
public void callPgFunction() {
final SimpleJdbcCall jdbcCall = new SimpleJdbcCall(jdbcTemplate).withFunctionName("pg_calc_rate");
final Map<String, Object> result = jdbcCall.execute();
logger.info("jdbcCall result: {}",result.get("returnvalue"));
}
pg_calc_rate:
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.pg_calc_rate()
RETURNS integer
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $$
declare
v_condition integer := -100;
v_product t_fundingrate.product%type := 'BTCP';
v_session t_fundingrate."session"%type := 'T+1';
v_trade_date t_fundingrate.trade_date%type := to_char(current_date-1,'yyyymmdd');
v_rate_type t_fundingrate.rate_type%type;
v_funding_rate t_fundingrate.funding_rate%type;
v_benchmark_price t_fundingrate.benchmark_price%type;
result integer;
begin
if not exists (select * from t_askbidprice where price_time/1000>=extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int
and price_time/1000<=extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int) then
raise info 'Not exists impactmid data between [%,%]',cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp,cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp;
v_condition := -200;
elsif not exists (select * from t_bticoin_index where index_time/1000>=extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int) then
raise info 'Not exists bticoin_index data >= %',cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp;
v_condition := -100;
elsif not exists (select * from t_bticoin_index where index_time/1000>=extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int) then
raise info 'Not exists bticoin_index data >= %',cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp;
raise info 'To generate Tentative funding rate';
v_condition := 0;
v_rate_type := 'Tentative';
else
raise info 'To generate Confirmed funding rate';
v_condition := 100;
v_rate_type := 'Confirmed';
end if;
if v_condition >= 0 then
select funding_rate,benchmark_price
into v_funding_rate,v_benchmark_price
from(
select
avg((GREATEST(0::decimal,t2.impact_bid_price-t1.index_value)-GREATEST(0::decimal,t1.index_value-t2.impact_ask_price))/t1.index_value) as funding_rate,
avg(t1.index_value) as benchmark_price
from t_bticoin_index t1
inner join t_askbidprice t2 on t1.index_name=t2.product and t1.index_time=t2.price_time
where t1.index_time/1000<=
extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int
and t1.index_time/1000>=
extract(epoch FROM cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int
group by t1.index_name
) t;
if exists (select * from t_fundingrate where product=v_product and "session"=v_session and trade_date=v_trade_date) then
raise info 'Update exists record product=%,session=%,trade_date=%',v_product,v_session,v_trade_date;
update t_fundingrate set funding_rate=v_funding_rate,remark=v_rate_type,rate_type=v_rate_type,publish_time=(extract(epoch from now())*1000)::bigint,benchmark_price=v_benchmark_price
where product=v_product and "session"=v_session and trade_date=v_trade_date;
else
raise info 'Insert new record';
insert into t_fundingrate
(product, "session", trade_date, funding_rate, remark, rate_type, publish_time, benchmark_price, currency)
select v_product,v_session,v_trade_date, v_funding_rate,
v_rate_type,v_rate_type,(extract(epoch from now())*1000)::bigint,v_benchmark_price,'USD';
end if;
end if;
select v_condition into result;
RETURN result;
END;
$$
;
5.2 .NET npgsql
https://github.com/npgsql
about composite array Normal Array
Array of Composite Type (custom type) Feature added in 4.0 http://www.npgsql.org/doc/release-notes/4.0.html https://github.com/npgsql/npgsql/blob/fc1e183103ac6246bcb5d7ceacbf509e18248583/test/Npgsql.Tests/Types/CompositeTests.cs https://github.com/npgsql/npgsql/commit/fc1e183103ac6246bcb5d7ceacbf509e18248583
Composite https://github.com/npgsql/npgsql/issues/1678
Why do I get “Invalid attempt to call HasRows when reader is closed” with an open connection? https://stackoverflow.com/questions/13968342/why-do-i-get-invalid-attempt-to-call-hasrows-when-reader-is-closed-with-an-ope
about inout parameters in stored procedure 这个问题是我测试当时最新版本的postgresql并且用了最新的npgsql driver的时候遇到一个问题, 就是存储过程的inout参数拿不到返回结果,经过研究发现奇怪的行为: 1.通过更改npgsql的代码采用simple query这种不安全的协议就可以拿到结果; 2.但是用ngpsql自身默认的extend协议就拿不到; 后来跟ngpsql作者沟通,npgsql作者又跟pgsql的团队沟通,证明确实是pgsql的一个bug,沟通见下面我提的ticket: INOUT parameters from Procedure https://github.com/npgsql/npgsql/issues/2078 https://github.com/npgsql/npgsql/issues/2006
下面是我思考并研究的大致过程, 大致思路就是我发现用某些pgsql客户端调用这种存储过程有返回,有些没有返回,比如pgadmin有返回,dbeaver没有返回, 所以就抓包pgadmin,对比通过npgsql调用的包,最后发现pgadmin是用simple query方式调用, 所以最终修改了npgsql驱动让其支持simple query,因为本身simple query就不安全,所以我没有给出代码, 当然如果有人感兴趣可以联系我
Test Scripts
call pg_test('9cc4afef-aab7-4c35-bdcd-a9f3d0152eb4','');
begin
call pg_test2('9cc4afef-aab7-4c35-bdcd-a9f3d0152eb4','');
fetch all in cur;
commit;
end
-- PROCEDURE: sgc2.pg_test(character varying, text)
-- DROP PROCEDURE sgc2.pg_test(character varying, text);
CREATE OR REPLACE PROCEDUREpg_test(
userid character varying,
INOUT results text)
LANGUAGE 'plpgsql'
AS $BODY$
DECLARE
BEGIN
select cast(999 as decimal) as result;
END;
$BODY$;
c# code:
public string Execute2(string spName, IEnumerable<NpgsqlParameter> parameters)
{
string result;
try
{
using (var conn = new NpgsqlConnection(_connectionString))
{
conn.Open();
List<NpgsqlParameter> _params = parameters.ToList();
using (var cmd = conn.CreateCommand())
{
_params.Add(new NpgsqlParameter("", "")); // Add empty string for refcursor param
cmd.CommandText = BuildQuery(spName, _params);
//cmd.Parameters.Add(new NpgsqlParameter() { ParameterName = "results", Direction = ParameterDirection.InputOutput, Value = "" });
var res = cmd.ExecuteScalar();
result = res?.ToString();
}
//string sql = "select pg_test3('9cc4afef-aab7-4c35-bdcd-a9f3d0152eb4');";
//var cmd2 = new NpgsqlCommand(sql, conn);
//var result2 = cmd2.ExecuteScalar();
//var test = JsonConvert.DeserializeObject<ResultModel>(result);
conn.Close();
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
_log.Exception(e);
throw;
}
return result;
}
debug output: Check from Immediate window System.Text.Encoding.Default.GetString(Buffer)

然后用wireshark抓包请求call sp之后的返回

Failed idea: Compare with SP which has return value(refcursor)
Not what I want!
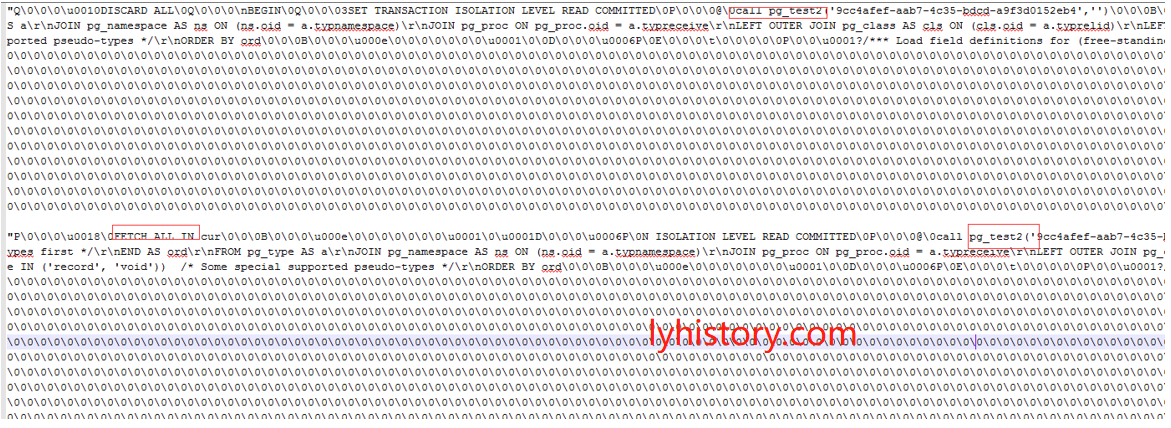
Idea: compare with pgadmin4, because pgadmin4 works!
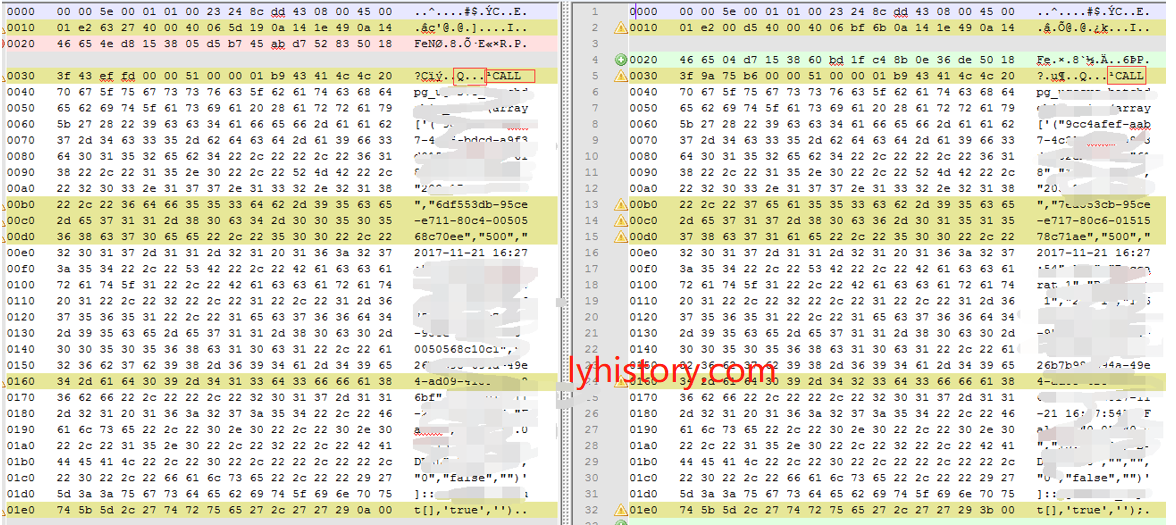
改源码 simple query
 有返回,离成功近了
有返回,离成功近了
但是npg抛错

Idea: Compare with simple function( and procedure) to observer the result

最终

Nuget Update-Package –reinstall https://docs.microsoft.com/en-us/nuget/consume-packages/reinstalling-and-updating-packages
Simple query https://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/static/protocol-flow.html#id-1.10.5.7.4 Message flow https://www.postgresql.org/docs/10/static/protocol-flow.html
Explain https://www.postgresql.org/docs/9.5/static/sql-explain.html
Refer https://www.asciitable.com
6. Monitor
simple way: use postgres exporter
https://github.com/prometheus-community/postgres_exporter#/
nohup sudo -u postgres DATA_SOURCE_NAME="user=postgres host=/var/run/postgresql/ sslmode=disable" ./postgres_exporter &
Troubleshooting
删除“重复”的function或stored procedure,比如:bpchar和varchar:

psql: error: FATAL: Ident authentication failed To configure IDENT authentication, add entries to the /etc/postgresql/12/main/pg_ident.conf file. There are detailed comments in the file to guide you.
?# can’t start postgres
postmaster[22235]: 2024-05-25 14:48:24.000 +08 [22235] FATAL: data directory “/test/data” has invalid permissions postmaster[22235]: 2024-05-25 14:48:24.000 +08 [22235] DETAIL: Permissions should be u=rwx (0700) or u=rwx,g=rx (0750).
todo
CREATE OR REPLACE FUNCTION public.pg_calc_nightsession_funding_rate()
RETURNS integer
LANGUAGE plpgsql
AS $function$
declare
v_condition integer := -100;
v_nightsession_flag boolean := false;
v_from_timestamp integer;
v_to_timestamp integer;
v_total_points_count integer;
v_instrument t_fundingrate.instrument%type := 'BTCP';
v_session t_fundingrate."session"%type := 'T';
v_trade_date t_fundingrate.trade_date%type := to_char(current_date,'yyyymmdd');
v_rate_type t_fundingrate.rate_type%type;
v_funding_rate t_fundingrate.funding_rate%type;
v_benchmark_price t_fundingrate.benchmark_price%type;
result integer;
begin
if CURRENT_TIMESTAMP>=cast(current_date+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp then
v_nightsession_flag := true;
end if;
if v_nightsession_flag then
v_from_timestamp := extract(epoch from cast(current_date+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int;
v_to_timestamp := extract(epoch from now())::int;
else
v_from_timestamp := extract(epoch from cast(current_date-interval '1 day'+interval '19 hour'+interval '1 minute' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int;
v_to_timestamp := extract(epoch from cast(current_date+interval '5 hour' as text)::timestamp AT TIME ZONE 'SGT')::int;
end if;
if extract(dow from current_date)::int = 5 and v_nightsession_flag then
v_trade_date := to_char(current_date+3,'yyyymmdd');
raise info 'Next trading date is %',v_trade_date;
elsif extract(dow from current_date)::int = 6 then
v_trade_date := to_char(current_date+2,'yyyymmdd');
raise info 'Next trading date is %',v_trade_date;
end if;
if not exists (select * from t_impactmid where price_time/1000>=v_from_timestamp and price_time/1000<=v_to_timestamp) then
raise info 'Not exists impactmid data between [%,%]',v_from_timestamp,v_to_timestamp;
v_condition := -200;
elsif not exists (select * from t_bticoin_index where index_time/1000>=v_from_timestamp) then
raise info 'Not exists bticoin_index data >= %',v_from_timestamp;
v_condition := -100;
elsif v_nightsession_flag or not exists (select * from t_bticoin_index where index_time/1000>=v_to_timestamp) then
raise info 'To generate Tentative funding rate';
v_condition := 0;
v_rate_type := 'Tentative';
else
select count(1) into v_total_points_count from t_bticoin_index
where extract(second from to_timestamp(index_time/1000)) = '00'
and index_time/1000<=v_to_timestamp
and index_time/1000>=v_from_timestamp;
if v_total_points_count <= 300 then
raise info 'bticoin_index data is less than 50 percent';
v_condition := -300;
else
raise info 'To generate Confirmed funding rate';
v_condition := 100;
v_rate_type := 'Confirmed';
end if;
end if;
if v_condition >= 0 then
select funding_rate,benchmark_price
into v_funding_rate,v_benchmark_price
from(
select
avg((GREATEST(0::decimal,t2.impact_bid_price-t1.index_value)-GREATEST(0::decimal,t1.index_value-t2.impact_ask_price))/t1.index_value) as funding_rate,
avg(t1.index_value) as benchmark_price
from t_bticoin_index t1
inner join t_impactmid t2 on t1.index_name=t2.instrument and t1.index_time=t2.price_time
where t1.index_time/1000<=v_to_timestamp and t1.index_time/1000>=v_from_timestamp
group by t1.index_name
) t;
if exists (select * from t_fundingrate where instrument=v_instrument and "session"=v_session and trade_date=v_trade_date) then
raise info 'Update exists record instrument=%,session=%,trade_date=%',v_instrument,v_session,v_trade_date;
update t_fundingrate set funding_rate=v_funding_rate,remark=v_rate_type,rate_type=v_rate_type,publish_time=(extract(epoch from now())*1000)::bigint,benchmark_price=v_benchmark_price
where instrument=v_instrument and "session"=v_session and trade_date=v_trade_date;
else
raise info 'Insert new record';
insert into t_fundingrate
(instrument, "session", trade_date, funding_rate, remark, rate_type, publish_time, benchmark_price, currency)
select v_instrument,v_session,v_trade_date, v_funding_rate,
v_rate_type,v_rate_type,(extract(epoch from now())*1000)::bigint,v_benchmark_price,'USD';
end if;
end if;
select v_condition into result;
RETURN result;
END;
$function$
;
refer:
https://www.tutorialspoint.com/postgresql/index.htm https://serverfault.com/questions/110154/whats-the-default-superuser-username-password-for-postgres-after-a-new-install
https://serverfault.com/questions/110154/whats-the-default-superuser-username-password-for-postgres-after-a-new-install
10个使用POSTGRESQL 需要避免的错误 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/DD27oiNL7_qNzgHN6S0XJw