回目录 《GIT》
1.Basic
1.1 Concepts
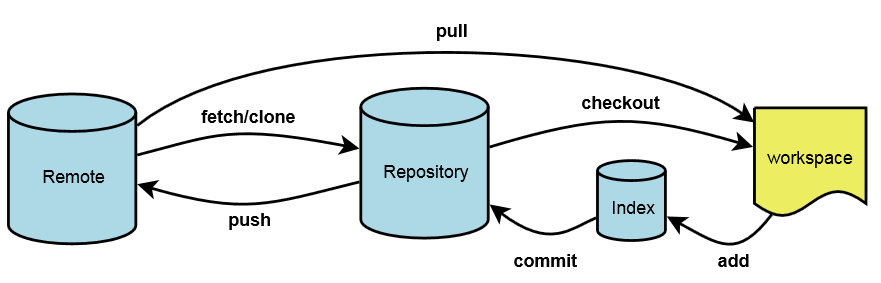 Tracking branch
Non-tracking branch
Understanding Tracking Branches in Git https://lornajane.net/posts/2014/understanding-tracking-branches-in-git
Tracking branch
Non-tracking branch
Understanding Tracking Branches in Git https://lornajane.net/posts/2014/understanding-tracking-branches-in-git
1.2 Config
Authentication
git config --global --list
git config --global user.name "***"
git config --global user.email "***"
//如何更新用户密码:
for linux:
git config --global --unset user.password
for macos:
$ git credential-osxkeychain erase
for windows:
git config --global credential.helper wincred
or
Edit the git entry under Windows Credentials
for ubuntu:
git config credential.helper 'store [options]'
$ git config credential.helper store
$ git push http://example.com/repo.git
Username: <type your username>
Password: <type your password>
[several days later]
$ git push http://example.com/repo.git
[your credentials are used automatically]
username/password VS SSH: 生成ssh后也是要通过命令行上传到repo的目录下: scp ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub YOUR_USER@YOUR_IP:~/.ssh/authorized_keys/id_rsa.pub 或者登录git repo网站,在setting或Preferences找到SSH Keys并将公钥贴到里面, 上述过程中自然是需要验证用户credentials的,所以这就是ssh跟username/password绑定替代的过程
cmdline:
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/8588768/how-do-i-avoid-the-specification-of-the-username-and-password-at-every-git-push
github:https://help.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account
for windows user .ssh is under c:/users/
ls -al ~/.ssh
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"
# start the ssh-agent in the background
$ eval $(ssh-agent -s)
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
~/.ssh/config 可以配置多个不同git站点的ssh key,以及给同一个git站点配置多个account;
注意:
1.非交互式的脚本使用的,在生成ssh key的时候最好不要带passphrase
2.第一次ssh连接需要交互记住figureprints,如果要避免,可以try to sign in to the remote server to accept the fingerprint 主动连一次:
ssh example.com
或者echo -e "Host *\n\tStrictHostKeyChecking no\n\n" >> ~/.ssh/config
或者ssh-keyscan <IP/HOST OF THE GIT SITE> >> ~/.ssh/known_hosts
一个账号配置多个git站点
Step 1: 创建公私钥
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "your-email-address"
cat .ssh/id_rsa_liuyue.pub
Step 2: github/gitlab 配置公钥 Next, log in to your second GitHub account, click on the drop-down next to the profile picture at the top right, select Settings, and click on SSH and GPG keys.
Step 3: Add the SSH Key to the Agent 为了使用这些密钥,我们必须在我们机器上的 ssh-agent 上注册它们
eval `ssh-agent -s`
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa_liuyue
Step 4: 让 ssh-agent 为不同的 SSH 主机使用各自的 SSH 密钥
方法一:创建 SSH 配置文件
touch ~/.ssh/config
vim config
#Default GitHub
Host github.com
HostName github.com
User git
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa
Host github.com-liuyue
HostName github.com
User git
IdentityFile ~/.ssh/id_rsa_liuyue
然后重点这里要用自定义的domain: github.com-liuyue
git remote set-url origin [email protected]:username/repo.git
方法二: ssh-agent 中每次指定一个活跃的 SSH 密钥
ssh-add -l
每次手动清空然后加入相应的ssh key
$ ssh-add -D //removes all ssh entries from the ssh-agent
$ ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa_liuyue // Adds the relevant ssh key
?# Add correct host key in /c/Users/用户名/.ssh/known_hosts to get rid of this message
solve: rm -rf ~/.ssh/known_hosts
Ignore
//首次添加
echo "**/.idea/*" >> .gitignore
git status
git add .gitignore
git commit -m "ignore idea subfolders"
//Add to ignore after Commit and pushed
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/7927230/remove-directory-from-remote-repository-after-adding-them-to-gitignore
git rm -r --cached desktop/res/
git commit -m "remove ignored directory /desktop/res"
git status
git add .
git commit -m "ignore /desktop/res"
git status
git push origin feature/desktop-magiclink
display Chinese character
git config core.quotepath false
1.3 About repo
git remote -v
Change repo url:
git remote set-url origin git://test.com/repo.git
example: move git with full commit history https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/git-move-repository
1.4 About branch
git branch -vv
git branch (-r/-a)
git branch -m old_branch_name new_branch_name
git checkout (-b) master
//make it tracking remote branch
git branch -u origin/branchname
//delete local
git branch -d <branch_name>
//delete remote branch
git push --delete <remote_name> <branch_name>
Pushing to a remote https://help.github.com/articles/pushing-to-a-remote/
tag
Tags are ref's that point to specific points in Git history. Tagging is generally used to capture a point in history that is used for a marked version release (i.e. v1.0.1). A tag is like a branch that doesn’t change.
git tag git tag -a v0.0.1 -m “inital release 0.0.1” git push origin –tags git checkout tags/v1.0.8
清空commits
git checkout --orphan tmp-master # create a temporary branch
git add -A # Add all files and commit them
git commit -m 'Add files'
git branch -D master # Deletes the master branch
git branch -m master # Rename the current branch to master
git push -f origin master # Force push master branch to Git server
1.5 About commit
Clean up / reset / revert
http://sethrobertson.github.io/GitFixUm/fixup.html
Git reflog List commit history
Git reset
git reset --hard <sha-id> git reset --hard origin/master
git reset HEAD^ (unstage)
//un-commit last un-pushed git commit without losing the changes
git reset HEAD~1 --soft https://stackoverflow.com/questions/19859486/how-to-un-commit-last-un-pushed-git-commit-without-losing-the-changes/19859644
Git revert
a.to revert changes made to your working copy : git checkout .
b.to revert changes made to the index which also called as unstage (i.e., that you have added): git reset (e.g. git reset HEAD index.html)
git reset did a great job of unstaging octodog.txt, but you'll notice that he's still there. He's just not staged anymore. It would be great if we could go back to how things were before octodog came around and ruined the party.
c.to revert a change that you have committed: git revert
git clean -f (remove untracked file: new files,generated files)
git clean -f (to remove the untracked changes) and -fd (to also remove untracked directories) http://stackoverflow.com/questions/61212/remove-local-untracked-files-from-my-current-git-branch
Stash
git stash
or
git stash --include-untracked
git stash list
git stash apply/pop
pop和apply有区别:
git stash apply 后仍然在list中,需要 git stash drop掉
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/15286075/difference-between-git-stash-pop-and-git-stash-apply
Cherry pick
git cherry-pick 60b3ccd807343ccce957aceecb36b1da81d34a45 https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/cherry-pick
1.6 Version history and blame
主要工具和命令:
tig / git blame / git log
-p代表path
--follow代表是否跟踪某个文件重命名前后
//所有log
git log --graph --oneline --decorate --all
//对比branch
git log --graph --oneline currentbranch otherbranch
git log --graph --oneline --decorate currentbranch otherbranch `git merge-base currentbranch otherbranch`^!
//Particular File Change History:
git log -p -- src/pages/basic/table/table/SeperateTable.jsx
git log --follow -p -- test/src/main/java/test.java
//Show all of the various changes to a single line in a specified file over the entire git history
git log -L 292,292:src/pages/basic/table/table/SeperateTable.jsx
//recent commit log
git log -n 1 --pretty=format:%H -- test/src/main/java/test.java
First git log -p | grep "Disruptor"
Then git log –S ‘search text’
//Show what revision and author last modified each line of a file
git blame
git show commit-hash
git show REVISION:/path/to/file
git show 15928170ffecd7022301a***:****.java
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/1057564/pretty-git-branch-graphs
git diff master..standardised-meetup-contract-xml
git diff mybranch master -- myfile.cs
1.7 Github personal token
$ git clone https://github.com/username/repo.git
Username: your_username
Password: your_token
2.Advance
2.1 About submodule/subtree/worktree
1) submodule git submodule update –init –recursive https://kalyanchakravarthy.net/blog/git-discard-submodule-changes/ git submodule update –recursive https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=UQvXst5I41I
2) subtree https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t3Qhon7burE
3) worktree
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=h1bifLAnrXA
tig
git worktree add ../TestWT
tig
git worktree list
git worktree remove --force TestWT
2.2 About fork & upstream
When you clone a Forked repository to your local, the forked repository is considered as the remote origin, and the repository you forked from is upstream.
初始化
$ git remote rename origin upstream
C:\Workspace\Repository\test>git remote -v
upstream http://<anotherip>/test.git (fetch)
upstream http://<anotherip>/test.git (push)
$ git remote add origin git@<ip>:/git_home/test.git
$ git remote -v
origin git@<ip>:/git_home/test.git (fetch)
origin git@<ip>:/git_home/test.git (push)
upstream http://<anotherip>/test.git (fetch)
upstream http://<anotherip>/test.git (push)
$ git push origin master
同步upstream到origin / sync forking repo
git checkout master
git pull upstream master
git push origin master
OR
https://docs.github.com/en/free-pro-team@latest/github/collaborating-with-issues-and-pull-requests/syncing-a-fork
git fetch upstream
git checkout master
git merge upstream/main
提交到upstream
正常merge
git push upstream master
强制同步到upstream
https://github.community/t/syncing-a-fork-leaves-me-one-commit-ahead-of-upstream-master/1435
git checkout master
git reset --hard upstream/master
git push --force
normal fork
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=_NrSWLQsDL4
Sync with upstream https://help.github.com/articles/syncing-a-fork/ https://help.github.com/articles/configuring-a-remote-for-a-fork/
git remote add upstream https://github.com/AlphaWallet/alpha-wallet-android.git git fetch upstream git checkout master git merge upstream/master git push git checkout feature/desktop-magiclink git merge master git push
fork from other source
https://gist.github.com/DavideMontersino/810ebaa170a2aa2d2cad https://stackoverflow.com/questions/6286571/are-git-forks-actually-git-clones Example:
git clone https://github.com/lyhistory/xmlsectool.git
cd xmlsectool/
git remote rename origin upstream
git remote add origin git://git.shibboleth.net/xmlsectool
git remote -v
git pull origin master
git push upstream master
git add .
git status
git commit -m "add support for rfc4050"
git push upstream master

auto sync from upstream/origin
https://stackoverflow.com/questions/23793062/can-forks-be-synced-automatically-in-github
pull request
https://docs.github.com/en/pull-requests/collaborating-with-pull-requests/proposing-changes-to-your-work-with-pull-requests/creating-a-pull-request-from-a-fork
2.3 About workflow - wrap up all the previous knowledge
shelve changes / git stack https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Zb8k8q8n8Ao
3) git merge and git rebase https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/merging-vs-rebasing
Git merge
Git pull origin master
git merge --abort
git checkout --theirs -- Lib/test.dll
git rebase
branch master & develop
commit changes in develop branch ( don't push!)
switch to master and git pull
switch to develop git rebase master
if got conflict follow instruction, manually resolve it and git add to mark it as resolved and then git rebase –continue now is good to do merge
Basic Branching and Merging https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Branching-Basic-Branching-and-Merging GIT: FETCH AND MERGE, DON’T PULL http://longair.net/blog/2009/04/16/git-fetch-and-merge/
create merge request / pull request How to Git PR From The Command Line https://hackernoon.com/how-to-git-pr-from-the-command-line-a5b204a57ab1
? not-by-me changes/files never touched by me, merge的时候出现很多并非自己做的更改待commit https://stackoverflow.com/questions/9189867/after-a-git-merge-conflict-a-lot-of-files-i-didnt-touch-become-changes-to-be-c 属于正常现象: 解释
git checkout qa
git pull
git checkout feature
git merge qa
git status 此时可能出现一堆待committed的变动,并非本人更改,其实是正常的,因为远程的feature上面并没有qa最新的改动,如果这里不带上其他人的改动,
那么在远程上创建从feature到qa的merge request就会出现很多不一致
3.Best Practice
The seven rules of a great git commit message: https://chris.beams.io/posts/git-commit/
使用ssh!
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"
eval $(ssh-agent -s)
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
更改passphrase密码
ssh-keygen -p -f /path/to/ssh_key
clip < ~/.ssh/id_rsa.pub
# Copies the contents of the id_rsa.pub file to your clipboard
加入到github
https://docs.github.com/en/github/authenticating-to-github/adding-a-new-ssh-key-to-your-github-account
加入到gitlab
https://gitlab.com/help/ssh/README#rsa-ssh-keys
Make Your Life Easier With These Git Workflows:
https://hackernoon.com/make-your-life-easier-with-these-git-workflows-part-i-mb243ztb
!$ replaced with last used argument
git commit --amend append changes to the previous commit
git reset HEAD~1 undo the latest commit
--soft keep workspace changes
--hard discard workspace changes
--force overwrite existing code in repository
4. Git server
A bare Git repository is typically used as a Remote Repository that is sharing a repository among several different people. You don’t do work right inside the remote repository so there’s no Working Tree (the files in your project that you edit), just bare repository data. And that’s it.
https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-on-the-Server-Setting-Up-the-Server
从头创建空仓并提交
$mkdir test.git
$cd test.git/
$git init --bare
Initialized empty Git repository in /git_home/test.git/
本地:全新提交
# on John's computer
$ cd myproject
$ git init
$ git add .
$ git commit -m 'Initial commit'
$ git remote add origin git@gitserver:/git_home/test.git/
$ git push origin master
本地:已有git转成空仓发布
假定带工作目录的git仓库已创建,并位于/git_home/src 目录下。
https://blog.csdn.net/chenzhengfeng/article/details/81743626
cd /git_home/test
git clone --bare /git_home/src
touch sw/git-daemon-export-ok
例子:windows本地用git创建备份
在移动硬盘上创建远程repo
$ git init --bare test.git
Initialized empty Git repository in H:/Backup/test.git
在本机上拉取
git clone H:/Backup/test.git
然后将本机需要备份的内容扔进去提交即可
5.Troubleshooting
?#1.If you are running git under a file system that is not case sensitive (Windows or OS X) this will occur if there are two branches with the same name but different capitalisation, e.g. user_model_changes and User_model_changes as both of the remote branches will match the same tracking ref. Delete the wrong remote branch (you shouldn’t have branches that differ only by case) and then git remote prune origin and everything should work
?#2.The remote end hung up unexpectedly while git cloning With this kind of error, I usually start by raising the postBuffer size by: git config –global http.postBuffer 524288000 (some comments below report having to double the value): git config –global http.postBuffer 1048576000 http://stackoverflow.com/questions/6842687/the-remote-end-hung-up-unexpectedly-while-git-cloning
?#3.error: Your local changes to the following files would be overwritten by merge: ** Please, commit your changes or stash them before you can merge.
a.give up all local changes, and force update with latest source from remote
git fetch –all git reset –hard origin/master
b.only discard specific files which have conflicts
git checkout folderName/fileName.ext (ext: git checkout
–
Apendix:«Merging and Branching Strategy»


1. introduce git flow
Because most of us have to deal with GIT every day, it’s necessary to level up a little bit in order to collaborate with each other more efficiently.
git enables people working from a remote place, streamlining the development process, maintain all the code changes history, it keeps all the states of the application at each time point of commits, so it’s easier for us to find bugs and blame the people who made the changes.
Let’s first look at git flow, so we can have a basic idea of how git may help our application development.
This one is a relatively general git flow.
Git flow is a well-known method to manage git branches.
the development will happen in feature branches, here we have features for future release and feature for next release, when programmer starts to develop a module or a feature, he will create a new feature branch initialled from develop branch, once done the development, feature branch owner will do the merge to develop, after develop branch has some features or reach a milestone, it will be merged to release branch, and QA will do the testing, if any issue is found, it will be fixed in release and merge back to develop, and once the release branch is fully tested, someone will create a pull request for merging to master, after reviewer or project leader reviewed the code changes, he may approve the request and do the merge, ideally master branch should be ready for product deployment at any point of time, but if any defects detected or urgent changes required, we will do it in hotfix branch, once done, it will be merged to master branch and merge back to develop branch as well.
2. common scenario - git merge & git rebase
Consider what happens when you start working on a new feature in a dedicated branch, then another team member updates the develop branch with new commits. This results in a forked history.
Assume now you have done the development work on feature, you want to merge it to develop branch: how many options you have: cherry-pick or merge or rebasing+merge
because cherry-pick is not a structured way to do the merge, so I'm not going to discuss it.
this is what happens behind the scene when you git merge in command line or use GUI tool.
it will merge between C3&C4 and their most recent common ancestor C2 and create a new commit C5
rebase works by going to the common ancestor of the two branches C2, getting the diff introduced by each commit of feature C4 , saving those diffs to temporary files, resetting feature branch to the same commit as develop (the branch you are rebasing onto), and finally applying each change in turn C4 prime.Now you switch to develop branch, and do git merge, it will do a fast-forward merge.
but what will happen if someone updated develop branch in between, I mean between you have done rebase and start to do merge on develop.
if your purpose is to keep a linear clean commit history on an active branch, rebase can help you .
3. when to use rebase
Bad practice
rebase develop onto your feature.
The problem is that this only happened in your repository. All of the other developers are still working with the original develop. Since rebasing results in brand new commits, Git will think that your develop branch’s history has diverged from everybody else’s.
Golden rule - never use it on public branch(Is anyone looking at this branch?)
Good practice (go to previous slide)
Now, let’s say that the new commits in develop are relevant to the feature that you’re working on.
One typical situation,
when someone has done a hot-fix for master,
by right, this hot-fix will be merged back to develop branch,
and you cannot continue with your development without this hot-fix in your feature branch,
then you may consider using rebase to get latest from develop
To incorporate the new commits into your feature branch,.
most of the time you may work solely on one feature branch, but if more than one developer working on same feature branch
you want to keep updated with latest changes or you want to keep a clean graph/commit history
conclusion:
conflict is inevitable, by adopting appropriate merging strategy, we can mitigate the risk of getting too many conflicts.
another suggestion is always examine your current status, which branch you are in,is there any other people working on this branch, and are you behind remote branches or ahead of remote branches with how many commits
hopefully you may have a better understanding of the merging strategy and understand what happens behind the scene.
https://git-scm.com/book/en/v2/Git-Branching-Rebasing
1. rebase is in local
all changes apply onto parent's latest changes
then can do the merge
question: 1.how abt someone push new changes to parent branch
2.before rebase you pushed to remote, cannot do the fast-forward merge
2. merge in remote - pull request
latest changes and common ancestor changes
A forked commit history
active 'parent' branch
https://www.atlassian.com/git/tutorials/merging-vs-rebasing/conceptual-overview
git rebase is good for local cleanup,
local cleanup? team policy?
https://www.atlassian.com/git/articles/git-team-workflows-merge-or-rebase/
don't commit so frequently, like writing 1 line code then commit, other people who commit later will suffer
https://steemit.com/bitcoin/@sblue/what-is-git-github-the-3-minute-journey-through-bitcoins-github-history
http://csci221.artifice.cc/lecture/collaboration-with-git.html
http://flsilva.com/blog/git-branching-and-merging/
https://longair.net/blog/2009/04/16/git-fetch-and-merge/
# what’s Git
GIT stores the state of your application at points in time known as commits. It does this in a clever way that means you don't have to store the whole state of your application, it just records a series of changes.
In GIT you have a master branch which (usually) stores the working, production state of your application. You can also create other branches for working on specific things such as features or bug fixes. This allows you and other developers to continue development without affecting the master branch.
Once testing is complete, you can merge these branches into your master/production branch. If you are developing a website using GIT, you might have the repository stored on a server somewhere. You can set up a hook in GIT that pushes your master commits to this repository, but no others.
One advantage this has over FTP is that GIT will just push the changes and not the files themselves, making uploading new versions a lot quicker.
GIT, however, has a few other fantastic features. Finding the source of bugs in GIT is extremely easy. It has built in tools for finding where a piece of code stopped working.
# Git vs SVN
Git is not better than Subversion. But is also not worse. It's different.
The key difference is that it is decentralized. Imagine you are a developer on the road, you develop on your laptop and you want to have source control so that you can go back 3 hours.
With Subversion, you have a Problem: The SVN Repository may be in a location you can't reach (in your company, and you don't have internet at the moment), you cannot commit. If you want to make a copy of your code, you have to literally copy/paste it.
With Git, you do not have this problem. Your local copy is a repository, and you can commit to it and get all benefits of source control. When you regain connectivity to the main repository, you can commit against it.
# bitcoin team
Team
The Bitcoin Core project has a large open source developer community with many casual contributors to the codebase. There are many more who contribute research, peer review, testing, documentation, and translation.
Maintainers
Project maintainers have commit access and are responsible for merging patches from contributors. They perform a janitorial role merging patches that the team agrees should be merged. They also act as a final check to ensure that patches are safe and in line with the project goals. The maintainers’ role is by agreement of project contributors.
Contributors
Everyone is free to propose code changes and to test, review and comment on open Pull Requests. Anyone who contributes code, review, test, translation or documentation to the Bitcoin Core project is considered a contributor. The release notes for each Bitcoin Core software release contain a credits section to recognize all those who have contributed to the project over the previous release cycle. A list of code contributors for the last year can be found on Github.
Ref:
Cheatsheet
https://illustrated-git.readthedocs.io/en/latest/
Take your Git practice to the next level
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=eZRJyduqGuQ
git仓库与项目源码分离
https://blog.csdn.net/sinat_34349564/article/details/52442526