回目录 《公钥基础设施Public key infrastructure》
# Clarification
注意本篇主要是在应用实现层面描述PKI,密码学层面参考 Cryptograhy Fundamental,下面总结一下密码学层面的知识点: private reference- cryptography:
https://www.youtube.com/playlist?list=PLoJC20gNfC2gAB-eg7oaUTheB_JgQY4-q http://crypto-textbook.com/
PKI infrastructure:
- Ensuring the contents of the document are encrypted such that the document is kept confidential.
- Ensuring the document is not altered during transmission.
- Since Alice does not know Bob, he has to somehow prove that the document is indeed sent by him.
- Ensuring Alice receives the document and that she cannot deny receiving it in future. PKI supports all the above four requirements with methods such as secure messaging, message digests, digital signatures, and non-repudiation services.
Keys
Authentication
provides some degree of certainty that a given message has come from a legitimate source. Digital signature with private key
Integrity/Tamper detection
merely shows evidence that a message may have been altered. Over Distance: when communicate, hash function Over time: merkle tree Centralize integrity Decentralize integrity
Non-repudiation
is a concept, or a way, to ensure that the sender or receiver of a message cannot deny either sending or receiving such a message in future. One of the important audit checks for non-repudiation is a time stamp. The time stamp is an audit trail that provides information of the time the message is sent by the sender and the time the message is received by the receiver.
Public key cryptography
Public key cryptography (negotiating exchange symmetric master secret key) Rsa dsa ecdsa ecc Symmetric (Exchange message) Des … Hash function (Integrity) Md5 hmac
下面开始从软件应用层面总结:
# 1.Overview
# 1.1 Secure messaging
To ensure that the document is protected from eavesdropping and not altered during the transmission, Bob will first encrypt the document using Alice’s public key. This ensures two things: one, that the document is encrypted, and two, only Alice can open it as the document requires the private key of Alice to open it. To summarize, encryption is accomplished using the public key of the receiver and the receiver decrypts with his or her private key. In this method, Bob could ensure that the document is encrypted and only the intended receiver (Alice) can open it. However, Bob cannot ensure whether the contents are altered (Integrity) during transmission by document encryption alone.
# 1.2 Message digest
In order to ensure that the document is not altered during transmission, Bob performs a hash function on the document. The hash value is a computational value based on the contents of the document. This hash value is known as the message digest. By performing the same hash function on the decrypted document the message, the digest can be obtained by Alice and she can compare it with the one sent by Bob to ensure that the contents are not altered. This process will ensure the integrity requirement.
# 1.3 Digital signature
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_signature In order to prove that the document is sent by Bob to Alice, Bob needs to use a digital signature. Using a digital signature means applying the sender’s private key to the message, or document, or to the message digest. This process is known as as signing. Only by using the sender’s public key can the message be decrypted.
Bob will encrypt the message digest with his private key to create a digital signature. In the scenario illustrated in the image above, Bob will encrypt the document using Alice’s public key and sign it using his digital signature. This ensures that Alice can verify that the document is sent by Bob, by verifying the digital signature (Bob’s private key) using Bob’s public key. Remember a private key and the corresponding public key are linked, albeit mathematically. Alice can also verify that the document is not altered by validating the message digest, and also can open the encrypted document using her private key. Message authentication is an authenticity verification procedure that facilitates the verification of the integrity of the message as well as the authenticity of the source from which the message is received.
# 1.4 Digital certificate
By digitally signing the document, Bob has assured that the document is sent by him to Alice. However, he has not yet proved that he is Bob. To prove this, Bob needs to use a digital certificate. A digital certificate is an electronic identity issued to a person, system, or an organization by a competent authority after verifying the credentials of the entity. A digital certificate is a public key that is unique for each entity. A certification authority issues digital certificates. In PKI, digital certificates are used for authenticity verification of an entity. An entity can be an individual, system, or an organization. An organization that is involved in issuing, distributing, and revoking digital certificates is known as a Certification Authority (CA). A CA acts as a notary by verifying an entity’s identity. One of the important PKI standards pertaining to digital certificates is X.509. It is a standard published by the International Telecommunication Union (ITU) that specifies the standard format for digital certificates. PKI also provides key exchange functionality that facilitates the secure exchange of public keys such that the authenticity of the parties can be verified.
# 2.Methods
# 2.1 Certificate authority or Self-signed with X.509
如果有域名建议用 CA的证书,可以用Let's Encrypt获取,或者可以使用第三方DNS解析自带的,比如cloudflare的证书;
如果没有域名比如本地测试环境那只能用自签名证书;
ca 证书链 chain of trust
PGP VS X.509 http://world.std.com/~cme/html/web.html
# 2.2 WOT
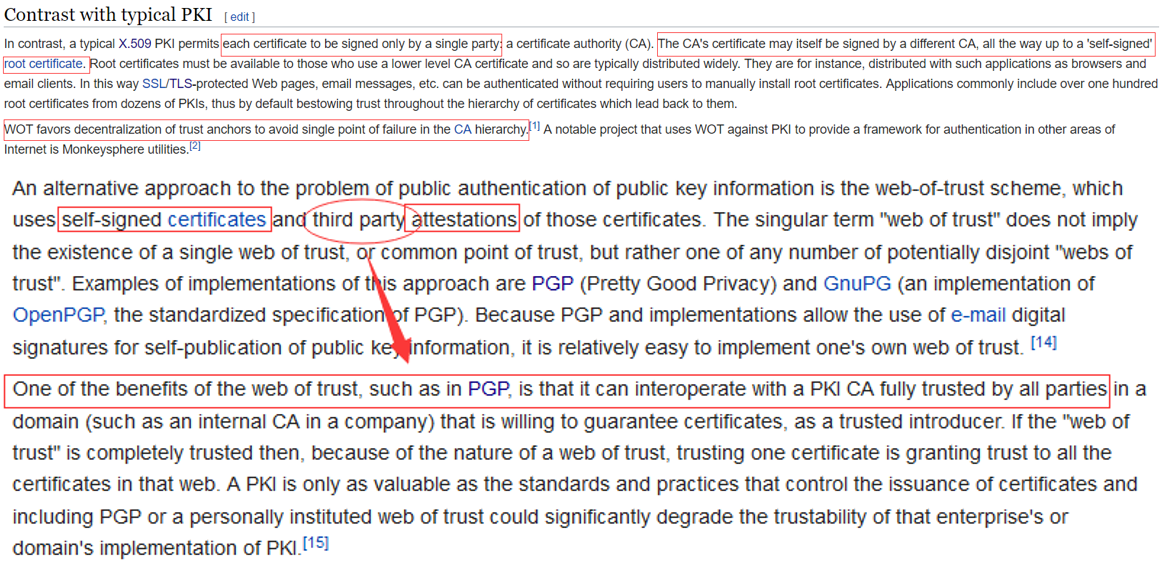
# 2.3 PGP
How PGP works ? and how to make it Pretty Great Privacy OpenPGP Message Format: https://tools.ietf.org/html/rfc4880
How PGP works https://users.ece.cmu.edu/~adrian/630-f04/PGP-intro.html Explanation of the web of trust of PGP https://www.rubin.ch/pgp/weboftrust.en.html
Both when encrypting messages and when verifying signatures, it is critical that the public key used to send messages to someone or some entity actually does 'belong' to the intended recipient. Simply downloading a public key from somewhere is not a reliable assurance of that association; deliberate (or accidental) impersonation is possible. From its first version, PGP has always included provisions for distributing user's public keys in an 'identity certification ', which is also constructed cryptographically so that any tampering (or accidental garble) is readily detectable. However, merely making a certificate which is impossible to modify without being detected is insufficient; this can prevent corruption only after the certificate has been created, not before. Users must also ensure by some means that the public key in a certificate actually does belong to the person or entity claiming it. From its first release, PGP products have included an internal certificate 'vetting scheme' to assist with this, a trust model which has been called a web of trust. A given public key (or more specifically, information binding a user name to a key) may be digitally signed by a third party user to attest to the association between someone (actually a user name) and the key. There are several levels of confidence which can be included in such signatures. Although many programs read and write this information, few (if any) include this level of certification when calculating whether to trust a key.
From Pretty Good To Great Enhancing PGP using Bitcoin and the Blockchain https://arxiv.org/abs/1508.04868 Bitcoin pgp?? https://bitcointalk.org/index.php?topic=186264.msg1929410#msg1929410 https://www.quora.com/What-are-the-main-benefits-of-using-blockchain-techs-Vs-PGP
# 2.4 Blockchain-based PKI
# 3.Fundametal
# 3.1 SSL/TLS
SSL is deprecated predecessor of TLS, latest version is TLS1.3 https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Transport_Layer_Security#Protocol_details Encryption is through the following Algorithm and Protocol Identification is guaranteed by CA

# 3.1.1 Implementation
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Comparison_of_TLS_implementations
openssl:
is a software library for applications that secure communications over computer networks against eavesdropping or need to identify the party at the other end. It is widely used by Internet servers, including the majority of HTTPS websites.
经常被用来配置https
Bouncy Castle (cryptography):
is a collection of APIs used in cryptography. It includes APIs for both the Java and the C# programming languages
参考我写的一个密码学小工具:《blockchain_cryptography.md》
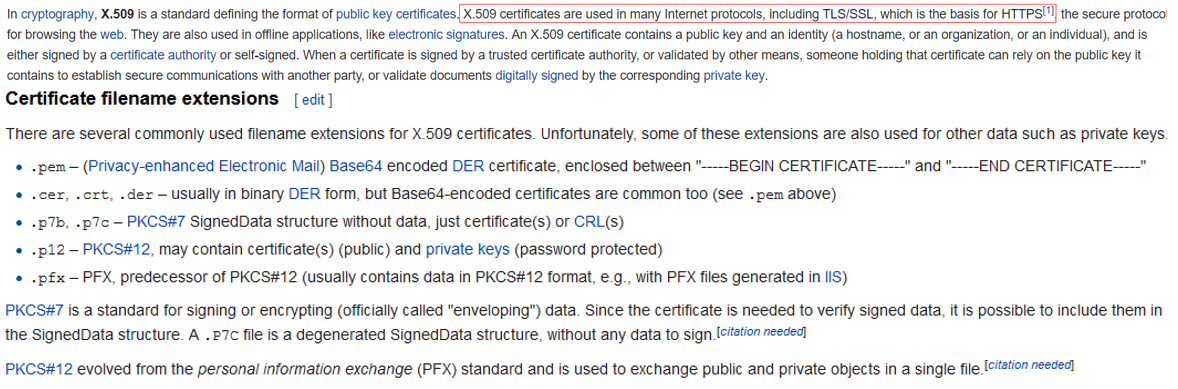
# 3.1.2 Certifications - X.509 cert - always related to CA party
a standard defining the format of public key certificates https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/X.509
# 3.1.3 Algorithm for TLS whole flow
Step 1:Key exchange or key agreement algorithm
Purpose: to negotiate and generate master secret key https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5551094/
RSA
Diffie hellman Perfect Forward Secrecy https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=IkM3R-KDu44
ECC
服务端配置例子:
-- redhat服务器配置:
https://access.redhat.com/documentation/en-us/red_hat_enterprise_linux/7/html/security_guide/sec-hardening_tls_configuration
#openssl ciphers -v
#openssl ciphers -v 'HIGH'
Cipher Suites are named combinations of:
Key Exchange Algorithms (RSA, DH, ECDH, DHE, ECDHE, PSK)
Authentication/Digital Signature Algorithm (RSA, ECDSA, DSA)
Bulk Encryption Algorithms (AES, CHACHA20, Camellia, ARIA)
Message Authentication Code Algorithms (SHA-256, POLY1305)
Type of Encryption TLS v1.3, v1.2, v1.1, v1.0 or SSL v3, v2
Here is an example of a TLS v1.2 cipher suite from Openssl command 'openssl ciphers -v' output:
ECDHE-RSA-AES256-GCM-SHA384 TLSv1.2 Kx=ECDH Au=RSA Enc=AESGCM(256) Mac=AEAD
Key Exchange: ECDHE
Signature: RSA
Bulk Encryption: AES256-GCM
Message Authentication: SHA384
-- apache httpd服务端配置:
/etc/httpd/conf.d/ssl.conf
# SSL Engine Switch:
# Enable/Disable SSL for this virtual host.
SSLEngine on
# SSL Protocol support:
# List the enable protocol levels with which clients will be able to
# connect. Disable SSLv2 access by default:
SSLProtocol all -SSLv2 -SSLv3
# SSL Cipher Suite:
# List the ciphers that the client is permitted to negotiate.
# See the mod_ssl documentation for a complete list.
SSLCipherSuite HIGH:3DES:!aNULL:!MD5:!SEED:!IDEA
注意有些SSLCipherSuite存在风险,需要配置好
Step 2-Part 1: Cipher to exchange message with master secret key
Step 2-Part 2: Data integrity

解释:
1.秘钥交换一般都是用DH(什么情况用RSA ECC?)
2.第二步的通信过程一般都是采用对称加密,因为比非对称快
3.为什么有了第一步的DH和第二步的对称加密,很多情况还需要设置RSA,比如nginx需要设置ssl_certificate(RSA公钥和认证信息)和ssl_certificate_key(RSA私钥),因为第一步的key exchange过程,客户端也需要验证服务端的身份,所以服务端需要用私钥加密,然后客户端通过服务端的证书包含的公钥进行验证,防止通话对象是黑客而不是真正的服务器。
4.为什么第一步不干脆用RSA呢
简单讲,就是为了预防将来如果服务器私钥泄露,那么之前的对话如果没记录了,所有客户端跟服务端的对话将被解密,影响比较大,所以不应该使用私钥直接跟所有客户端对话,而应该进一步提升安全性(有点类似密码加盐的策略)
The downside of this handshake is that the messages secured by it are only as safe as the private key. Suppose a third party has recorded the handshake and the subsequent communication. If that party gets access to the private key in the future, they will be able to decrypt the pre-main secret and derive the session key. With that they can decrypt the entire message. This is true even if the certificate is expired or revoked. This leads us to another form of handshake that can provide confidentiality even if the private key is compromised.
https://blog.cloudflare.com/keyless-ssl-the-nitty-gritty-technical-details/
5.为什么需要pre-master secret key,pre-master VS master key
The client generates a random number, called a Pre-Master Secret key. Upon receiving a Certificate message, it checks authentication of the server's certificate and extracts its public key. The Pre-Master Secret key is encrypted by the server's public key and sent via the ClientKeyExchange message to the server.
The point of the pre-master key is to have a uniform format for the master key (e.g. this helps sharing session parameters between multiple front-ends). SSL is generic: it supports several kinds of key exchange algorithms, in particular RSA asymmetric encryption, and various Diffie-Hellman (opens new window) variants. All these methods do not yield "shared secret" of the same size and format. Notably, with DH, you get a group element, in whatever group you are working, which can be an elliptic curve or something else; the shared secret is, as a binary string, somewhat biased, and is not chosen by the client.
Defining that the key exchange mechanism yields a pre-master secret (with characteristics derived from the actual key exchange mechanism), to be hashed into a master secret, thus allows for a better modularity.
https://security.stackexchange.com/questions/54399/whats-the-point-of-the-pre-master-key
https://crypto.stackexchange.com/questions/27131/differences-between-the-terms-pre-master-secret-master-secret-private-key
简单来说就是为了统一master key的格式,比如pre-master key可能是通过DH或者其他的方式交互产生的(比如服务端发给客户端8即23,客户端选一个比如4及22,然后将4发给服务端,然后客户端和服务端都各自可以算出 (22)3=26=64,作为pre master key),然后至于master key何时生成:
3.The client generates a random number, called a Pre-Master Secret key. Upon receiving a Certificate message, it checks authentication of the server’s certificate and extracts its public key. The Pre-Master Secret key is encrypted by the server’s public key and sent via the ClientKeyExchange message to the server. Meanwhile, the Key Derivation Function (opens new window) (KDF) generates a master key derived from the Pre-Secret Master key.
4.On the server side, the ClientKeyExchange message is decrypted by the server’s private key, resulting in the Pre-Master Secret key. Using the same KDF as the client, the master key is derived from the Pre-Master Secret key.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/topics/computer-science/master-secret-key
6.master key vs session key?
The client and server then use the master secret to calculate several session keys for use in that session only – 4 session keys, to be precise.
The 4 kinds of session keys created in each TLS handshake are:
- The "client write key"
- The "server write key"
- The "client write MAC key"
- The "server write MAC key"
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/ssl/what-is-a-session-key/
7.TLS handshakes occur after a TCP connection has been opened via a TCP handshake.
# 3.1.4 Protocol - Handshake
Tcp handshake => TLS/SSL Handshake
The TLS handshake happens after the TCP handshake. For the TCP or for the transport layer, everything in the TLS handshake is just application data. Once the TCP handshake is completed the TLS layer will initiate the TLS handshake.
https://medium.facilelogin.com/nuts-and-bolts-of-transport-layer-security-tls-2c5af298c4be
A walk-through of a TCP handshake http://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art058 The TLS Handshake at a High Level http://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art057 A walk-through of an SSL handshake http://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art059 SSL Certificate Exchange https://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art061
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=iQsKdtjwtYI

# 3.2 Manager tools
管理:private key public key certificate
比如我们可以使用openssl工具手动生成自签名的证书,也可以通过ca购买证书(也要先通过openssl工具生成csr);
一个web应用如果需要提供以https的方式访问的服务的话,我们需要一个数字证书,这个证书的配置是在nginx或apache的配置文件或者其他web容器的配置文件中进行配置的。当然这个可以保存在keystore中。
例子:nginx https配置 参考《buildingblock/nginx.md》
private key:
- ASN.1 syntax for that DER-encoded string https://crypto.stackexchange.com/questions/21102/what-is-the-ssl-private-key-file-format
- ppk PPK files are PuTTY Private Key Files developed by Putty
# 3.2.1 交互工具:Openssl keytool
openssl是常用的一个开源安全通信library,这里指其开源的toolkit
keytool是JDK里面内置的一个数字证书生产工具
证书类型:
.PEM:
(originally “Privacy Enhanced Mail”) is the most common format for X.509 certificates, CSRs(Cerificate Signing Request), and cryptographic keys. A PEM file is a text file containing one or more items in Base64 ASCII encoding, each with plain-text headers and footers (e.g. -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE----- and -----END CERTIFICATE-----). A single PEM file could contain an end-entity certificate, a private key, or multiple certificates forming a complete chain of trust.
are usually seen with the extensions .crt, .pem, .cer, and .key (for private keys), but you may also see them with different extensions
.DER:
(Distinguished Encoding Rules) is a binary encoding for X.509 certificates and private keys. Unlike PEM, DER-encoded files do not contain plain text statements such as -----BEGIN CERTIFICATE-----. DER files are most commonly seen in Java contexts.
DER-encoded files are usually found with the extensions .der and .cer
PKCS
PKCS#7 (also known as P7B)
is a container format for digital certificates that is most often found in Windows and Java server contexts, and usually has the extension .p7b. PKCS#7 files are not used to store private keys.
PKCS#12 (also known as PKCS12 or PFX)
is a common binary format for storing a certificate chain and private key in a single, encryptable file, and usually have the filename extensions .p12 or .pfx.
#View contents of PEM certificate file
openssl x509 -in CERTIFICATE.pem -text -noout
#Convert PEM certificate to DER
openssl x509 -outform der -in CERTIFICATE.pem -out CERTIFICATE.der
#Convert PEM certificate with chain of trust to PKCS#7
openssl crl2pkcs7 -nocrl -certfile CERTIFICATE.pem -certfile MORE.pem -out CERTIFICATE.p7b
#Convert PEM certificate with chain of trust and private key to PKCS#12
openssl pkcs12 -export -out CERTIFICATE.pfx -inkey PRIVATEKEY.key -in CERTIFICATE.crt -certfile MORE.crt
#View contents of DER-encoded certificate file
openssl x509 -inform der -in CERTIFICATE.der -text -noout
#Convert DER-encoded certificate to PEM
openssl x509 -inform der -in CERTIFICATE.der -out CERTIFICATE.pem
#Convert DER-encoded certificate with chain of trust and private key to PKCS#12
https://www.ssl.com/how-to/create-a-pfx-p12-certificate-file-using-openssl/
# 3.2.2 存储:Truststore & Keystore
keystore可以看成一个放key的库,key就是公钥,私钥,数字签名等组成的一个信息。
truststore是放信任的证书的一个store truststore和keystore的性质是一样的,都是存放key的一个仓库,区别在于,truststore里存放的是只包含公钥的数字证书,代表了可以信任的证书,而keystore是包含私钥的。
- Truststore
(as name suggest) is used to store certificates from trusted Certificate authorities(CA) which are used to verify certificate presented by Server in SSL Connection
- Keystore
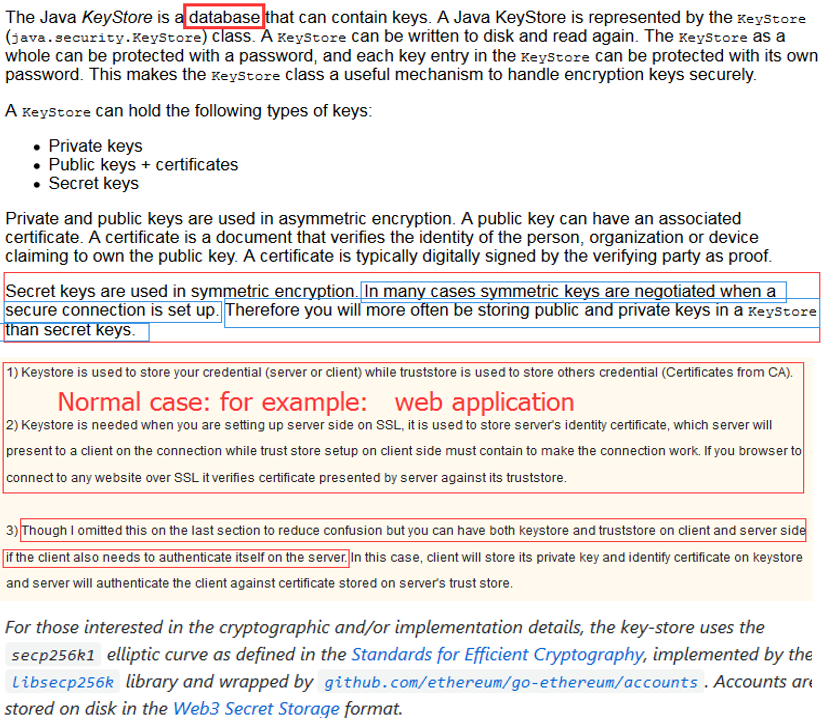
while keyStore is used to store private key and own identity certificate which program should present to other parties (Server or client) to verify its identity
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Keystore Import a private key into a Java Key Store http://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art049 Import an encrypted private key into a Java KeyStore https://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art050 A Utility for Viewing Java Keystore Contents http://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art045
KEYSTORE vs private key vs certificate
Difference between trustStore vs keyStore in Java SSLRead more: http://www.java67.com/2012/12/difference-between-truststore-vs.html#ixzz5UBSznugK www.java67.com/2012/12/difference-between-truststore-vs.html
Manage keys, certificates and keystores https://www.ibm.com/support/knowledgecenter/en/SSCQGF_7.2.0/com.ibm.IBMDI.doc_7.2/adminguide63.htm#ktrustmgmt
https://github.com/ethereum/go-ethereum/wiki/Mobile:-Account-management
# 3.2.3 Example:
How to retrieve certificate from remote server and import to truststore
Method 1:
keytool -printcert -sslserver host[:port] -rfc >tempfile
keytool -import [-noprompt] -alias nm -keystore file [-storepass pw] [-storetype ty] <tempfile
Method 2:
Step 1 Option 1:
>openssl
OpenSSL> version
OpenSSL 0.9.8k 25 Mar 2009
>where openssl
C:\strawberry\c\bin\openssl.exe
openssl s_client -showcerts -connect <hostname>:<tls_port>
Step 1 Option 2:
Firefox: Add Exception -> Get Certificat -> View -> Details -> Export...
Step 2:
keytool -importcert -file <certificate_location> -keystore <keystore_name> -alias "<alias_name>"
# 4. Use case
Encryption and decryption, digital signature, and key exchange are the three primary functions of a PKI.
# 4.1 Authenticate / Digital Signature
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Digital_signature schnorr signature
Example: Securely install software with gnupg https://www.linuxbabe.com/security/verify-pgp-signature-software-downloads-linux https://medium.com/@lukedashjr/how-to-securely-install-bitcoin-9bfeca7d3b2a
JSON Web Token (JWT) Signing https://auth0.com/blog/json-web-token-signing-algorithms-overview/ https://stackoverflow.com/questions/38588319/understanding-rsa-signing-for-jwt
# 4.2(1) SSL/ TLS / HTTPS
read more TLS in redis https://docs.redis.com/latest/rc/security/database-security/tls-ssl/ TLS in https => /software/network/http_ssl_tls_setup.md
SSL stands for Secure Sockets Layer and, in short, it's the standard technology for keeping an internet connection secure and safeguarding any sensitive data that is being sent between two systems, preventing criminals from reading and modifying any information transferred, including potential personal details.
TLS (Transport Layer Security) is just an updated, more secure, version of SSL. We still refer to our security certificates as SSL because it is a more commonly used term, but when you are buying SSL from DigiCert you are actually buying the most up to date TLS certificates with the option of ECC, RSA or DSA encryption.
HTTPS就是TLS over HTTP
SSL和SSH是不同的protocol,原理类似,SSH is generally a tool for technicians, and SSL/TLS is a mechanism for securing websites that is transparent to the user.
SSL Certificate Installation Instructions&Tutorials https://www.digicert.com/ssl-certificate-installation.htm How about move from installed server to a new server? SSL Certificate Export/Import Explained https://www.digicert.com/import-export-ssl-certificate.htm
With .NET IIS Using Microsoft IIS to generate CSR and Private Key(export from mmc,later when complete importing certificate, it also managed by mmc) https://docs.druva.com/Knowledge_Base/inSync/How_To/Using_Microsoft_IIS_to_generate_CSR_and_Private_Key Use pfx file when you export the cert&privatekey to another server https://www.digicert.com/ssl-support/pfx-import-export-iis-7.htm
With Java Keytool https client and https server Usually for web application, we generate private key stored in keystore, import to web server host, and get it signed by CA, get a cert file stored in truststore which contains public key and ca’s signature Use Keytool https://www.javacodegeeks.com/2013/06/java-security-tutorial-step-by-step-guide-to-create-ssl-connection-and-certificates.html Use Pure Java code(keytool shipped with jdk) Generate keystore and truststore https://www.pixelstech.net/article/1409966488-Different-types-of-keystore-in-Java----JKS Https client and https server demo https://www.pixelstech.net/article/1445603357-A-HTTPS-client-and-HTTPS-server-demo-in-Java
Self signed CA with openssl Play all parties: prvatekey-publickey pair => create csr with publickey => create ca => ca sign csr How to setup your own CA with OpenSSL https://gist.github.com/Soarez/9688998 On windows for iis https://medium.com/the-new-control-plane/generating-self-signed-certificates-on-windows-7812a600c2d8 https://medium.com/@tbusser/creating-a-browser-trusted-self-signed-ssl-certificate-2709ce43fd15 https://www.sslshopper.com/article-how-to-create-a-self-signed-certificate-in-iis-7.html
# 4.2(2) DNS over TLS and DNS over HTTPS different
Each standard was developed separately and has its own RFC* documentation, but the most important difference between DoT and DoH is what port they use. DoT only uses port 853, while DoH uses port 443, which is the port that all other HTTPS traffic uses as well.
Because DoT has a dedicated port, anyone with network visibility can see DoT traffic coming and going, even though the requests and responses themselves are encrypted. In contrast, with DoH, DNS queries and responses are camouflaged within other HTTPS traffic, since it all comes and goes from the same port.
https://www.cloudflare.com/learning/dns/dns-over-tls/
# 4.2(3) SSL PIN (Key Distribution Problem)
这里说的 Key Distribution Problem 是应用层面,密码学层面指的密码学上的密钥交换算法参考 Diffie–Hellman key exchange (DHKE) https://owasp.org/www-community/controls/Certificate_and_Public_Key_Pinning
主要是指app开发,对于浏览器来说由于历史原因 HKPK 已经被淘汰;
具体是在 ssl handshake过程中加入: The client (such as a mobile app) establishes an SSL/TLS connection with the server. The server sends its public key, which is used to encrypt the data exchanged between the client and the server. The client verifies the server’s identity by checking the server’s digital certificate issued by a trusted Certificate Authority (CA). With SSL pinning, the client also checks that the server’s public key matches the hard-coded public key into the client’s code or configuration. If the public keys match, the connection is allowed to proceed. If the server’s public key does not match the pinned key, the client assumes that a MITM attack is underway and terminates the connection. This prevents any communication from being intercepted and tampered with. If the client needs to update the pinned public key, the app must be updated with a new pinned key.
注意:不要直接pin certificate,否则certificate更新会很麻烦要同时更新app,可以pin public key(更新证书的时候保持public key不变)或者pin上一层CA的证书: it is recommended to place the pin on the intermediate certificate of the CA that issued the server certificate, to ease certificates renewals and rotations.
# 4.3 SSH
跟SSL的区别: SSL的公钥信息和身份信息(填的地区邮箱网址等)需要用x.509自签或者ca对证书进行签名(自签就是自己用自己的私钥签名,相当于我生成了一对公私钥,现在要对公钥认证,自己再拿着这个私钥签名,所以叫自签; 如果是ca签发,当然是ca机构用他们自己的私钥对请求认证的公钥进行签名), 签名后生成证书,证书就包含了请求公证的公钥信息和身份信息以及ca的签名信息; 而SSH生成的公私钥不需要认证,都是放在机器的某个目录下如.ssh,然后将公钥拷贝到互信的其他机器的相应.ssh目录,这样几台机器之间就可以免密登录(需要加载私钥到内存中);当然如果是比如github,则需要拷贝到github的设置中: Adding a new SSH key to your GitHub account (opens new window)
ls -al ~/.ssh
ssh-keygen -t rsa -b 4096 -C "[email protected]"
# start the ssh-agent in the background
$ eval $(ssh-agent -s)
ssh-add ~/.ssh/id_rsa
SSL presents public keys in the context of an X.509 certificate, which itself includes a lot of information about the principal identified by the public key as well as its own digital signature, signed by yet another keypair. SSH does not normally use certificates to contain public keys; instead, the identity associated with a public key is determined by its location in the file system (i.e. whose home directory it's installed in). SSL SSH (opens new window)
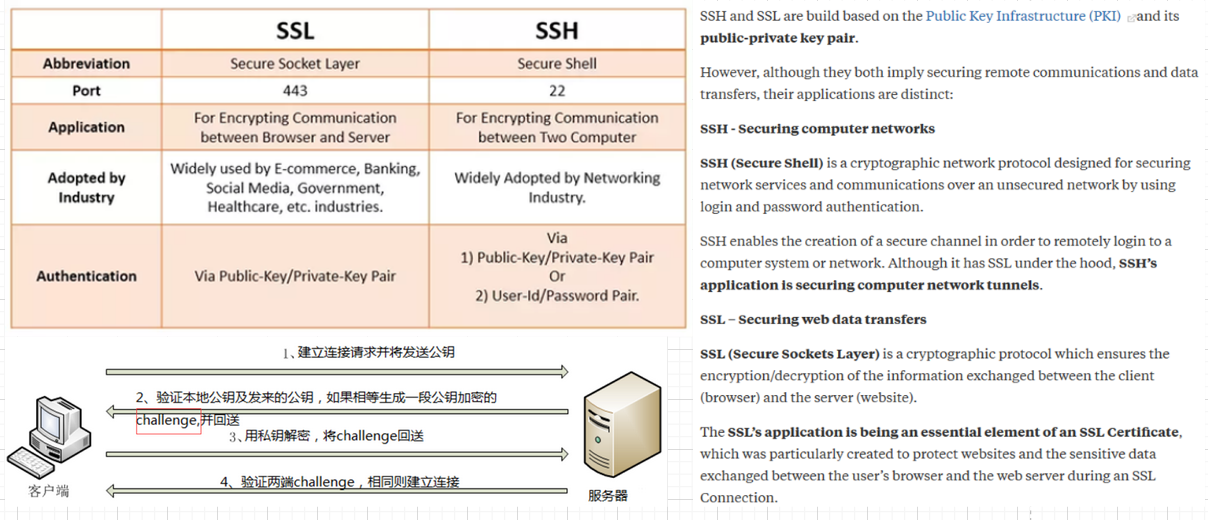 https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-SSL-and-SSH-Are-they-both-just-a-way-to-safely-access-a-remote-computer-through-encryption-Do-they-also-transfer-data
https://www.quora.com/What-is-the-difference-between-SSL-and-SSH-Are-they-both-just-a-way-to-safely-access-a-remote-computer-through-encryption-Do-they-also-transfer-data
# 4.4 authroize&authentication
OAuth2.0 JWT https://jwt.io/
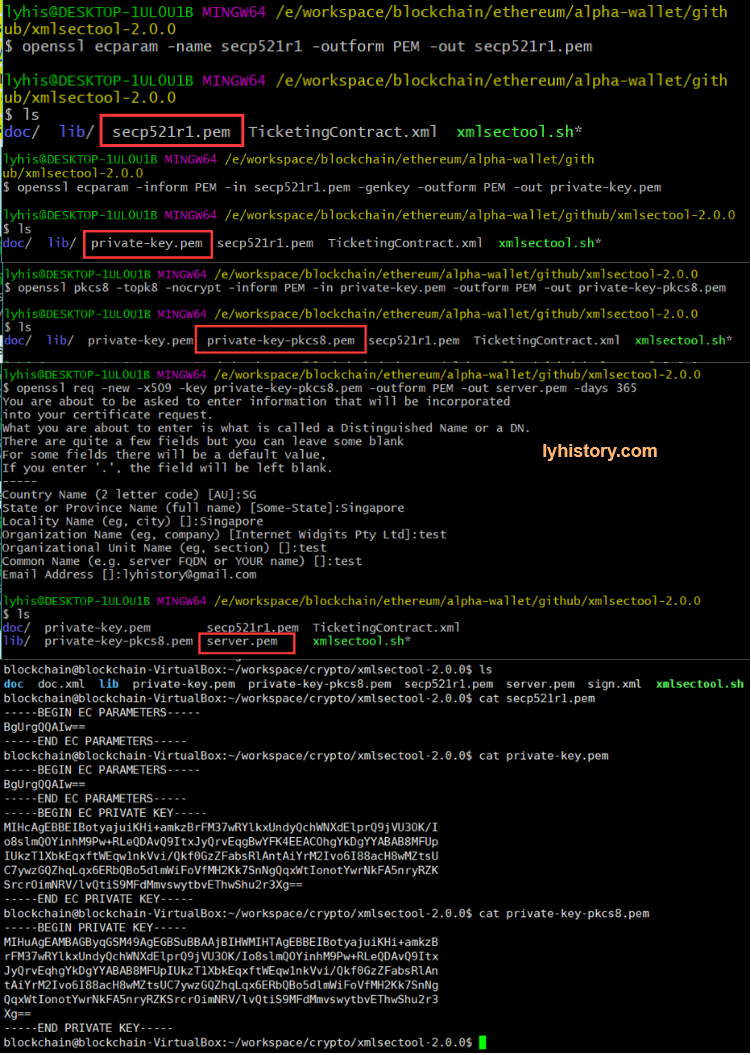
# 4.5 blockchain - ECC
https://wiki.openssl.org/index.php/Command_Line_Elliptic_Curve_Operations
# Generate curve parameters
openssl ecparam -name secp521r1 -outform PEM -out secp521r1.pem
# Generate the private key
openssl ecparam -inform PEM -in secp521r1.pem -genkey -outform PEM -out private-key.pem
# Convert private key to pkcs8
openssl pkcs8 -topk8 -nocrypt -inform PEM -in private-key.pem -outform PEM -out private-key-pkcs8.pem
# Generate the certificate for the private key
openssl req -new -x509 -key private-key-pkcs8.pem -outform PEM -out server.pem -days 365
# Sign the document
./xmlsectool.sh --sign --signatureAlgorithm
'http://www.w3.org/2001/04/xmldsig-more#ecdsa-sha256' --inFile ../doc.xml --outFile ../sign.xml --key private-key-pkcs8.pem --certificate server.pem
# Verify the signature
./xmlsectool.sh --verifySignature --certificate server.pem -inFile ../sign.xml
# Troubleshooting
# certificate verification failed, e.g. CRL, CA or signature check failed
provide 'top' certificate, 即使用上一级CA证书
# 更多内容参考另一篇文章
Genrally speaking:
If you have data in flight, use TLS; If you have data at rest, use PGP;
ref:
How Certificates Use Digital Signatures https://commandlinefanatic.com/cgi-bin/showarticle.cgi?article=art012
The Untold Story of the Man That Made Mainstream Encryption Possible (opens new window)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Public_key_infrastructure https://hub.packtpub.com/public-key-infrastructure-pki-and-other-concepts-cryptography-cissp-exam/
From symmentic to man in the middle attack https://ssd.eff.org/en/module/deep-dive-end-end-encryption-how-do-public-key-encryption-systems-work https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Man-in-the-middle_attack
How do you sign a Certificate Signing Request with your Certification Authority? (opens new window)